How long does it take for gums to heal after tooth extraction?
Tooth extraction can be emergency or planned, but in each case healing occurs the same way.
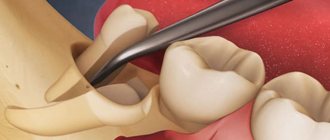
Extraction of the organ is carried out when it is not possible to preserve the crown, in case of severe inflammation, or in advanced periodontal disease. The operation is performed under anesthesia, so there is no pain during removal. Unpleasant symptoms appear after the end of the dentist’s visit. The gums in the area of the removed organ hurt, but normally this goes away after seven days.
When the gums still hurt seven days after the tooth extraction is completed, and the inflammation does not subside for a long time, this indicates a complication. The most common consequences of organ extraction are alveolitis, bleeding, fracture, and injury to the socket.
How many days does it take for the socket and gums to heal?
During a complex operation, the dentist may damage the jaw or push the tooth root into the maxillary sinus. If you do not seek help from a dentist for a long time with such complications, even more terrible conditions appear - gumboil, cyst, osteomyelitis.
Complete healing of the gums after tooth extraction occurs within several weeks. All this time, the mucous membrane hurts a little, but is simply anesthetized with local drugs.
The healing time of the hole is personal for each patient. Recovery takes a long time if care recommendations are not followed. The gums after tooth extraction do not heal even after a couple of weeks, if an infection was introduced during the operation or after the end.
The gum heals in 14 days, and complete restoration of the socket occurs in six months.
What can be dangerous about tooth socket infection?
Prolonged tightening of the hole becomes dangerous when a sour, putrid odor appears, which indicates infection and, of course, inhibits the healing process. Complications may develop when the wound does not heal after tooth extraction. Among them:
- abscess;
- sepsis;
- osteomyelitis.
It is important to know that infection of the socket is especially dangerous in the case of removal of a wisdom tooth in the lower jaw.
The wound heals for a long time when the tooth is located in the lower row, since it is surrounded by many soft tissues with abundant blood supply and practically nothing prevents microorganisms from entering the wound. The infection can go further - deep into the tissues, leading to inflammation of the gum pocket and even the jaw. Blood poisoning can occur when infection enters the bloodstream.
It is worth paying attention if the gums do not heal for a long time and there is acute pain at the site of the extracted tooth for more than 3 days after the operation with a putrid odor coming from the mouth. This also happens with osteomyelitis. Serious consequences in case of damage to the jaw bone can become irreparable. The inflammatory process will go to the brain.
The body reacts sensitively to the oozing wound after tooth extraction. It happens that against the background of the development of the inflammatory process, unpleasant symptoms appear that can no longer be ignored. In case of suppuration in the hole, the following conditions occur:
- Heavy bleeding does not stop for a long time;
- puffiness, swelling, swelling on the cheek, gumboil appears;
- temperature rises;
- headache;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. The recovery is beginning to take a protracted nature.
If there is a strong accumulation of blood clots in the form of a tumor, irreversible processes may develop, in which case it will be necessary to amputate the affected part of the jaw. Osteomyelitis will begin to develop, for which even dentists with extensive experience do not give forecasts.
The degree of tolerance of the body and the state of protective immune forces will be of great importance. Typically, the hole heals faster and does not lead to infection when a person is healthy and there is no deficiency of vitamins and minerals.
Why does the hole take a long time to heal?
Epithelization of the gums after the operation begins after a couple of days, and a white coating appears on it. Now it doesn’t hurt so much anymore, and there are no signs of inflammation. At this time, it is better not to touch the mucous membrane, but just continue to properly take care of the hole. It may not heal for a long time due to the patient’s personal quirks, at a time when there are diseases of the circulatory system or chronic inflammatory processes in the body.
