Proper oral care after tooth extraction
To prevent unwanted consequences from occurring, it is important not to do the following:
- touch the wound with your tongue or use other foreign objects for this,
- rinse your mouth generously in the first two days,
- make sudden movements with the facial muscles,
- plunge into hot water or rinse with it,
- Hard to work,
- eat food in the first 3 hours that follow the procedure, it is permissible to drink, but refrain from boiling water.
- You should also abstain from cigarettes at this time,
- alcohol is contraindicated within 24 hours after surgery. If your doctor prescribes the use of antibiotics, you should not drink alcohol until the end of the course of therapy.
A cold compress will prevent swelling
Immediately after the manipulations, it is necessary to apply a cold compress, since after tooth extraction the cheek may swell.
To do this, take some chilled meat products or ice and apply it, after wrapping it in a cloth. Such actions will help to minimize or even eliminate swelling of the soft areas of the face that can form in the event of a serious intervention.
It is recommended to keep the ice for about 5 minutes, apply it 3-4 times, taking a break between applications. It is important to apply cold immediately after surgery, since further this action will not bring the desired effect. Under no circumstances should you use a warm compress or warm the tissue in any other way - thoughtless intervention can cause suppuration.
If your gums bleed after tooth extraction
You can stop bleeding in a number of effective ways. In most cases, this disease affects people with high blood pressure with hypertension or patients who have had a large vessel damaged.
It is worth noting that due to psychological overload and stress during activities, even in people with normal health, blood pressure may rise. The first step is to apply a tightly rolled piece of sterile bandage to the bleeding site, and then measure the patient’s blood pressure. If it is elevated, you need to resort to medications.
With increased blood pressure, the chance of hematoma and blood appearing after tooth extraction increases. This development of events is dangerous due to suppuration, which will then have to be opened, and bleeding can cause dizziness and weakness.
If bleeding appears several hours after removal, you should not wait for the situation to normalize, but seek medical help.
Diabetes mellitus during tooth extraction
If a person has this disease, it is recommended to measure their sugar levels immediately after surgery. Tension leads to the production of adrenaline, which can increase the rate. By measuring sugar, a person will know about his condition and will be able to prevent side effects.
If a gauze pad is placed on the gum
A gauze swab is placed on the hole if it is etching. In other situations, the use of this remedy is undesirable, as it can provoke inflammation. As the tissue is removed, the blood clot that has formed in the socket is also removed.
If the tissue lining is on the wound, it is necessary to carefully remove it after a certain period of time after removing the tooth. A tampon that has absorbed a certain amount of liquid automatically becomes a breeding ground for a wide range of bacteria. You should not keep it in your mouth for a long time to prevent the appearance of inflammatory processes in the hole that remains after tooth extraction.
Antiseptic rinses for suppurations
There is no need to rinse your mouth intensively; instead, use “baths”. In order not to disturb the damaged tissues, take a special anti-inflammatory solution into your mouth, keep it inside, and then spit it out.
Installation of a temporary prosthesis
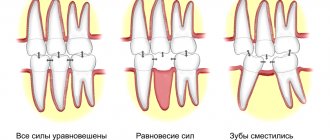
After extraction, an empty area is formed in the dentition. Leaving everything as it is for a long time is extremely undesirable, since even a single adentia causes a number of unpleasant consequences. Among them:
- Displacement of adjacent teeth towards the empty space and weakening of their fixation in the sockets.
- Changes in bite, which can lead to problems with the temporomandibular joint.
- Disorders of the stomach and intestines caused by difficulty in chewing food.
- Changing the shape of the face, weakening the tone of its muscles, thinning of the lips, and the appearance of wrinkles.
So, if a tooth is removed, after what time can prosthetics be done? To prevent the problems listed above, it is advisable to act as quickly as possible. Already three to four days after extraction, you can begin to prepare for the installation of a temporary crown. Such a prosthesis will help quickly eliminate an aesthetic defect, restore chewing function, and prevent adjacent teeth from moving. You can wear it for up to a year.
Baths should be carried out if:
- an incision was made to expose the gumboil;
- the tooth was removed due to inflammatory processes;
- there are harmful deposits on the teeth and caries;
- removal of the root of a tooth with caries
For procedures with baths, you can use an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine with a concentration of 0.05%. This drug is inexpensive, it can be purchased ready-made, it has excellent antiseptic effects, and tastes bitter. Such procedures must be carried out 3 times a day. The solution must be kept in the mouth for 1 minute.
