Why is X-ray examination needed in dentistry?
X-ray examination (dental x-ray) is the basis of quality treatment with a good prognosis.
Without high-quality x-ray diagnostics, it is almost impossible to create a competent treatment plan. Our clinics have the best equipment, innovative software, and we use artificial intelligence for accurate diagnostics.
Dental x-rays can reveal:
- inflammatory process inside the tooth;
- presence, size and location of the cyst;
- presence of a tumor;
- quality of dental canal filling;
- how deep is the caries;
- abscess in periodontal elements;
- crack in the tooth;
- the presence of unerupted teeth (including wisdom teeth);
- various anomalies in the structure of bones;
Only after an adequate X-ray examination has been carried out can the doctor make a diagnosis with complete confidence and prescribe the correct treatment.
Dental X-rays are necessary during therapeutic treatment (especially during root canal treatment), prosthetics, implantation, and also before starting orthodontic treatment (bite correction).
In addition, X-ray diagnostics allows the doctor to confirm the effectiveness of the treatment.
CT scan
Computed tomography of teeth is a real breakthrough in modern dental technologies. A tomogram is a series of layer-by-layer high-definition X-ray images. This method allows you to study in detail the condition of teeth, periodontal and periodontal tissues, the temporomandibular joint and the maxillary sinuses.
A 3D computer image has the following advantages:
- Clearly shows the smallest structures that are not visible on the targeted image and OPTG.
- Allows you to accurately determine the location and size of the inflammatory process inside the bone without surgical intervention;
- Helps to carefully plan the dental implantation process;
- Makes it possible to diagnose small tumors.
Types of X-ray examinations in dentistry
Dentists use several options for x-ray examinations, which allow them to study both one tooth individually and the entire jaw: bone structures, joints, connective tissues.
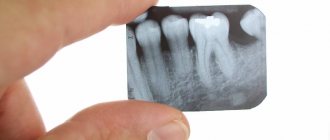
- Sight shot
is the most common type. It is performed on a visiograph with low radiation dose. This method is used to make a diagnosis in the area of 1-2 teeth. - CBCT (computed tomogram, 3D image).
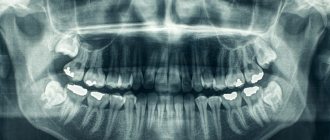
This is the standard in dentistry today. CBCT will be required for volumetric therapeutic treatment, in preparation for implantation, prosthetics, and orthodontics. It can be used to identify deep dental lesions, bone changes, and malocclusion. - Panoramic
dental x-ray is a 2D overview image of the entire oral cavity. The doctors at our clinic work according to world standards, so we plan treatment based on 3D image data (CBCT). But we don’t take panoramic photographs in our clinic - this diagnosis is not enough for accurate planning.
Radiology
Radiography has two significant unavoidable disadvantages. Every doctor must understand the limits of radiography and, when taking and analyzing x-rays, take into account the limitations that this diagnostic method cannot overcome.
Firstly, an Rg image, like a regular photograph, is a two-dimensional projection of three-dimensional space. In the scientific literature, the term “3D object” is used to refer to the object being photographed, and “2D views” are used to refer to the resulting images. From a school drawing course or from a university course in engineering graphics, you may remember that in order to fully represent an object, it is necessary to depict three of its projections on paper. A tube of toothpaste will look like a circle in one projection, like a triangle in another, and like a rectangle in a third.
The anatomical shape of teeth and their internal structure are much more complex than a tube. Channels can meander in three-dimensional space, bifurcate and converge. It is impossible to reliably judge the structure of a tooth from one photograph. If there are two channels in the path of the beam, in the projection we will see them as one object. In order to see all the richness of the tooth structure, it is necessary to take at least two photographs from different angles.
The second disadvantage of radiography is the mixing in the resulting images of the projections of all objects located in the path of the X-rays. The image appears dirty. The doctor analyzing the X-ray image must have special knowledge and experience in order to highlight the objects he needs on it, without confusing them with others. The most revealing illustration of this deficiency is a teleradiographic photograph of the skull in profile. Teeth, branches of the lower jaw, nasal sinuses and other objects appear double in the image. It is impossible to reliably determine on which teeth the fillings are installed from this image; for this, other diagnostic measures must be carried out.
Sighted intraoral photographs of individual teeth appear clearer, but this appearance is deceptive. As we have already said, the tooth has a complex structure. Two channels located far from each other, when projected onto a plane, can coincide and look like one object with a fuzzy outline. In this case, it is not possible to determine whether both canals are sealed, and if not, which one.
