In the last century, when asked whether it is painful to remove the root of a tooth if the crown is completely destroyed, many dentists would have given an affirmative answer. Pain during and after the procedure, complications from anesthesia and discomfort plagued many patients. But today the situation has changed - a sick tooth and its root can be pulled out absolutely painlessly
.
When is tooth root removal required?
The decision to remove a tooth root can only be made by the attending physician, taking into account the patient’s indications in a particular case. If the affected tooth root can be treated, then the necessary procedures can be carried out and used as a support for the crown. However, there are a number of scenarios that require mandatory root removal.
- If, as a result of advanced periodontitis, the tooth has become mobile.
- When the root of a tooth is broken or cracked and hurts, and the gums and cheek are swollen.
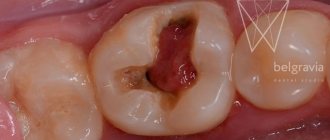
- If the tooth is destroyed to the level of gum tissue and cannot be restored.
- When a wisdom tooth interferes with the development and alignment of other teeth or causes constant pain.
- If there is a cyst that cannot be removed without removing the root.
- If the wall of the tooth breaks off, and the resulting fragment extends under the gum.
- When part of the root remains after tooth extraction.
Separately, it is worth noting the removal of the root of baby teeth - usually dentists prefer to let the tooth fall out on its own, but sometimes intervention is necessary, for example, when more than half of the tooth is damaged by caries; when the tooth is very loose; if a tooth is broken and its remainder injures the gums; when the root is affected by caries and there is a risk of spreading to the adjacent tooth; with severe inflammation in the root area, which cannot be eliminated without resorting to removal.
Is it possible to put a crown on a decayed tooth?
An important condition must be met here - the root should not have any damage. If the tooth is destroyed below the gum level, you will most likely have to contact a surgeon. The crown is permanent, and the tooth underneath must remain healthy. If there is injury, the root of the tooth may begin to rot, causing infection and severe pain.
If the area above the gum is intact, the doctor determines whether the damaged tooth can be restored. If the answer is positive, he will do everything possible to save the tooth, because the natural root tissue is much stronger. A good dentist always strives to save the root, and modern medicine offers effective methods for restoring even severely damaged teeth.
Is it possible to leave it?
Some patients can walk for years with a tooth destroyed to the ground, not realizing that rotting roots are a breeding ground for infection and, at a minimum, provoke constant bad breath. Affected roots absorb bacteria and food particles like a sponge. Over time, plaque and stone form on the remnants of the root, causing the gum tissue to become inflamed.
Often patients ignore the problem, hoping that root removal without a tooth will not be necessary, since it will come out on its own. This is a big misconception - in rare cases, a fragment of a tooth can actually come out, but not its root. Delay will only lead to the root becoming overgrown, which is why the gum will have to be cut to remove the root of the destroyed tooth.
The body's constant fight against infection in the root area means that the human immune system directs part of its resources to solve the problem. Ultimately, this will provoke the development of infection and inflammation, and for patients this turns out to be a surprise every time. In some cases, if the rotten tooth root is not removed in time, infection in the upper jaw can spread to the maxillary sinuses, and in the lower jaw it can lead to a fracture or osteomyelitis.
Signs that a root remains after tooth extraction
If the root remains in the gum after a tooth extraction was performed poorly, then the problem is difficult to identify without diagnosis. But if a lot of time has passed since the extraction, and you feel twitching or pulsation in the area of the missing tooth, acute pain due to mechanical impact, observe redness or bleeding from the gums, or increased temperature, this may very likely indicate the presence of a tooth root remnant. If a root remains in the gum after tooth extraction, the consequences will not take long to arrive. Therefore, as soon as you have such a suspicion, contact a specialist as soon as possible.
What happens if you don’t see a doctor in a timely manner?
