From this article you will learn:
- why does the socket hurt after tooth extraction,
- what is alveolitis: photos and videos,
- How is alveolitis treated?
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
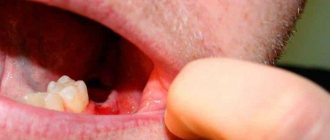
Alveolitis is a classic complication that occurs after tooth extraction and consists of the development of inflammation of the socket of the extracted tooth. Often alveolitis is also called “dry socket” (this is due to the fact that the alveolar bone in the depths of the socket is exposed due to the loss of a blood clot).
On average, alveolitis develops after tooth extraction in 3-5% of cases, but this applies to teeth of any location with the exception of wisdom teeth. When the latter are removed, alveolitis occurs in 25-30% of cases, which is associated with the greater complexity and traumatic nature of the removal process.
Dry socket after tooth extraction: photo
You can see what normal healing of a socket should look like (at different times from the moment of extraction) in the photo in the article: → “What a socket should look like after tooth extraction”
Natural processes
Even if the tooth extraction was “simple”, pain in the socket at the site of the extracted tooth is a natural consequence that will bother you for 3-4 days.
This is normal and nothing to worry about, but if the pain causes you severe discomfort, consult your doctor and he will recommend that you take painkillers.
Sometimes regular cold compresses applied to the cheek in the area of the extracted tooth will help relieve pain. This could be a cloth soaked in cold water or ice from the freezer wrapped in a cloth.
Tooth socket
In the case of “complex removal”, in which the gums were cut and sutured, special tools were used to gouge out the root, the pain after the procedure will be felt much longer (the doctor will definitely warn you about this), but will still gradually go away on its own.
If the pain does not go away for more than ten days, consult your doctor: there may be complications in the tooth extraction and you will need dental intervention to eliminate them.
What are the stages in the rehabilitation process?
To be able to identify the problem in time, you should know how and how long the hole heals, how long it can bleed and hurt after removal. And for this it is worth familiarizing yourself with the main stages of healing. Let's look at each of them in a little more detail.
Gradual restoration of soft tissues
A few hours are enough for a protective blood clot to form. You should not touch it or try to remove it, because it acts as a kind of barrier that prevents harmful microorganisms from entering an open wound. During the soft tissue healing stage, you should conscientiously brush your teeth at least twice a day, but without affecting the causative area. You should also rinse your mouth every time after a snack, but again without excessive intensity. Around day 2-3, epithelization begins, which is accompanied by the formation of granulation tissue. The patient loses severe pain, swelling and redness disappear. Next, the wound is covered with a white coating. To understand what a properly healing hole looks like, take a look at the photo below.
The photo shows a properly healing hole after removal
If plaque of a different color has formed in the hole, there is cause for concern. A yellowish or even black color of the hole, coupled with bad breath, indicates the onset of inflammatory processes. It should also be taken into account that after wisdom tooth extraction, the recovery process takes longer. Typically, figure eights initially grow in the wrong position, which is why, to remove them, the doctor has to cut the gum and then suture it. This involves more extensive intervention and, accordingly, longer rehabilitation.
Bone tissue regeneration
Bone tissue begins to form only 7-8 days after surgery. The blood clot should still remain in the socket, but the depression where the tooth used to be is no longer as clearly visible. The patient almost completely loses the feeling of discomfort; there is no more pain or discomfort. The bone regeneration process is usually completed by the end of the second week.
Consolidation of new bone tissue
New hard tissues become denser and stronger. After a certain period of time, they turn into full-fledged bone. This is a fairly long period, which, however, does not cause any discomfort to the person. However, the entire process takes about 4 months.
Fusion of bone with gum
The final stage of rehabilitation involves the fusion of new bone tissue with the jawbone. This stage also takes about 4 months, but only if the operation was successful and there were no complications. If inflammatory processes have occurred, fusion can take up to 6-10 months.
The photo shows the healing pattern after removal
Alveolitis
Very often, after the removal of any tooth, the patient develops alveolitis - the tissues in the socket of the extracted tooth become inflamed due to the fact that a protective blood clot has not formed there (or was washed out during brushing or rinsing the teeth).
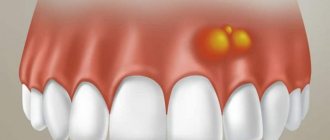
The main symptom of alveolitis is significant pain in the area around the socket of the extracted tooth. At the same time, the gums swell, the temperature rises and general malaise is observed.
Alveolitis can be cured only by relieving inflammation, for which special anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, and sometimes physiotherapy.