If your gums hurt very badly after seven days, this is possible:
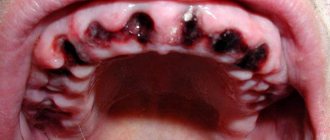
- Dry socket or alveolitis - this complication often appears when the rules for organ removal are not followed, while part of the crown or root remains in the socket. Under such conditions, the blood clot, which should protect against infection, falls out. This complication much more often begins on the 5th day after the end of the operation. Common symptoms are gum discoloration, unpleasant odor, halitosis, soreness, slight bleeding;
- Chronic bleeding - this complication is observed in people with hypertension and in the case of blood diseases. This may result in alveolitis. Before sending the patient home, the dentist stops the bleeding and places a hemostatic sponge on the hole;
- A fracture or dislocation of the lower jaw is a rare complication that occurs more often during the removal of a wisdom tooth; the risk increases if there is a cystic formation or acute inflammatory process in the root area;
- Perforation of the maxillary sinus is possible as a result of complex removal of chewing teeth in the upper jaw.
If the hole hurts for a long time, and it does not go away after seven days, you should immediately consult a doctor. It is forbidden to cope with complications that appeared during the removal on your own. Apart from this, there is no way to prevent them, so first aid is provided immediately after the procedure is completed.
Complications due to improper care, which slow down gum healing, can be prevented on your own.
How long does it take for a hole to heal after removal?
After the tooth has been removed from the socket, the healing process begins. The circular ligament, which is located near the tooth, contracts and the edges of the gums move closer together.
Several hours should pass. During this period of time, a blood clot is formed, which protects the open wound from harmful substances entering the hole. During the healing process, the blood clot cannot be removed from the socket. You should avoid rinsing your mouth; you should not pick with a toothpick or touch the healing gum with your finger.
There are several stages of healing:
- The stage of formation of granulation tissue 2-3 days after the intervention. This tissue is the basis for the growth of new epithelium.
- The formation of the epithelium begins on days 7-14 after the intervention.
- Formation of the bone tissue of the socket from the edges to the center - 2-3 weeks.
- Mineralization of osteoid – 21 days from the moment of surgery.
- Calcification of bone trabeculae – after 2-3 months.
For quick healing, you need to follow the rules of hygiene. Brushing your teeth should be done at least twice a day, but you should not touch the area of the extracted tooth with a brush. You can start rinsing your mouth after eating, but not too intensely. Around day 2-3, epithelization begins, which is accompanied by the formation of granulation tissue.
The soreness of the face goes away, and the swelling and redness of the gums should already disappear. At the next stage, the hole is covered with a white coating.
What to do after the extraction is complete
It is possible to realize that the hole is healing correctly on the 3rd day. The gums hurt moderately, and a white coating appears on it. It is extremely important not to remove it, since it is new epithelium. After 2 weeks, the onion should be completely covered with granulation tissue. After a month, bone tissue begins to regenerate in the entire socket. After 50 days, bone tissue fills the entire hole. And only after five to six months the hole is completely healed and does not differ from other bone tissue.
The gums will recover faster after tooth extraction is completed if you follow easy recommendations.
In the first days after surgery, minor bleeding may occur. Under such conditions, you need to take a small piece of cotton wool or gauze, soak it in hydrogen peroxide, and apply it to the hole. It is much better to go to the pharmacy immediately after removal and buy a hemostatic sponge. A small piece must be applied to the hole; it will dissolve on its own.
Do not rinse your mouth for the first 24 hours.
It is necessary to avoid warm foods and drinks, and not to take alcohol or blood thinners. It is possible to numb the wound with drugs such as Nimesil, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol. While brushing your teeth, you must avoid moving the bristles near the removed organ. If bleeding starts unexpectedly after a couple of days, you should immediately go to the doctor. This also applies to those cases when the pain is not relieved by simple analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
On the third day, it is already possible to start rinsing the oral cavity with warm antiseptic solutions and herbal decoctions. This will speed up the healing of the hole and prevent inflammation and infection of the wound. For a couple more days you need to refrain from heat, sports, saunas, baths.
Some medications can have the opposite effect, leading to bleeding, so the medication must be coordinated with the dentist. Before removing the doctor, it is imperative to give a warning about concomitant and previous diseases. Tooth extraction has contraindications, and if they are missed, complications cannot be avoided.
Why Dry Socket Syndrome May Occur
Some possible causes contributing to the occurrence of pathology are identified. This may happen due to the fault of the dental surgeon if pieces of the root remain in the wound and he did not notice it. This also happens in cases where the gums are severely injured during surgery - this is a direct threat of complications.
