Features of clasp dentures
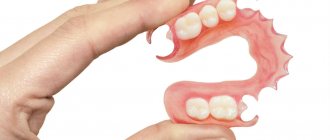
The first clasp dentures had the shape of an arc. Even the name of this design is literally translated as “arc”. The main advantage is that the clasp denture distributes the chewing load across all supporting teeth and hard tissues of the oral cavity. But unlike removable dentures, they do not completely cover the palate or most of the gums. This means that they do not distort the sense of taste, do not affect diction, and getting used to them takes less time.
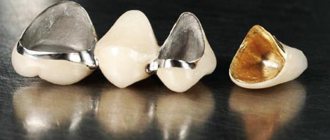
In the form of fastening on clasp dentures, a beam, locks and clasps are used. All of them do not injure tooth tissue and do not interfere with chewing or talking. In addition, their special installation ensures an aesthetically pleasing appearance while smiling.
Clasp prosthesis is partially removable. Patients can take it off in one motion and put it on just as easily. But it is worth noting that there is no particular need to remove the clasp dentures at night, as happens with removable plastic dentures. In most cases, patients remove it only to perform hygiene procedures. Due to the special type of fastening, the clasp denture will never fall off during chewing or talking, which is considered its main advantage over other dentures.
The structure of the clasp prosthesis
The main parts of a clasp denture are a metal frame, the fasteners listed above, an arch, and also a base on which artificial teeth are attached. The arch, clasps and base are responsible for fixation in the prosthesis. Support-retaining structures in clasp dentures are solid, individually cast from metal and then soldered, and also soldered wire. The choice is made purely individually depending on the number of missing teeth and the condition of the jaw.
In most cases, clasps are used. They are special hooks that hold the clasp denture on the supporting teeth:
There are several ways to make a clasp for clasp dentures:
- It is considered simple to bend the wire in accordance with the shape of the prosthesis model.
- A complex clasp is cast as a solid crown from a special alloy during the manufacture of the arch of the clasp prosthesis.
But the holding elements are divided not only according to the manufacturing method.
There are clasps:
- supporting;
- holding;
- performing these two functions at once.
The first distribute the load from the clasp denture, which occurs during talking, chewing, clenching teeth, onto the supporting teeth and partially onto the mucous membrane. In contrast, the retaining clasps of clasp dentures transfer the load to the mucous membrane, plunging into it when pressure occurs. The latter are capable of performing the functions of both the former and the latter.
All clasps consist of several parts. The clasp body of the clasp denture is located on the supporting tooth in its upper area. The clasp arm touches the side surface of the tooth. Due to the presence of an occlusal pad, the clasp prosthesis does not sink deep into the gum and does not injure it during chewing. In addition, it is able to restore the height of crowns. In addition, there is a process of the clasp or that part of it that is located in the body of the base of the clasp prosthesis.
Clasp dentures with locking fastening look and attach differently. Unlike dentures with clasps, they are completely invisible to others, because fixation is carried out by micro-locks that are located in the clasp denture system.
In this case, metal-ceramic crowns are placed on the supporting teeth, in which one part of the lock is attached. Its second part is fixed in the clasp prosthesis. During dressing, the clasps are fastened and the denture is securely held in the oral cavity and does not fall off during chewing. In this case, the load from the clasp denture falls only on the supporting teeth, so you should not use this method of fixation in cases where the teeth have mobility.
Based on the fastening methods, it remains to conclude that a clasp denture is indicated only in cases where there are supporting teeth. Without them, the clasp prosthesis will not hold.
In addition to the support system, the clasp prosthesis has a base. The teeth are attached to it. Today, prosthetics are carried out using various dental manufacturing companies. Due to this, you can achieve high aesthetics and an attractive appearance. The same applies to the plastic used for the base of the clasp prosthesis. High-quality materials have a long service life and are distinguished by their perfect resemblance to living gums and natural teeth. The price of such a prosthesis will be a little more expensive, but it will have virtually no disadvantages.
You can choose a suitable clasp prosthesis from the photo, but it is better to hold it in your hands. Therefore, only a visit to the dentist will provide comprehensive information about the clasp denture.
Varieties
With rectangular profile
The rectangular beam, which became widespread, was first invented by K. Rumpel. Its peculiarity is that the main pressure is transferred to the beam and only a small part falls on the mucous membrane of the alveolar process. There is a gap of 1–2 mm between the bar and the gum to perform hygienic procedures.
With an ovoid profile
The beam structure, developed by E. Dolder, has an ovoid profile with a height of 3 mm and a width of 2 mm. A metal strip 0.2 mm thick acts as a bushing. The gap between the middle of the bushing and the highest point of the beam is 1 mm. As chewing load increases, the sleeve moves, thereby improving the functionality and performance of the system.
With T-profile
Research conducted by Selchukov S.G. allowed us to come to the conclusion that the T-shaped profile has the least deflection compared to other structures. The beam made of cobalt-chrome-nickel alloy is attached to push-button cylindrical locks and is equipped with platforms along the entire length. The matrix is made of polypropylene. In order to improve the shock-absorbing and fixing properties of the system, a gap of 1 mm is left between the upper part of the beam and the matrix. Push-button locks provide reliable adhesion to the supporting teeth, which generally has a positive effect on the strength of the structure.
With cast blanks
The first use of cast blanks for a beam-type prosthesis was proposed by RT Williamson in 1991. Their installation required preliminary processing of the remaining teeth. Its goal was to obtain smooth surfaces without sharp corners and an occlusal gap for fixation of artificial units.
