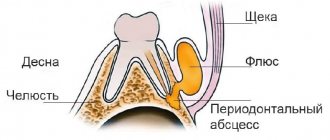
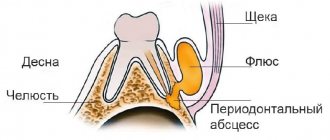
In a completely healthy person, the base and roots of the teeth are covered with durable soft gum tissue. Thanks to it, they are held in place and are saturated with nutrients. But sometimes during brushing or examination, a phenomenon such as raised gums is noticeable. This pathology is called “exposure” by dentists. If timely treatment is not started, complications such as periodontal disease, bleeding and tooth loss are possible.
The gums have risen on the teeth
Why does the gum rise above the tooth?
About 10% of patients turn to dentists with such a defect. Their gums rise noticeably above the tooth and voluminous periodontal pockets form. Outwardly, it looks very ugly, as a result of which a person is obliged to hide his smile from others. In addition, he experiences pain when eating cold or hot food.
The following reasons can influence the development of the pathological process:
- Impaired metabolism and hormonal imbalance (most often people with diabetes, pregnant women and women during menopause turn to the dentist with a similar problem);
- Lack of minerals and amino acids. The reason is an unbalanced diet and strict diets that require a strict diet.
- Lack of proper oral care. If you brush your teeth incorrectly, plaque appears on the enamel, which over time hardens and turns into stone.
- Congenital malocclusion pathologies or incorrect positioning of the incisors.
According to statistics, most often the gums rise in people in adulthood and are practically not diagnosed in young children. The risk group includes people who often drink strong drinks or smoke cigarettes. Frequent damage from using a hard toothbrush and untreated infections also soften periodontal tissue, leading to mobility and bleeding.
Raising the gums above the crown in older people is a natural process. Soft tissues age, become thin and less flexible. They are unable to hold teeth and dentures in ideal position. As a result, this leads to deformation and fracture of the bridge.
Reasons why gums rise
Under the influence of provoking factors, periodontal disease, gingivitis and periodontitis develop.
At first, the gums, rising by a third, do not cause pain. Next, the base of the tooth is exposed, bleeding occurs during cleaning, and an unpleasant odor appears due to rotting food debris in the periodontal pocket.
The periodontium softens, becomes unable to hold the teeth, and they become loose. The patient experiences pain that makes drinking and eating difficult. The affected mucous membrane is vulnerable to microbes, becomes inflamed, and suppurates.
Periodontal disease
This is usually a consequence of metabolic disorders. All dental parts, when the gingival margin rises up or falls below the neck, can become exposed. The tissues are sensitive, painful, and bleeding.
In the absence of obvious inflammation, we are talking about periodontal disease as such.
But the exposure of teeth and an increase in their mobility subsequently leads to infection and inflammation of periodontal pockets.
Gingivitis
Inflammation of the gums without compromising the integrity of the periodontal transition can be of several types:
- Simple marginal (marginal), acute catarrhal or chronic gingivitis.
- Atrophic, with loss of tissue volume.
- Desquamative, with desquamation of the epithelium.
- Hypertrophic (hyperplastic), with an increase in the volume of the periodontal papillae, the gum hangs over the tooth, rises in the form of a lump or granuloma.
- Ulcerative, with tissue erosion.
Gum lesions are more common in adulthood. In preschoolers and schoolchildren, marginal changes occur.
Periodontitis
With periodontal inflammation, the destruction of the alveolar process of the jaw progresses, which is facilitated by the accumulation of bacteria in the expanded periodontal pocket.
In addition to the fact that the gum rises noticeably above the neck of the tooth, there is swelling, redness, and pain in this area. Gums bleed when brushing and eating solid foods.
If left untreated, purulent fistulas form, teeth become loose and fall out.
Causes of the disease
It is impossible to restore the gum without determining the exact cause of its receding, so it is not even worth starting treatment without this. The following diseases can affect the development of periodontal pathology:
- periodontal disease;
- gingivitis in severe stage;
- periodontitis.
In addition to soft tissue diseases, the next factor is poor oral hygiene, as a result of which deposits accumulate in the periodontal pocket. This creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. As a result, the depressions expand, and toxins released by bacteria corrode the tissue around them.