Taking into account the shortcomings of the method, developers of X-ray technology and radiologists are developing special X-ray techniques. For example, the location of the sensor (sensor) directly in the oral cavity, filming one tooth from different angles, and others. In most cases, this is enough for successful dental treatment.
But there are difficult cases. Patients have problems that patients and doctors do not even always associate with dentistry. For example, a chronic runny nose or frequent sinusitis is a matter of concern for an otorhinolaryngologist (ENT doctor), but the cause of these diseases can be the tips of the roots of teeth or implants sticking out in the maxillary sinus. By the way, if you are really concerned about such problems and treatment by an otolaryngologist does not help, consult with him about sending you for an x-ray of the nasal sinuses.
The task of X-ray examination can be compared to determining the internal structure of an apple. Even in a smooth, beautiful fruit, the core may not be centered. The seeds can be either small or large, immature, eaten by worms. The entrance of a worm into an apple can be almost imperceptible, but the passages it digs are extensive and winding.
Get a complete picture of the structure of the bones of the facial skeleton, the location of the teeth, the condition of the temporomandibular joints, etc. allows computed tomography (CT) - a unique x-ray research method that involves obtaining a series of images on a special device - a tomograph - and further analysis of these images using a computer. This is a complex type of examination. The patient's head is fixed in the tomograph, after which the device takes a series of images parallel to each other, with an interval of 0.1 millimeters. It's like he's cutting an apple into thin slices. Each snapshot shows the status of the corresponding slice. For the study and diagnosis of the maxillofacial area, a special type of tomography has been developed - cone beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Subsequently, with the help of special computer programs, a complete picture can be assembled from the resulting images - a three-dimensional virtual model. It can be rotated in 3D space, displayed on the screen from different angles. You can examine not only the resulting sections; the assembled model can be cut in any other planes. Moreover, the doctor can draw a curve and obtain an image that is not available with any other examination methods. For example, by placing a curve along the arch of the teeth, you can get an ideal, interference-free panoramic image. By moving the curve from the vestibular (outer, cheek) surface of the teeth to the lingual (inner, palatal or tongue), the doctor can get a complete picture of the condition of the teeth and bones. Computed tomography provides the doctor with maximum information; all the anatomical features of the patient are available to him, defects and anomalies are visible, every “wormhole”.
Diagnocat artificial intelligence: fast CBCT analysis, accurate diagnosis
Our clinic uses Diagnocat artificial intelligence for CBCT analysis! The program uses 3D images to determine the condition of the teeth, finds problems and suggests how to treat them. In just a few minutes, Diagnocat will examine your CT scan, identify problem areas, and generate a report for each tooth. And the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis! More about Diagnocat here.
Initial consultation
To decide on treatment tactics, the dentist must first conduct an initial examination of the oral cavity using instruments that help determine the degree of damage to the dental tissues and mucous membranes. This is done for:
- determining the extent of previous diseases;
- analysis of the general condition of the patient’s oral cavity;
- establishing the fact of treatment using orthoconstructions earlier;
- clarification of the symptoms that forced the patient to see a dentist.
Visual diagnostics helps the doctor assess the condition of the teeth. The conclusion is made based on a number of criteria:
- pain syndrome (the point of localization of pain and the frequency of pain impulses are determined);
- condition of dental tissues, ratio of jaw sizes.
In addition, the dentist must pay attention to the symmetry of the nasolabial and chin folds.
How is x-ray examination (dental x-ray) performed?
- The study can only be done in an X-ray room specially equipped for this purpose;
- The patient must remove all metal jewelry, removable plates, and piercings from the head;
- If you need a picture of one or more teeth, a radiologist places the visiograph sensor against a specific area;
- 3D scanning occurs using a rotating module (it is important to sit still);
- All images are immediately transferred to the computer;
- The duration of the study is only a couple of minutes.
Where can I get a dental x-ray done in Moscow and how much does it cost?
- You can take an X-ray of a tooth in Moscow at our Belgravia Dental Studio clinics;
- Our clinics are equipped with the most modern diagnostic equipment: safe and high-precision X-ray machines, visiographs, computed tomographs, allowing us to conduct all types of studies.
| X-ray diagnostics of dental condition: cost | |
| Sight radiography | 1 090 ₽ |
| BiteWing X-ray series | 1 790 ₽ |
Price list for Belgravia Dental Studio services
Our promotions