Then plastic pins are inserted into the previously prepared root canals for the subsequent production of their metal counterparts. The cavities into which the pins will be installed are covered with cotton balls and a bandage, which eliminates the risk of infection. Based on the impressions obtained, metal pins are cast, which, after polishing, are fixed to the patient. If necessary, correction is carried out, and then a prosthesis is made by a specialist in a dental laboratory. After polymerization of the plastic base, the prosthesis is ground and polished. Replacement clamps are then installed. This technique significantly reduces the cost of prosthetics, and also improves the fixation of the structure and the condition of the periodontium by shortening the crown.
Clasp dentures have a number of advantages over bridges:
- Installation of clasp removable dentures does not require preparation of some teeth and does not limit their mobility.
- Chewing pressure is evenly distributed between the alveolar processes and the remaining teeth.
- Clasp dentures are hygienic; they can be cleaned mechanically outside the oral cavity.
To individually assess the condition of your teeth and make various solutions to your problem, you need to have a free consultation with an orthopedic dentist. A highly qualified specialist will help in any of your situations.
Features of clasp prosthetics on the upper and lower jaws
The differences between the upper and lower dentures lie in the location of the bridge and retainers. The arch model depends on the topography of the dentition defect, the shape of the palate, the relief of the alveolar process and other factors.
When restoring the upper jaw, the thickness of the bridge should be 0.9-1.2 mm and the width 4-10 mm. In this case, the arc should be located 0.5 mm from the mucosa. In most cases, the upper jaw prosthesis is fixed on the lateral incisors or molars.
The lower jaw prosthesis must be made with an arch that is unevenly spaced from the mucous membrane: at the upper edge it extends by 0.5-0.6 mm, at the lower edge - by at least 1 mm. In this case, the jumper should not come into contact with the underlying tissues and injure the frenulum. In most cases, the structure is attached to the lateral incisors.
Conclusion: Indications for the use of removable clasp dentures
In persons with partial absence of teeth, along with end defects, combined and included defects are often encountered. Plate and clasp removable dentures can successfully replace end defects. Clasp dentures have a number of significant advantages over removable plate dentures:
- The base part of clasp dentures is minimal.
- The arch in the prosthesis ensures uniform distribution of the load between its sides.
- The prosthesis contains supporting clasps, which allow partial transfer of the load through the tissues of the supporting teeth.
- Compared to other complete removable dentures, clasp dentures can be slightly adjusted.
- The oral mucosa and gingival papillae are partially released.
- Reliable fixation of the prosthesis speeds up adaptation.
Indications and contraindications
Installation of beam prostheses is indicated for:
- existing extensive defects: loss of several teeth (4–5);
- defects in the lateral part of the dentition, combined with minor defects in the terminal and anterior parts;
- the presence of defects in the end and side sections of the row;
- the need to splint abutment teeth by connecting them into one structure with a beam and artificial crowns;
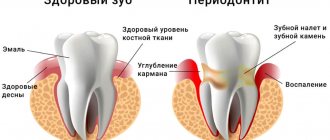
- treatment of periodontal diseases with complications in the form of partial tooth loss.
Contraindications include:
– insufficient height of the supporting teeth, which does not allow reliable fixation of artificial crowns;
– a small gap between the toothless alveolar processes or the process and the antagonist tooth;
– fragile fixation in the absence of 1-2 teeth: support-retaining clasps are required to strengthen the structure.
Caring for a clasp denture
As already mentioned, the clasp prosthesis does not need to be removed at night. You can wash it in the morning after sleeping and in the evening after eating using a toothbrush. There are many products for caring for dentures, including rinses. The doctor can explain to you how they work and help you choose based on the materials of the clasp prosthesis.
Clasp dentures are not suitable for everyone. The condition of the teeth is important, as well as the general reaction to the materials from which the prosthesis is made. However, here too experts have found a way out, using a special type of plastic that does not cause allergies. The cost of such a clasp prosthesis will be a couple of thousand rubles more than a simple one, but you will be able to use it with great pleasure.
No patient can choose a denture option on their own. Only the dentist will determine the condition of the jaw and supporting teeth, and also select the type of clasp denture.
All you have to do is make an appointment with a dentist at our center and receive all the comprehensive information from him. Once you understand what a clasp prosthesis is, we are confident that you will give us a positive review, like many others.
Secondary medical education
- General midwife
- Dental assistant
- Dentist
- Dentist
- Dental Technician
- General expert research laboratory assistant
- Blood service laboratory technician
- AIDS service laboratory technician
- Laboratory assistant of forensic biological departments
- Laboratory assistant of forensic histology departments
- Laboratory assistant of physical and technical departments
- Laboratory assistant at chemical and toxicological departments
- Gynecological nurse
- Neonatology nurse
- General practice nurse
- Nurse of the intensive care and anesthesiology departments
- Ophthalmic nurse
- Pediatric nurse
- Physical therapy nurse
- Nutritional Nurse
- Massage nurse
- Care nurse
- Healthy lifestyle nurse
- Tuberculosis service nurse
- Psychoneurological nurse
- Blood service nurse
- AIDS service nurse
- Dental nurse
- Therapeutic nurse
- Physiotherapeutic nurse
- Surgical nurse
- Medical statistician
- Laboratory assistant doctor
- Nurse's assistant
- X-ray technician
- Paramedic laboratory assistant
- Narcology paramedic
- General practitioner
- Paramedic of the public education system