The doctor may leave pieces of the tooth root in the socket or injure the gums
This also happens when the patient violates the doctor’s recommendations: for example, he rushed to eat after removal. The clot has not yet formed, and the person has already eaten solid, rough food. Or, for example, contrary to the doctor’s prohibition, the patient rinsed his mouth, simply washing out the clot.
Dry socket syndrome may occur if the rules for caring for the socket after tooth extraction are not followed.
This pathology is also observed in those who have had teeth treated/removed against the background of decreased immunity, after a long illness, etc. The patient's addiction to alcohol and smoking increases the risk of complications.
Smoking and alcohol cause dry socket
Women taking birth control pills are also at risk - such drugs have a negative effect on blood clotting.
When to see a dentist
A visit to the doctor should not be delayed in the following cases:
- Initially or after a couple of days, a blood clot falls out;
- A purulent lump appears in the area of the hole;
- The pain does not go away for a long time and inflammation appears;
- The entire jaw begins to ache, radiating to the temple and eye areas;
- There is a constant iron taste of blood in the mouth;
- Pain appears in the area of the adjacent tooth;
- Within 5 days the gums are not covered with white plaque.
If you are worried about your teeth, you will be helped at the Doctor-RAF Dental Clinic (Almaty, Muratbayev St., 101). Our highly qualified specialists will help you solve all your dental problems.
During the operation, a neighboring organ may be damaged. This will manifest itself as symptoms of pain, and perhaps the tooth will begin to loosen.
Complex removal will require additional care and the use of bactericidal drugs, but only those prescribed by the dentist. Self-prescribing antibiotics is prohibited. An exception would be local gels and ointments, which are available without a prescription and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
8 reasons why the hole does not heal after tooth extraction, ways to speed it up.
After tooth extraction, it seems that the worst is over. However, this is a surgical operation that does not exclude the possibility of complications, especially if you do not follow the doctor’s recommendations. What to do when the hole does not heal?
Attachment of a secondary infection
The oral cavity is the most microorganism-rich place in the human body. Many pathogenic microbes can penetrate with food. The hole in the hole creates a kind of reservoir of food waste, leading to the accumulation of pathogenic microflora and the development of secondary infection (inflammatory process and suppuration). This interferes with the rapid healing of the holes. Alveolitis begins to develop against the background of infection when it gets into the wound.
Of course, it is unlikely that suppuration will occur after tooth extraction if you provide proper care and oral hygiene, wash your hands before eating, and do not put foreign objects into your mouth in order to pick out stagnant blood clots. In the first 2–3 days after tooth extraction, you should not:
- chew on the sore side;
- thoroughly brush your teeth, rinse your mouth to wash away blood clots;
- Use old toothbrushes that have a lot of bacteria on the bristles.
It is the infected tissue that is difficult to restore, so the healing process is slowed down. The time frame can drag on for many months, until the hole after tooth extraction heals on its own, leading to tissue granulation and the formation of normal young bone.
A fresh wound in the mouth is overly sensitive to various microorganisms and therefore does not heal for a long time. That is why it is so important to follow hygiene and all the doctor’s recommendations after tooth extraction, so that the hole heals faster and the regeneration process is accelerated.
The addition of a secondary infection leads to inflammation and suppuration of the socket and the development of alveolitis. It happens that when brushing your teeth, blood clots literally pop out under the pressure of water and nothing prevents bacteria from penetrating into the wounds again. After an extracted tooth, patients begin to complain of the following conditions:
- excessive bleeding;
- an increase in temperature to +38…+39ºС, as a characteristic sign of the development of inflammation;
- soreness;
- enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw;
- the appearance of flux.
It is normal for bleeding to stop 1 day after surgery. If signs of alveolitis appear, you should contact your dentist again as soon as possible.
Healing process
The stages of wound healing are as follows:
- The first day: the hole fills with blood, which turns into a clot due to coagulation. It becomes the basis for bone formation in place of the void, and also protects against infection.
- 3-4 days: the clot is replaced by granulation tissue. By this time, the severity of pain decreases, and sometimes the area of surgery stops hurting completely.
