Free webinars on anti-aging medicine Learn about the features of the Anti-Age Expert International School, as well as the opportunities for improving your medical practice every day.
The webinar program also includes fascinating reviews of innovations in anti-aging medicine and analyzes of the most complex clinical cases with recommendations that really work. Find out more
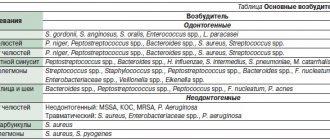
Caries
According to a study published in the medical journal The Lancet, 2.83 billion adults and children worldwide have tooth decay.
Cavities typically form when bacteria in plaque combine with sugar to form an acid that erodes enamel.
Treatment:
If you or your dentist catches tooth decay early enough, you may be able to reverse the process with fluoride medications. Otherwise, the classical treatment of caries is provided - filling.
However, if the decay gets so bad that a filling doesn't help, your dentist may crown the tooth or remove it. Again, early detection can prevent tooth decay and loss.
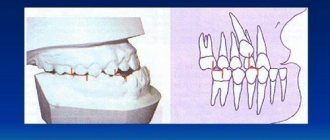
Gum diseases
Some form of gum disease, also called periodontal disease or periodontitis, affects nearly half of adults age 30 and older. Severity ranges from mildly swollen gums to bleeding gums and complete loss of teeth.
Most gum diseases develop in several stages:
- Plaque and tartar build up on the teeth, leading to gingivitis (inflammation of the gums).
- Gingivitis irritates the soft tissue along the gum line, which gradually leads to periodontitis.
- Periodontitis occurs when the gums separate from the teeth, forming pockets. This can lead to further gum infection, requiring treatment with antibiotics, surgery, or tooth extraction.
Treatment:
Like tooth decay, gum disease in the gingivitis stage is highly treatable if detected early. If it can't be corrected, your dentist will likely suggest scaling, a professional deep cleaning to remove all plaque from your mouth. As noted, antibiotics may also be prescribed. If periodontitis is advanced, surgery may be required.
“Periodontal disease is indeed a common problem. If such diseases are left untreated, sooner or later this will lead to the formation of deep and painful periodontal pockets, and ultimately to tooth loss. In addition, the microflora that lives in the mouth is very aggressive. Once it enters the bloodstream, it can spread and complicate the course of chronic diseases of the joints, heart, lungs, and brain, causing disruption in their functioning. The relationship between the presence of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity and diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease has been proven. Getting dental plaque or the contents of periodontal pockets into the lungs when coughing can worsen the prognosis of any acute respiratory viral infection, as well as aggravate the course of COVID-19. Therefore, it is so important to monitor the condition of the periodontium, undergo preventive examinations every 6 months, and have a professional. oral hygiene, remove dental plaque, both hard and soft. When diagnosing gum disease, it is imperative to carry out timely treatment. For prevention, it is important to use simple care methods at home - brushing your teeth with high-quality toothpaste - 2 times a day, and also use dental floss, irrigators, and special rinses for additional hygiene.”
Kalashnikova Oksana Yurievna
dentist, implantologist-orthopedist, gnathologist, maxillofacial surgeon, specialist in aesthetic dentistry, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category, doctor of integrative interdisciplinary anti-aging medicine Work experience: 30 years
Other dental diseases: list of dental diseases with photos
Next, we propose to analyze ailments that may appear as a result of teething or age-related changes.
Grinding
A pathology in which there is a rapid decrease in hard tissue. Provokes thinning of enamel and damage to dentin. It can affect both individual units and full-fledged rows.
Erosion
A process in which a violation of enamel integrity is recorded. Some areas are damaged symmetrically. Main signs: changes in pigment, various cosmetic defects, painful reaction to cold or spicy food.
Pathological resorption
Loss of root tissue caused by chronic diseases, advanced periodontal disease or progressive pulp disease. It can be one-sided or combined. In the absence of rehabilitation and therapeutic therapy, tooth loss occurs.
Deposits and build-ups
They are mineralized residues that form above or below the gums. The main material for formation is food particles, the results of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, as well as components of saliva. They trigger processes that provoke periodontitis.
Infectious diseases
An infection of the oral cavity leads to the development of a disease in which the mucous membranes become inflamed. The pathological process can involve the teeth and gums. Symptoms of infections in the mouth are often hidden, but sooner or later they appear.
Online training in Anti-Age medicine Learn the intricacies of anti-aging medicine from anywhere in the world.
For the convenience of doctors, we have created the Anti-Age Expert online training platform: Lectures from our educational programs are consistently posted here, and are accessible 24/7. Doctors can study the materials as many times as necessary, ask questions and discuss interesting clinical cases with colleagues in special chats. Find out more
Causes of infectious diseases of the oral mucosa:
- Uncontrolled medication use.
Treatment of any disease should be under the supervision of a doctor. Improper use of antibiotics, antibacterial and other agents leads to consequences, including diseases of the oral cavity.
- HIV and AIDS.