You should not try to cure alveolitis yourself based on the recommendations of friends (“I’ve already had this happen”) or information from the Internet (“the best dentists recommend”). Such treatment can lead to more serious consequences, in the worst case - even osteomyelitis: inflammation of the bone tissue of the jaw.
Dry socket after tooth extraction: causes
There are many reasons why alveolitis develops. It can arise due to the fault of the doctor, the fault of the patient, and for reasons beyond anyone’s control. If we talk about the patient’s responsibility, then alveolitis can occur when -
- poor oral hygiene,
- the presence of untreated carious teeth,
- due to smoking after removal,
- when ignoring doctor's recommendations,
- if you rinse your mouth vigorously and simply rinse the blood clot out of the hole.
Alveolitis can also occur in women due to increased levels of estrogen in the blood during the menstrual cycle or as a result of taking oral contraceptives (birth control pills). A high concentration of estrogen leads to fibrinolysis of the blood clot in the socket, i.e. to degradation and destruction of the clot.
It is because of fibrinolysis that a blood clot is destroyed both with poor oral hygiene and with carious teeth. The fact is that pathogenic bacteria, which live in large numbers in dental plaque and in carious defects, secrete toxins, which, like estrogens, lead to fibrinolysis of the blood clot in the socket.
When alveolitis occurs due to the fault of the doctor –
- If the doctor left a tooth fragment, bone fragments, or inactive fragments of bone tissue in the socket, which lead to injury to the blood clot and its destruction.
- A large dose of a vasoconstrictor in an anesthetic - alveolitis can occur if, during anesthesia, the doctor injected a large volume of an anesthetic with a high content of a vasoconstrictor (for example, adrenaline). Too much of the latter will result in the hole simply not filling with blood after the tooth is extracted. If this happens, the surgeon must scrape the bone walls with an instrument and cause socket bleeding.
If the doctor left a cyst/granulation in the socket, when removing a tooth with a diagnosis of periodontitis, the doctor must necessarily scrape out the cyst or granulations (Fig. 10), which might not come out with the tooth, but remain in the depths of the socket. If the doctor did not inspect the socket after extracting the tooth root and left a cyst in the socket, the blood clot will fester.
- Due to the large trauma to the bone during removal, this usually happens in two cases: firstly, when the doctor cuts out the bone with a drill without using water cooling of the bone at all (or when it is not cooled sufficiently).
Overheating of the bone leads to its necrosis and the start of the process of destruction of the clot. Secondly, many doctors try to remove a tooth for 1-2 hours (using only forceps and elevators), which causes such trauma to the bone with these instruments that alveolitis is simply bound to develop. An experienced doctor, seeing a complex tooth, will sometimes immediately cut the crown into several parts and remove the tooth fragment by fragment (spending only 15-25 minutes), and thereby reduce the trauma caused to the bone.
- If, after a complex removal or removal against the background of purulent inflammation, the doctor did not prescribe antibiotics, which in these cases are considered mandatory.
Conclusions: thus, the main causes of destruction (fibrinolysis) of a blood clot are pathogenic bacteria, excessive mechanical trauma to the bone, and estrogens. Reasons of a different nature: smoking, loss of a clot while rinsing the mouth, and the fact that the hole did not fill with blood after the tooth was extracted. There are also reasons that do not depend on either the patient or the doctor, for example, if a tooth is removed due to acute purulent inflammation - in this case it is stupid to blame the doctor for the development of alveolitis.
Socket bleeding
Socket bleeding most often appears immediately after surgery, although sometimes several days pass between tooth extraction and the onset of bleeding.
Bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth can occur for several reasons:
- The patient actively disturbs the socket of the extracted tooth - he feels it with his tongue or hands, inaccurately brushes his teeth or aggressively treats the sore spot with an irrigator;
- Physical damage in the socket area - gum injury, fracture of the alveoli, and so on;
- Concomitant diseases of the patient: hypertension, leukemia, etc.
Treatment for alveolar bleeding depends on the cause and source of bleeding.
Healing of the hole
If the gums bleed in the area of the socket, then the problem may be complications after surgery, and the wound will need to be stitched.
If blood comes from the vessels directly in the walls of the socket of the extracted tooth, then it is first cooled, after which the vessels are compressed and a tampon with a hemostatic agent is placed in the socket for 4-5 days.
If local remedies do not give the desired effect, the dentist prescribes the patient to take general hemostatic agents.
