A high-quality and rapid wound healing process after tooth extraction depends not only on the professionalism of the doctor who performed the extraction (removal) of the tooth, but on the correct behavior of the patient after the procedure, who must strictly follow the recommendations given by the doctor for the period of healing of the wound surface. If you correctly and clearly follow the advice of a specialist, the recovery process occurs quickly and as painlessly as possible.
For example, patients who do not listen to the recommendations given to them make rinsing movements in the area of the healing wound; this washes out the blood clot, which performs a protective function against the entry of bacteria and microbes, as a result of which there is a high risk of wound suppuration.
In this article we want to give recommendations on what should and can be done after tooth extraction, and what should not be done.
1. A gauze swab on the hole. When can it be taken out?
As a rule, the doctor does not immediately release the patient after removal, but asks him to wait for 15-20 minutes within the clinic to then examine and make sure that everything is in order with blood clotting and the tampon can be removed without fear. In rare cases, keeping the tampon in your mouth may take 30-40 minutes, usually 10-20 minutes. There is no need to keep it longer and it is even dangerous, because bacteria accumulate on it and there is a possibility of infection. There are exceptions, when the wound continues to bleed a little, then the old tampon is replaced with a new sterile one and kept for some time.
For some time, saliva may still be pinkish due to staining with secreted ichor, this should not be alarming, this situation can be distinguished from bleeding. At this moment, saliva can be easily swallowed; there is no need to accumulate it in the mouth.
Possible side effects
Nimesil in some cases provokes the appearance of many side effects, manifested in the form of:
- Attacks of headaches and dizziness
- Problems with stool
- Nausea and vomiting
- Increased sweating
- Allergic reaction in the form of skin rashes
- Anemia
- Decreased vision
- Increased blood pressure
- Increased nervousness
- Insomnia
- Shortness of breath
- Stomatitis and hepatitis
- Urinary retention
Basically, the negative consequences that occur when taking Nimesil are associated with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Side effects manifest themselves in the form of diarrhea, constipation, pain localized in the abdomen.
2. After what time can you eat and drink?
After removal, you can drink water. After two hours you can eat. The limiting condition is not to chew rough food on the side of the extracted tooth in the first few days. Hard food can damage the blood clot, which is located in the socket and is needed for wound healing. If the patient experiences an acute feeling of hunger, then no one forbids eating cool yogurt or kefir. In the first days of healing of the hole, it is better to completely avoid eating rough, hard, solid foods, so as not to make strong chewing movements, as well as spicy, salty foods, so as not to irritate the oral mucosa. It is also important to monitor the temperature of food and drinks; they should not be too hot.
Release forms and dosages
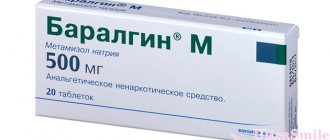
The drug is produced in granules, from which a suspension is prepared for oral administration. The granules are placed in sealed bags of 2 g. You can buy Nimesil in packages of 9, 15, 30 sachets. The drug is prescribed only to adults. For elderly people, the dosage is selected individually based on the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of the drug. Take the medicine only after meals.
Composition and active substance
The main active ingredient of Nimesil is Nimesulide. One two-gram sachet of the drug contains one hundred milligrams of the active substance. Nimesulide is supplemented with other components - sucrose, ketomacrogol, anhydrous citric acid, maltodextrin and orange flavor.
3.Applying ice.
After tooth extraction in our Center, a specialist will give you ice specially prepared for such procedures to apply in the first hours after extraction. Ice is applied for a certain time, at certain intervals, which the doctor will instruct you about. At home, this procedure will need to be continued for some time (the first few hours after removal). This is done in order to minimize or completely eliminate tissue swelling.
Under no circumstances should you heat the area in the area of the extracted tooth; in this case, suppuration will develop.
Popular questions about Nimesil:
Nimesil how to take the drug?
Adults and adolescents over 12 years of age are prescribed 1 sachet orally twice a day after meals.
How to dilute Nimesil?
The powder from the bag is dissolved in half a glass of warm water, mixed and the finished solution is drunk.
How to take Nimesil for toothache?
An adult and a teenager are prescribed to drink 1 sachet, which is dissolved in half a glass of water and taken twice a day. The time interval between doses is 12 hours. The single dose is not increased.
How often can you take nimesil?
Doctors prescribe the drug in a short course to eliminate pain and symptoms of inflammation. The medicine should not be taken for more than two weeks.
6. Medications after removal.
After the procedure, the doctor prescribes a number of medications to take. Under no circumstances should you take any medications on your own, without consulting a doctor.
Painkillers should be taken in case of pain, at intervals and in the amount recommended by the doctor. Each case is individual; it happens that the patient does without taking painkillers.
Antibiotics. In some cases, after removal, antibiotics are prescribed for 5-7 days. As a rule, these are situations when the doctor removes a tooth in the stage of inflammation, complex extraction or removal of several units of teeth. Only a specialist surgeon decides whether to take antibiotics or not.
