ICD - pharyngitis:
- J02 - acute pharyngitis
- J02.0 - streptococcal pharyngitis
- J02.8 - acute pharyngitis caused by other specified pathogens
- J02.9 - acute pharyngitis, unspecified
- J31.2 - chronic pharyngitis
- J31.1 - chronic nasopharyngitis
Pharyngitis is rarely isolated as a separate disease; the diagnosis is usually acute respiratory viral disease (ARVI).
ARVI is a general name; the doctor usually specifies how exactly ARVI manifests itself.
This may be rhinitis (runny nose), pharyngitis (red throat), nasopharyngitis (inflammation of the nose and throat), etc.1,2
It is important not to confuse pharyngitis with tonsillitis.
To do this, let's understand the structure of the pharynx and oral cavity.
Other reasons for finding red dots in the sky
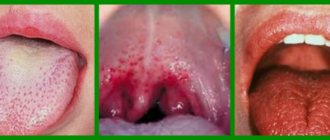
Red dots on the upper palate may be the result of the following rare diseases:
Pyogenic granuloma
Occurs in a place often subject to trauma. It is necessary to excise the tumors at the root, after which electrocoagulation therapy is prescribed.
Kaposi's sarcoma
It is a malignant neoplasm with a purple hue. Local chemotherapy is prescribed, and measures are taken to increase the patient’s immunity.
Pathechia in the sky
These are small flat spots that often appear during mononucleosis. May be a manifestation of smallpox, thrombocytopenia, typhoid fever and endocarditis.
If a red rash occurs in the mouth, you do not need to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment yourself.
It is necessary to consult with a specialist, find out the cause of the spots and receive appropriate treatment. The DentalGuru dental clinic employs experienced and professional dentists who guarantee painless and effective treatment of stomatitis and other dental diseases. This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
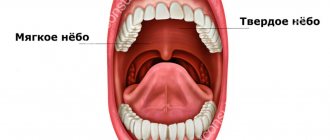
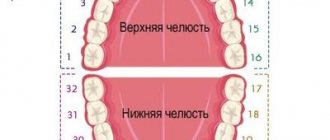
Structure of the pharynx
The pharynx is divided into 3 sections:
- upper (nasopharynx)
- middle (oropharynx)
- lower (larynx)
This division is very conditional, because There are no clear boundaries between departments. When inflammation occurs, it rarely happens that the inflammatory process is localized in one section; usually infectious processes spread and move throughout all sections of the pharynx5,7
As can be seen in the picture below, the oropharynx is composed of the velopharyngeal arches, the uvula and the soft palate.
Pharyngitis usually affects:
- temples
- tongue
- soft sky
- posterior wall of the pharynx
The doctor uses a spatula to completely examine the pharynx. It is needed to improve visibility of the back of the throat.
The palatine tonsils also become inflamed with pharyngitis, because it is impossible to limit the inflammation process. This widespread nature of inflammation in pharyngitis distinguishes it from tonsillitis, where the tonsils are predominantly affected.
Probable Causes
Red spots in the throat are the main sign of the occurrence of pathological processes in the mucous membrane of the airways. The following factors can trigger their development:
- dry air;
- inhalation of volatile chemicals;
- hypothermia;
- vitamin deficiency;
- allergic reactions;
- decreased body reactivity;
- infectious diseases;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- endocrine disorders;
- bad habits.
The cause of the appearance of red spots on the throat and palate can be identified by their location, number and accompanying manifestations.
Most often, the causes of the occurrence lie in the development of bacterial and viral infections. However, in order to make sure that such suspicions are correct, you need to seek help from a doctor.
How common is pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis, like a common ARVI (viral infection), occurs quite often. The incidence rate increases during the season from September to May, with a peak in February and March. A decrease in the incidence of pharyngitis by 3-5 times is observed in the summer months.10,11
Acute pharyngitis occurs more often in childhood than in adults. Children under 5 years of age suffer viral infections, including pharyngitis, 6-8 times a year.8,9
In the first year of visiting a preschool institution, the incidence of the disease is 10-15% higher than in children at home. But, unfortunately, “home” children subsequently get sick more often at school age.
