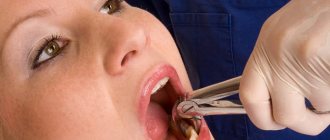
A dystopic tooth is a tooth with an abnormal location (dystopia): it grows at the wrong angle, erupts in the wrong place or turns the wrong way. The appearance of a dystopic tooth often brings not only aesthetic problems; The choice of treatment method for the anomaly depends on various factors.
To obtain good functional and aesthetic results of treatment, it is necessary to contact specialists in time; it is advisable to contact them before the age of 15 years, when the growth of the facial skeleton is not complete. Correcting the position of teeth at this age will be faster and easier. In adults, treatment is technically more difficult, often requiring complex manipulations, for example, compactosteotomy - surgical intervention into bone tissue to move an abnormal tooth.
Dystopic wisdom tooth: what is it?
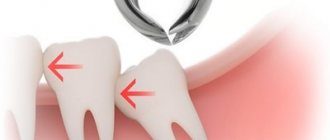
A dystopic wisdom tooth is a third molar, also known as a “figure eight”, which is positioned incorrectly relative to the rest of the dentition. Such a tooth almost always needs to be removed.
A special case of a dystopic wisdom tooth is an unerupted, but fully formed figure eight, which turns out to be turned parallel to the gum. In this case, the tooth is there, although it is not visible, and it is in an incorrect position, so we can talk about dystopia.
Two examples of dental dystopia
When is it necessary to remove an impacted tooth?
Despite millions of years of evolution, humans still continue to develop and improve. Our ancestors had massive jaws, and therefore they accommodated more teeth, which were adapted for biting and tearing food, as well as for chewing it. Now, due to changes in diet, the jaws have begun to shrink, and therefore sometimes there is simply not enough space for all the teeth. This is how impacted teeth appear, i.e. teeth, the rudiments of which formed in the jaw, but there was not enough space for them to erupt, and therefore they remained in the bone, never growing into the dentition.
Causes of dystopic wisdom teeth
Very often, dental dystopia is associated with genetic reasons. A predisposition to shifting dentition is inherited along with small jaw size and other aspects of individual appearance that can cause teeth to shift. Doctors call other factors that provoke improper growth of molars, incisors and fangs:
- atypical formation of the tooth germ in the embryonic period;
- macrodentia, partial adentia, supernumerary teeth and other diseases;
- improper eruption (can be caused by early removal of the primary bite);
- small jaw size;
- mechanical damage, dental trauma;
- bad habits such as chewing foreign objects, thumb sucking (affect the development of malocclusion);
- late eruption of canines, for which there is no longer room in the dentition.
Modern dentistry successfully cures the patient, regardless of the causes of tooth dystopia and its position in the gum. The main thing is to seek help in time.
Kinds
Dystopia comes in several forms. Let's take a closer look at them.
Oral and vestibular
Oral dystopia is a position when teeth erupt on the upper jaw from the side of the palate (palatal position), or on the lower jaw, from the lingual side (lingual), in which they go deep into the oral cavity .
The most common lingual and palatal position occurs when teeth change; if they erupt incorrectly, adjacent lateral incisors and premolars suffer.
This type of dystopia most often occurs in childhood, when the milk line changes to permanent .
The causes of oral dystopia are:
- lack of space in a row;
- bad habits;
- underdevelopment of the alveolar process of the upper jaw in the anterior region;
- disruption of the process of changing dairy products to permanent ones.
Consider the vestibular position, in which there is a displacement outward from the dentition . Very often fangs are susceptible to this.
The causes of vestibular dystopia are:
- bias;
- lack of space for new growth;
- disruption of the development process, including eruption;
- narrowing of ranks;
- bad habits.
Mesial
In dentistry, there is a type of dystopia called mesial, in which the teeth move forward. They interfere with the teething of others, which in turn leads to the formation of an incorrect bite.
Also, due to their incorrect position, injury to the lips, tongue, and cheek tissue occurs. In addition, it is impossible to carry out normal oral hygiene procedures and remove plaque, which in turn leads to the development of caries.