Antihistamines. Reduces the likelihood of swelling.
Antiseptics. Used as a rinse. BUT, remembering that rinsing movements are prohibited in the first days. A small amount of solution is taken into the mouth and simply held in the mouth, then calmly spit out. Such baths must be done if the tooth was removed during the inflammation phase, if the flux was exposed, if there are teeth affected by caries in the oral cavity.
Enlargement of wisdom teeth
The growth of wisdom teeth is associated with various pathological processes and pain. Nimesil is used to block them. The product has a preventive effect, reducing the risk of attachment of viral flora. The dose is prescribed by a medical specialist in accordance with the clinical picture.
Symptoms of gingivitis are inflammation of the gums. In this case, you can note blood circulation, pain, swelling and overflow of blood vessels. The effective action of Nimesil makes it possible to use it to eliminate the clinical picture.
7.High blood pressure.
In patients with high blood pressure, there is a risk that the wound may bleed longer than usual. In this case, you need to regulate the pressure by taking appropriate medications to reduce it. In our SDent dental medical center, even before the start of manipulations, the doctor always finds out the main points about the general health of the patient. If the patient has hypertension, the specialist knows about this problem in advance and then gives the necessary recommendations appropriate to the case.
Nimesil for colds
Indications for using the drug for colds are:
- increase in body temperature is 37.5 degrees,
- increased sweating,
- pain in muscles and joints,
- nasal congestion,
- hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the throat,
- coughing,
- discomfort in the throat,
- fast fatiguability,
- dizziness.
The antipyretic effect makes it possible to prescribe the drug at fever. The effect itself occurs half an hour after administration and lasts for three to six hours. The dose of the medication is selected individually in accordance with the characteristics of the pathology.
8.What happens to the sutures after removal.
After the tooth is removed, the surgeon places sutures on the wound surface. This promotes faster healing, reduced pain, less risk of inflammation, minimizes the risk of bleeding, and protects the blood clot from falling out.
At the SDent clinic we use the most modern and safe materials. The thread with which the surgeon sews the edges of the hole is self-absorbing. But during the process, the ends of the thread can cause discomfort to the patient and interfere with the oral cavity. Therefore, for the comfort and safety of the patient, the doctor always sets an appointment date for examination and removal of sutures in approximately 10 days.
Indications for taking Nimesil
The action of the product is interconnected with its ability to reduce the sensitivity of pain, reduce fever and eliminate inflammatory processes. The main indications for use of the product include:
- pain in the back,
- joint pain,
- toothache,
- muscle pain of varying severity,
- inflammatory processes in the tendons,
- acute or chronic inflammation of the synovial bursa,
- menstrual irregularities,
- pain during menstruation,
- severe headache.
After tooth extraction, you should not do the following.
- In the first couple of days, taking a hot bath is excluded, only a warm shower.
- During sleep, you need to be careful not to lie on the side where the tooth was removed, this provokes the appearance of swelling.
- Visiting the gym and active physical activity should be postponed in the first days.
- Do not touch the wound with your tongue or foreign object.
- Do not open your mouth very wide, do not use active chewing and facial movements to avoid the sutures coming apart.
- Aspirin is not suitable as an anesthetic due to the fact that it has a thinning effect on the blood and may cause bleeding and hematoma.
- Do not rinse during the first few days. This can negatively affect the loss of a blood clot from the socket and the occurrence of inflammation.
For more information and to make an appointment with a specialist, call:
+7,
Nimesil granules for suspension 100 mg sachet 2 g 9 pcs ➤ instructions for use
Undesirable side effects can be minimized by using the minimum effective dose of the drug for the shortest possible short course.
Nimesil® should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease), since exacerbation of these diseases is possible.
The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation of an ulcer increases with increasing doses of NSAIDs in patients with a history of ulcers, especially those complicated by bleeding or perforation, and in elderly patients, so treatment should be started at the lowest possible dose. Patients receiving drugs that reduce blood clotting or suppress platelet aggregation also increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. If gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers occur in patients taking Nimesil®, treatment with the drug should be discontinued.
Since Nimesil® is partially excreted by the kidneys, its dosage for patients with impaired renal function should be reduced depending on the level of urination.
There is evidence of rare cases of liver reactions. If signs of liver damage appear (itching, yellowing of the skin, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, increased activity of liver transaminases), you should stop taking the drug and consult your doctor.
Despite the rarity of visual impairment in patients taking nimesulide concomitantly with other NSAIDs, treatment should be stopped immediately. If any visual disturbance occurs, the patient should be examined by an ophthalmologist.
The drug can cause fluid retention in tissues, so patients with high blood pressure and cardiac dysfunction should use Nimesil® with extreme caution.
In patients with renal or heart failure, Nimesil® should be used with caution, as renal function may deteriorate. If the condition worsens, treatment with Nimesil® should be discontinued.
