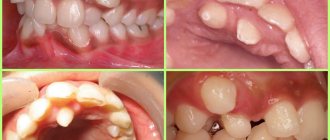
Causes of jaw clenching during trismus
- inflammation of the masticatory muscles;
- inflammation of the gums;
- caries;
- abscess;
- inflammation of the periosteum of the lower jaw;
- jaw injuries (cracks, fractures, dislocations);
- dousing with cold water;
- animal or insect bites.
Trismus can also be a consequence of the following diseases:
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- periostitis;
- neurosis;
- epilepsy;
- meningitis;
- hysteria;
- arthrosis of the jaw joint;
- cancerous tumors;
- convulsions;
- rabies;
- tetany;
- paralysis;
- tetanus;
- pulpitis in the acute stage, etc.
The main stages of trismus
- third - a person can open his mouth 10 mm, the most difficult stage;
- second - the patient can open his mouth 10-20 mm;
- first - the patient opens his mouth 30-40 mm, respectively.
In all cases, a person should immediately consult a doctor. You may need treatment in a hospital setting. In the process of clenching the jaw, there is a high probability of damage to the gums and chipped teeth. If help is not provided in time, oxygen starvation may occur.
Dental diagnosis of trismus involves:
- visual examination of the patient;
- to unclench the jaw, the dentist injects a drug that relaxes the muscles;
- To make the diagnosis more comfortable for the doctor and patient, an anesthetic drug is also administered;
- In addition to the dentist, you may need to consult a neurologist, surgeon, or traumatologist.
How to properly treat trismus of the masticatory muscle?
Treatment of the problem involves:
- immobilization of the jaw by applying a bandage or splint;
- eliminating the underlying cause of trismus (disease or specific condition);
- taking neuropsychic stimulants and sedatives;
- a course of taking muscle relaxants;
- a course of antibiotics (for inflammatory processes);
- physiotherapy;
- peace and release from physical work.
If the patient’s condition is severe, observation in a hospital is necessary under the supervision of a maxillofacial surgeon, neurologist, traumatologist, etc.
After eliminating acute symptoms, a person is recommended a special diet:
- plenty of fluid;
- chopped food;
- vegetables and fruits;
- natural juices.
If it is impossible to eat normally, food is supplied through a tube, and liquid is supplied through the skin.
To restore the functions of the masticatory muscle, the patient is recommended to perform special therapeutic and preventive exercises.
It is important to completely cure trismus, and not just suppress its symptoms. If the cause is not removed, the problem will reoccur. Spasms put a powerful strain on the teeth, gums, and nervous system. It is very important to contact an experienced dentist with a surgical profile, who will help cure the disease and tell you what to do in emergency situations. The 32 Dent network of clinics in Moscow employs specialists who will provide such comprehensive assistance for trismus of the masticatory muscle and other serious problems.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Numbness of the face
Stroke
Diabetes
37178 March 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Numbness of the face: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Numbness of the face occurs when the sensitivity of skin and muscle receptors to various impulses is impaired. This symptom may develop gradually or appear suddenly. Loss of facial sensitivity is described as burning, tingling, sometimes pain, and in some cases as a complete absence of sensation. When the face is numb, the color of the skin over the affected area may change in the form of pallor or redness.
In severe cases, sensory impairment is accompanied by a decrease in the motor function of the facial muscles.
Types of facial numbness
Any external influence, be it heat or cold, light touch or strong pressure, leads to activation of skin receptors and muscle structures. Each receptor is associated with a specific type of nerve fiber that transmits a specific type of sensitivity (sensation of pressure on the skin, vibration, stretching of the skin, and temperature sensitivity). An impulse is generated in the receptor, which is sent through nerve fibers at high speed to the nerve ganglia, which are a collection of sensory neurons. This is where primary information processing occurs to activate vital reflexes. Subsequently, the impulse goes to the brain, where it is processed in special nerve centers, and the person feels pain, pressure, vibration, etc. Thus, we can talk about the following types of sensitivity disorders:
- Violation of surface sensitivity
occurs when receptors (temperature, tactile, pain, etc.) and nerve fibers of the facial skin are damaged. - Violation of deep sensitivity
occurs when the receptors and nerve fibers of the facial muscles are damaged. - Violation of complex types of sensitivity
. A similar type of disorder occurs when the cerebral cortex is damaged. There is no recognition of two different stimuli that simultaneously affect the skin, or the person cannot determine the location of the touch.