Blood Center
Dear donor! Here we list the most common health conditions and diseases that prohibit donation temporarily or permanently.
Please be guided by these restrictions only if you are absolutely sure that you have the relevant disease or health condition.
If you have any doubts or do not find an answer to your question, be sure to consult with a medical worker at the Blood Center by calling 617 3009 or 617 3042 during the Blood Center’s opening hours (Mon., Fri. 8.00 - 16.00 and Tue.-Thurs. 11.00 - 19.00) .
- to wear a mask when coming to Donor Day (if necessary, you can obtain one from the blood center registrar).
- A COVID certificate (COVID certificate of vaccination, negative test or disease history) is not required from donors, since donated blood is necessary to provide vital services in the country. All healthy people who meet the donor selection criteria can donate blood.
Restrictions on donating blood due to the spread of Covid-19:
If a donor has COVID-19, he or she can donate blood 14 days after symptoms disappear or the RNA test is negative.
If a donor has been in contact with a person with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19, they can donate blood 14 days after contact with the patient or after a negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR test result on day 10.
For donors traveling to high-risk areas (countries with 150 coronavirus infections per 100,000 population or higher), donation bans may be consistent with the travel restrictions described here:
https://vm.ee/et/teave-riikide-ja-karantiininouete-kohta-euroopast-saabujatele
Restrictions on donating blood due to Covid-19 vaccination:
After vaccination with a killed virus, non-replicating viral vector vaccine (eg, AstraZeneca and Janssen vaccines), component vaccine or mRNA vaccine (eg, Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna vaccines), blood donation is permitted if the donor is well.
After vaccination with a weakened virus (for example, vaccines based on a replication-competent viral vector, live attenuated viral vaccines), blood donation is allowed after 4 weeks. Currently this type of vaccine is not used in Estonia.
If it is not possible to determine what type of vaccine was used, blood donation is allowed after 4 weeks.
- Dental treatment
- Respiratory diseases
- Tumors
- Diseases of the genitourinary organs
- Ear diseases
- Skin diseases
- Infectious diseases
- Operations and injuries
- Travel restrictions
- Pregnancy and postpartum period
- Medications
- Digestive diseases
- Disorders of internal secretion and metabolism
- Intestinal infections
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Vaccination
- Diseases of the circulatory system
- Disease conditions related to blood, hematopoiesis and immune mechanisms
- Restrictions due to other reasons
DENTAL TREATMENT | |
| Dental treatment | Blood donation is allowed 24 hours after treatment if there are no complications |
| Removal of a tooth | Blood donation is allowed 1 week after removal |
| Inflammation of the root tissues of the tooth, inflammation of the gums | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after recovery |
| Stomatitis (inflammation of the mouth) | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after recovery |
| Outpatient dental surgeries | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after surgery |
RESPIRATORY DISEASES | |
| Bronchitis | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
| Bronchial asthma | Regular treatment is required - blood donation is prohibited; regular treatment is not required - blood donation is allowed 1 month after the last dose of the drug and symptoms of the disease |
| Colds (runny nose, cough, sore throat) | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after recovery |
| Flu | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after recovery |
| Pneumonia | Blood donation is allowed 6 months after recovery |
| (Only) runny nose | Blood donation is allowed 1 week after recovery |
| Sinusitis | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
| Inflammation of the tonsils, sore throat | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
| Tuberculosis | Blood donation is allowed 2 years after the doctor declares recovery |
TUMORS | |
| Benign tumor | Blood donation is allowed after recovery, it is decided individually |
| Malignant tumor | blood donation is prohibited |
DISEASES OF THE GINOROGENITAL ORGANS | |
| Prostatitis | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
| Cystitis without fever | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after recovery |
| Cystitis with fever (hospital treatment) | Blood donation is allowed 3 months after recovery |
| Inflammation of the ovaries and appendages | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
| Inflammation of the renal pelvis | Blood donation is allowed 12 months after recovery, if necessary, the opinion of the attending physician |
EAR DISEASES | |
| Non-suppurative otitis media | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after recovery |
| Purulent otitis media | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
SKIN DISEASES | |
