The Esthetic Classic Dent clinic employs only experienced surgeons who expertly perform impacted tooth removal of any complexity quickly, efficiently and painlessly. Thanks to the professionalism of our doctors, our patients do not experience complications after such operations, and they tolerate the rehabilitation period easily and without significant discomfort.
Why is an impacted tooth dangerous?
Why doesn't the tooth erupt? Perhaps in childhood the patient had his baby teeth removed too early, which is why the molars initially formed incorrectly. Also, the cause of this phenomenon may be the displacement of neighboring molars in relation to their physiological position.
Impacted teeth can be called a time bomb, since sooner or later they can provoke the following problems:
- Caries;
- Inflammation of the gums around the area of the unerupted tooth;
- Curvature of neighboring teeth due to constant pressure;
- Vomiting sensations, swelling of soft tissues, numbness of the face due to the effect on nerve endings;
- Periodontitis;
- Periodontal disease;
- Bite disorders.
Is it necessary to remove an impacted tooth?
A tooth that has not fully erupted or remains under the gum may not make itself felt for a long time. Only x-rays will show that it is positioned incorrectly. But is it worth having surgery if you don’t experience any discomfort? Dentists unequivocally say yes!
Even if the tooth is not causing concern, it continues to grow under the gum and will eventually begin to dislodge its neighbors. With partial teething, hygiene becomes more difficult - it is almost impossible to reach some areas with a brush, which is why bacteria accumulate on them and caries develops. By the way, it is also almost impossible to cure it qualitatively.
Over time, the infection can spread throughout the entire oral cavity and even move higher - to the pharynx and ear canal, causing inflammatory processes in them.
By the way, the sooner an impacted tooth is detected and removed, the easier the operation itself will be. In addition, surgery is always easier to tolerate if there is no acute inflammation at the time. If you find a tooth on an x-ray that is growing incorrectly and is unlikely to ever fully erupt, it is better to immediately contact a surgeon.
An impacted tooth interferes with dental implantation in a 60-year-old patient
Problem: during diagnostics before dental implantation, an impacted tooth (canine) was discovered in the bones of the upper jaw.
Solution: in one operation under sedation, an impacted tooth (canine) was removed, 4 teeth that could not be treated, bone grafting was performed in the area of the impacted tooth to restore bone volume, and Astra Tech dental implants were installed.
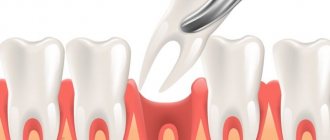
How is impacted wisdom tooth removed?
The operation to remove an unerupted “eight” is quite complex and sometimes lasts up to three hours. The smaller the part of the tooth that appears above the surface of the gum, the more time and effort the surgeon will have to spend.
- First of all, the doctor injects anesthesia - without it, manipulation is impossible.
- He then makes an incision into the gum and lifts the flap to gain access to the bone.
- Using a special instrument, the surgeon makes holes in the bone tissue. If the tooth is large enough, it is sawed down and removed piece by piece.
- The doctor places medicine into the resulting hole and stitches the wound.
–>
Wisdom teeth and joint diseases
Since wisdom teeth are often located outside the dentition and, at the same time, do not have an antagonist, dentoalveolar elongation occurs and traumatic nodes appear in the bite, in other words, overload zones. Traumatic nodes disrupt the functioning of the dental system, uncoupling the physiological mechanisms of receptor feedback, thereby leading to diseases of the temporomandibular joints, masticatory muscles, and neurological disorders.
A wisdom tooth growing in the bone tissue causes displacement of the chewing teeth. When the bite has already been formed by this time, a violation of the correct relationship between the dental cusps of the upper and lower teeth occurs, leading to the occurrence of a difficult-to-treat pathology - dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. The cause of joint pain in the vast majority of patients aged 18-25 years is the rudiments of wisdom teeth growing in the bone.
Impacted and dystopic teeth
Impacted tooth
- this is a tooth that has already fully formed, but cannot fully erupt, since it is partially or completely covered by either the gums, the jaw bone, or another tooth located nearby. As a result, such a tooth gets stuck in the jaw, the gums become swollen and inflamed, causing severe pain.
This is one of the most common dental anomalies. The most common impacted “wisdom teeth” are the eights in the lower jaw. In fact, this is why wisdom teeth are most often removed. While they are in their rudimentary, “dormant” state, they do not cause pain or discomfort, but if they begin to erupt incorrectly, they can not only provoke inflammation, but also damage other teeth.
In this regard, dentists recommend removing the impacted tooth immediately after it begins to cut, without waiting or delaying. Retention of a wisdom tooth before age 25 is not considered an anomaly.
