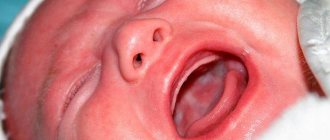
Plaque in the throat (tonsils) is a common occurrence in children and adults.
And it, as a rule, is a symptom of some disease. Plaque in the throat is usually called plaque on the tonsils (tonsils). This is an organ (paired) located between the pharynx and mouth. The tonsils are easy to see if you open your mouth. There are also tonsils, which are located under the tongue, deeper in the throat, and also in the nose. They are no longer visible.
The tonsils play an important role. When entering the body, they trap viruses, microbes and bacteria, and thereby protect a person from the effects of harmful microorganisms.
The tonsils also belong to the immune system; they take part in the development of immunity. They also perform a hematopoietic function.
The tonsils are a fairly sensitive organ, especially in the cold. With reduced immunity, a person begins to have a sore throat, and the tonsils may become covered with a specific coating. Thus, they neutralize germs and viruses that enter the body through the mouth.
That is why the tonsils are called the first shield on the way to the body of harmful microorganisms . However, the role of tonsils in the immune system is not yet fully understood.
Reasons for the raid
So, plaque in the throat is a reaction of the palatine tonsils to viruses, bacteria and microbes entering the body. Plaque appears in the recesses (the so-called tonsil crypts) - food debris collects there, as well as harmful microorganisms that multiply under the influence of microflora. Then they decompose, and this leads to suppuration, which envelops the tonsils and creates plaque.
The appearance of plaque in the throat is the first signal for the body that it has been attacked by a disease and that it is necessary to urgently take measures for prevention, since the protective function of the tonsils is reduced, they cannot cope with protecting a person from further penetration of microorganisms (for example, into the trachea , bronchi, lungs, etc.).
Plaque in the throat can have various causes: • scarlet fever; • angina; • diphtheria; • candidiasis (thrush); • stomatitis; • lichen planus; • leukoplakia (leukoedema); • actinomycosis; • syphilis; • chemical burns of the mucous membrane due to taking irritating medications (for example, aspirin).
Plaque symptoms
White plaque is a common companion to many infectious diseases of the throat. A white soft mass forms in the body. It accumulates in the crypts - small depressions in the tonsils. It is this that causes bad breath, and this causes discomfort for the owner of the tonsils.
Usually this process does not cause harm to health and ends on its own, without requiring any treatment. But, as noted above, with a weakened immune system, the tonsils become an entry point for infection.
Plaque is one of the main symptoms of tonsil inflammation. Plaque can be of different colors. It depends on the stage, the specifics of the disease that develops: white plaque, gray (dirty gray), yellow; Sometimes ulcers may appear.
The entire process may be accompanied by severe pain. If you do not pay attention to the plaque at all, the infection will gradually spread and can cause the diseases mentioned above, or even lead to their complications, including heart disease, which is not immediately treatable.
Therefore, doctors advise contacting a medical facility in the following cases: • plaque does not go away for several days; • deterioration of health; • rise in temperature; • a sore throat began; • enlarged lymph nodes; • if there is a history of rheumatism; • appearance of a rash on the skin.
There is no point in trying to determine the color of plaque yourself in order to establish a more precise reason for its appearance. It is better to immediately contact a specialist (preferably an otolaryngologist), who will determine the color more reliably. It is important to determine the shade of color in order to accurately diagnose the disease and, accordingly, prescribe precise treatment. For a clear diagnosis, a throat smear is also used (determination of the type of pathogen).
How to remove white dots
In order to remove white lumps in the tonsils, use local antiseptic bactericidal agents. They are available in a wide range in the form of sprays, lozenges or tablets. Rinsing helps a lot. Traditionally, solutions of soda, table salt with iodine, furatsilin, chamomile and sage decoctions are used for this. You can use a solution of Metrogyl, Miramistin.
It is impossible to clean the tonsils from white lumps at home. This is done by an otolaryngologist by vacuum extraction of plugs or washing the tonsils with antiseptic solutions.
It is not recommended to remove a white dot containing pus from the tonsil on your own. In the acute period of the disease, this is prohibited.
Sore throat without fever
Sometimes, when a plaque appears in the throat, the temperature remains normal. However, even in this case, there is no need to take risks, but still consult a doctor.