Infectious diseases of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity often occur against their background.
- The occurrence of infections in the oral cavity
may be associated with a weakened immune system.
- Poor nutrition.
If the mucous membrane is exposed to aggressive food, it injures it. Thus, the mucous membrane becomes more vulnerable and susceptible to infection.
In addition, smoking and alcohol provoke oral diseases. Those whose bodies are dehydrated or experience hormonal imbalances also face similar problems.
- Stomatitis.
There are many bacteria living in the mouth, and due to a decrease in immunity, they are activated. Thus, an infectious disease develops. One of the most common is stomatitis. It usually develops in people who brush their teeth incorrectly or not thoroughly enough. The disease can also occur due to tonsillitis or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. There are several types of stomatitis:
- Catarrhal.
It is manifested by swelling of the oral mucosa. As catarrhal stomatitis progresses, plaque appears on the tongue.
- Ulcerative.
In this case, the lymph nodes become enlarged. This stomatitis is manifested by dizziness and weakness. May occur in people with stomach ulcers or enteritis.
- Aphthous stomatitis.
Leads to damage to the oral mucosa, on the surface of which erosions form. Aphthous stomatitis is associated with an imbalance in the gastrointestinal tract. Signs of aphthous stomatitis: swelling of the oral mucosa, malaise, erosion in the mouth.
- Diseases caused by viruses.
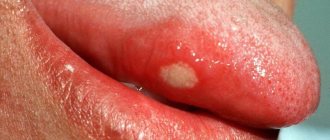
The best known oral infection is herpes, clinically known as herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). It is often found in children between 6 months and 5 years of age.
Once HSV-1 enters a child's body, he will carry the virus throughout his life. It is estimated that 50-80% of adults live with herpes simplex, either dormant or active.
The herpes virus manifests itself as rashes around the mouth. As the disease progresses, ulcers form in the mouth: they are localized on the inside of the lips and cheeks. Herpes can also infect tissues near the teeth.
After the first attack of oral herpes, the body produces antibodies to fight the virus and its effects. This way, your subsequent outbreaks of HSV-1 may not be as severe or the virus may remain dormant.
Otherwise, taking antiviral drugs may help.
- Candidiasis.
This is a manifestation of a fungal infection. Candida fungus microorganisms live in the mouth and are activated under the influence of unfavorable factors. Candidiasis occurs in people with weakened immune systems. To avoid illness, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system and avoid hypothermia. There are several types of candidiasis:
- Pseudomembranous.
It occurs in an acute form. As the pathology progresses, the mucous membrane of the cheeks begins to dry out, and the same thing happens with the lips and tongue. A coating of curd consistency forms on the tongue. Pseudomembranous candidiasis causes discomfort when chewing and itching. The disease can occur in people with a weakened immune system, as well as against the background of blood pathologies. Other causes of pseudomembranous candidiasis are diabetes mellitus and hypovitaminosis.
- Atrophic candidiasis.
In this case, the mucous membrane of the mouth becomes red and dry. The chronic form of the disease develops in those who use dentures for a long time.
- Hyperplastic candidiasis
may be acute or chronic. In chronic cases, plaque forms on the mucous membranes, including the tongue. When you try to remove it, the mucous membrane becomes more inflamed. Brushing your teeth may cause bleeding.
- A disease that occurs due to HIV.
Secondary immunodeficiency is characterized by the active proliferation of pathogenic flora in the oral cavity. Early diagnosis will allow faster initiation of treatment and improve the prognosis of immunodeficiency.
It is important to note that diseases of the oral cavity that occur against the background of HIV often become chronic.
What affects the health and color of teeth [2,3]
Sometimes, despite careful oral care, teeth do not have the desired snow-white “Hollywood” shade. Most often, the reason for this is the natural color of the enamel and/or dentin: there are many people whose teeth are yellowish or grayish from birth. In this case, persistent bleaching using chemical or abrasive agents is fraught with increased sensitivity of dentin.
Color can also depend on the food you eat and bad habits. Tea, coffee, jam, natural juices, tobacco affect the shade of enamel, and smoking and alcohol abuse worsen its condition.
Another factor is eating habits. Lovers of sweets and foods rich in carbohydrates (baked goods, pasta, etc.) are at increased risk of caries, since sugar is the favorite food of bacteria that cause the development of caries.
The habit of eating soft pureed food has a bad effect on the natural cleansing of the oral cavity. That is why, from childhood, everyone is recommended to chew fairly hard vegetables and fruits: carrots, apples, celery, cucumber, kohlrabi. During chewing, natural cleansing of the surface of the teeth, cheeks, gums and tongue occurs.
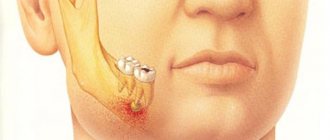
Oral cancer
Oral cancer most often affects the tongue, tonsils, gums and oropharynx. Since its various types often do not cause obvious signs and symptoms in the early stages, regular dental examinations are the most important method of detecting them.