, but normally after 25 these teeth still erupt. Sometimes they are removed at an early age to prevent them from erupting in the future.
Often, an impacted tooth is also called a dystopic tooth, in which it is displaced inside the gum and grows into the cheek, palate or gum, and not as it should.
Causes of retention and dystopia of teeth
- Hereditary factor;
- Too early loss of baby teeth. If, after the loss of a baby tooth, the molar does not immediately grow in this place, the position of the teeth that have not yet erupted in the jaw may shift, resulting in dystopia. The later a molar erupts, the greater the risk of it becoming dystopic;
- Malocclusions, crowded dentition.
Among baby teeth, dystopic ones are rare, but this problem can arise due to too dense gums, through which it is difficult for weak teeth to break through, as a result of which they grow incorrectly. In its normal state, a child’s gums, before the eruption of baby and molar teeth, become more elastic and easily part, making room for new teeth.
In addition, in the case of childhood retention, it is often not the wisdom teeth that fail to erupt (as in most adults), but the canines and small molars, which grow later than all the others. This is not only a rather painful process, but also potential problems with the correct bite of the teeth.
On a note!
The evolutionary version explains tooth retention by the fact that after a long period of time, our jaw has significantly decreased and lost capacity, which now creates an obstacle to the eruption of wisdom teeth and, as a result, leads to dental dystopia.
Removal of wisdom teeth (and buds)
The problems of wisdom teeth and frequent complications from their eruption or simple presence are relevant in modern surgical dentistry.
Wisdom teeth are also the eighth teeth, third molars. The rudiments of the third molars begin to form at 6-7 years of age, and the roots of the eighth teeth - at 15-17 years. Wisdom teeth finish forming at 21-22 years of age (in rare cases, at 25-27 years of age). Therefore, if wisdom teeth did not erupt until the age of 27, then it is pointless to expect that they will erupt on their own later.
A wisdom tooth is a rudiment that has lost its function in the process of human evolution. The jaw has become smaller, since the diet of modern people is dominated by soft food and the chewing load is low. At the same time, there are as many tooth rudiments left as there were thousands of years ago.
Sometimes, when wisdom teeth are optimally erupted, they can be used as autografts to replace the extracted teeth. But so far the possibilities of this procedure are limited.
92% of adults have a complete set of third molars (one on each side of each jaw). At the same time, in more than 25% of people, wisdom teeth remain impacted, that is, they do not erupt at all. As a rule, this is due to a lack of space in the dentition. In 78% of cases, wisdom teeth erupt with complications. This may be pericoronitis, destruction, change in the position of adjacent teeth, malocclusion, tumor-like and/or cyst-forming processes, etc.
The eruption of wisdom teeth, in more than 80% of cases, is accompanied by various purulent-inflammatory complications and poses a threat to the patient’s health. A hood of mucous membrane is formed over the erupting tooth and a pocket is created around it, where plaque, food debris and bacteria actively accumulate.
This creates conditions for the development of purulent inflammation (the so-called pericoronitis), which, due to the proximity of the purulent focus to vital organs and structures, is a dangerous condition. Excision of the hood of the mucous membrane is only a temporary and not always effective measure, since it quickly recovers and makes further treatment difficult due to the formation of scars.
Types of Impacted Teeth
The position of an unerupted tooth inside the gum varies, and depending on how it is located there, the doctor decides whether to remove the tooth or relieve inflammation and allow the tooth to erupt.
Degree of retention:
- Complete (the tooth is completely hidden by the gum and bone, it cannot be seen or felt. Most often this refers to impacted wisdom teeth);
- Partial (a small part of the crown is visible, the rest is hidden);
- Retention in hard tissues (bones);
- Retention in soft tissues (gums).
Inclination of impacted tooth and crown:
- Mesial (the tooth is slightly tilted forward - this is the type of retention that most often occurs);
- Vertical (the tooth grows correctly, but cannot erupt due to lack of space);
- Horizontal (the tooth lies completely inside the gum or bone with the tip facing the other teeth);
- Distal (tooth tilted back).
In addition, although quite rare, retention occurs not of one tooth, but of several adjacent teeth of the same type (for example, two molars). This problem most often occurs in children.
How to identify an impacted tooth?
The most difficult thing to determine is retention when something simply hurts, and what exactly is unclear. Especially if it is an impacted tooth in a child, it is more difficult for the child to realize and tell about it. However, it can be quite difficult for an adult to understand that the problem is an impacted wisdom tooth, especially if you have never had to deal with this before.