Possible causes of facial numbness
In many cases, numbness in different parts of the face is short-term, passing within a few minutes.
Such episodes can occur when the head is positioned in an awkward position, for example during sleep.
This occurs due to compression of the nerve fibers and a temporary disruption of impulse conduction. There is a burning and tingling sensation in the affected area. Partial loss of sensitivity is observed with prolonged exposure to the cold due to vasospasm. After gradual warming of the skin, sensitivity is restored.
However, facial numbness can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.
Acute cerebrovascular accident, or stroke
– a common cause of sudden numbness of the face in combination with a violation of facial activity. Hemorrhage or blockage of brain vessels by a thrombus (blood clot) occurs, acute oxygen deficiency and damage to neurons with disruption of their functions develops. Symptoms develop unexpectedly, sometimes accompanied by headache.
The main signs of a stroke are: numbness of the face and limbs on one or both sides, sudden weakness, speech impairment (inability to clearly pronounce words), drooping of the corner / corners of the mouth, uncoordination of movements.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help. A cerebral aneurysm
can cause numbness in the face due to compression of nerve fibers and sensitive centers of the brain. It usually develops gradually; at the onset of the disease, symptoms may be completely absent. Numbness first affects one area of the face (for example, perioral), and with further growth of the aneurysm, the affected area gradually expands. Sensations may also change: from tingling, burning at first - to a complete absence of sensations later.
There is a danger of rupture of a cerebral aneurysm; in this case, the symptoms are similar to those of a stroke and appear quickly.
Trigeminal neuritis
often accompanies inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (caries, periodontitis), ear (otitis), paranasal sinuses (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis), parotid glands (mumps). The branches of the trigeminal nerve are irritated, which can lead to numbness in the corresponding areas of the face.
Impaired sensitivity with increased tone of the masticatory muscles
occurs due to compression of the branches of the trigeminal nerve by muscle fibers. Hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles is characteristic of damage to the temporomandibular joint due to arthritis and arthrosis, incorrectly selected braces, and certain diseases of the pharynx, for example, peritonsillar abscess.
Diabetes
– with this disease, the process of utilization of glucose from the blood is disrupted, which leads to damage to the vascular wall and disruption of the nutrition of nerve bundles. In the absence of maintenance therapy, tingling and partial loss of sensitivity in areas where the blood supply is impaired may occur.
Numbness of the face in multiple sclerosis
occurs due to demyelination (disappearance of the outer sheath) of the nerve fibers of the trigeminal nerve. Numbness is often preceded by severe pain not only in the face, but also in the limbs.
Tumors of the brain and its membranes
lead to impaired sensitivity in the facial area due to compression of the neurovascular bundles or tumor growth in them.
Which doctors should I contact if I have facial numbness?
If your face becomes numb, you should consult a neurologist or therapist. In some cases, consultation with an otolaryngologist, endocrinologist, or dentist may be required.
Diagnosis and examinations for facial numbness
Depending on the suspected cause of facial numbness, the following laboratory and instrumental studies may be required:
- clinical blood test;
How long does it take to cure trismus?
Typically, full muscle recovery can take one to three weeks, depending on the cause of the trismus. More time will be needed for fractures of the jaw, which must heal properly and subsequently develop.
To prevent trismus of the masticatory muscle, you must:
- do not cause diseases of teeth and gums;
- get vaccinated against rabies and tetanus (rabies and, as a result, lockjaw can be fatal);
- In case of blows or damage to the jaw, seek emergency help from dentistry;
- avoid stressful situations, nervous tension;
- when engaging in contact sports, wear special helmets and mouthguards for protection;
- undergo regular preventive examinations with a trusted dentist. These are the doctors who work in the 32 Dent network of clinics, where you will be happy to see you at any time. Contact us!
Why does my chin go numb?
Trigeminal neuralgia
The main symptom of neuralgia is painful paroxysms provoked by shaving, tension of facial and masticatory muscles, contact with wind, cold water and air.
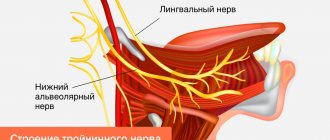
Involvement of the trigeminal nerve trunk is characterized by numbness of the entire half of the face, which develops during the chronic course of the pathology. Numbness of the chin is observed with an isolated lesion of the 3rd branch (n.mandibularis). Along with a decrease in sensitivity in the chin area, there is numbness in the lower part of the cheek, lower lip, lower jaw area, buccal mucosa, gums, teeth, lower half of the tongue and oral cavity. The clinical picture is complemented by peripheral paralysis of the masticatory muscles, accompanied by facial asymmetry. Possible deviation of the lower jaw in the direction of the lesion.