Your dentist may also test you for oral cancer during your exam, especially if you have any of these symptoms:
- Persistent pain in the mouth or lip;
- Red or white spot in the mouth;
- Loose teeth;
- Painful swallowing, constant pain in the mouth or ears.
Treatment:
Depending on the type and stage of oral cancer, treatment may include a combination of surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Stomatitis
This is a group of diseases characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa with hyperemia, swelling, and an increase in the amount of mucus in the oral cavity.
Depending on the severity and depth of the lesion, even ulcers or foci of necrosis may form in the oral cavity, sharply disrupting the general condition - fever, weakness, anxiety, refusal to eat. There are many causes of the disease: mechanical, chemical, thermal, bacterial factors. Often the cause of the disease in infancy is contaminated nipples, toys and other objects that fall into the child’s mouth. Stomatitis often develops as a result of infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever, influenza, whooping cough, etc.). The mucous membrane of the oral cavity acquires a bright red color, becomes swollen, and tooth marks are visible on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and tongue. Saliva becomes viscous and viscous. The mucous membrane is covered with a whitish coating. The tongue is dry, swollen, often with a brown tint, chewing is painful. The duration of the disease is from 1 to 3 weeks, the prognosis is favorable.
A general preventive rule for children and adults is to maintain good oral hygiene.
Prevention
Maintaining oral health is not difficult if you follow simple recommendations:
- Eat a balanced diet.
The diet should contain a sufficient amount of protein foods, as well as foods containing amino acids, trace elements and vitamins. Carbohydrate foods, on the contrary, are best consumed in small quantities.
- Careful oral hygiene.
It is important, for example, to use dental floss and brush your teeth with toothpaste or gel twice a day.
- Use of vitamins and nutritional supplements (as prescribed by a doctor).
This will make up for deficiencies in the body that affect oral health.
- Regular visits to the dentist.
You should visit your dentist for a checkup at least once a year. Even if there are no complaints.
How to use a toothbrush correctly [1,2]
The best way to learn how to properly brush your teeth is to visit your dentist or hygienist. Consultation is especially important for people with braces, dentures, dentition defects, etc.
Standard recommendations include several cleaning steps, none of which should be skipped.
- Wet a toothbrush and apply a pea-sized amount of toothpaste. Place the toothbrush at a 45 degree angle to the surface of the teeth. Start cleaning movements from the upper right chewing teeth (the farthest ones) and from the side of the cheek, then from the side of the tongue, sequentially moving to the front ones. Using a toothbrush, make sweeping movements from the gum to the edge of the tooth.
- Move to the chewing surface and brush it by moving the toothbrush horizontally back and forth. Try to penetrate as deeply as possible.
- Continue brushing the lower chewing teeth and then the entire lower jaw.
- Close your jaws and massage the gums of both jaws in a circular motion.
- Final stage: use a special scraper or pad on the back of the toothbrush head to clean the surface of the tongue.
- Clean between teeth using dental floss or tape. Then use mouthwash.
- After each meal, also rinse your mouth thoroughly with clean water or mouthwash.
Medical expert: Oleg Sergeevich Shchekin
Last updated: July 21, 2021
Brief conclusions
- The most common oral diseases are tooth decay, gum disease, infectious diseases and oral cancer.
- Caries and gum disease are highly treatable in the early stages.
- The causes of infectious diseases of the oral cavity vary - from viruses to poor diet and uncontrolled use of medications.
- For prevention, it is important to review “life hygiene” and regularly visit the dentist.
Anti-Aging Medicine Seminars Gain knowledge based on evidence-based medicine first-hand from the world's leading experts. As part of the Anti-Age Expert Modular School, in-person two-day seminars are held every month, where the intricacies of anti-age medicine are revealed to doctors of more than 25 specialties
Find out more
Symptoms of oral dysbiosis
Symptoms designated by the term “oral dysbiosis” occur in many different diseases and syndromes, so the disease is difficult to diagnose. Let's name the signs of an imbalance in the oral microflora:
- bad breath (halitosis);
- metallic taste, burning sensation in the mouth;
- the development of candidiasis, or thrush - a white coating on the tongue and mucous membranes of the cheeks;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes and gums;
- swelling, redness and soreness of the tongue;
- The appearance of so-called jams in the corners of the mouth is characteristic.
The pathology of normal microflora in the mouth is fraught with the danger of endogenous infections.
The listed manifestations are due to the following changes:
- colonization resistance (local immunity) of the mucous membrane is disrupted - yeast-like fungi easily adhere to the surface of the epithelium, where there are optimal conditions for reproduction;
- the bacterial antagonism of normal microflora changes significantly - normally, antagonistic microbes do not allow pathogenic fungi to actively multiply, but with dysbiosis, the former are destroyed, which provokes rapid proliferation of Candida fungi;
- In patients, a significant shift in local protective factors is detected - the weakened defense does not cope with its function, so the volume of pathogenic microflora increases unhindered.