Symptoms of an impacted tooth:
- Swelling, redness and painful swelling of the gums around it;
- The crown of a half-erupted impacted tooth may be partially visible, or the tubercle if it is completely hidden by the gum;
- Neighboring teeth may move forward slightly, become mobile, and ache, as if something is pressing on them from the impacted tooth;
- The pain intensifies when moving the jaw, opening the mouth, or eating. On the side where the tooth cannot erupt, it may be impossible to chew at all;
- In the worst cases, when an impacted tooth remains asymptomatic for a long time, a cyst may form with complications - the patient’s general health worsens, and the temperature may rise.
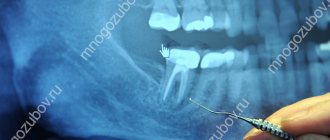
Diagnosis of an impacted tooth is carried out in the clinic, through an orthopantomogram of the jaw
or x-ray. It is necessary to determine where exactly the impacted tooth is located, how deeply it is hidden, and whether it has the opportunity to erupt.
The decision to remove an impacted tooth is made individually in each specific case. If there are no complaints, the tooth is located correctly in the jaw, then it may well erupt and perform its function in the future. However, due to pain and possible complications (loose roots of adjacent teeth, inflammation, displacement of teeth), a decision is most often made to remove such a tooth.
Prices for surgical services at the clinic
| Service | Price |
| Tooth extraction | |
| Removal of a tooth | RUB 3,900 |
| Removal of a tooth of III degree of mobility | 2,000 rub. |
| Wisdom tooth removal | 5,500 rub. |
| Simple tooth extraction | RUB 3,900 |
| Surgery to remove an impacted tooth | 7,500 rub. |
| Other | |
| Bone grafting | 25,000 rub. |
| Sinus lift closed | RUB 18,900 |
| Open sinus lift | 26,500 rub. |
| Excision of the tooth hood | 2,800 rub. |
| Resection of a single-root tooth | 9,500 rub. |
| Resection of a multi-rooted tooth | 7,000 rub. |
| Alveolar ridge correction | RUB 5,900 |
| Opening a periodontal abscess | RUB 3,800 |
| Lip frenuloplasty | 5,500 rub. |
| Plastic frenulum of the tongue | RUB 5,900 |
| Socket curettage | 800 rub. |
| Treatment of alveolitis | 2,500 rub. |
| Dental implantation | |
| Adin implant installation | RUB 21,500 |
| OSSTEM implant installation | RUB 26,700 |
| Installation of the Nobel Replace Select implant | 40,000 rub. |
| Ankylos implant installation | 41,000 rub. |
| Installation of Hi-Tech implant | RUB 29,500 |
| Implant installation Mis | 32,000 rub. |
Removing an impacted (unerupted) wisdom tooth is a complex operation that is performed by an experienced dental surgeon with mandatory anesthesia.
Sign up Duration 15-60 minutes Cost from 840 rub. All prices
One of the common pathologies in dentistry is an impacted tooth. An impacted tooth is a tooth that, for some reason, cannot erupt on its own and take its place in the dentition. Removal of an impacted tooth is the most likely outcome of having such a tooth in the oral cavity. Very often, upper or lower “wisdom teeth” or, as they are also called, “eight teeth,” grow in this way.
Removing an impacted wisdom tooth is a rather complex operation that is performed only by an experienced dental surgeon with mandatory anesthesia. An impacted wisdom tooth can cause malocclusion, serious misalignment of teeth in a row, and can also negate efforts to straighten and correct teeth. Additionally, if this tooth becomes infected, it can become a source of infection for other teeth and lead to serious problems. Removal of an impacted tooth is carried out in EXPERT dentistry painlessly and without complications for patients!
What complications may arise?
The operation to remove the impacted lower “eight” is quite traumatic, and the following negative consequences may occur:
- Pain syndrome - to relieve it, the doctor prescribes painkillers. If they do not help, then you should urgently consult your doctor.
- Prolonged bleeding - some time after the operation, a bloody clot should form in the wound, closing it. If this does not happen, then you need to apply a gauze swab soaked in hydrogen peroxide to the wound, and a five-minute cold compress to your cheek. If the bleeding does not stop, then you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
- Chills and high body temperature as a reaction to anesthesia. Taking antihistamines and antipyretics helps to cope with this. If these drugs do not help, then you need to consult a doctor, as such symptoms may indicate the development of inflammation.
- An unpleasant odor from the mouth with an elevated temperature may indicate the development of alveolitis. This happens when the wound gets infected.
