Modern dentistry cannot be imagined without accurate diagnostics. A set of measures to establish a diagnosis is indispensable in the treatment of teeth and gums; it plays a key role in implantation and prosthetics, and is also important during orthodontic treatment.
Diagnostics is carried out at all stages of preventive and therapeutic tasks. The dentist-therapist resorts to full diagnostic measures when the patient comes to the clinic. The specialist also uses operational diagnostic measures as an intermediate stage of treatment after installing a filling. Upon completion of prosthetic procedures, full diagnostics allows you to evaluate the results and correct them in a timely manner.
Dental diagnostics is, without exaggeration, 50% of the success of treatment and prevention.
Diagnostics involves the following activities:
- History - information about the problem from the patient himself. Mandatory primary stage of diagnosis. The patient indicates the area of concern - which tooth hurts, where there is increased sensitivity, etc.
- Introduction to medical history . Modern technologies make it possible to provide a specialist with images and examination results taken earlier. The information in the medical history card can greatly facilitate the doctor’s work when developing the optimal treatment strategy, so it is important to have it with you whenever possible.
- A thorough visual examination and examination of the condition of the teeth and gums. The specialist determines the problem by the appearance of the tissue.
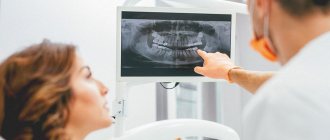
- Instrumental (X-ray) examination is a study using special equipment. A key element of modern dental diagnostics.
X-rays of teeth
Stages of dental examination
The patient undergoes examination in three stages.
- clarification of complaints and medical history;
- examination using physical methods (inspection, palpation, percussion, auscultation);
- research using special methods (laboratory, x-ray).
The final clinical diagnosis is made after clarifying complaints and other aspects of the disease and collecting additional information about the patient. All this will allow appropriate treatment to be carried out at the next stage.
X-ray diagnostics
The use of X-rays and other high-precision equipment in diagnostics allows us to obtain, in real time, accurate images of the desired areas of the oral cavity in optimal resolution.
What equipment is used for instrumental diagnostics:
- Radiovisiograph (visiograph, videograph, dental imaging apparatus) is a device that converts X-ray data into a digital image on a computer in real time. The dentist, using a visiograph, controls the treatment procedure without leaving the chair with the patient. The device allows you to quickly take a photo and obtain an image of the problem tooth.
- Digital 3D orthopantomograph - allows you to take a panoramic image of the desired area of the skull or an individual tooth. The device is indispensable for prosthetics, treatment, implantation, bite correction (orthodontics), etc.
- Rheodentograph is a device for accurately assessing the functional state of the pulp (tissue containing nerve endings) of a tooth according to hemodynamic indications. Allows you to quickly, painlessly and accurately determine the extent of tissue damage. The device is important in the gentle treatment of pulpitis.
- A tool for diagnosing early and latent caries. Pathological processes of hard tissues in the early stages are often difficult to determine. At the same time, treating caries in the early stages allows you to solve the problem with minimal impact on the tissue. The device allows you to effectively identify crisis areas on the tooth.
The capabilities of the equipment allow you to print the results or transfer them to electronic media.
Diagnostic measures include control modeling methods, as well as taking impressions. These methods can significantly increase the effectiveness of orthodontic treatment and prosthetics.
The main task of the dentist is to maintain the health of teeth and gums, maximize tissue preservation, and ensure functionality and aesthetics. All these problems cannot be solved without competent dental diagnostics.
Pain symptom
The pain symptom is an important indicator for making a diagnosis. By clarifying complaints, the patient is questioned. The dentist determines the causes of pain, its nature (pulsating, twitching, aching pain), time of occurrence (at night or during the day), duration (constant or attacks), and where pain occurs.
All this information forms the basis for making a diagnosis. The duration of existence of symptoms is established, the dynamics of the pathological process is formed. After this, it is necessary to collect information about the treatment being carried out. Was it carried out and, if so, how effective was it? The patient is questioned about previous diseases, allergy and epidemiological history, and working conditions.
An objective dental ( and not only ) examination consists of examination, palpation (basic methods), percussion and a number of additional methods.
Therapeutic dentistry
Therapeutic dental treatment is reduced to eliminating the manifestations of dental diseases using conservative methods.
The following areas of development of this industry are identified:
- treatment of non-carious dental diseases (hypoplasia, fluorosis and enamel erosion, wedge-shaped defects, hyperesthesia and pathological abrasion of teeth, necrosis of hard dental tissues, injuries);
- fight against caries and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis, periostitis);
- treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa (traumatic, infectious, symptomatic and specific stomatitis, glossitis, cheilitis, etc.);
- aesthetic restoration of teeth;
- dental hygiene.