In addition, such a tooth can cause a violation of chewing function, and a person’s speech is also impaired.
The causes of the mesial anomaly are: any disturbances during teething, their presence in excess of the norm, as well as the atypical position of the rudiments. All this is revealed at a dentist’s appointment when diagnosing the patient’s oral cavity.
Distal
Distal dystopia is usually understood as a phenomenon such as tooth displacement back along the arch . The causes of this disease are considered to be disturbances that occurred during eruption, the atypical position of the rudiments, as well as the presence of extra units.
Some patients can identify this disease themselves, especially when it is severe. In order to prescribe the necessary treatment, the patient must visit a dentist, namely an orthodontist.
Its task is to normalize the shape and size of the dentition. For this purpose, orthodontic removable and fixed structures are used.
Transposition and tortoposition
Such phenomena as tortoposition and transposition are less common in practice than other anomalies associated with teeth, but can lead to serious consequences associated with a person’s bite, as well as with health in general.
Let's take a closer look at this problem:
- tortoposition is a phenomenon in which there is a turn around its axis; both canines and incisors are susceptible to this.
This can even lead to tooth loss. By contacting a dentist with such a problem, the patient will receive appropriate treatment and save his teeth; - transposition this is an incorrect position in which a rearrangement occurs, for example, the incisors change places with the canines. The reason for this is the incorrect formation of tooth germs.
The choice of treatment method in this case depends on the degree of inclination, as well as displacement of the roots.This can be surgical intervention (removal of some teeth) or orthodontic intervention, using braces, mouthguards, and their restoration with artificial crowns or veneers is also possible.
Types of wisdom teeth dystopia
Wisdom tooth dystopia is classified depending on which direction the crown is shifted. The following types of disease are distinguished:
- vestibular (forward displacement);
- oral (teeth located behind the entire row);
- mesial (forward bend);
- distal (backward tilt);
- with supraposition (above the dentition);
- with infraposition (below the dentition);
- with tortoposition (the tooth is rotated around its axis);
- with transposition (the tooth is in the place of another tooth).
In the most severe cases, you can observe the appearance of a tooth outside the oral cavity: for example, inside the nose. This is very dangerous and requires immediate treatment.
Main signs of pathology
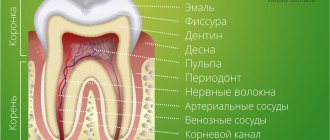
A dystopic tooth is a tooth with a disturbed correct location. Dentists consider the correct position of the dentition to be one in which each tooth has its own specific position and place among its “brethren.” It is also important to have the correct dental relationship between the upper and lower dentitions.
With dystopia, the teeth are located inside the dental arch (or outside it) incorrectly in relation to their “brother teeth”. Often, representatives of the dentition with this disease are displaced or rotated. The eruption of the remaining teeth is not disturbed and occurs without pathologies.
Sometimes a dystopic tooth is rotated around an axis or can “locate” with its neighbors (occurs in occlusion pathologies).
With dystopia, patients most often experience discomfort and pain. If such a pathology concerns representatives of the dentition from the “smile zone” (pathology of incisors or canines), then the aesthetics of the bite also suffers. Correcting dystopia is a very complex, painful and expensive process. This requires a lot of effort from specialists and patients themselves.
Symptoms of dystopia
Symptoms of dental dystopia are most often visual and easily noticeable. It is enough to look at the position of all the elements of the dentition to see that some of them are in the wrong places or are simply growing unevenly. Other symptoms:
- there is no tooth in the bite, and the period of eruption has already passed;
- inflammation and pain are felt at the site of the wisdom tooth;
- The wisdom tooth did not appear on time
It is interesting that in a number of cases there is no wisdom tooth at all - it does not form and does not erupt. Dentists call this option a variation of the norm.
How does the postoperative period proceed?