What reasons can there be for a plaque in the throat without fever: • burn, trauma to the pharynx; • fungal plaque (it looks more like a cheesy mass and affects not only the tonsils, but also the tissue of the nasopharynx); • sore throat in the initial stages; • syphilitic tonsillitis (in this case, erosions form on the thickened tonsil); • purulent plugs in lacunae (look like white plaque); • stomatitis (sore throat, no fever).
White plaque
Diseases that may cause white plaque on the tonsils: • sore throat; • leukoplakia (another name is leukoedema); • scarlet fever; • candidiasis (thrush); • actinomycosis; • stomatitis; • burns of the mucous membrane of the mouth and throat.
Leukoplakia (leukoedema)
This is called swelling of the oral mucosa. It occurs more often in people who smoke or sniff tobacco. The causes of the violation have not been studied. These disorders are quite common, but are not cause for great concern. With this disease, changes in the mucosa are not common. However, it is necessary to be under the supervision of a specialist, since there is a risk of developing cancer. And such a disease, as we know, is easiest to treat in the early stages. Although in 80% of cases the plaques are benign .
If the white plaques suddenly thicken, then it is advisable to submit a piece of tissue for a detailed cytological examination to clarify the nature of the disease. The substance is taken for analysis under local anesthesia, so as not to cause discomfort to the patient.
To prevent leukoplakia, doctors advise giving up chewing tobacco and smoking, because these unhealthy habits can become a trigger for the development of the disease.
For the treatment of leukoplakia, carotene is prescribed in large doses for a month. Vitamin A therapy should be carried out under the close supervision of a doctor, since any overdose can cause damage to health.
Angina
In most cases, white plaque means tonsillitis - inflammation of the tonsils. There are many types of sore throat. White plaque means lacunar tonsillitis. The main symptoms of lacunar tonsillitis: • white coating on the tonsils, has a yellowish tint; • plaque covers the entire tonsils; • plaque can be easily removed with a spatula; • general weakness; • acute sore throat; • elevated temperature.
Purulent plaque
With follicular (purulent) tonsillitis, ulcers form on the tonsils. The festering follicles are visible through the mucous membrane.
Symptoms of follicular tonsillitis: • high temperature; • very poor general health; • lack of appetite; • weakness; • headache.
This type of sore throat takes a long time to treat and is difficult. May develop into a chronic form. Then, even with a minor cold, a person suffers from purulent plaque on the tonsils. If the sore throat is purulent, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. For follicular sore throat, home treatment methods (herbs, rinses, poultices) will be completely insufficient, and sometimes traditional methods can be dangerous.
If you have a sore throat, it is important to consult a doctor about how to remove pus from the tonsils. Therapy and prevention must be taken very seriously to prevent the disease from returning.
Scarlet fever
Symptoms: • plaque in the throat; • pain when swallowing; • general weakness; • headache; • temperature; • nausea; • drowsiness (persistent); • swelling.
Syphilis
Damage to the mucous membrane of the trays with syphilis has a whitish tint. Three weeks after the onset of the disease, they turn red.
Actinomycosis
Occurs in people who are accustomed to chewing grass stems. This habit causes fungal infections in the oral mucosa. Actinomycosis appears as a white coating on the tongue and palate.
Lichen planus
Damage to the oral mucosa. Resembles a white grille in appearance. The disease does not require therapy if there is no pain. It is caused by malfunctions in the body's defense system - autoimmune reactions. No special treatment is required if there is no pain.
Thrush (candidiasis)
Symptoms: • white plaque on the tonsils; • gradually spreads to the entire mouth.
Stomatitis
Main symptoms: • slight plaque in the mouth; • irritation of ulcers during meals; • temperature increase.
Burns to the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat
Occur as a result of resorption of tablets (for example, aspirin) or after exposure to other chemicals. The burn areas appear to turn white.
Causes of red throat
Redness of the throat may be due to factors unrelated to infection2:
- Mechanical injuries to the mucous membrane of the pharynx due to solid food and bones.
- Eating hot food that can cause thermal burn2.
- Irritation or burn of the pharynx with chemicals (acids, alkalis, alcohol-containing liquids)2.
- Eating excessively spicy foods (hot pepper, ginger, horseradish, mustard can cause irritation of the mucous membranes).
- Inhalation of tobacco smoke, dust or air contaminated with mechanical and chemical impurities.
Eating food containing red food dyes. In this case, the throat is red, but does not hurt.
Up to contents
Gray plaque on tonsils
Diphtheria
A rather dangerous acute infectious disease is diphtheria. Its harbingers are white dots on the tonsils. The coating has a grayish, dirty tint.