| Acute allergic rash | Blood donation is allowed after the rash disappears |
| Acne | in case of treatment with Roaccutane, blood donation is allowed 1 month after the end of treatment |
| Atopic dermatitis | Blood donation is allowed if the course is mild and if there is no rash at the puncture site |
| Eczema | If there is a rash at the site of vein puncture, blood donation is not allowed |
| Psoriasis | blood donation is allowed if there are no symptoms, no need for immunomodulatory therapy and no complications; in other cases, blood donation is prohibited |
| Removal of birthmarks, papillomas | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after surgery |
INFECTIOUS DISEASES | |
| Borreliosis | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
| Tick-borne encephalitis | Blood donation is allowed 1 year after recovery |
| Hepatitis A disease | Blood donation is allowed 1 year after recovery |
| Hepatitis B disease | blood donation is prohibited |
| Hepatitis C disease | blood donation is prohibited |
| Sexual contact with a person who has had hepatitis B or C or is a carrier of viral markers | blood donation is prohibited; if 4 months have passed since the last sexual contact, then blood donation is allowed if the test result is negative |
| Household household contact with a patient with hepatitis | Blood donation is prohibited for 4 months after the last contact |
| Herpes zoster (shingles) | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after recovery |
| Herpes simplex | Blood donation is allowed 1 week after recovery |
| HIV AIDS) | blood donation is prohibited |
| Sexual contact with an HIV-positive person | blood donation is prohibited; if 12 months have passed since the last sexual contact, then blood donation is allowed if the test result is negative |
| Carriage of papilloma virus | allowed if the person is left under observation and does not need treatment; in case of treatment, the decision is made by the donor’s doctor on an individual basis |
| Mycoplasma infection | Blood donation is allowed 4 months after recovery |
| Toxoplasmosis | Blood donation is allowed 6 months after recovery |
| Tuberculosis | Blood donation is allowed 2 years after the doctor declares recovery |
OPERATIONS AND INJURIES | |
| OPERATIONS | |
| Removal of the appendix Removal of the gallbladder Spinal surgeries Joint surgeries Endoscopic surgeries | Blood donation is allowed 4 months after surgery |
| Tonsil removal Operations on the nose and paranasal sinuses Eye operations (except laser) | Blood donation is allowed 2 months after surgery |
| Partial removal of the stomach or large intestine | blood donation is prohibited |
| Gynecological surgeries Open abdominal surgeries | Blood donation is allowed 6 months after surgery if there are no disease-related contraindications |
| Laser eye surgery | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after surgery |
| Multiple injuries | Blood donation is allowed 1 year after recovery |
| Removal of birthmarks, papillomas | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after surgery |
| BONE FRACTURES | |
| Home treatment: - single fractures of the limbs, - fractures of the metacarpal bones and bones of the foot, - fractures of the ribs | Blood donation is allowed 2 months after recovery |
| Hospital treatment | Blood donation is allowed 4 months after recovery |
TRAVEL RESTRICTIONS | |
| Persons who have been in the area where the West Nile fever virus has spread (USA, Mexico, Canada, EU and neighboring countries, see areas HERE ) | blood donation is allowed 28 days after leaving an area where there is ongoing transmission of the virus to people; the restriction applies to travel to the EU and neighboring countries from June to November, to the USA and Mexico - all year round |
| Persons who have been in a malaria area (see HERE for areas ) | Blood donation is allowed 12 months after leaving the area |
PREGNANCY AND POSTPARTUM | |
| Abortion | Blood donation is allowed 6 months after an abortion |
| Pregnancy | blood donation is prohibited |
| Lactation | Blood donation is prohibited during breastfeeding |
| Childbirth | Blood donation is allowed 6 months after birth |
MEDICATIONS | |
| Painkillers (aspirin, ibuprofen, etc.) | Blood donation is allowed if no more than 1-2 tablets have been taken in case of mild illness and if there are no other contraindications |
| Course of antibiotics | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after completion of the course of treatment, unless there are other contraindications |
| Contraceptive drugs | blood donation allowed |
| Hormone replacement therapy in women during adolescence | blood donation allowed |
| Antidepressants | Blood donation is allowed if you feel well |
| Roaccutane, accutane | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after finishing the medication |
| Medicines for heart problems | blood donation is prohibited |
| Cardiac glycosides | blood donation is prohibited |
| Hormonal drugs | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after finishing the medication |
| Growth hormones | blood donation is prohibited |
| Medicines taken for high cholesterol | The possibility of donating blood is decided individually |