After removal of an impacted wisdom tooth, minor pain and swelling in the cheek are quite natural. They usually go away 2-3 days after surgery. To reduce these phenomena, the doctor prescribes painkillers, and ice can be applied to the cheek on the extraction side. Incomplete opening of the mouth and discomfort in the throat when swallowing and chewing are also considered normal, which goes away on its own after 3-4 days.
But severe pain after removal of an impacted wisdom tooth is a reason to visit the doctor who performed the operation, because
this may be a sign that the wound needs additional treatment. Another reason that should force you to immediately see a doctor is an increase in body temperature above 37.5°. To the list of posts
Consequences of dystopia
Although dental dystopia does not seem like a terrible disease, it can create many problems. This is why wisdom teeth that have grown incorrectly are most often removed. Among the most unpleasant consequences of the disease:
- disruption of the entire dentition, because due to one incorrect element, the rest move or cannot erupt correctly;
- injury to the tissues of the cheeks, tongue, lips, which can cause ulcers and even provoke the development of tumors;
- complication of oral hygiene, which leads to inflammation, caries, both on the dystopic and adjacent teeth;
- the appearance of gingival pockets where bacteria accumulate, leading to pericoronitis;
- impaired chewing function, which in turn reduces the quality of food and can lead to deterioration of the gastrointestinal tract;
- difficulty pronouncing words, poor diction;
- violation of the facial skeleton, unaesthetic appearance of the lower part of the face.
Almost always, dystopia leads to unpleasant aesthetic consequences, which causes complexes and rejection of one’s appearance in the child, and then in the adult. Of course, this can be worked out with a psychologist, but it is much wiser and more correct to deal with the cause than to deal with the consequences.
What it is?
In dentistry, dystopia is understood as a phenomenon such as the incorrect position of a tooth germ as a result of a violation of embryonic development or due to genetic and external factors.
Most often, wisdom teeth and canines are susceptible to this phenomenon..
A person suffering from this disease feels very awkward in society. He tries to smile as little as possible and talk with strangers, because, for example, with the abnormal position of the fangs, the impression of a “vampire” smile is created.
In addition, the disease negatively affects the health of the entire oral cavity . It can lead to changes in the shape of the jaw, making cleaning difficult, which in turn gives rise to periodontal disease and caries.
Diagnosis of dystopia
An orthodontist or even a dental therapist can easily determine tooth dystopia during a routine examination if the anomaly is not complex. In some cases, when an element of the dentition remains in the gum, ends up in the palate or another place, during the examination one can only suspect a problem.
If the doctor has not found one of the teeth that should have already erupted in a child (or an adult, if we are talking about eights), he will refer the patient for an x-ray examination. The picture clearly shows all the irregularities and you can see the formed teeth in the soft tissues. To clarify the position and for subsequent treatment, arthopantomography, creation of plaster models of the jaws, and teleradiography are used.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The owner of dystopic teeth does not feel entirely confident in society and is embarrassed by his smile, so as not to advertise the anomaly. In addition, this phenomenon negatively affects human health.
A malocclusion occurs, which is associated with eruption anomalies . Correct speech and chewing function are impaired, and this in turn leads to problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
A person suffering from dystopia develops a large amount of plaque and stones, and all because it becomes difficult to properly care for the oral cavity.
It also often provokes the formation of periodontal pockets in which food accumulates. This can lead to inflammatory processes.
Photo: dystopia of wisdom teeth in the picture
A person suffering from dystopia can diagnose this disease himself. But in order to carry out therapeutic measures, it is necessary to contact a general practitioner or orthodontist.
During a clinical examination, the dentist will prescribe the necessary procedures for final diagnosis and determination of the position of dystopic teeth in the gums.
Before starting treatment, the following measures must be taken::
- orthopantomography , that is, it is necessary to take a picture of the jaw in order to see the condition of the roots, bone tissue, and determine the location of the diseased tooth in relation to the others;
- creating a jaw model from plaster , for which the necessary measurements are taken, subsequently used for treatment;
- teleradiography , thanks to which the ratio of the sizes of the jaw and teeth is measured;
- classification of the patient’s bite according to ICD-10, which allows for an assessment of defects.
