From this article you will learn:
- how to rinse your mouth if your gums are inflamed,
- comparison of the effectiveness of funds,
- The best mouthwash for sore gums.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Mouth rinses for gum inflammation can be divided into – 1) antimicrobial, 2) anti-inflammatory, 3) combined action. Rinse solutions with an antimicrobial effect contain antiseptics or antibiotics, and these components act directly on the cause of gum inflammation - pathogenic bacteria. In dentistry, antiseptics such as chlorhexidine, hexitidine or cetylpyridine are usually used, and among antibiotics, triclosan.
In turn, rinses with anti-inflammatory effects may contain: methyl salicylate, phenyl salicylate, allantoin, bisabolol, thymol and eugenol, as well as medicinal plant extracts. All of them have the property of blocking the so-called “inflammatory mediators,” thereby stopping the inflammatory reaction in the tissues. Some mouth rinses have a combined composition, combining both antiseptics and anti-inflammatory components.
In this article, we will analyze the best mouthwashes –
- chlorhexidine solution,
- LACALUT Active,
- PRESIDENT PROFI Antibacterial “Powerful protection against bacteria”,
- Hexoral (0.1% hexitidine solution),
- miramistin,
- PRESIDENT PROFI Active,
- Periodontocide,
- LISTERINE Expert “Gum protection”,
- Stomatophyte.
Combination of rinses and application gel –
The selection of rinse aid and gel is carried out in such a way that both antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects are equally realized.
Those. if you choose a rinse with antimicrobial components - such as chlorhexidine, hexitidine, cetylpyridine, triclosan, then in parallel you need to use a gum gel containing anti-inflammatory components (this can be choline salicylate, phenyl salicylate, methyl salicylate, etc.). But if you use a rinse primarily with anti-inflammatory components (for example, Parodontocid mouthwash), then you need to choose a gum gel that contains an antiseptic and/or antibiotic. Such gels include Perio-Aid, PRESIDENT Effect gel and others. For more information about anti-inflammatory gels for the treatment of gum inflammation and patterns of their use, read the article:
→ Rating of the best gels for gum inflammation
Treatment of throat diseases in the clinic
For the treatment of throat diseases, different techniques can be used - separately or in combination:
- Taking antibiotics.
- Local treatment with antibacterial and antiseptic agents.
- Ultrasound treatment.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, UHF, galvanization, etc.).
- Laser treatment.
DAY CARE SERVICE
If conservative therapy does not help, surgical treatment may be prescribed:
- Adenotomy (removal of adenoids).
- Tonsillotomy (reduction of tonsils).
- Adenotonsillotomy (removal of adenoids and partial removal of tonsils).
- Tonsillectomy (removal of tonsils).
Mouth rinses may be unsafe -
You may notice that the instructions for rinses with antiseptics and antibiotics (at least from some manufacturers) recommend using them for 3-4 weeks, and in some cases even up to 1-2 months. It is absolutely impossible to follow such recommendations, because... Long-term use of antiseptics radically changes the composition of the oral microflora, and not for the better. Pathogenic microflora tends to get used to antiseptics (as they say, the fittest survive), and therefore, after the end of the use of antiseptics, the rate of destruction of the attachment of teeth to the bone and gums can only increase. Therefore, the course of rinsing with antiseptics should not last more than 10-12 days.
In addition, clinical studies (source) revealed that after just 7 days of rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine, the ratio of microflora in the oral cavity changed in such a way that strains of pathogenic bacteria that produce large amounts of lactic acid received an advantage. This leads to a shift in the pH of the oral fluid to the acidic side, to a decrease in the buffer capacity of saliva and a decrease in its ability to neutralize lactic acid, which is secreted by cariogenic bacteria. Thus, the risk of developing dental caries increases.
Important for patients with cardiovascular pathology -
Several reputable scientific studies have shown that chlorhexidine interferes with the ability of oral bacteria to convert nitrates (found in foods) into nitrites. This bacterial activity is called “nitrate-reducing” and is one of the mechanisms for maintaining normal blood pressure. Normally, nitrites entering the blood help lower blood pressure and, accordingly, a decrease in their production will lead to an increase in blood pressure.