In 95% of cases, neuralgia develops as a result of nerve compression. The cause of compression may be a change in the diameter of the adjacent vessel in arterial hypertension and cerebral atherosclerosis. Another provoking factor is tumors of the brain and skull bones. Sometimes the disease is provoked by a narrowing of the bone canals due to chronic ENT diseases, traumatic brain injuries or dental pathologies.
Traumatic injuries
Numbness of the chin due to injuries is caused by a violation of the integrity or compression of the mandibular nerve. The symptom can be caused by damage to the soft tissues of the face in the projection of the small molars - in this place a branch of the nerve emerges from the canal of the lower jaw, providing sensitivity to the chin and lower lip. With bruises and hematomas, compression is usually observed; the symptoms quickly disappear after the swelling decreases.
With open wounds, the branch may be crossed with long-term numbness. When the lower jaw is fractured, compression or rupture of the n. alveolaris inferior, located in the intraosseous canal. The injury is accompanied by pain, swelling, hemorrhages in the skin and mucous membranes, articulation disorders, and facial asymmetry. Stepping of the dentition, mobility and dislocation of teeth may be detected.
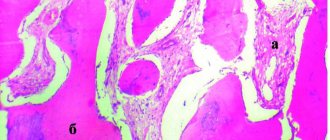
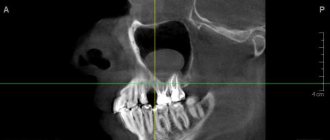
Fractures of the lower jaw
Osteomyelitis of the lower jaw
The infectious-inflammatory process develops as a result of diseases of the teeth and gums, purulent wounds, open fractures, boils and carbuncles of the face, some ENT diseases, and the spread of infection from distant foci. Accompanied by pain, fever, discharge of purulent contents from the gum pockets, limited mouth opening, and breathing problems. Chin numbness may be accompanied by a tingling or crawling sensation.
Tumors of the lower jaw
The cause of numbness in the chin is cancer of the lower jaw. The occurrence of the symptom is often caused by nerve sprouting. The pathology is characterized by early onset of pain, rapid intensification of pain to unbearable, impaired closure and opening of teeth, infiltration of the cheeks and floor of the mouth, ulceration, and bleeding. Sometimes the symptom is provoked by some intraosseous or locally destructive benign neoplasia: ameloblastoma, osteoma, osteoblastoclastoma.
Diseases of the cervical spine
In some cases, numbness of the chin is caused by muscle tension and compression of the dorsal roots of the spinal cord against the background of spinal pathologies: osteochondrosis, protrusion, intervertebral hernia, spondyloarthrosis, etc. Pain and forced positioning of the head are observed. There may be numbness of the upper limb on the affected side.
Migraine with aura
One of the variants of aura during migraine is transient loss of sensitivity in the fingers with numbness spreading to the entire limb, half of the neck, face and chin. Subsequently, a typical clinical picture of migraine is formed with pressing or throbbing pain in half of the head, slight dizziness, nausea, and increased sensitivity to light and sound stimuli.
Shingles
The disease develops against the background of persistence of the herpes virus and is diagnosed in people who have had chickenpox in the past. Along with neuritis of the intercostal, facial and trigeminal nerves, skin rashes are observed along the listed nerve trunks. In children, catarrhal inflammation of the upper respiratory tract may be detected. Symptoms of shingles last for 2-3 weeks.
Other diseases
Sometimes numbness of the chin is determined by the following pathologies:
- Multiple sclerosis.
A characteristic feature of the disease is damage to the sensory pathways and individual cranial nerves, including the trigeminal nerve. Paresis, optic neuritis, ataxia, and dysfunction of the pelvic organs are observed. - Pernicious anemia.
Numbness of the chin is combined with sensitivity disorders in the face and limbs, muscle weakness, and changes in gait. Tachycardia, hepatosplenomegaly, and “varnished tongue” are detected. - Mental disorders
. The symptom most often occurs during hysteria. It is found in an unusual context that does not fit into the clinical picture of a certain somatic disease. In some cases, it is observed with depression.