Based on the results of the research, the dentist decides on the treatment of the patient.
When is the best time to treat dental dystopia?
Like any dental disorder, dystopia should be treated immediately after the problem is discovered. The easiest time to change the position of teeth is during childhood and adolescence (up to about 18 years of age). This is due to the time of formation of the jaw bones. Until adulthood, the bone is still quite soft, which makes it easy to align the bite.
Sometimes, although rarely, trainers are used to treat dystopia. Read more about them in the article: Trainers for teeth straightening: description, varieties, tips for use
If we are talking about dystopic molars , then they are almost always removed. The third molars themselves are considered an atavism and an optional element in the dentition; moreover, their treatment is associated with problems and difficulties. Therefore, doctors do not try to save these teeth.
Sometimes treatment is associated not with removal, but with grinding of the tooth. This decision is made if the dystopic element does not interfere with the chewing function and does not violate the aesthetics of the oral cavity. In this case, it is recommended to be constantly monitored by a doctor, since such elements of the dentition are easily affected by caries. Moreover, the consequences are much more serious than in ordinary cases: incorrect tooth position stimulates the development of bacteria, inflammation, and complications.
Installation of braces for the treatment of canine dystopia
Is it necessary to remove an impacted tooth?
This question worries all people who are faced with the described problem. In fact, there is no definite answer - it all depends on the characteristics of the clinical situation. To make a final decision, you need to undergo an x-ray, determine the location of the teeth from the images and consult with a specialist.
But, according to statistics, dentists still have to perform surgery more often. This is due to the fact that:
pathology leads to gum inflammation and severe pain;- an incorrectly positioned impacted tooth makes the bite incorrect and looks unaesthetic, protruding forward/backward against the background of its neighbors;
- partially impacted specimens are very difficult to treat if a carious cavity forms on their surface (not to mention pulpitis);
- retention is often the cause of the appearance of a fistula and the development of an abscess.
If the impacted dystopic tooth is not removed, osteomyelitis, cysts, and pericoronitis may develop. All these are dangerous diseases that cause serious damage to the entire body.
Removal of dystopic wisdom tooth
Removing a dystopic wisdom tooth is a fairly serious operation that requires professionalism and care from the doctor. Incorrect actions can lead to dislocation of adjacent teeth, lower jaw, injury to the mandibular canal and other problems. Therefore, it is very important to contact experienced specialists who are familiar with the specifics of removing complex teeth.
Indications for removing a dystopic tooth
Clear indications for removal:
- detection of a jaw cyst;
- traumatic dystopia;
- diseases of the jaw caused by this tooth;
- difficulties in treating caries in adjacent teeth;
- the appearance of pulpitis and periodontitis.
The practice is that the decision to remove a child is made taking into account all these factors. In an adult, it is more likely to decide whether to keep a tooth or not – removal is considered a universal solution, the simplest and safest. They resort to it in almost all cases.
Stages of removing a dystopic wisdom tooth
The removal operation is carried out in several stages. Compliance with technology allows you to protect the patient and simplify the operation for the doctor. Also, before starting work, detailed studies must be carried out: a full x-ray of the jaw is taken, all available caries is cured, etc.
During tooth extraction, the surgeon performs the following actions:
- Introduction of anesthetic. This may be local anesthesia or general anesthesia if several teeth are to be removed at once.
- Complete exposure of the tooth. To do this, a flap of mucous membrane and periosteum are peeled off.
- I sawed off the walls using a drill. This is necessary to align the element and make it easier to remove.
- Tooth extraction. The entire molar is removed using forceps. If the tooth was previously destroyed, its fragments are removed. It is important that the doctor removes all the fragments, otherwise inflammation will occur.
- Application of antiseptics to prevent the development of wound infection.
- Returning the mucosal flap to its place.
- Applying seams.