- Hematoma, bruise, swelling on the face from the side of the extracted tooth. To avoid this, you need to apply a cold compress to your cheek for five minutes. This can also be done if a hematoma has already appeared; the cold will help to cope with it faster.
- Loss of sensation in any part of the face (paresthesia), this occurs when the mandibular nerve is damaged. Physiotherapeutic procedures and drug therapy can help solve the problem.
- Dislocation or fracture of the lower jaw as a result of excessive physical effort when removing an impacted wisdom tooth.
Some of these complications arise as a result of the patient’s failure to comply with medical recommendations, and some are due to the mistakes of the dental surgeon due to insufficient qualifications. Therefore, you should be attentive to the advice that the doctor gives regarding the rehabilitation period, and follow them exactly.
Indications for removal of an impacted tooth
Removing impacted eights is a serious surgical procedure. The more complex the operation, the longer it takes, and the more severe the anesthesia must be. Indications for removal of impacted teeth include the following factors:
- an impacted tooth interferes with the correct placement of other teeth in the dentition
- after orthodontic treatment to correct the bite, since an impacted tooth can disrupt an already corrected bite
- the appearance of a cyst. In this case, it is necessary not only to remove the impacted tooth, but also the cyst. To remove a cyst, it is often necessary to remove the pulp from an adjacent healthy tooth.
- if the impacted tooth is in close contact with the adjacent tooth
- during the formation of a gingival hood
- the development of an inflammatory process around the impacted tooth, which can lead to an abscess.
Rules for retination
Traction takes place in two stages, each of which must be carried out in absolute accordance with the protocol. The process itself is quite labor-intensive and lengthy, so both the patient and the treating orthodontist should be patient. Upon completion of treatment, the patient will undergo a course of rehabilitation.
Locating the anomaly
The main task is to bring the pathology site to the required position. If the stage is successfully completed, it is possible not only to restore the damaged tooth, but also to maintain excellent periodontal condition.
To complete the stage, 2-3 visits to the dentist are needed. The doctor first cuts the periodontal fibers and then returns the root to its correct position. This is followed by a short period of healing and growth of periodontal fibers.
Determining the diagnosis
Diagnosis consists of x-rays and computed tomography (CT). From the x-ray, the doctor will understand whether there is retention, what is the angle of the cut and in what sector is the impacted element located.
CT makes it possible to draw up a detailed plan for further treatment with absolute accuracy.
Important: if the CT scan determines that the root of the impacted canine abuts the adjacent teeth, then they will certainly need to be removed.
Preparation stage
The dentist assumes the following actions:
- The inner part of the root is filled with a pin, which is equipped with a hook at the end.
- A wire spacer is placed on the adjacent teeth.
- Using a special elastic band, the root is attached to the crossbar. The rubber band gradually pulls the tooth out of the gum.
If the aesthetic side of the issue is important to the patient, then the dentist may offer a composite veneer for the period of traction. It will easily hide the defect.
Main part
The protocol for this operation divides the doctor’s actions into two parts: first, a place is prepared in the jaw for a new tooth, then the tooth is moved into the correct position. Most often, the operation involves complete exposure of the crown.
The main stages of the operation:
- Removing the crown of a problematic tooth.
- Installation of a lock on the defective and adjacent teeth.
- Pulling out the canine using an elastic band.
- Extraction of the canine using an elastic arch.
Orthodontic traction of an impacted tooth
This is the second part of long-term treatment. It begins with diagnostics, which consists of a CT scan. This will allow you to determine the angle of germination. The course of further restoration depends on the result.
Before the operation, preparation is necessary. First of all, it is necessary to cure all the teeth in the oral cavity. The doctor gives a painkiller injection.
The essence of the operation is:
- use of orthodontic forceps;
- installing the pin and bracket;
- cementation of the pin;
- installation of elastic fiber and traction;
- cutting the fibers around the tooth (fibrotomy).
After 7-10 days, when everything has healed and the swelling has gone down, the problematic root is moved to the desired position.
Possible complications
Let us warn you right away that if you strictly follow the doctor’s instructions for hygienic care of the oral cavity and teeth, complications almost never occur. However, the process can take much longer and be more painful and problematic if the bone tissue that the orthodontist was able to create during the first stage of treatment is allowed to resorb.
Naturally, after such a problem arises, the only way out is to remove not only the problematic tooth, but those adjacent to it.
About the pros and cons of treatment
The advantages of this type of restorative dentistry include, first of all, the absence of the need to manufacture and install bridges, which significantly saves the patient’s money. In addition, this type of treatment is more aesthetically pleasing. People who do not want to exchange their “native tooth” for an implant insist on tooth extraction.