How the disease develops
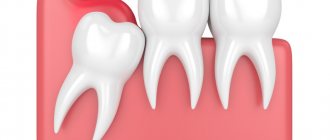
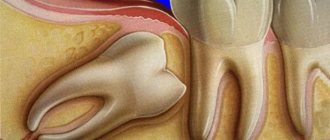
In a healthy person, the tooth is located in the gum. Only the upper part, the crown, is raised outward. It is protected by a layer of enamel from temperature changes, harmful bacteria and other damage. When the neck or root is exposed, the patient feels pain every time he touches the gum or eats cold or hot food. The reason for such symptoms is the absence of a protective layer.
Healthy periodontium versus unhealthy periodontium
When the gums rise above the upper tooth, causing its base to become visible, this is a sign of periodontal disease. This unpleasant disease has increasing symptoms and develops in several stages:
- First stage . 1/3 of the gums are lifted, with no pain or discomfort.
- Second . There is a strong detection of the base of the teeth, bleeding during brushing and the presence of a putrid odor.
- Third . Periodontitis tissues become soft and are unable to hold molars and incisors in the correct position. Patients feel severe discomfort and pain, which prevent them from eating fully or drinking cool drinks.
If the gums rise above the crown as a result of periodontitis, there is a risk of infection spreading to the exposed areas. Suppuration occurs and fistulas form. Pathogenic microflora leads to inflammation in the roots, which threatens tooth extraction.
Diagnostics
If an adult or a child has raised gums, treatment measures are carried out after a thorough diagnosis. First, the reason for the exposure of the neck and root is determined.
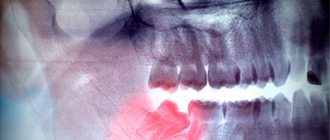
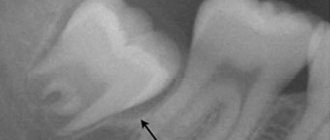
Diagnosis begins with examination of the oral cavity. The dentist will assess the degree of elevation and record the width and depth of the recession. Afterwards, instrumental studies are prescribed. Using radiography, the height of the interdental septum and the degree of damage to the cortical plate are assessed.
After examination and x-ray examination, the doctor will determine the degree of elevation. It comes in several classes:
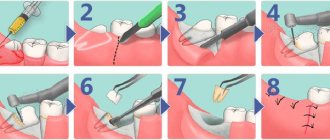
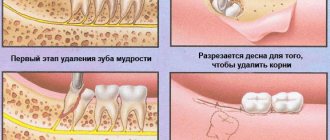
- Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth
- In the first class, only an insufficient amount of gingival tissue is present.
- The second class is characterized by a moderate displacement of 3 mm towards the root, an interdental septum of normal structure, around which the mucous membranes become pale.
- In the third class of recession, a complete uplift occurs, resulting in the root being visible.
- With the fourth class of elevation, a decrease in both soft tissue and bone occurs. There is pronounced dystrophy of the interdental space.
If the gums have risen in one place, then the possibility of the defect spreading to neighboring teeth cannot be ruled out. As a result, treatment will be more difficult and longer. Therefore, if one of the above symptoms is noticed, you need to visit a dentist.
Treatment of pathology
Lateral flap
Using this method, it is possible to lift the gums. But it is rarely used due to the fact that healthy tissue has to be displaced onto damaged areas. This defect affects almost the entire jaw, so it is difficult to apply a lateral flap.
The positive quality of this method is the instant result. If all preventive standards are followed, the risk of relapse is minimized.
Surgery to correct gum recession
Collagen membrane
It is placed on the cortical plate of the alveolar process for tissue regeneration. When its functions are restored, it will be deleted. Although some dentists use absorbable materials that dissolve on their own after a certain period of time. But they just cost more. Due to the membrane, approximately 80% of tissues are restored.
Rinse preparations
You can purchase ready-made mouth rinses at the pharmacy. The most effective remain:
- Chlorophyllipt;
- Furacilin;
- Miramistin;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Forest balm;
- Malavit;
- Rotokan.