- Week: a clot remains inside the socket, but most of it has already been replaced by granulation tissue.
- Two weeks: the wound is filled with granulation tissue, turning into bone along the edges and bottom.
- 2-3 months: the hole completely turns into bone.
In order for recovery to occur correctly, you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Why doesn't the hole heal?
The timing of wound healing is an individual question. It is determined by several factors - the traumatic nature of the removal, the presence of postoperative sutures, and the age of the patient. It is believed that partial epithelization takes about 2 weeks, complete - up to two months. These deadlines may increase for the following reasons:
- The bone was severely damaged. This happens, for example, during a complex extraction, when the tissue around the tooth has to be cut out with a drill.
- The clot has fallen out, so there is no basis for the formation of granulation tissue.
- Due to the doctor's fault, bone fragments remained in the wound.
- The patient ignores the recommendations received. The most common mistake is rinsing out the clot, after which an infection from the oral cavity gets into the wound.
- The mucous membrane around the wound is mobile, and no stitches were applied.
- Carious remains entered the cavity and inflammation began.
- The surgeon did not take into account individual characteristics. For example, with arterial hypertension, heavy bleeding begins, so drugs that lower blood pressure are additionally prescribed.
- Old age of the patient.
Ways to speed up healing
The best thing a patient can do to speed up epithelialization is to create conditions in the oral cavity that are close to sterile. To do this, you must follow some rules:
- Squeeze the cotton swab applied after surgery tightly with your teeth for 15-20 minutes.
- Do not eat for 3 hours so as not to interfere with the clot formation process.
- In the first days, do not smoke, give up alcohol and solid food.
- Avoid heavy physical activity, temperature effects (hot drinks and dishes, trips to the bathhouse, sauna).
- Do not chew on the injured side for two days.
- Avoid rinsing and use chlorhexidine baths instead.
- Take prescribed medications - for example, antibiotics, which are prescribed after a complex removal, in the presence of purulent processes.
- After consulting with your doctor, use Solcoseryl, a gel that helps accelerate epithelization.
It is important to remember that the area where the deletion took place is a very vulnerable place. The mouth is home to a large number of opportunistic microorganisms, which, in the presence of a source of bleeding, become pathogenic, triggering the inflammatory process. To perform the operation, you should choose an experienced surgeon and strictly follow his recommendations after the procedure.
Diseases that cause gum pain
Unfortunately, no one is immune from unpleasant consequences after tearing out a root unit. Much depends on metabolism (metabolism), existing chronic pathologies, age, the functioning of the immune system, the tendency to develop allergies - a huge number of factors influence the regeneration processes.
It is necessary to consider whether the person is taking any medications. After all, there are medications that inhibit the formation of a blood clot, prevent blood from clotting quickly, or increase blood pressure. All of these effects are unacceptable during recovery from extraction.
Among the main diseases causing complications after extraction:
- Periostitis. Inflammatory lesion of the periosteum. Most often it occurs due to immunodeficiency or advanced chronic pathologies of the oral cavity. It can also be triggered by hidden infections localized in the maxillofacial area. Periostitis causes inflammation of the soft tissues after the root unit is pulled out. A person’s body temperature rises and their general health worsens. He becomes lethargic and weak. At the same time, the cheek swells. To slow down the inflammatory process and reverse it as soon as possible, combined anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial therapy and oral sanitation are carried out. If the disease has spread to deep-lying tissues, the patient is most often hospitalized in a hospital to avoid abscess and phlegmon of the jaw.
- Alveolitis. Inflammation of the walls of the alveoli after surgery. The disease occurs when tissue healing is slow, there are necrotic areas, or an “empty” socket. First there is pain, then it is accompanied by bad breath. In the area of the torn unit, a light gray coating characteristic of pathology appears. It is difficult to remove. Therapy includes frequent washing of the wound with an antiseptic solution and oral administration of anti-inflammatory drugs selected by a specialist.
Considering the seriousness of these diseases, it is important to treat extraction responsibly. During the preparation period, you should undergo treatment of all existing pathologies of the oral cavity and high-quality sanitation and professional hygiene.