Tooth root removal can be very simple or very complex. It all depends on the patient’s condition, his teeth and jaw bones. If the bone has partially resolved, then only a first-year medical student will not be able to cope with the operation. It’s another matter if the root of the tooth is fractured as a result of mechanical damage, or if it is intact but located deep in the alveolus. Mechanical damage can be caused by trauma (strong impact), or improper previous treatment.
The operation to remove a tooth root from the upper jaw has its own specifics; procedures vary depending on the type of tooth (incisors, canines, chewing teeth). The surgeon uses various tools to remove the roots of teeth: S-shaped, bayonet-shaped forceps. The latter are especially actively used when removing tooth roots from the upper jaw. In some cases, before the actual removal of the tooth root, it is divided into parts (usually using a drill). Tooth root removal is different from the process of removing an entire tooth and is usually more labor intensive.
Some patients ignore surgery to remove the root of the tooth if the crown part is no longer there. Motivation varies - usually the patient expects that the remaining tooth will come out on its own over time. Indeed, tooth fragments tend to come out on their own, but the root is not a fragment. It is often observed that the patient comes with an already drawn-out root - then it is necessary to make an incision in the gum to gain access to it. The root of the tooth itself, if not removed in a timely manner, can provoke severe pain and inflammation. Remember: the tooth root does not dissolve!
Many Moscow clinics take on any, even the most complex cases. The experience and qualifications of doctors - specialists with extensive experience - will not allow them to complicate the operation themselves by causing mechanical damage to the tooth root or making mistakes when removing it. But they can correct other people's mistakes. Tooth root removal can be performed with forceps, elevators, or, when previous techniques have failed, by sawing.
Removing the root of a tooth in the upper and lower jaws has technological differences. For different teeth (canines, incisors, chewing teeth), forceps of different shapes (straight, S-shaped, bayonet-shaped) and elevators (working on the principle of a lever) are used. The procedure itself is performed under local or general anesthesia. The dentist will choose a method for removing the roots of the teeth, and anesthetic agents are selected in such a way as to eliminate the likelihood of side effects (individual intolerance, allergic reactions).
If the root of the tooth is already overgrown, you will have to open it by cutting into the gum. This operation is also performed under anesthesia. After surgery, stitches may be placed and special medications may be used to speed up gum healing. Doctors will remove the root of any tooth, regardless of why only the crown was removed. Painless, fast, high quality.
The main causes of pathology
There are a number of main reasons why a tooth can become overgrown with soft tissue. The most common reason is negligence towards periodontal tissues, refusal to visit the clinic after breaking off part of the crown. There are also quite often cases when a wisdom tooth that has not fully erupted is covered with gum on top. In the future, this figure eight can exert strong pressure on the entire dentition, which will lead to a gradual change in the bite and the appearance of serious orthodontic pathologies.
The patient may also encounter a similar situation when refusing to remove the root system of a broken tooth. As a result, a small piece of the top, as well as the root, remains under the gum, and over time they can begin to hurt and become inflamed.
It is important to note that a person’s bad habits, poor diet, consumption of junk food, chronic diseases and lack of oral hygiene can lead to teeth becoming more sensitive and brittle. As a result, the slightest pressure will be enough to cause part of the crown to break off.
Possible complications
The gums after wisdom tooth removal are inflamed and vulnerable to irritants. Infection or injury from rough food can cause complications. Therefore, the doctor gives patients recommendations in the postoperative period and advises them to carefully adhere to oral hygiene.
There are such complications:
- Alveolitis - inflammation of the socket;
- Dry socket of an extracted tooth;
- Wound bleeding;
- Paresthesia;
- Suppuration (abscess, phlegmon);
- Osteomyelitis (inflammation of the bone and bone marrow of the jaw).
To the list of posts
Consequences
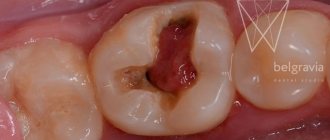
If the root and part of the tooth are left inside the gum tissue, some complications may occur. Inflammation in the pulp chamber can begin as a result of dirt and infection; this process is accompanied by severe pain, the appearance of purulent discharge, rotting, etc. To avoid sepsis, surgical removal of the root and nerve endings is recommended.
Another dangerous disease is periodontitis. In the absence of timely treatment, the unit can become very loose; it is surrounded by voids where germs, food particles, and infection can get in. In this case, the root moves away from the coronal part quite quickly and it becomes almost impossible to save it. If the problem is not corrected in time, there is a high risk of damage to other organs and even blood poisoning. The latter threatens with very serious complications and is dangerous to human health.