Once the wound is stitched, the operation is over, but the treatment is not. After a week, you should definitely see a doctor to have the stitches removed. It is also advisable to be observed by a specialist for 1-2 months to make sure that the removal had no consequences.
Removal of a dystopic tooth in pictures
Is an impacted tooth always subject to extraction?
No not always. There are a number of indications for the removal of impacted teeth in which surgical intervention cannot be avoided. These include cases:
- development of pulpitis or periodontitis in an impacted tooth. This applies to teeth that have not fully erupted. Due to the fact that they are difficult to clean and are often covered with a gingival hood, such teeth are more susceptible to caries and inflammatory processes. Considering their special position in the mouth and the extremely difficult access to them, there is no point in sanitizing impacted units, because In any case, treatment will be unsuccessful.
- swelling of the cheek due to the formation of pericoronitis - inflammation of the gingival fold covering an incompletely erupted tooth. Food often gets clogged under the hood, which is quite difficult to clean out with ordinary hygiene products, so the inflammatory process is quite common in such situations.
- formation of periostitis, or flux, against the background of caries or pulpitis of the impacted unit. If the process had formed around the “correct” tooth, then the doctor would have the opportunity to eliminate the inflammatory process either with the help of pharmaceuticals, or by making an incision in the gum and installing drainage into it. However, when it comes to impacted teeth, such measures are ineffective, so the patient has to say goodbye to the “troublemaker.”
- constant discomfort and pain due to the pressure of the unerupted unit on the nerves running along the jaw. In this case, the tooth can be absolutely intact and not interfere with the rest of its brethren.
- the need for orthodontic treatment to correct the bite. If an impacted tooth interferes with its neighbors, for example, moves them and causes them to crowd together, then this is a direct indication of removal. In addition, impacted units must be removed if they impede the movement of the remaining teeth in the dentition.
- preparing the oral cavity for prosthetics. If an impacted tooth cannot be “pulled out” using orthodontic methods and placed in the dentition in order to be used in the future as a support, for example, for a bridge structure, it is removed, because it only worsens the situation and reduces the quality of the treatment provided.
Please note: even if nothing bothers the patient and the impacted figure eight does not affect the general situation in the oral cavity in any way, a consultation with a dental surgeon and a computed tomography scan of both jaws is necessary. The doctor will be able to comprehensively assess the whole picture and draw conclusions about the advisability of removal. He will talk about the immediate and long-term consequences of removing an impacted wisdom tooth, and the prognosis of surgical treatment in relation to the patient’s orthodontic health.
It also happens that a person complains of headaches or clicking in the temporomandibular joint, but it turns out that the problem lies in abnormally erupted or incorrectly positioned third molars. Naturally, in such cases, the best solution would be to remove the problem teeth.
Forecast of dystopia
The appearance of a dystopic tooth in a child is not such a serious problem (especially if there is only one). Before a person’s facial skeleton stops growing, the position of the main teeth can be normalized quite quickly. Therefore, it is recommended to begin treatment immediately after identifying the problem. In this case, all the teeth will most likely fall into place and in the future, in adulthood, will no longer cause concern.
If correction of dystopia in an adult is required, this almost always causes many difficulties. After 18-20 years, teeth are no longer so mobile, so correcting their position requires many preparatory interventions. It is much easier to remove a problematic tooth than to try to put it back in place.
Being cured in a timely manner, dystopia has virtually no negative impact on a person’s future life. Most often, the correct bite is maintained for a long time and does not require supervision by a doctor.
What is the risk?
The best option is to begin treatment for dystopia in adolescence, when the jaw is not yet fully formed. This will make it possible to fully normalize the position of the teeth and, in turn, achieve aesthetic results.
When visiting a dentist as an adult, the treatment will take longer, but it is still worth it.
If you do not contact specialists with this problem in a timely manner, this will lead to a number of negative consequences , namely:
- a dystopic wisdom tooth causes destruction of the adjacent one and provokes the occurrence of periodontitis;
- an incorrect bite is formed;
- the chewing process is disrupted, which in turn leads to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- speech defects occur;
- injury to the oral mucosa occurs;
- it becomes difficult to carry out full hygienic procedures;
- Accelerates the formation of tartar on damaged teeth;
- There is a tendency towards facial asymmetry.