Before using any of the above medications, read the instructions, as some medications need to be diluted with water.
Surgery
If drug therapy does not produce the desired results, then the gums at the bottom of the tooth can be lowered using surgical intervention. This will restore the level of the gums, covering the exposed roots of the tooth. For these purposes, soft tissues are transplanted from the upper palate or moved from nearby areas, provided they are of sufficient volume.
If tissue is removed from the upper palate during the operation, scars may form at the site where it is planted. This will reduce aesthetics, so it is better to use the option of moving the fabric from a nearby area.
Folk remedies
Tincture of calamus root and propolis
Required components:
- propolis – 10 g;
- alcohol – 0.5 l.
Combine the presented components and place the container with the tincture in a dark place. Keep her there for 14 days. Now grind the calamus root and pour in 0.5 liters of spit. Also leave for 2 weeks. At the end of the specified time, combine an equal amount of tincture. Use the resulting composition to rinse the mouth 3 times a day.
Propolis tincture
Herbal decoctions
The following plants are used for these purposes:
- chamomile;
- yarrow;
- mint;
- Melissa.
These herbs were not chosen by chance, as they have an anti-inflammatory effect. Take 20 g of finely chopped plant and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Simmer for 15-20 minutes, cool, filter and use for rinsing after each meal. The use of herbal infusions has a positive effect on the condition of tissues.
You can get a positive result only if you use the decoction on a regular basis.
Beetroot compress
Peel the fresh root vegetable and grate it. Add 2 drops of sage essential oil. Wrap the resulting pulp in a bandage and apply to the gums for 20 minutes. Carry out such events 2 times a day. You can use boiled beets, but then cut off a plate from it and grease it with oil, and only then apply it to the gums.
Chamomile infusion
Homemade ointment
Required components:
- olive oil – 20 ml;
- rose oil – 4 drops.
Rub the resulting composition into the gums 3 times a day for a month.
Infusion of rose petals
Pour 10 g of raw material into 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for 6 hours in a thermos. Filter and use as a mouth rinse 3 times a day.
Treatment of raised gums above the tooth
The dentist will tell you how to treat a defect due to raised gums, and the sooner the better.
For successful therapy, it is important to consistently eliminate the factors that caused the gums to lift and the tooth to become exposed, and to cure infections.
First, the dentist will remove tartar and plaque, perform professional teeth cleaning, and inspect existing implants and fillings. Damaged crowns are removed.
Carry out antiseptic treatment of pockets. If necessary, filling and grinding are done.
The treatment is long because it is not easy to return the tissue to its place so that it fits onto the tooth.
Anti-inflammatory, regenerating agents, and antibiotics are used in accordance with the sensitivity of oral bacteria to them.
Antiseptics (ointment, spray) and anesthetic sprays with lidocaine are used locally.
Uncontrolled use of medications threatens to increase symptoms and complications.
Additionally prescribed:
- acupuncture;
- gum massage;
- electrophoresis of anti-inflammatory drugs on the affected areas;
- infrared laser therapy.
In the absence of periodontal disease, the following is also used:
- Fluoridation with liquid gel on the exposed area. The gel hardens under special lighting, reducing sensitivity in the area.
- Remineralization with calcium compounds (10 sessions), strengthening the enamel, creating resistance to infections and chemical agents. Teeth become whiter and pockets become smaller in volume.
- Installation of ceramic veneers, eliminating discomfort, reducing the sensitivity of the affected area, the risk of plaque formation, and improving aesthetics.
As a result, either the gum will grow to the tooth, or they will resort to surgical plastic surgery under anesthesia: so that the gum lies on the tooth, they cover the exposure with a flap:
- from the trapezoid process of the temporal bone;
- from the back surface of the gum;
- from the mucous membrane of the palate.
There is a risk of scarring and graft rejection, especially if the oral cavity is susceptible to infection.
Lateral flap
The defect from taking the flap affects almost the entire gum, but the operation provides a quick result. If you follow all oral care tips, the risk of recurrent lifting of gum tissue is minimal.
Flap surgery
Collagen membrane
This is a synthetic drug used to cover exposed parts of the tooth. The membrane is placed on the cortical plate of the alveolar process, activating regeneration.