It is worth noting that therapeutic sanitation of the oral cavity is the starting point for any dental procedures, both orthodontic or orthopedic, and surgical.
Periodontitis
Caries
Pulpitis
Wedge-shaped defect
Basic examination methods
Patient interview. This is done at every appointment. The doctor collects information about complaints, existing symptoms, past illnesses, medications taken, etc.
Inspection. The dentist examines the mucous membranes, teeth, evaluates the structure of the face, the closure of the dentition, the presence of swelling, edema, and other signs of inflammation. After a general examination, the condition of each of the teeth in the upper and lower jaw is assessed.
Crowns are examined using a dental mirror (allows you to see hard-to-reach areas and direct light to them). A sharp probe is used to assess the condition of the enamel. If there is a possibility of inflammation, percussion is performed, tapping the tooth (along the cutting edge or chewing surface). Normally it should be painless.
To assess the condition of the periodontium, the gums are examined, the presence of swelling, reddened, swollen, and injured areas is checked. Shallow probing may be performed to detect bleeding. If there is swelling or swelling, palpation (feeling) is performed. It is also used to assess tooth mobility.
Diagnostics in dentistry
The primary task for a dentist is to make the correct diagnosis for the patient. The diagnosis is the starting point for planning the treatment process, and the achievement of a successful result depends on its accuracy.
Why is accurate comprehensive diagnosis so important?
Nowadays, some patients perceive dentistry in a distorted way. Among the reasons we can highlight competition between clinics that, in search of patients, are ready to promise everything at once. In this case, insufficient time is devoted to diagnosis, and the correctness of the diagnosis remains in question.
Doctors are also contributing to this negative trend. Some of them quickly make a diagnosis based only on images or a simple examination, and are ready to immediately begin treatment. This practice is common not only in therapeutic dentistry, but also in prosthetics and implantation. One can only imagine what risks exist for the patient without a full diagnosis, and what complications may arise as a result of such an approach.
When contacting a general practitioner at a clinic, we all understand the appointment of many tests and images, as well as referrals to other specialists. Why shouldn’t dentists adopt this approach? We know well that everything in the human body is interconnected. The dental system also interacts with other systems of the body, so simple dental treatment can affect them as well. It can be difficult to establish the root cause of dental diseases without additional diagnostics, because by the time the patient comes to the clinic, his condition may worsen under the influence of psychosomatics.
Thus, thanks to the diagnostics carried out in each specific case, the correct diagnosis can be made. This is the only way to confidently exclude diseases of the respiratory system and spine, as well as neurological diseases. An individual approach to each patient includes personal communication with the dentist to establish contact and clarify the medical history. Thanks to this, the upcoming treatment will take place in an atmosphere of mutual trust and cooperation.
Palpation
One of the standard diagnostic methods is muscle palpation. Using this method, you can analyze the work of the muscles of the head and neck. When comparing muscle function with bilateral palpation, dysfunctions in the functionality of the muscular system can be identified. Thus, having basic anatomical knowledge, the dentist diagnoses problems of the dentofacial apparatus as a whole.
Bite analysis
Wax plates are used to record occlusion and articulation indicators in dentistry. They are used to determine the movements of the lower jaw and the contact of teeth at rest. Using plates is a simple and effective way to evaluate the closure process. However, in addition to this, a general examination is also important, during which you can find out about the condition of the periodontium and teeth, the presence of removable structures and restorations. Thanks to this, the dentist can draw conclusions about oral hygiene and the condition of the mucous membrane. This information is extremely important because malocclusions are often accompanied by periodontal problems.
Photo protocol
Currently, photography is widely used in diagnostics. To optimize the process, a protocol has been developed that the specialist follows.
For a complete diagnosis, it is necessary to take two groups of images – extraoral and intraoral.
Extraoral photographs record the position of the patient's head in individual positions. Based on these images, one can judge the characteristic features of appearance, asymmetry and facial features, muscle tension in the neck and head.
Intraoral photographs can reveal the position of the jaws, the condition of the dentition and other features.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
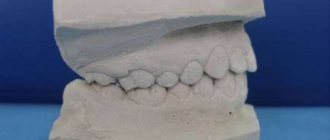
Diagnostic models
One of the most important components of the diagnostic process is the production of models based on casts. At this stage, an articulator is used, which shows the position of the upper and lower jaws with maximum accuracy. The articulator is adjusted individually in each specific case, thanks to which the dentist receives comprehensive information about the dental system.