If, after much thought about what to do with a decayed tooth, you decide to leave everything as it is, you are seriously risking your health. Damage to the gums can affect neighboring teeth, and pathological changes in soft tissues will not take long to occur. Many people, without thinking about the consequences of their decision, walk around with a tooth destroyed at the very base, believing that they are in no danger: after all, at first glance, there are no changes in their well-being. However, in some cases they may be invisible only at first. If the crown part of the tooth is destroyed, changes can be observed with the naked eye. However, in the case of a root this is not possible. Damage to it can lead to infections. As a result, at a minimum, a person will experience constant bad breath, which is difficult to get rid of, and in more severe cases, plaque and tartar may form, which will gradually spread to neighboring teeth.
If there is an infection, the condition of not only the tooth root, but also the entire oral cavity worsens. Which can negatively affect the state of the microflora of the digestive system as a whole, since pathogenic organisms will be swallowed along with saliva. The immune system will have to expend considerable effort to maintain normal health. In the long term, it is possible to develop sinusitis, inflammation of bone tissue and other serious diseases.
Stages of removing the root of a decayed tooth
The operation of removing the root of a tooth is a procedure even more labor-intensive than removing a whole tooth. Preparation standardly includes a visual examination of the oral cavity, diagnosis using special equipment and sanitation. The test results allow you to draw up a treatment plan in accordance with medical indications, age, health status and other characteristics of the body, as well as select the optimal instruments and anesthetics for the procedure.
How is root removal done without a tooth?
- The doctor injects the patient with a local anesthetic, selected in such a way as to exclude allergies and other body reactions.
- After 10 minutes (when the anesthetic has taken effect), the circular ligament is separated from the neck of the tooth. If there is no inflammation of the gum tissue, then they are also moved away from the edge of the alveoli. If the root is deeply recessed into the hole or has become overgrown, then you will need to cut the gum and drill out part of the bone tissue to access the root.
- Next, the tooth root is removed using forceps or a dental elevator. If the tooth has a multi-root system, it will first be separated using a drill or ultrasound, and then removed in parts. This is called complex removal.
- After removing the tooth root, the hole is treated with a special solution. If the gum is cut, then after the operation sutures are placed and the operated area is treated with drugs that will help speed up healing.
Note!
Removing the root of the upper teeth is somewhat different from removing the roots of the lower jaw tooth. The roots of the lower jaw are most often removed using elevators: the instrument is placed between the gum bone tissue and the root and the handle is rotated. When removing the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw, bayonet-shaped forceps are often used - medium for canines, incisors and premolars and wide for molars. Using a tool, the circular ligament of the tooth is first peeled off, then single roots are twisted, and those connected to each other are dislocated.
What to do if the root remains in the gum?
Now you know why you should not leave the roots of decayed teeth in the gums, but sometimes situations arise when the presence of roots is not obvious: the patient is not bothered by anything, and he thinks that there is nothing left in the gums. This happens, for example, with an illiterate tooth extraction: as a result of the actions of an unqualified employee, the root or part of it remains in the soft tissues, and they find out about it too late. If you suspect that a tooth root remains in the gum, contact specialists who will conduct a thorough diagnosis. Signs indicating the possible presence of a tooth root include:
- frequent and significant pain even after a long period of time after visiting the surgeon,
- redness of the mucous membrane, bleeding,
- pulsation and painful sensations when pressing, chewing,
- heat.
If the answer to the question “can a decayed tooth be cured” is negative, it is removed, like the root. When it turns out that the root of the tooth, for one reason or another, remains in the gum, and its removal is required, the procedure is carried out as follows.
- First, the attending physician gives an injection of an anesthetic, which is necessary to ensure that the operation is completely painless.
- Then, after about 5-10 minutes, when the remedy has taken effect, the doctor makes an incision in the gum, and in severe cases, also makes a hole in the bone tissue using a drill.
- Having firmly grasped the root with forceps, the doctor removes it from the hole. Because some teeth may have multiple roots, they may require root division. This is done using a traditional burr or a modern method - ultrasound.
- Then the place that was subjected to such a traumatic procedure is treated with an antiseptic and a composition that accelerates healing. If there are incisions, stitches are applied.