| Medicines taken for high blood pressure | donation of whole blood is permitted provided that the drug has been used for at least 2 weeks, blood pressure is stable and within normal limits; apheresis procedures are not permitted |
| Radioactive iodine | Blood donation is allowed 1 year after stopping the medication |
| Use of gold preparations | blood donation is prohibited |
| Mild sleeping pills, sedatives | blood donation allowed |
| Medicines taken for high stomach acidity | Blood donation is allowed if there are no other contraindications |
| Laxatives | blood donation allowed |
| Medicines for nausea and vomiting | blood donation allowed |
| Medicines used for diabetes | blood donation is prohibited |
| X-ray contrast agents (containing iodine) | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after finishing the medication, unless there are other contraindications |
| Oral antifungals | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after finishing the medication |
| Medicines for epilepsy | blood donation is prohibited; In case of cured epilepsy, blood donation is allowed 3 years after recovery and completion of medication |
DISEASES OF THE DIGESTIVE ORGANS | |
| Gastritis | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
| Acute ulcer of the stomach and duodenum | Blood donation is allowed 6 months after recovery |
| Chronic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum | blood donation is prohibited |
| Acute cholecystitis | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
| Chronic cholecystitis | blood donation is prohibited |
DISORDERS OF INTERNAL SECRETION AND METABOLISM | |
| Thyroid deficiency | in case of hypothyroidism compensated by L-thyroxine, blood donation is allowed if the daily dose of L-thyroxine has not changed during the last 6 months |
| Diabetes | blood donation is prohibited |
INTESTINAL INFECTIONS | |
| Mild diarrhea | Blood donation is allowed 1 week after recovery |
| Dysentery | Blood donation is allowed 1 month after recovery |
| Salmonellosis | Blood can be donated 2 weeks after recovery and if the results of control tests are negative |
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES | |
| Genital herpes | Blood donation is allowed 4 months after recovery from primary infection; in case of repeated exacerbation of the disease, blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after recovery |
| Gonorrhea | Blood donation is allowed 4 months after recovery |
| Chlamydia | Blood donation is allowed 4 months after recovery |
| Condyloma | Blood donation is allowed 4 months after recovery |
| Mycoplasma infection | Blood donation is allowed 4 months after recovery |
| Syphilis | blood donation is prohibited |
| Ureaplasma | Blood donation is allowed 4 months after recovery |
VACCINATION | |
| BCG, yellow fever, rubella, measles, mumps, polio (oral), attenuated typhoid vaccine, attenuated cholera vaccine | Blood donation is allowed 4 weeks after vaccination if the donor is healthy |
| Viral hepatitis B | Blood donation is allowed 2 weeks after vaccination if the donor is healthy |
| Cholera, typhoid fever (killed bacteria vaccine) | Blood donation is allowed if the donor is healthy |
| Diphtheria, tetanus viral hepatitis A tick-borne encephalitis papilloma virus | Blood donation is allowed if the donor is healthy |
| Influenza, polio (shot), Japanese encephalitis | Blood donation is allowed if the donor is healthy |
| Cervical cancer (HPV vaccine) | Blood donation is allowed if the donor is healthy |
| Rabies | Blood donation is allowed if the donor is healthy. If bitten by an animal infected with rabies, blood donation is prohibited for 1 year. |
DISEASES OF THE CIRCULAR ORGANS | |
| Hypertonic disease | Blood donation is allowed if there are no complications, blood pressure as a result of treatment started at least 2 weeks ago is stable and within normal limits |
| Myocarditis | Blood donation is allowed 2 years after the end of treatment |
| Myocardial infarction | blood donation is prohibited |
| Repeated venous thrombosis | blood donation is prohibited |
DISEASE CONDITIONS RELATED TO BLOOD, BLOODPOISIS AND IMMUNE MECHANISMS | |
| Chronic anemia | blood donation is prohibited |
| Rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis | |
LIMITATIONS DUE TO OTHER REASONS
MenstruationDonating blood is prohibited during menstruation and for 3 days after its end.Skin and mucous piercing, tattooBlood donation is allowed 4 months after piercing/tattooAcupunctureIn the case of reused needles, blood donation is allowed 4 months after acupunctureTick biteBlood donation is allowed 2 months after the biteContact of damaged skin or mucous membrane with someone else’s blood (also from sexual partners)Blood donation is allowed 4 months after the last contactIf your gums hurt after tooth extraction
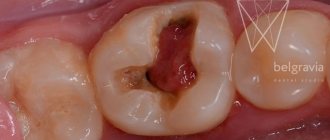
Tooth extraction leads to damage to soft tissues, which contain a large number of nerves. The doctor performs the procedures under local anesthesia, so the patient feels discomfort only in one thing - the need to spend a certain amount of time with his mouth wide open.