When diagnosing, an important role is played by the analysis of information about the patient’s bite. Maximum contact between teeth is not informative enough for the doctor. The primary task is to calculate the unforced posterior position of the mandible. Thanks to this, it is possible to determine the real relationship of the jaws and identify the source of the detected pathology.
Condylography
An effective method for diagnosing TMJ is condylography. It allows you to calculate the characteristics of movement in a joint. By analyzing the information obtained during condylography, the dentist can determine the presence of pathologies and make the correct diagnosis. Of course, data from other diagnostic methods are also taken into account.
Due to its non-invasiveness, condylography is an easy-to-use method. However, it requires special knowledge and skills from the dentist, without which it is impossible to obtain accurate data.
It is important to mention that condylography data is used both to clarify the diagnosis and for subsequent orthopedic work.
Other diagnostic methods
Currently, the following types of diagnostic methods are used in dental practice:
- Computed tomography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the central nervous system;
- Orthopantomogram;
- Teleradiogram, etc.
Let's talk briefly about some of these methods.
Teleradiogram
This method allows you to obtain accurate data on the structure of the skeleton and soft tissues. It is carried out according to a standard scheme, which increases the efficiency and effectiveness of treatment. In reconstructive dentistry, the importance of TRG analysis cannot be overestimated.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the HFNS
MRI is one of the most important methods for diagnosing dysfunctions of the HFNS. It helps to analyze the condition of the joint and soft tissues with maximum accuracy. However, the effectiveness of tomography directly depends on the qualifications of the doctor and his ability to interpret the image.
CT scan
Computed tomography is another common diagnostic method. It is used when making an initial diagnosis and in preparation for dental implantation.
Approximate prices for x-ray diagnostics
It is difficult to name the exact cost of treatment - it all depends on the initial clinical picture and the extent of the lesion. But an X-ray examination is required in most situations, and the choice of a specific technique remains at the discretion of the doctor. To figure out how much an x-ray of a tooth or entire jaw costs, check out the approximate prices for procedures.
| Methodology | Approximate cost, rub. |
| Sight shot | 350 |
| Orthopantomogram (panoramic) | 1200 |
| Computed tomography (CT) | 1500 |
| Cone beam CT | 2500 |
The table shows average prices, and the exact cost will depend on the region of treatment and the level of the medical institution. So, for example, in specialized diagnostic centers prices can be much higher, and this is due to the use of more professional, high-precision equipment. Please keep in mind that before serious treatment, including complex implantation, very careful preparation is required with a detailed study of the condition of the patient’s bone tissue. Therefore, it is recommended to contact specialized centers for X-ray images.
Panoramic shot
An orthopantomogram is a panoramic image that gives the doctor accurate information about the condition of the patient’s teeth, bone tissue, jaw joints and maxillary sinuses.
Often, a panoramic photograph is taken for children to detect supernumerary teeth or, on the contrary, the absence of the rudiments of permanent teeth. An orthopantomogram shows all restorations, fillings, any pathological formations in tissues, and at a very early stage
Indications for a panoramic photo:
- Therapeutic treatment - the image will qualitatively visualize each tooth, carious lesions, destroyed fillings, granulomas and cysts, if any.
- Periodontal treatment - in the image, the periodontist will be able to see the depth of the periodontal pockets, the thickness of the bone tissue and other details necessary for the treatment of periodontal disease
- Implantation - an orthopantomogram will allow you to develop an effective implantation plan and determine the most suitable points for implantation.
- Correction of the bite - before choosing a corrective system and placing braces on the patient, the orthodontist needs to understand the position and direction of growth of the roots of each tooth.
Surgical dentistry
So, surgical dentistry is one of the most significant and complex sections of modern medical science. Many people mistakenly believe that the competence of specialists in this field includes only performing simple tooth extraction operations. In fact, doctors of this profile perform a huge variety of different manipulations, ranging from tooth-preserving procedures to plastic surgery.
The competence of specialists in the field of dental surgery includes:
- treatment of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity (periostitis, periodontitis, osteomyelitis, abscesses, phlegmon, etc.);
- carrying out implantation;
- treatment of tumor diseases of the oral cavity;
- carrying out tooth-preserving procedures;
- treatment of pathologies of the temporomandibular joint;
- tooth extraction;
- combating diseases of the trigeminal nerve;
- performing operations on periodontal tissues;
- elimination of malfunctions of the salivary glands;
- primary treatment of wounds in the neck, face and oral cavity;
- carrying out reconstructive and plastic surgeries.
Dental surgery is directly related to such branches of medical science as implantology, orthodontics, orthopedics and aesthetic dentistry. This is why dental surgeons work closely with specialists in these fields.