Causes of pharyngitis and tonsillitis
Etiology (origin, cause) of pharyngitis. In 70-90% of cases, pharyngitis is caused by viruses. Pharyngitis can also be caused by bacteria, fungi, allergies, injuries, and exposure to irritating factors.
The most common viruses are rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, influenza, parainfluenza, enteroviruses, Coxsackie A, coronaviruses, a group of herpes viruses (Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, HSV).12
There are pharyngitis, which are classified as a separate diagnosis depending on the pathogen, for example streptococcal pharyngitis ICD J02.0
Classification of pharyngitis
Pharyngitis can be acute or chronic. Acute is inflammation that just arose (suddenly), and chronic is a disease that persists for a long time, and it may not bother a person, but under certain circumstances again cause complaints and anxiety.3
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | Classification of pharyngitis due to its occurrence: | a comment: | viral bacterial fungal allergic traumatic caused by exposure to irritating factors caused by gastrointestinal diseases (gastroesophageal reflux, stomach diseases, etc.) |
| classification: | Pharyngitis associated with specific pathogens: | a comment: | Epstein Bar virus for infectious mononucleosis Yersinia enterocolitica for yersinial pharyngitis gonococcus for gonorrheal pharyngitis Leptotrix buccalis for leptotrichosis of the pharynx |
| classification: | Types of chronic pharyngitis: | a comment: | hypertrophic (enlargement of the mucous membrane) atrophic (depletion of the mucous membrane) catarrhal (standard inflammation) mixed |
Forecast
With timely, complete and systematic treatment of the disease, the prognosis for the patient is favorable. In this case, it is possible to stop pathological changes in the mucosal tissues. After quality therapy, exacerbations of the disease are extremely rare.
If treatment is started late, when the throat lesion is already quite serious, then the prognosis for the patient is relatively positive, since it will not be possible to ensure a long remission, but at the same time the risk of complications will be eliminated.
Diagnosis of pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis can be determined by patient complaints and examination of the oropharynx (pharyngoscopy).
Objective symptoms of pharyngitis, which are assessed by a doctor when examining the throat:
- swelling and hyperemia (redness) of the pharyngeal mucosa
- purulent or mucopurulent plaque on the walls of the pharyngeal mucosa
- the presence of inflammation in the arches, tonsils, orifices of the auditory tubes
- the presence of bright red tubercles on the back surface of the pharynx and on the side - hypertrophied (enlarged) lymphoid follicles
- thinning of the mucosa with areas of exfoliating epithelium, crusts and viscous mucus (atrophic pharyngitis)
Based on this, the doctor can make not only a diagnosis of pharyngitis, but also suggest its cause (viral inflammation, fungal infection, etc.).
Despite the fact that 70% of acute pharyngitis is a viral disease, sometimes it is necessary to exclude a bacterial cause. This is very important for further treatment tactics and prevention of complications. To do this, you should conduct a rapid test to exclude the streptococcal nature of pharyngitis.
In some cases, with fever, long-term complaints, or a temperature exceeding 3 days, it is also necessary to take a general blood test to understand the cause of acute pharyngitis.
Causes of hematoma formation on the oral mucosa
The general scheme of hematoma formation is as follows: a rupture of a vessel causes the leakage of a certain amount of blood, followed by its compaction and the appearance of a blood clot. A bubble forms, noticeable on the smooth surface of the mucosa due to its dark coloring and relief. Often a similar picture can be observed during teething, when the gums bleed and become inflamed. The formation of multiple small hematomas, covering the entire surface of the mucous membrane in the mouth with unattractive dark spots, looks very unpleasant for the patient. But don’t panic if you suspect you have a serious illness. As practice shows, most of these phenomena occur due to mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane. But there are exceptions when the symptom indicates:
- allergic reaction;
- chronic injury;
- consequences of stressful situations;
- burns or cuts to the mucous membrane.