This is primarily important for patients who already have chronic cardiovascular pathology. This information is confirmed by the clinical study “The increase in plasma nitrite after a dietary nitrate load is markedly attenuated by an antibacterial mouthwash. Nitric Oxide" (2008), authors – Mirco Govoni, Emmelie Å. Jansson, and others. If you wish, you can familiarize yourself with this study using the link above, for example, using a browser translator.
What you don't need to rinse your mouth with -
Many patients who try to be treated at home sometimes treat their gums with hydrogen peroxide.
Of course, hydrogen peroxide is a good antiseptic, and it is excellent in treating many infectious processes (for example, purulent wounds). It can also be used in dentistry, but not for rinsing the mouth, but for rinsing periodontal pockets with a syringe. When hydrogen peroxide comes into contact with any organic matter, it begins to foam, releasing atomic oxygen. When rinsing periodontal pockets, 3% peroxide is drawn into a syringe and the sharp edge of the needle is broken off (so as not to pierce the gum). Then the blunt end of the needle is inserted along the tooth root into the lumen of the periodontal pocket and washed under pressure. As a result, all infection and pus are washed out of the pockets.
But when rinsing the mouth, peroxide will react most quickly only with oral fluid, and other than a full mouth of foam, you will not get any effect. You won’t be able to rinse your pockets with a syringe at home yourself. For this you need a doctor, because... if you suddenly inject peroxide not into the lumen of the periodontal pocket, but directly into the soft tissue of the gums, you will receive a severe chemical burn with subsequent necrosis.
Gargling with infusions of medicinal herbs –
Many patients prepare their own rinse solutions by brewing medicinal herbs such as chamomile or oak bark. Such infusions actually have a good astringent effect, moderate anti-inflammatory, and also a weak antiseptic effect. And this can really help reduce swelling and bleeding of the gums, but such herbal infusions also have one big disadvantage.
The fact is that self-brewed herbal infusions contain a lot of pigments and tannins, which are very quickly deposited on the teeth in the form of pigment plaque. This plaque forms very quickly, and it will serve as a good basis for the already microbial plaque to attach to the surface of the teeth. But it is microbial plaque and tartar that cause gum inflammation. Therefore, if you use solutions with herbs, it is better in the form of ready-made rinses (since manufacturers remove from them all pigments that stick to tooth enamel).
Gargling
Irrigation of the throat soothes irritation and makes swallowing easier. And for this it is not necessary to use pharmaceutical sprays - regular rinsing will also help. It also cleanses the mucous membrane of microorganisms and their waste products, washes away plaque and reduces pain.
Rinse solutions should be warm, but not hot, so as not to further damage the mucous membrane. It is advisable to carry out the procedure half an hour before meals, its duration is up to 5 minutes.
And you can find a lot of ingredients for gargling in the kitchen.
- The simplest and most proven method is to gargle with water, salt, soda and iodine. Dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of boiled water. salt, 0.5 tsp. soda and a few drops of iodine. Gargle with this mixture 3-4 times a day.
- Rinsing with decoctions of medicinal herbs will help relieve the inflammatory process. For these purposes you can use raspberry fruits and leaves, chamomile, honeysuckle, eucalyptus, black currant leaves, sage, calendula, etc. For 1 glass of water you will need 1 tbsp. dried herbs. Cook the broth in a water bath for half an hour. After cooling to an acceptable temperature, gargle with it.
- In case of severe irritation, rinsing with warm water with 1 tsp diluted in it helps soften the mucous membrane. honey, 1 tsp. grated ginger and 0.5 tsp. lemon juice. The procedure should be done 2-3 times a day.
- You can also use apple cider vinegar to gargle. Dissolve 1 tbsp in a glass of water at room temperature. vinegar and honey. Also use 2-3 times a day.
- Gargling with turmeric helps relieve pain, removes mucus and disinfects the throat. A glass of heated water will require 0.5 tsp. salt and 1 tsp. this spice. A glass of warm boiled milk with a teaspoon of turmeric reduces irritation in the throat.