Another common occurrence is when a previously filled tooth breaks and particles of the composite get into the hole. These particles can react with tissues, which leads to the development of inflammation. In this case, not only the root of our broken tooth can become inflamed, but also nearby units. If inflammation is left unattended by a specialist for a long period of time, a cyst may appear.
What happens if the root remains under the gum?
- inflammation of the pulp is a consequence of infection, accompanied by inflammation of the nerve and rotting of the root from the inside. In case of purulent pulpitis, urgent removal of the root and nerve is recommended;
- Periodontitis is a common gum disease in which the root gradually becomes loose, leaving an empty space around it where infection accumulates. The root gradually moves away from the tooth. With such a problem, the chances of saving the root part are extremely small. If periodontitis is not treated in a timely manner, the inflammatory process can affect other systems and organs;
- toxic effects of filling residues are a common occurrence when a tooth with a filling breaks off and particles of material remain in its place. They react with the mucous membrane and gums, provoking an even greater pathological process. Not only the root of the lost crown becomes inflamed, but also the neighboring roots and nerves;
- cyst is a consequence of the inflammatory process in the gum and pulp area. The destruction spreads to the entire tooth and it is no longer attached to the root. Rotting gradually spreads to both the root and the space around it.
What to do
Of course, you shouldn’t sit and wait for the pain and discomfort in the area of a tooth overgrown with gums to go away on its own. It is best to immediately contact a specialized dental clinic for medical advice. Only he will be able to conduct a comprehensive examination of the oral cavity, prescribe the necessary tests, conduct an X-ray examination and prescribe the correct treatment.
As a rule, a broken tooth that is overgrown with soft tissue is carefully removed. This requires making an incision in the gum. If the tooth is healthy, then after opening the hole the doctor can install an artificial root and prosthesis into it.
If it is not possible to save the tooth, then a procedure is performed to extract its root system. To do this, the specialist uses a special tool called an elevator, with which he cuts the top of the unit and gradually brings it to the surface. Such manipulations are carried out under local anesthesia and do not take much time. After extraction of a diseased tooth, a medicinal drug can be applied to the wound, which promotes faster healing. The stitches are removed after a few weeks.
Indications
If the condition of the tissues around the root is good and there are no inflammatory processes, then it can be preserved. Indications for extraction are usually:
- root fracture, cracks and other mechanical damage;
- inflammation of surrounding tissues;
- complete destruction of the upper part without the possibility of installing a pin or tab to fix the prosthesis;
- preparation for subsequent implantation.
What can happen if you refuse the help of a specialist?
If the tooth root remains under the layer of gum tissue, decay can spread to neighboring units. In this case, treatment will be longer and more expensive. The main symptoms of this problem are a strong odor from the mouth and periodic pain that radiates to the head. Harmful microorganisms will begin to accumulate under the gums, which can lead to the development of caries.
In 99% of cases, the patient has a small sac with purulent filling at the apex of the root. After some time, it inevitably turns into a painful swelling called gumboil. The only correct solution when gums grow on a tooth is to quickly contact an experienced dentist. It will not only eliminate inflammation, but will also be able to save the destroyed unit.
previous post
What happens if you swallow toothpaste?
next entry
Postoperative period
Very often, patients have gum pain after the removal of a wisdom tooth; you can read more about how dystopic teeth are removed here.
After surgery, the patient may be concerned about the following:
- Pain in the retromolar area;;
- Unpleasant and painful sensations when opening the mouth;
- Discomfort in the oral cavity;
- Swelling and hyperemia of soft tissues;
- Bleeding;
- Swelling and asymmetry of the face;
- Inability to eat food normally;
- Deterioration of general condition: weakness, fever, headache.
Is it possible to put a crown on a decayed tooth?
An important condition must be met here - the root should not have any damage. If the tooth is destroyed below the gum level, you will most likely have to contact a surgeon. The crown is permanent, and the tooth underneath must remain healthy. If there is injury, the root of the tooth may begin to rot, causing infection and severe pain.
If the area above the gum is intact, the doctor determines whether the damaged tooth can be restored. If the answer is positive, he will do everything possible to save the tooth, because the natural root tissue is much stronger. A good dentist always strives to save the root, and modern medicine offers effective methods for restoring even severely damaged teeth.
How to pull out the remaining root in the gum
It is always easier for a dental surgeon to remove the entire tooth than just the remaining root parts.
First, the doctor carries out diagnostic measures, which include:
inspection;- reorganization;
- taking pictures.