The infection is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. Pathogenic microorganisms (rod-shaped microbes) can penetrate the mucous membranes of the eyes, upper respiratory tract, genitals and skin.
Depending on the place of introduction of the diphtheria bacillus, there are several types of diphtheria: • diphtheria of the pharynx; • diphtheria of the larynx; • nasal diphtheria; • eye diphtheria; • diphtheria wounds.
If the diphtheria bacillus enters through the mouth, it leads to inflammation in the pharynx and plaque on the tonsils.
There are different forms of diphtheria of the throat. If the form is localized, then the plaque is almost visible; it resembles a film with a gray pearlescent sheen.
With toxic diphtheria, the plaque is dirty gray crusts, very painful. If the form is common, then the plaque can be from light gray to dark gray, and the plaque is located not only on the tonsils themselves, but also beyond them.
A little anatomy
The pharynx is part of the respiratory tract and digestive tract. It contains a whole complex of lymphoid formations called the Pirogov-Waldeyer pharyngeal ring. The ring includes the palatine, pharyngeal, lingual, tubal tonsils, as well as lymphoid granules and ridges that are located on the lateral walls of the pharynx.
The tissues of the pharynx are penetrated by a huge number of blood vessels. Their superficial location provides warming or cooling of the air inhaled through the mouth and nose. In contact with the mucous membrane, the air is cleared of dust, chemical impurities and various microorganisms. Dust particles, substances and microbes settled on the mucous membrane irritate it, which sometimes causes inflammation and redness of the throat1.
Up to contents
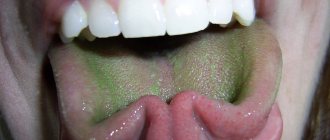
Yellow plaque
Such plaque may be a sign of the same diseases as white plaque, however, the shade is individual for each person, since it depends on various factors.
Sometimes a yellow coating can indicate the first stage of the appearance of pus on the tonsils, and subsequently this pus can turn into very painful ulcers.
Yellow plaque most often accompanies a sore throat (tonsillitis), especially if it is accompanied by difficulty breathing, cough, high temperature, and sore throat.
The main therapy is carried out with antibiotics, since the causative agents of sore throat are bacteria. Traditional medicine can alleviate some of the symptoms of the disease.
Fungal plaque
Often children and adults have a fungal type of plaque. It is caused by a fungus of the genus Candida, which penetrates the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, nose and mouth, and eyes. The difference between fungal sore throat and any other is that it cannot be treated with antibiotics. Antifungal medications and vitamins will be required. If the fungus cannot be cured with medications, then they resort to surgery - removal of the tonsils.
Fibrinous plaque after tonsillectomy
Tonsil removal surgery can have complications, just like any other surgery. In particular, pharyngeal bleeding may occur on the first day or one day after surgery. It occurs when the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding the postoperative regimen.
After the operation, an open wound is formed at the site of the removed tonsils. Over time, the wound is covered with a fibrinous film, which serves as a hemostatic barrier. And approximately 5 days after tonsillectomy, fibrinous plaque on the tonsils disappears on its own .
Curdled coating
With pharyngomycosis, candidiasis of the tonsils, mycosis of the pharynx, plaque in the throat has a thick curd consistency. After the fungus infects the oral mucosa, a whitish or grayish coating appears. It can be removed quite easily, but after a while it appears again. In this case, the patient may have bad breath, since plaque occurs as a result of the functioning and decomposition of microorganisms.
A person may have several types of fungi present at the same time. If a cheesy coating appears in your mouth, you should consult a doctor. There are many drugs for fungus, but each has its own specifics, it is aimed against certain types of fungi, so it is important to choose the right one.
Sore throat in a child
Children have weaker immunity than adults. Children's tonsils cannot cope well with infections that await them in kindergarten or school, or on the street, especially if these infections are spread by airborne droplets. For these reasons, children more often than adults suffer from sore throats and fungal diseases of the mouth and pharynx.
A child’s tonsils sometimes immediately react to the introduction of the disease by the appearance of plaque. There is no need to hesitate to see a doctor; you should not wait for the disease to develop or, worse, complications .
Experts recommend that parents engage in timely prevention of diseases in children and strengthen their immune system.
After ARVI in a child
Children suffer from acute respiratory viral diseases quite often. This is due to:
- immaturity of the child’s immune defense mechanisms;
- high crowding in children's groups.