- An effective folk remedy for sore throat is oak bark, which has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Brew 1 tsp. crushed bark in a glass of boiling water and after cooling, gargle with the solution every 2 hours.
- Propolis is also suitable for fighting throat diseases, of course, if you are not allergic to it. Dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of warm water. its tinctures and gargle 5-6 times a day.
In what cases are rinses ineffective?
The author of the article has 10 years of experience as a “periodontologist” (documents on advanced training of the state standard in the “Parodontology” program - can be viewed in the editorial section), and we would like you to listen to our experience. The fact is that knowing what to rinse your mouth with when your gums are inflamed is not enough to cure their inflammation (24stoma.ru). Various mouthwashes (even the strongest ones), anti-inflammatory gels are only secondary means.
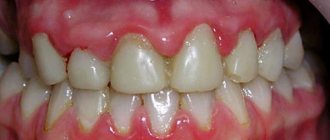
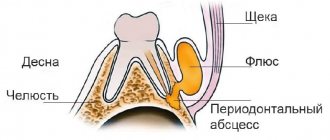
There are 2 main types of gum inflammation – gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the initial stage of inflammation, the main symptoms of which are: swelling, redness or bluishness of the gums, pain and bleeding when brushing teeth, bad breath (Fig. 3-4). With periodontitis, these symptoms are accompanied by mobility of teeth, suppuration from periodontal pockets, destruction of bone tissue around the teeth, and in later stages, changes in the position of the teeth (Fig. 5).
Gingivitis and mild periodontitis –
The cause of gum inflammation in both cases is soft microbial plaque, as well as hard supra- and subgingival dental deposits (Fig. 3-5). This is the main cause of inflammation, which is a consequence of insufficient oral hygiene. And the most important part of treatment should not be to reduce symptoms, but to eliminate the real cause of gum inflammation. And for this purpose, dental plaque is removed by a dentist (usually this is done using ultrasound).
Antiseptic rinses act only on the most superficial layer of microbial plaque or tartar. They do not act on the deeper layers, which also consist of pathogenic bacteria, and therefore the use of antiseptics does not lead to complete “disinfection”. Therefore, rinsing with antiseptics and gels for gums (without removing dental plaque) lead only to temporary improvement, and the inflammation in this case will be constant chronic - with periodic exacerbations.
Television advertising very actively promotes all sorts of products for gums, but it does not say that the main treatment is precisely the removal of dental plaque. Remember that a mild form of gingivitis can unnoticeably turn into a severe form of periodontitis if you try to treat the inflammation only with antiseptic rinses and anti-inflammatory gels - without periodic removal of dental plaque by the dentist.
→ How to properly treat gingivitis → Treatment regimens for periodontitis
Toothpastes for gum inflammation -
In complex therapy for the treatment of gum diseases, you can use not only rinses and gel applications, but also special anti-inflammatory toothpastes for gums, which will reduce bleeding and swelling of the gums even faster. Some of these pastes are also suitable for preventing inflammation. We hope that our article on the topic: How to rinse the mouth with gum inflammation was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a periodontist, 3. PubMed.gov scientific research base, 4. “Optimization of conservative treatment of patients with periodontitis” (Komleva A.S.), 5. Composition of products taken from official websites manufacturers.
Inhalations for sore throat
Inhalations can also help soothe an irritated throat. The simplest of them is to breathe steam over boiled potatoes in their jackets. For the best effect, you need to cover yourself with a towel. You need to breathe the steam for at least 15 minutes.
For inhalation, you can also prepare a decoction of herbs: sage, mint, chamomile, eucalyptus. Pour their mixture (1 teaspoon each) into 2 liters of boiling water and cook for 3 minutes. Breathe steam 3 times a day for 10 minutes.
Three times a day you can do inhalations from string and chamomile. For this, 2 tsp. Brew these medicinal plants in 400 ml of boiling water. After an hour, when they have infused, strain the solution and bring to a boil.
Inhalation with eucalyptus oil added to hot water, over which you need to breathe through each nostril alternately, also relieves sore throat.