When the analgesic effect ends and the tooth has already been removed, the pain returns. Usually they are of a “aching” nature and do not fundamentally interfere with normal life activities. But in some cases the pain can be intense.
If the tooth extraction was not caused by inflammatory processes, you can avoid the use of painkillers. If pain relief is necessary to avoid severe pain after tooth extraction, it is recommended to take an analgesic until the anesthetic wears off.
Using painkillers after tooth extraction
If you experience intense pain, you can resort to using “Ketans”; The medicine is dispensed by pharmacists in pharmacies only with a prescription - this is due to the presence of side effects. Severe pain can occur during complex and lengthy medical intervention, especially if it was accompanied by drilling of the bone around the tooth, or if the operation was performed poorly, unprofessionally and traumatically.
“Ketorol” (an analogue of “Ketanov”), “Analgin” (will help reduce mild pain syndrome), “Spazmalgon” (in addition to the analgesic effect has an antiseptic effect), “Baralgin” (a drug that contains “Analgin” in its composition).
Indications and contraindications for immediate implant placement
Indications
- Mechanical damage to the root - fracture, dislocation
- Restoration of frontal units
- Therapeutic treatment did not bring results
- Sufficient bone volume
- No contraindications
Contraindications
- Deficiency, looseness of bone
- Inflammation at the root apex
- Enlarged socket after removal
- Inflammatory processes of the oral cavity, gum pathologies
- Reduced immunity, systemic diseases
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding period
Wisdom tooth removal
Wisdom teeth are the painter or chewing teeth located at the end. When chewing, they do not play a significant role; the structure is no different from ordinary teeth.
There are several generally accepted indications for removal:
- ingrowth of roots into the maxillary sinus,
- partial eruption
- facial neuralgia,
- inclined or lateral position,
- caries damage.
When removing a wisdom tooth, painkillers are used to relieve pain. Consequences after the operation may occur depending on the complexity of the operation, surrounding tissues, location, and access to the tooth.
Negative consequences may occur if the patient does not adhere to the doctor's orders. Baths of soda and herbal decoctions will also help alleviate the condition after removal. It is forbidden to rinse; it is important to preserve the blood clot, which protects the wound from infection.
Reasons for difficult removal
Removing wisdom teeth is significantly more difficult than removing other teeth.
This situation is due to many factors:
- distant and non-standard placement of “eights”, which makes them difficult to access for surgical interventions;
- abnormal development or inability to erupt;
- a large number of deeply located and branched roots.
The complexity of the operation is significantly influenced by the location of the third molars. The lower jaw is wider and denser than the upper, which allows the roots to branch greatly and penetrate much deeper. Therefore, removing a lower wisdom tooth is much more difficult than removing an upper one.
In some cases, difficult removal of a wisdom tooth in the lower jaw can cause suppuration of the socket, which can lead to abscess, sepsis, lymphadenitis, phlegmon, and osteomyelitis. Therefore, if pus is detected, you must immediately contact your dentist.
The upper jaw is narrower and looser, as it has many holes. Therefore, in most cases, removing the upper wisdom tooth is not difficult for the surgeon. In addition, the upper jaw is easier to anesthetize.
Removing a wisdom tooth in the upper jaw becomes more difficult if the “eight” is severely damaged or has curved roots.
In what cases is it necessary to remove the nerve of a tooth?
Removing the nerve from a tooth kills it. Almost no nutrients are supplied, causing it to become darker and weaker. During treatment, dentists try to keep the dental nerve alive, but sometimes they have to take forced measures to put the oral cavity in order.
Nerve removal is necessary if:
- Deep caries.
If the disease has destroyed almost the entire tooth, there is nothing to save; the main thing for the doctor is to prevent further destructive process.
- Prosthetics.
To install the prosthesis, an incision must be made in the pulp chamber. This is especially necessary in situations where teeth grow at an inclined angle.
- Incorrect treatment in the past.
This can happen if during treatment the doctor resorted to opening the pulp chamber. In this case, it is necessary to partially remove the nerve.
- Mechanical damage.
Injury can lead to chips in the enamel where the nerve is located. If the front teeth are damaged, the nerve is not completely removed.