There have also been cases when multiple hematomas in the oral cavity are signs of:
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension;
- renal failure;
- complex types of stomatitis;
- blood diseases;
- vitamin deficiency, which causes fragility of blood vessels.
The exact cause and stage of formation of the pathology can only be determined after a thorough examination and diagnosis. For this reason, you should not self-medicate, so as not to further injure damaged tissues.
Complications of pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis usually responds well to treatment. The prognosis for viral pharyngitis is recovery.
Bacterial (streptococcal pharyngitis) can be complicated by the formation of a retropharyngeal abscess, and subsequently have a negative effect on the heart and kidneys, causing endocarditis and glomerulonephritis.
Symptoms of pharyngitis can persist even with proper treatment, if the true cause of pharyngitis is not eliminated. For example, if gastroesophageal reflux disease (damage to the gastrointestinal tract) is not treated, then pharyngitis will constantly remind itself.
Acute pharyngitis can become chronic.
What not to do
During the treatment period there are certain restrictions, by violating which the patient risks significantly aggravating his condition. The doctor will not be able to guarantee the patient a positive result of therapy if the following actions are allowed:
- smoking during treatment;
- use of alcohol preparations for gargling;
- eating spicy food;
- staying in a dusty room;
- violation of medical instructions regarding treatment.
If there are no violations in the course of therapy, then it is possible to stop the disease at the beginning of its development without the use of surgical methods of therapy. Treatment of hypertrophic pharyngitis in adults and children is the same.
Prevention of pharyngitis
To prevent pharyngitis, it is recommended:
- avoid hypothermia and dress appropriately for the weather
- avoid contact with tobacco and chemical irritants
- carry out frequent ventilation of working and living spaces
- walk outdoors more often. Walking will help strengthen the body's defenses in the fight against pharyngitis.
- don't drink ice water
- do not share food and cutlery, cups
- avoid crowded places and, if possible, stay in them for as little time as possible
- use disinfectants, including in public places,
- transport, etc.
- wash your hands often
Drug-induced stomatitis
Occurs when there is an allergy to a drug. Often, allergies can occur to antibacterial, antimicrobial drugs, vaccines, iodine. The mucous membrane is red, swollen, the lips and tongue also often swell, blisters appear, which burst, leaving erosion. The gums are inflamed and bleed when touched. General manifestations are possible, such as urticaria, nausea, vomiting. In severe cases, anaphylactic shock occurs (an emergency condition manifested by decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, fainting, suffocation), Quincke's edema (an atypical reaction of the body, manifested by rapid and severe swelling)
Both conditions are extremely dangerous and require immediate action and calling an ambulance!
Pharyngitis in pregnant women
During pregnancy, a woman's body's protective properties decrease. In this regard, the risk of contracting infectious diseases, as well as exacerbation of chronic diseases, greatly increases.
Pregnant women need to carefully monitor their health and prevent diseases: avoid contact with people with respiratory diseases, avoid crowded places, wash your hands, eat regularly and properly.
If you develop acute pharyngitis or exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis, treatment is required. It is not recommended to use drugs that can affect the entire body. They can pass through the placenta to the baby and cause harm to him. To treat pharyngitis, pregnant women are advised to consult a doctor and use saline mouth rinses.
Herpetic sore throat in children
Children usually become infected at school or kindergartens2,3. Due to pain and fever, they are restless, tearful, and often refuse to eat and drink because food irritates erosions on the mucous membrane and causes discomfort. But due to refusal to drink water or juices, children often develop dehydration. At the same time, the child’s tongue becomes dry, and the elasticity of the skin decreases1. Convulsions may occur due to high temperature1.