If you are bothered by frequent pain in your jaw, although there are no apparent reasons for this, you should not hope that the pain will go away on its own. Contact qualified dentists at a specialized dental clinic, whose staff have many years of experience and will be able to find out the cause of the ailment. They will determine whether it is possible to restore a damaged tooth if the cause of the pain lies in it, and will do everything possible to save and restore the tooth, as well as quickly and painlessly remove it if there is no other option.
"AlfaDent" - we remove the problem at the root.
Features of wisdom tooth root removal
When removing the root of wisdom teeth, the complexity of the procedure is added by the fact that figure eights often grow at an angle; accordingly, their roots are located perpendicular to the roots of neighboring teeth. Therefore, the procedure is carried out using x-rays, especially if the crown is destroyed. The procedure should be carried out by an experienced specialist to eliminate the possibility that a root remains after the removal of a wisdom tooth.
Causes of root damage
The root of a tooth can crumble under the influence of several factors. The most common reasons for damage are:
- injuries,
- inaccurate expansion of root canals, their careless mechanical processing in preparation for filling,
- violation of pin implantation technology,
- uneven distribution of chewing load after installation of the prosthesis,
- complex tooth extraction.
The root can crumble if damaging pressure is transmitted parallel or perpendicular to its longitudinal axis. The most serious damage occurs from impacts and falls from heights.
Tooth root removal under anesthesia
As a rule, root removal is performed under local anesthesia, but if the patient has a complex tooth root extraction, or if he has intolerance to local anesthetics or dentophobia, the specialist performs the procedure for tooth root removal under general anesthesia. This allows all manipulations to be carried out with complete comfort for the patient - while he is sleeping. However, this method has a number of serious contraindications: its use can have a negative effect on the heart, kidneys and brain. In addition, patients often experience nausea, headache, and confusion as they emerge from anesthesia. Therefore, they try to resort to anesthesia only as a last resort, giving preference to sedation. This is a modern type of general anesthesia, which involves deep relaxation, during which the patient remains conscious and can contact the doctor, but with this type of tooth root removal, pain and stress are completely eliminated.
How are tooth roots removed if a tooth is destroyed?
When a tooth is destroyed and the roots are not removed in a timely manner, gum tissue gradually covers the exposed area, causing the root to become “buried” underneath. This significantly complicates the root removal procedure, since it will require cutting the gums. As a rule, this is not required if the root is removed along with the tooth or if a short time has passed since the destruction and removal of the tooth. Also, a gum incision is required when removing large wisdom teeth that have strong, durable roots. Remember to visit the dentist annually for preventative purposes. By promptly identifying problems in the condition of dental tissue and detecting any pathologies, the dentist will be able to promptly intervene in the course of the disease and prevent serious consequences. However, he will not be able to guarantee a 100% successful outcome if you delay your visit!
Tooth root amputation as a treatment
In some cases, complete tooth root removal can be replaced by a tooth-saving operation called amputation. This is the removal of part of the tooth root, allowing you to save a healthy fragment. During the procedure, the affected area is cut off and the cavity is filled with osteoplastic mass.
Tooth-preserving extraction operations also include hemisection, in which part of the root system is removed along with the adjacent crown area. These two methods allow you to preserve the physiological function of the tooth and use it to install a bridge. It is important to understand: no doctor can guarantee that such a tooth will last a long time, since partial loss of the root will lead to a violation of the stability of the tooth. Therefore, if you notice that for a long time after root removal the tooth hurts or causes you other discomfort, you should definitely contact your doctor.
Treatment
To restore a crumbled tooth root, an X-ray examination is first performed to determine the extent of the damage. Based on its results, the dentist decides on the choice of method of restoration of the dental unit.
- Single-rooted teeth with a broken root must be removed. It is impossible to save them. In addition, there is a high risk of developing an inflammatory process.
- Multi-rooted teeth with crumbled roots can be restored. In such cases, hemisection and other tooth-preserving operations are performed. They allow you to remove only the damaged element, while preserving the viable ones. The remaining roots will be used in the future as a support when installing a microprosthesis.