Sometimes after an acute respiratory viral infection, white dots or spots are found on the child’s tonsils, enlargement, swelling of the tonsils, and redness of the palatine arches. This indicates the addition of a bacterial infection and the development of a sore throat. In this case, you should immediately seek medical help.
Timely and correct treatment of sore throat will protect the child’s body from complications.
A white coating may appear on the child’s tonsils without fever. This happens when oral thrush occurs. Thrush is a fungal disease caused by pathogenic fungi of the genus Candida. Candidiasis often develops during antibiotic treatment. The diagnosis is made based on examining a smear from the tonsil under a microscope. Specific antifungal drugs are used in treatment.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of plaque on the tonsils itself is simple. You need to stand facing the light source, take a mirror, open your mouth and look - the plaque will be immediately visible. But only a doctor can understand the nature of the infection and determine the type of fungus or microbe after conducting appropriate studies (analysis of a smear from the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and pharynx).
What characteristics are taken into account when analyzing plaque: • results of a smear from the mucous membranes; • plaque color; • plaque consistency; • presence or absence of ulcers on the tonsils; • presence of fever; • presence or absence of sore throat.
There is no need to try to make a diagnosis yourself; it is better to consult an otolaryngologist. After all, any disease is fraught with transition to the chronic stage, and there is also a high risk of infection of the immediate environment.
How to deal with plaque in the throat
Leukoedema (leukoplakia) does not require self-treatment. With lichen planus there is also no particular danger. But if there is pain when swallowing, the doctor will most likely prescribe hydrocortisone (tablets or ointment).
When the first symptoms of a viral infection occur (plaque on the tonsils, fever, general weakness, sore throat), it is advisable to take an antiviral drug (for example, Amizon, Amixin).
To soothe a sore throat and remove plaque, including sore throat and pharyngitis, rinsing is recommended - the most popular and accessible method of symptomatic treatment. Options for gargling solutions for a sore throat: • saline (or soda) solution with added iodine - half a teaspoon of salt or soda + 3 drops of iodine per 1 glass of warm (not hot!) water. Carry out the procedure often, after meals; • rinsing with furatsilin solution - a ready-made pharmaceutical solution or prepared at home from tablets. Take one tablet, crush it and pour a glass of boiling water. Rinse with warm solution several times a day; • for stomatitis and inflamed tonsils, gargling with the pharmaceutical solution “Stomatidin” helps. For a sore throat, lozenges with an analgesic effect can help - decatylene, faringosept, septefril, etc.
Treatment
Correctly prescribed treatment will quickly eliminate symptoms. Complex therapy will be the most effective.
- Local treatments are recommended for healing ulcers. Special gels and ointments prevent the proliferation of pathological bacteria.
- Soreness and fever are relieved with the help of painkillers and antipyretics.
- Those factors that provoke the disease are eliminated.
In addition, the diet is selected, the bite is corrected, and concomitant diseases are treated. Drugs prescribed:
- Against candidiasis - “Chlorhexidine”, “Stomatofit”, “Rotokan”;
- Rinse solutions;
- Combined-action medications, for example, Cholisal-gel.
- Vitamins to strengthen the body's defenses.
- Calcium supplements to reduce allergic reactions.
- Iron supplements.
Treatment of plaque in the throat with traditional methods
You can try to treat plaque on the tonsils with folk remedies: • gargling with tinctures or infusions of medicinal flowers and herbs (chamomile, calendula, sage). Take one tablespoon per glass of boiling water, leave for 15-20 minutes, then strain. Rinse several times a day, the infusion should be warm. You can take a collection of herbs; • gargling with water in which beets have been boiled (helps with sore throat). Before boiling beets, of course, you need to rinse them thoroughly. Perform this rinsing procedure twice a day; • chewing small pieces of garlic. Garlic juice helps destroy bacteria; • chewing lemon slices, drinking tea with lemon (lemon juice cleanses the tonsils well and has pain-relieving properties); • resorption of a small amount of honey in the mouth (in the absence of allergies to bee products). Can be done often. Honey is known to have antibacterial properties; • onion inhalations. Grind the onion (it is very rich in phytoncides) into a puree. Bend low over the bowl of this puree and inhale deeply through your mouth for about 5 minutes. Repeat twice or thrice a day. Following such simple folk recommendations helps to quickly cope with diseases.
Additional events
• hydration of the oral cavity. Some doctors recommend drinking an extra glass of water with meals and before bed (unless you have kidney disease); • additional air humidification (installation of humidifiers, growing indoor plants, etc.); • frequent ventilation of the room.