Clinical studies and epidemiological data suggest that NSAIDs, especially at high doses and with long-term use, may lead to a small risk of myocardial infarction or stroke. There is insufficient data to exclude the risk of such events when using nimesulide.
The drug contains sucrose, this should be taken into account by patients suffering from diabetes mellitus (0.15–0.18 XE per 100 mg of the drug) and those on a low-calorie diet. Nimesil® is not recommended for use in patients with fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption or sucrose-isomaltose deficiency.
If signs of a cold or acute respiratory viral infection occur during treatment with Nimesil®, the drug should be discontinued.
Nimesil® should not be used simultaneously with other NSAIDs.
Nimesulide can change the properties of platelets, so caution must be exercised when using the drug in people with hemorrhagic diathesis, however, the drug does not replace the preventive effect of acetylsalicylic acid in cardiovascular diseases.
Elderly patients are particularly susceptible to adverse reactions to NSAIDs, incl. the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and perforations that threaten the patient’s life, deterioration of kidney, liver and heart function. When taking Nimesil® for this category of patients, proper clinical monitoring is necessary.
There is evidence of the occurrence in rare cases of skin reactions (such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) to nimesulide as well as to other NSAIDs. At the first signs of a skin rash, damage to the mucous membranes or other signs of an allergic reaction, Nimesil® should be stopped.
The effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. The effect of the drug Nimesil® on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery has not been studied, therefore, during treatment with the drug Nimesil®, care should be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Analogs
If you suffer from toothache, Nimesil is an ideal emergency remedy. However, the German drug is in a high price category (from 600 rubles) and is not always available to patients. What can replace Nimesil? There are a wide range of drugs based on nimesulide that will have a similar effect on the body.
List of medications:
- Aulin;
- Nise;
- Novolid;
- Mesulide;
- Nemulex;
- Flolide;
- Nimulid;
- Mesulide.
- Aponil.
However, this is an incomplete list of drug substitutes. Dozens of drugs are produced based on nimesulide, the availability of which can be obtained from your pharmacist. It is not recommended to choose a generic (medicine substitute) on your own, because the nimesulide content in each drug varies, and only your therapist can choose the correct dosage.
All analogues can be found in pharmacies. Many patients, after taking generics, note that they are completely identical to Nimesil, and are quite satisfied. The main advantage of generics is their significantly lower price with the same method of action.
What is better - Nimesil or generic? The difference between the original and the substitute lies in the composition of excipients (flavors, preservatives) and production features. The increase in the price of the drug depends on the country of production, the equipment used, investment in development, customs duties when transporting across the border and other circumstances. As a result, with the same therapeutic effect, the price differs significantly.
It is important to keep in mind: expensive drugs have not only generics, but also counterfeits. The fake costs a little less than the original, but does not contain the necessary medicinal substances. To avoid buying a useless counterfeit instead of a real drug, you should contact large pharmacies. A reputable pharmaceutical establishment may slightly increase the price of a drug, but will never sell a counterfeit.
Another group of drugs
In addition to nimesulide-based medications, there is another group of drugs with similar effects. These drugs have an analgesic effect, but they contain other active agents. Substitute drugs are prescribed if the use of Nimesil is prohibited. These include the following medications:
- Indomethacin;
- Meloxicam;
- Amtolmetin;
- Diclofenac;
- Diacerin.
These medications may have other names and their own analogues. Only your therapist can understand so many drugs, so trust him with the choice. Any medication is selected taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body, the presence of chronic ailments, age and characteristics of the perception of medicinal substances.
Remember that self-medication carries the risk of complications of chronic illnesses or the emergence of a new disease. Potent chemicals always have side effects on the systems and organs of the human body, so there is no need to experiment on yourself. No one knows what the consequences of taking a medication that has not been approved by your doctor might be. All responsibility will fall on you.
Sources used:
- Khan RA, Rahman SZ Nimesulide Induced Coronary Artery Insufficiency – A Case Report (English) // J Pharmacovigilance Drug Safety : journal. — 2004.
- Anesthesia in dentistry / S.F. Gritsuk. - M.: Medical Information Agency (MIA), 1998.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547948/
Types of dental cysts
Tooth cysts have different classifications, each of which is formed according to certain characteristic parameters of the pathology.
According to the nature of the disease, they are distinguished:
- residual cysts – occur after tooth resection (removal) surgery; this is the most common type of cyst;
- retromolar – formed during severe eruption of wisdom teeth;
- radicular - cysts are located on or near the tooth root;
- follicular – at the heart of such cysts is the germ of a permanent tooth; follicular neoplasms arise as a result of poor quality care of baby teeth.
Classification of neoplasms according to their origin:
- odontogenic – arise as a result of the transition of the inflammatory process from other dental diseases;
- non-odontogenic - the causes of the development of such cysts include problems not related to the teeth and oral cavity.
Locations of cystic formation:
- anterior teeth;
- teeth that are adjacent to the nasal sinuses with their roots;
- wisdom teeth.