If he deems it necessary, he may ask the client to take a blood test. On the appointed day, the patient is given an anesthetic. Local anesthesia is usually sufficient. When the anesthetic takes effect, the hard fragments are removed using special forceps. When the gums are completely overgrown, they are first excised, and the bone tissue is drilled out to gain access to the root zone. After this, using a dental elevator, all detected particles of the missing unit are removed. Such an operation is certainly complex and traumatic. Upon completion, stitches are applied.
Tooth fracture - symptoms and treatment
Transverse (horizontal) fracture
In case of a fracture of the crown part of the tooth without damage to the pulp, caries may develop in the absence of treatment and subsequently pulpitis and periodontitis. In case of a fracture accompanied by exposure of the pulp, acute pulpitis is a complication. The occurrence of pulpitis is accompanied by pronounced pain in the area of the causative tooth with irradiation (spread) along the branch of the trigeminal nerve to the area of neighboring teeth or antagonist teeth. The pain mainly occurs at night. Without appropriate treatment, acute pulpitis can turn into chronic pulpitis, and later into periodontitis, characterized by the symptom of an “overgrown tooth” (the feeling that a tooth has come out; you cannot bite on it, as it causes pain). You can clearly identify the causative tooth by performing percussion - tapping on the tooth. Pain also occurs when eating hot food.
In the absence of treatment, after some time the process of pulp sclerosis begins - degeneration, pulp atrophy, its replacement with connective tissue. As a rule, there is no acute pain at this stage, but chronic inflammatory processes - osteitis or radicular cysts - begin to develop in the bone surrounding the tooth.
Vertical tooth fracture
This injury is incompatible with the continued existence of this tooth in the alveolus. Without treatment (in this case it involves tooth extraction), the situation leads to the rapid development of an inflammatory local process - dental periodontitis, which can later develop into periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum), osteomyelitis (chronic inflammation of the bone, which leads to resorption of bone tissue in the area of the lesion). ) and into extensive inflammation of soft tissues - an abscess of the maxillofacial area.
In this case, a purulent infiltrate appears around the tooth, melting the surrounding tissue. The patient's general condition worsens, the temperature rises, and swelling of the buccal or submandibular area occurs. Without appropriate treatment (tooth extraction, opening of periostitis or abscess), the process quickly becomes diffuse. In this case, phlegmon of the soft tissues of the face and neck may occur. Such a rapid and dangerous course of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity is due to the structural features of the cellular spaces of the face and neck. Cellular spaces are located between the muscle fascia. They are loose connective tissue. A distinctive feature of this tissue is the rapid development of purulent inflammation in it, which then spreads to nearby muscles and tendons.
Complications of a fracture also include resorption (external and internal) of the tooth root after injury. It appears after a few months. Resorption can be in the area of the apex (apex) of the root or in the area of the tooth root fracture. It occurs due to the lack of a “replacement callus”, which should restore the tissues of the tooth root - dentin and cement. The symptoms are quite sparse. This may be tooth mobility or pain when biting on a tooth. As a rule, it is possible to clearly diagnose resorption after an X-ray examination. This situation is a late complication of a tooth fracture. The tooth must be removed [9].
Excision of the hood
This is the most commonly used technique in eliminating the consequences of pericoronitis. Intervention, especially in the early stages, is minimal, and rehabilitation is never long or painful. Operation stages:
- An injection of an anesthetic is given;
- The dentist uses a scalpel to remove the gingival hood;
- The resulting wound is disinfected with disinfectants.
The doctor will continue to provide therapeutic support to the patient for a number of weeks. A person will make special healing baths for the oral cavity at home based on a water-salt solution, and then come to the clinic for follow-up examinations. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed if the doctor notices bad activity of pathogenic bacteria on the teeth. It happens that the hood recurs and returns again, covering the problematic tooth. In this case, there is no other choice but to remove the source of trouble.
Final provisions
When a doctor diagnoses pericoronitis, it means that the gums around the erupting teeth - permanent or baby - have become inflamed, and the tooth is probably not growing properly. The abnormality creates a pocket called a hood between the new tooth and the soft tissue. The cavity quickly fills with a substrate consisting of plaque and bacteria, and decay begins. The main symptom is pain at the site of the growing tooth; in addition, other signs are present.
Pericoronitis is treated by removing the inflamed soft tissue (hood), or extracting the tooth (in extreme cases). Home methods, rinses, lotions will not help, they can only do harm if you rely on them completely and do not visit the hospital.
Treatment of pericoronitis can be quick - in the early stages, and long and painful - in advanced stages. A person can prevent the development of pathology while complying with hygiene standards. And it is worth remembering that modern dentistry is a very rapidly developing branch of medicine. Trust the professionals to help you maintain your health.