If it is impossible to save the tooth with a crumbled root, it is removed. To replace the aesthetic defect and restore chewing function, implantation is performed or a prosthesis is installed. The choice of the appropriate dental treatment option depends on the patient’s age, structural features of the dental system, the presence of chronic diseases, etc.
How much does tooth root removal cost?
As a rule, the price for tooth root removal is determined based on the complexity of the case, and can vary greatly depending on the segment of the clinic, the qualifications of the doctor and other factors. Standard removal starts at an average of 3,000 rubles, complex removal will cost at least 5,000 rubles. Your attending physician will help you make more accurate calculations based on the diagnostic results. In any case, the sooner you go to the clinic, the less likely it is that complications will develop, especially since modern dental offices have all the capabilities to carry out the procedure efficiently and minimize the unpleasant consequences of tooth root removal.
Reasons why only the root remains of a tooth
For clarity, we will divide them into two parts - external and internal.
The first include:
- Injuries (in addition to participation in boxing matches, no less dangerous is the habit of opening lids with your teeth or gnawing hard objects);
- Exposure of enamel to contrasting temperatures (hot after cold and vice versa);
- Chemical factors (for example, the harmful effects of carbonated drinks);
- Lack of proper oral hygiene.
To the second:
- Metabolic disease;
- Lack of vitamins due to poor diet;
- For women - pregnancy.
What do you need to know?
The procedures for removing baby and molar teeth are similar, but the latter are fixed in the tissues much more firmly and deeper. Before removal, make sure that the problem comes from this particular tooth. If there is blood during removal, you need to use tampons soaked in antiseptic.
After removal, you need to remove parts of the tooth and blood from your mouth, wash your hands, and apply cold to the injury site to reduce the risk of swelling. Over the next few days, you should stop smoking and avoid heavy physical activity.
You cannot pull a tooth out on your own without pain. This effect can only be achieved by professional pain relief. If the removal was successful, monitor the hole for a week. If suppuration or swelling appears, use an antiseptic and rush to the doctor. If, having started the removal, you cannot complete the process, there is severe pain, stop immediately and go to the hospital. Until this time, do not load the tooth or eat food.
The dentist must be informed:
- When the tooth was removed;
- When did the pain start?
- What means were used?
Types of tooth extraction
In medical practice, all removal procedures are divided into:
Easy removal
The doctor manages to extract the entire tooth using special forceps; its duration is up to 5 minutes. This is how single-rooted teeth or teeth affected by periodontitis are removed.
Difficult removal
To extract a tooth, the doctor uses auxiliary tools (most often an elevator), and the entire extraction process takes up to 15 minutes. It is most often performed when a part of the root or crown is broken during the removal of multi-rooted teeth.
Atypical removal
It has no clear boundaries in terms of time and extraction method and implies a complex and multi-stage procedure. For this, the doctor can use a bur, an elevator, forceps, a chisel, surgical sutures and needles to close the wound. Often such removal requires from 30 minutes to 2 hours.
This division is reflected both in the cost of the removal itself (due to the various labor costs of the doctor) and in the rehabilitation period:
Simple removal results in minimal damage to surrounding tissue. At the same time, squeezing them with an instrument (and stopping full blood circulation in this area) lasts no more than 5 minutes, and does not in any way affect the subsequent healing of the wound. If you follow the recommendations, the risk of complications is minimal.
Complex removal involves the use of more aggressive instruments and prolonged compression of the walls of the bone alveolus. After it, there may be difficulties with the formation of a blood clot and the development of alveolitis of the “dry socket” type, which is supervised by taking anti-inflammatory drugs and applying turunda with iodoform.
Atypical removal is a surgical intervention in which the doctor violates the integrity of the mucosa, periosteum, or a certain part of the bone. Pressure on tissue can last up to 2 hours, which greatly affects tissue microcirculation. Sometimes a hemostatic sponge is used to stop socket bleeding during such removal. The wound is sutured, which ensures the tightness of the hole and protects it from the development of alveolitis, but it is important to maintain a hygienic regime to avoid infection on the soft tissue.
The doctor’s further tactics, his prescriptions and recommendations for the recovery period depend on how the tooth was removed.