The non-absorbable membrane is removed after restoration of 80-90% of the gum tissue volume. There are more expensive absorbable membranes that do not require removal.
Rinse preparations
Ready-made rinses are sold in pharmacies. They contain nutrients for the structures of the oral cavity, remove bacteria from it, being antiseptics:
- Chlorophyllipt;
- Miramistin;
- Malavit;
- Maraslavin;
- Furacilin;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Stomatophyte;
- Rotokan.
A number of products are pre-diluted with water, according to the instructions for use. Rinse after each meal.
Folk remedies
Herbal tinctures and decoctions have an antiseptic and nourishing effect.
Propolis tincture
| Compound | Preparation | Rinse mode |
| Tincture of propolis and crushed calamus roots | 10 g of each product per 0.5 liter of alcohol, prepare each tincture separately. The mixtures are placed in the dark for 2 weeks, then combined into one mixture | 3 times a day |
| Decoctions: · calendula; · oak bark; · St. John's wort; · chamomile flowers; · yarrow. | For 1 tbsp. boiling water, take 20 g of chopped herbs, keep on low heat for 1/4 hour, let cool and filter | Rinse after eating |
| Tincture of rose petals | 10 g petals per 1 tbsp. boiling water infused in a thermos for 6 hours, filtered | 3 times a day |
Beetroot compresses are useful:
- Raw beets are peeled and finely grated.
- Add 2 drops. sage essential oil.
- The pulp is wrapped in a napkin.
- Place on the lifting zone for 15-20 minutes, 2 times a day.
Aloe is used in the same way.
An ointment is prepared from olive (20 ml) and rose (4 drops) oils. Rub into the raised area 3 times a day, 1 month.
Prevention
You can prevent receding gums by following the following preventive measures:
- Rinse your mouth regularly to prevent bacterial plaque and tartar from accumulating along the gum line.
- Visit the dentist’s office every six months for a preventive examination, timely dental treatment and prosthetics.
- Use flux thread correctly to prevent injury to periodontal tissues;
- Maintain proper nutrition, including as many vegetables and fruits as possible in your diet.
- Use high-quality oral hygiene products.
- Eliminate bad habits - smoking, drinking strong drinks.
Receding gums are a common phenomenon that can be successfully treated if you seek help from a specialist in time. Timely detection of recession will allow you to get rid of it using conservative methods without resorting to surgery.
Prevention of gum elevation
To avoid gum swelling, you need to:
- Maintaining hygiene: brushing teeth, gums, tongue, regular professional cleaning with medicated pastes.
- Examination by a dentist at least twice a year to remove plaque on enamel and tartar.
- Use dental floss without damaging the gums.
- A diet with sufficient amounts of solid fruits, vegetables and protein (meat, cheese, milk, cottage cheese), vitamins C, D, E, calcium, zinc.
- Quitting bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse.
- Timely and high-quality bite correction, use of braces, prosthetics.
Any disease is easier to prevent than to treat. But even if the gums rise and expose parts of the tooth, a quick visit to the dentist can restore a healthy appearance to the patient’s smile.
Bibliography
- Yakovleva V.I. – Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of dental diseases, Minsk 1994.
- Loginova N.K., Volozhin A.I. — Pathophysiology of periodontal disease (methodological manual), M., Medicine, 1993.
- Borovsky E.V. and co-authors - Therapeutic dentistry, M. 1998.
- Major M. Ash, Stanley J. Nelson - Wheeler's Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion - Saunders - 2002.
- Ijndhe J. - Textbook of Clinical Periodontology. 1995. Copenhagen.
- Muravyannikova Zh.G. — Dental diseases and their prevention, Rostov-on-Don, 2007.
- T. G. Robustova, V. V. Afanasyev [and others] - Surgical dentistry / 4th ed., M.: Medicine, 2010.
- Tsimbalistov A.V., Shtorina G.V., Mikhailova E.S. — Instrumental support for professional oral hygiene, St. Petersburg; LLC MEDI publishing house.— 2004.
- Doni L. Bird - Modern Dental Assisting - Saunders - 2011
Find a clinic