Blistering rashes in children can appear not only on the mucous membrane of the throat, but also on the hands and feet, and even on the buttocks and forearms. This manifestation of enterovirus infection is called viral pemphigus of the oral cavity and extremities or mouth-hand-foot syndrome. The disease is contagious in 100% of cases, is often mild, and can affect nails3.
Up to contents
FAQ
Can pharyngitis be treated at home?
Pharyngitis usually does not require hospitalization (hospital treatment). You can treat strep throat at home on your own by using topical remedies to relieve sore throat and sore throat. If, after self-treatment, the sore throat does not go away within 3 days, then you should consult a doctor. If you have a fever in addition to a sore throat, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Which doctor should I contact if I have a sore throat?
If you have a sore throat, sore throat, or difficulty swallowing, you should first consult a therapist or pediatrician if you are a child. If there are indications, the doctor will prescribe a consultation with an ENT doctor.
Very severe sore throat. Are you sure I don't have a sore throat?
With pharyngitis, the pain syndrome may be more pronounced than with tonsillitis (tonsillitis). To treat pharyngitis, it is good to use a remedy that has an analgesic effect, for example Tantum® Verde. To exclude sore throat (streptococcal tonsillitis) or streptococcal pharyngitis, it is recommended to conduct a rapid test (streptotest).
Do you need an antibiotic for pharyngitis?
The antibiotic is indicated ONLY for bacterial pharyngitis. For a quick diagnosis, perform a rapid test for streptococcus. It will allow you to exclude or confirm the bacterial nature of pharyngitis. If streptococcus is detected, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
Is strep throat contagious?
Most often, strep throat is a viral disease, so a person can shed the virus and infect other people. A sick person is contagious, so you should stay at home until you recover.
What happens if pharyngitis is not treated?
Complications may arise. If pharyngitis is not treated, complaints persist much longer, inflammation does not go away and begins to become chronic.
Is it possible to get vaccinated for pharyngitis and when?
Against the background of an acute illness or exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis, vaccination is contraindicated. Wait until you have fully recovered and then you can get vaccinated. The exception is vaccination against influenza. It can be done when the temperature is normalized, i.e. There is no need to wait for all symptoms to disappear.
Is it possible to eat cold food if you have a sore throat?
If you have pharyngitis, it is not recommended to eat very cold foods, including ice cream. This can increase inflammation and slow down recovery.
Symptoms
Gingivitis has a main symptom by which it is easily identified - inflammation affecting the child’s gums. The process begins with a slight redness that quickly gains strength. This signal often goes unnoticed by parents, and children go to the dentist with an active inflammatory process, bright red swollen gums, burning, and pain. These signs indicate that the disease has entered an acute phase.
Children suffer most from the catarrhal form of this disease, which can be chronic or acute. In the first case, the symptoms are not pronounced, pain occurs only when brushing, there is slight swelling, redness, and cyanosis of the gums.
A sign of an acute form of the disease is intoxication of the child’s body. It manifests itself as headache, nausea, lethargy, and fever.
The most complex type of disease, ulcerative gingivitis, manifests itself as follows:
- the inflammatory process progresses;
- their structure changes;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- lymph nodes in the neck enlarge;
- saliva is produced profusely;
- the skin turns pale.
If these signs are left unattended, an ulcerative-necrotic form of the disease may occur, when necrotic areas with a gray-green coating and a putrid odor appear on the gums, saliva becomes viscous, body temperature rises and the general condition significantly worsens.. All this indicates severe intoxication in organism.
During puberty in a teenager or if he has problems with hormones, hypertrophic gingivitis occurs. It occurs due to improper orthodontic treatment of dental anomalies. The inflammatory process is accompanied by increased growth of gingival tissue, which leads to partial closure of dental crowns. This form of the disease is usually localized. One or two gums are affected, sometimes the affected area expands. The most common location is the lower anterior incisors and canines.
Atrophic gingivitis does not have a pronounced inflammatory process and occurs without pain, although over time it can be complicated by periodontal disease.