General overview
From a technical point of view, socket curettage is a procedure for mechanical cleaning of the inner surface of the alveolar bed. The use of special instruments allows you to prevent the development of a pathological condition, remove foreign objects and deep deposits characteristic of periodontitis. During the planned removal of elements of the dentition characterized by the presence of cystic formations, as well as with diagnosed periodontitis, the procedure is included in the general protocol and is carried out immediately after extraction, eliminating the possibility of side effects.
How to avoid problems?
First of all, after tooth extraction, you must carefully follow your dentist’s recommendations for the rehabilitation period.
After the operation, the doctor will apply a cotton swab with a hemostatic solution to the wound for 30-40 minutes. You must remove it from the well after the designated time has passed very carefully so as not to damage the clot.
After tooth extraction, you should not eat any food for two hours so that its fragments do not fall into the fresh wound.
For several days, you should not disturb the socket of the extracted tooth - neither with your tongue, nor especially with your hands.
If, after the period indicated by the doctor, the pain in the socket does not go away, moreover, it intensifies, and at the same time there is redness and swelling of the gums, pus from the socket, fever and general malaise - be sure to consult a doctor.
There is no need to hope to fix the problem at home; self-medication will only make it worse for yourself.
How is the removal procedure carried out?
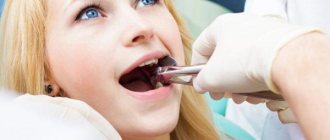
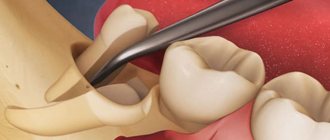
The procedure is always performed under anesthesia, most often local anesthesia. However, if a complex extraction is ahead or the patient has an overwhelming fear of dental treatment, the operation can be performed under general anesthesia or sedation. After the anesthetic begins to take effect, the specialist moves the gum tissue slightly away from the walls of the tooth, and then grabs it using special forceps. If we are talking about the upper jaw, then the doctor presses on the instrument with his entire right hand. When it comes to dealing with the lower tooth, the specialist also works with his right hand, but mainly with his thumb.
This is how a tooth is removed
Read more about how the procedure for removing upper teeth differs from the technique of extracting teeth from the lower jaw in our special article>>>
To extract a tooth from the gum and bone tissue, it is necessary to dislocate it. To do this, the doctor makes rotational and oscillatory movements. Regarding what is placed and what is used to fill the cavity after the hole is emptied, no specific manipulations are required here. The doctor only applies a sterile cotton swab to the wound, which must be held in the mouth until the bleeding stops completely. If a complex removal, for example, of a wisdom tooth, has been carried out, it will take more time for the tissue to heal, because the gum is first cut and then sutured, and this involves even greater trauma to the mucous membrane.
Next, the specialist gives important instructions on how to care for the hole and how to rinse it, tells how long it takes to heal and what to do if the wound does not heal for a long time. You need to listen to the dentist very carefully and then strictly follow his recommendations - this is the only way to protect yourself from the development of complications.
Diagnostics
Such a diagnosis is made only by a doctor when he examines the oral cavity. You can't diagnose yourself. After all, alveolitis of the socket is a serious disease.
If it is not treated promptly, serious complications are possible, including blood poisoning. If there is no blood clot at the place where the tooth was pulled out, then this indicates alveolitis.
Possible complications
If serious inflammatory processes arise in the gum, then after surgery it may change its color to bright red, blue or black. If all this is accompanied by pain, the gums become loose to the touch, and purulent discharge appears, then you should immediately contact the clinic for an examination.
The most common complications include the appearance of cysts. They are small formations containing a small amount of clear liquid inside. If you seek help in a timely manner, treatment may be limited to drug therapy.
Other common pathological processes that occur against the background of gum inflammation include alveolitis, periostitis and gumboil. Flux appears due to infection in the periosteum tissue. Alveolitis manifests itself in the form of redness and significant swelling in the wound area. The patient may complain of acute pain, the appearance of pus, fever and poor health. Also, the pathology is often accompanied by bleeding, which cannot be treated with improvised means.
Stages of the procedure
During curettage, purulent and serous contents, dental fragments, and necrotic masses are removed.
Cleaning is carried out in stages:
- anesthesia;
- washing out blood clots and purulent masses with an antiseptic solution;
- cleaning the hole with a curettage spoon from tooth fragments and damaged tissues;
- repeated antisepsis;
- application of medication, bandage.
If infection is present, additional antibacterial drugs are prescribed. After 1 or 2 days, the injured tissues begin to recover, redness and swelling subside.