Antibiotic therapy after removal of unhealthy teeth
Antibiotics are prescribed by the attending physician - dentist. Drugs are prescribed in case of difficult extraction, to prevent the risk of complications if the tooth was removed due to inflammatory processes.
The drug usually prescribed is Lincomycin 0.25. Take capsules after tooth extraction for 5 days, 2 capsules 3 times. If purulent inflammation is present, the antibiotic is prescribed as intramuscular injections.
Those who suffer from intestinal and stomach disorders can take antibiotics in effervescent forms, for example, Unidox Solutab and Flemoxin Solutab.
Clinic doctors
Modern tooth extraction without pain and shock!
And this is not an exaggeration. Even the most complex tooth extraction procedures, with the right approach, will be comfortable and quick.
The tooth extraction procedure at DentaBravo is painless, takes an average of half an hour and brings you great relief. And right in this section you will find answers to your questions. Read and get rid of your fears!
Removal (extraction) is one of the most common operations in dentistry. As a rule, it consists of the following stages:
- taking an anamnesis (the doctor finds out whether the patient is allergic to medications, whether the person suffers from high blood pressure, heart disease and some other diseases);
- anesthesia;
- preparing the tooth for extraction;
- extraction of a tooth from the alveolus;
- medicinal treatment of the hole.
When is it necessary to remove teeth?
Molar tooth extraction can be performed for planned or emergency reasons. In the first case, teeth are removed that cannot be treated, are incorrectly located and interfere with the growth of other teeth, or injure the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Emergency removal is necessary if a purulent inflammatory process develops in the periodontium, as well as in the presence of a number of diseases (periostitis, maxillary abscess, etc.)
Doesn't tooth extraction hurt?
Modern dentistry has all the means to remove a tooth absolutely painlessly. The most commonly used local anesthesia is an injection. Sometimes anesthesia is carried out in two stages: first, the doctor treats the gums with a solution or gel that reduces sensitivity, then the anesthetic solution is injected into the gums using a syringe.
What is complex removal?
This is a surgical operation that is performed if the tooth cannot be removed in the usual way. Complex tooth extraction in dentistry is necessary when it comes to unerupted (impacted) and incorrectly positioned (dystopic) teeth. It is difficult to remove the root of a tooth, as well as a tooth fused with bone tissue. The removal of a broken tooth can also be included in this category.
How long does it take to remove a tooth?
The tooth extraction procedure takes about fifteen to twenty minutes on average. In some situations, this may require more time (for example, if you have to remove a tooth in parts), but usually no more than thirty to forty minutes. Sometimes removal can take up to three hours. It all depends on the specific clinical case.
How many teeth can be removed at one time?
It is impossible to give an exact number. Usually no more than one or two teeth are removed at a time. If the teeth are mobile and the removal is simple, more can be removed. For complex extractions, it is not recommended to remove more than one tooth.
How long will it take for gums to heal?
If the tooth extraction operation is carried out correctly, the gums heal quite quickly - this may take about one week. Sometimes, if after extraction the tooth socket is not filled with a blood clot, it takes 2-3 weeks for complete healing.
How long after can I eat after tooth extraction? You are allowed to eat no earlier than two to three hours after surgery, and you can drink after an hour. However, during the first 24 hours, it is recommended to eat only soft or liquid foods to avoid additional injury to the gums. On the day of surgery, you should avoid hot and cold foods, as well as drinking alcohol.
How to care for your teeth after tooth extraction?
After tooth extraction, it is not recommended to rinse your mouth. This is due to the fact that during the rinsing process a blood clot may fall out of the hole, which can lead to inflammation. You need to brush your teeth very carefully, without touching the wound.
Is an examination necessary the next day after tooth extraction?
Usually this is not required. However, if a complex removal was performed, the doctor may order a follow-up examination. Then the next day you will have to visit the dentist to make sure that the procedure was successful, the socket is in order and there are no complications. If a visit to the doctor is not planned, but you have cause for concern, do not hesitate to go to see a specialist.
How soon can prosthetics begin?
Typically, prosthetics begin no less than one month after tooth extraction. If you plan to install a fixed bridge, it is enough to wait about three weeks. In those cases where dental implantation is proposed, it is advisable that more than a month pass.
How much does tooth extraction cost?
The cost of this service depends on the complexity of the procedure. For example, if a simple removal of a front tooth is required, dental manipulation will cost the patient much less than if it is necessary to remove an unerupted “wisdom tooth” from the mouth. The cost of tooth extraction in our dentistry can be found here.