Disadvantages include exposure of the neck or root of the tooth. Recession is not only considered a defect from a beauty point of view, but can also lead to gum infection.
What is the effectiveness of the method
| Click to sign up for a FREE consultation |
The finale of the restoration marathon occurs after the tooth has been completely pulled out. It is very simple to check how well the doctor managed to cope with the task: you need to show the treated tooth to a stranger. If he doesn’t see the differences between the norm and the once-problem area, then everything is fine!
To increase the operating time of the element, you should regularly visit the dentist’s office and, of course, constantly care for your oral cavity at home.
Stages of removing an impacted tooth
The difficulty of removing an impacted tooth is determined by the degree of its location and immersion (a distinction is made between bone immersion, in which the tooth has not even emerged from the jawbone, and tissue immersion, in which the tooth is located in the gum, but has not erupted outward). Upper impacted teeth are much easier to remove than lower teeth due to their physiological characteristics.
Removal of an impacted lower tooth is carried out in several stages:
- diagnostics. X-rays are taken to determine the degree of immersion of the tooth, the number of its roots and their location relative to each other and the roots of neighboring teeth.
- anesthesia. We use high-quality drugs and syringes with thin needles for local anesthesia
- removal of an impacted tooth. To do this, the dental surgeon, using special tools and equipment, opens the gum and, if necessary, the jaw, extracts the entire tooth or splits it into several parts and removes them one by one. Be sure to put a medicine into the resulting hole that relieves inflammation. If a large hole forms, sutures may be placed
- A repeat x-ray taken to ensure that all parts of the tooth have been removed.
Recommendations after removal
Removing an impacted wisdom tooth is a complex dental operation, so certain recommendations must be followed after the procedure:
- do not consume food or drink for at least two hours
- Apply ice to the cheek on the removal side during the day.
- do not drink hot drinks or food for the first three days after removal
- do not visit the bathhouse, sauna, reduce physical activity
- do not pick at the hole with sharp objects and do not “lick” it with your tongue
- maintain oral hygiene, brush your teeth carefully
- If your doctor has prescribed medications, you should definitely take them
- rinse your mouth after eating with boiled water
- try to chew with the opposite side of the jaw.
Cost of removing an impacted tooth in St. Petersburg:
An impacted tooth is quite difficult to remove. This is a full-fledged dental operation, which is performed under serious anesthesia and only by an experienced dental surgeon. For the removal of an impacted tooth, the price depends on many factors - the complexity of the removal, the determined depth of immersion and location of the impacted tooth, the chosen anesthesia, the time of the operation, etc.
Removal cost
| Local injection anesthesia (as a separate service) | 840 ₽ |
| Removal of a tooth (roots) with preliminary dissection of the soft tissues around the tooth (roots) | 4 400 ₽ |
| Removal of an impacted tooth with preliminary dissection of the surrounding soft and hard tissues | 6 300 ₽ |
| Removal of an impacted tooth | 4 210 ₽ |
| Surgical exposure of an impacted tooth | 1 540 ₽ |
Stages of the procedure
Removing lower impacted “eights” is a more complex and time-consuming operation compared to removing upper extreme molars. This is due to the larger size of the jaw and greater bone density. The complexity of the operation also increases due to the structural features of the dental root system.
At the preliminary stage of the operation, the doctor examines the oral cavity, conducts an X-ray or visiographic examination, and collects an anamnesis. This allows you to choose the method of tooth extraction, anesthesia and its dosage as accurately as possible.
The oral cavity is treated with an antiseptic, and an anesthetic is injected into the gum area above the tooth to be removed. The doctor prepares the necessary materials and instruments for the operation until the anesthesia takes effect. At this time, he can also tell the patient about the sequence of the operation and warn about the consequences.
Then, to gain access to the impacted figure eight, the doctor makes an incision in the gum and separates the soft tissue from the bone. It is necessary to cut or drill out a part of the bone above the “eight” to get to it.
Using dental forceps, the hidden figure eight is grasped and removed. Elevators can be used. If it is not possible to remove a tooth using this method, then a drill is used to cut the dental tissue into pieces and remove them separately.
Various materials (artificial bone) can be used for bone grafting. The wound is sutured using regular or self-absorbing threads. The wound is being treated. Recommendations regarding the recovery period are given.
After some time, you need to see the dentist again to remove the sutures (if regular material was used) and control. Most often, sutures are removed five days after surgery. Usually, in cases where an impacted wisdom tooth has been removed, the patient is issued a sick leave certificate. If there is severe pain or discomfort, then you need to visit the doctor immediately, without waiting for the appointment date.