Prevention of dystopia
Dentists are confident that if you carefully monitor your child’s dental health from early childhood, you can avoid most bite problems. Dystopic teeth are no exception, because their appearance is not always associated with hereditary factors. To prevent dystopia, doctors recommend the following:
- proper nutrition, adherence to the daily routine of a pregnant mother;
- prevention of jaw injuries from an early age;
- regular visits to the dentist, wearing devices to correct malocclusion;
- giving up bad habits (including weaning off the pacifier after a year and from thumb sucking in sleep), etc.
If you and your child regularly visit a dentist, he will give recommendations on what exactly to do in your case.
Conclusions. Expert advice
Dystopia is the incorrect position of a tooth in the jaw: its displacement forward or backward, down or up, as well as rotation around its axis or tilt. The appearance of such an anomaly is associated both with hereditary factors and with bad habits or mechanical damage to the jaw. The sooner dystopia is detected, the easier it is to cure. In adults, the wisdom tooth most often found to be dystopic is the third molar, because there may simply not be enough space in the jaw for it to erupt.
The consequences of such anomalies include general malocclusion, frequent inflammatory diseases, impaired chewing function, and much more. Depending on the complexity of the case, dystopia is treated either by tooth extraction or with the help of braces. If the decision is made to remove it, it is important to carry out the operation carefully and correctly. If treatment is started on time, the prognosis for the disease is positive.
Treatment of dystopia
Depending on the type and degree of dystopia, its treatment can be completely different. Various types of this pathology can be treated promptly and conservatively. For surgical treatment of this pathology, the following indications must exist:
- periodontitis;
- periostitis;
- osteomyelitis;
- pulpitis;
- caries of the seventh teeth;
- difficulties of prosthetics;
- jaw cysts.
Features of the treatment of this dental anomaly
- Dystopic “eights” (minimally involved in chewing) are usually recommended to be removed. It is especially often recommended to remove the teeth in the neighborhood if there is trauma to the “eight” teeth. But removal is not always justified, since this manipulation can provoke dislocation of the jaw or adjacent premolar and bleeding.
- Tooth extraction should be done in a hospital, since then competent rehabilitation of the patient is important.
- If there is enough space in the jaw for a dystopic tooth, braces are used to return the tooth to its rightful place.
- They usually try to preserve the dystopic canine because of its important role in chewing. If there is not enough space for a canine tooth, the adjacent premolar is often removed. A retainer must then be placed on this segment to prevent the canine from returning to the same incorrect position.
- For dental injuries, various splint-ligature methods are used. If this does not help, then teeth are removed followed by prosthetics or implantation.
- If dystopia is not a serious functional or aesthetic problem, then the tooth is not removed. If pathology causes constant trauma to the buccal mucosa, then it is often sufficient to grind down the excessively sharp dental cusps.
Today's dental trends consist of maximizing the preservation of “native” teeth. If it is impossible to avoid their loss, high-quality replacement with artificial analogues is practiced in the shortest possible time. Otherwise, the presence of unfilled spaces in the dentition forces their neighbors to shift and bend, “attracting” many dental and gingival problems.
And yet, most often the dystopic tooth has to be removed. It is important not only to quickly get rid of the culprit of the pathology, but also to restore its functions as quickly as possible through high-quality prosthetics. Then you will be able to effectively protect yourself from the consequences of this pathology. Take care of your teeth and be healthy!
Sources used:
- L.V. Kharkov and others. Directory of a dental surgeon / M.: Book Plus, 2003
- Bernardsky Yu. I. Fundamentals of maxillofacial surgery and surgical dentistry. - M.: Medical literature, 2000.
- T.N. Terekhov., T.V. Popruzhenko. Prevention of dental diseases. 2004
- First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov