Prices for services You can look at the price list or check by calling the phone number listed on the website.
The article was checked by an otorhinolaryngologist, Ph.D. Dubtsova E.A. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Throat diseases unite a whole group of diseases localized in the pharynx, larynx, tonsils, soft palate and palatine arches.
- At the Yauza Clinical Hospital, the diagnosis and treatment of all these diseases is carried out by specialists from the otolaryngology department - experienced doctors of the highest qualification category.
- To make an accurate diagnosis, after collecting an anamnesis and a medical examination, the necessary laboratory tests are carried out (general blood and urine tests, virological or bacteriological examination of a smear, etc.).
- The capabilities of our hospital allow us to carry out all studies in the shortest possible time and begin treatment immediately.
- 1st place in the structure of ENT diseases is occupied by diseases of the pharynx (primarily chronic pharyngitis and tonsillitis), 4th place by pathology of the larynx
- With a general weakening of the body and the absence of proper treatment, diseases can become chronic, worsening a person’s quality of life.
- Diseases of the ENT organs can lead to various complications. Considering this, it is difficult to overestimate the importance of timely contact with specialists
Sign up for a consultation
Throat diseases are a broad group of various pathological conditions, combining both acute and chronic throat diseases. Based on their origin, they are usually divided into infectious and non-infectious. Most ENT diseases of the throat are caused by viruses and bacteria that enter the mucous membrane from the outside. The wide prevalence of this pathology is associated with the structural features of the throat, which is the body’s first line of defense and always takes the brunt of infection.
The most common throat diseases:
- adenoids;
- pharyngitis;
- tumors of the larynx and oropharynx;
- laryngitis;
- peritonsillar abscess;
- tonsillitis;
- snore;
Most diseases are characterized by an acute onset with a significant deterioration in well-being. The main danger is that, if left untreated, the disease can become chronic and can also provoke the development of various complications - cardiovascular pathology, diseases of the paranasal sinuses, lungs, joints, and kidneys.
It is not customary to pay much attention to throat diseases. Many people try to treat them at home. This leads to the development of chronic forms of throat diseases. Do not self-medicate. Make an appointment with a doctor, get professional help and adequate therapy.
Symptoms of throat diseases
Most throat diseases have pronounced symptoms. Moreover, the clinical picture for each disease is individual. Among the common and most basic symptoms it is worth highlighting:
- sore throat that gets worse when swallowing;
- sore throat, dry throat;
- cough;
- hoarseness of voice;
- temperature increase;
- enlargement of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes;
- weakness and general malaise;
- headache;
- bad breath.
The combination of several of these symptoms at once is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. If symptoms increase and health deteriorates, prompt medical care is necessary.
Some throat diseases can cause rapid swelling of the larynx. As a result, without medical assistance, the patient can quickly die from suffocation. If you experience pain, immediately make an appointment with a doctor. This will help quickly and effectively eliminate the disease.
Signs and causes of diseases
The main factors for the occurrence of respiratory tract infections are weak immunity, hookah and e-cigarette smoking, nicotine and alcohol abuse.
In addition, the following reasons lead to diseases of the larynx and throat:
- exposure to allergens;
- damage to the mucous membrane by viruses, fungi and other pathogens;
- damage to the vocal cords;
- prolonged hypothermia;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- injuries after mechanical impact in the form of impact, suffocation, or foreign body entry.
Respiratory tract infections have pronounced symptoms, an acute course and are easy to diagnose. Diseases of the throat and larynx begin with a sharp deterioration in health. The main signs of ENT infections include:
- difficulty, pain when swallowing;
- high temperature, headache;
- swelling of the pharynx;
- redness of the mucous membrane, rashes;
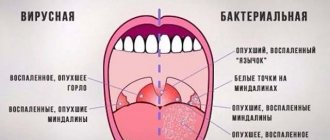
- purulent plaque on the tonsils and their inflammation;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- dryness, tickling, cough;
- bad breath.
At an advanced stage, the infection spreads to the tooth roots. Pain appears when chewing food. Over time, an abscess develops in the root system, which requires surgical intervention. Some infections lead to swelling of the larynx and suffocation.
Medical offers to make an appointment with an otolaryngologist (ENT) of the highest category. A full range of diagnostics and treatment of ENT diseases in Tula. Tel. for recording.
If one or more symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a specialist. Self-treatment at home helps relieve symptoms, but does not eliminate the cause of the pathology. The doctor will determine the type of disease and select effective therapy.
Causes of disease development
Acute and chronic throat diseases can occur for various reasons, among the most common are:
- microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi);
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD);
- allergens;
- adverse environmental impacts;
- voice overstrain;
- injuries;
- hypothermia;
- general decrease in immunity;
- smoking.
A combination of several reasons is possible. Their identification and elimination is an integral part of treatment.
Treatment of diseases of the throat and larynx
For any form of the disease, frequent and abundant drinking and rinsing is recommended; this allows you to “wash away” the waste products of viruses and bacteria, relieve inflammation and maintain the mucous membrane in the desired shape (it tends to dry out due to high body temperature during illness).
Most cases respond well to drug treatment if it is started on time. Surgical intervention is sought when purulent or tumor processes begin, that is, the disease takes on a severe form, threatening the patient’s life with suffocation.
What and how to treat:
- ARVI is the most common throat disease. It is characterized by dry throat, sore throat, runny nose, sneezing and coughing. The temperature usually stays between 37–38 degrees. Treated with antiviral drugs based on existing symptoms. Gargling with infusions of chamomile, sage and herbal lozenges helps with sore throat; they relieve irritation and make the treatment pleasantly tasty. Along with this, it is recommended to take vitamin C to support and strengthen the immune system, as well as plenty of warm drinks (herbal teas with honey are welcome);
- tonsillitis is an infectious-allergic disease that mainly affects the tonsils. It is characterized by high body temperature, up to 40 degrees, and unbearable pain in the throat. The larynx and tonsils are red - a sure sign of an inflammatory process - and have a white coating. High fever is accompanied by aching joints and headache. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor, since it is important to prevent complications. Drinking plenty of fluids, gargling with antiseptic herbs, and herbal lozenges help with a sore throat. Food should be taken pureed and liquid, not hot, so as not to injure damaged areas of the mucous membrane;
- pharyngitis is an acute inflammatory process in the pharynx, with a characteristic dry cough, soreness, stabbing pain, a feeling of a lump and inflammation in the mucous membrane, developing into purulent processes. During illness, all solid, spicy, sour and hot foods are excluded from the patient’s diet. Treatment is medicinal, the doctor prescribes antiseptics, since the disease is inflammatory in nature. Self-medication in this case is strictly prohibited: the disease develops quickly and becomes chronic;
- laryngitis - inflammation of the vocal cords and larynx is characterized by a barking cough with sputum, a hoarse voice until its complete disappearance, and a scratching pain in the throat. Children often suffer from laryngitis. Laryngitis causes swelling of the throat when lying down, which can lead to suffocation. Therefore, if you find that your child begins to choke while lying in bed, call an ambulance, lift the child to an upright position and take him to the bathroom, under a warm shower, to relieve the spasm. Laryngitis is treated with inhalations, warm compresses, warm drinks and silence. To alleviate the patient's condition, high humidity is needed in the room: a container of water, a diffuser or a wet towel on a radiator;
- Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, which is characterized by high body temperature, acute sore throat, and bad breath due to purulent plaque on the tonsils. The main causes of tonsillitis are viruses and bacteria. The course of treatment includes gargling with a solution of soda and salt - it acts as an antiseptic and “washes away” the pus.
Bacterial throat diseases develop very quickly, within a few hours. Viral ones - a little slower. But only a doctor can determine the real etiology of the disease, and then only based on test results.
The most common throat diseases
Among the most common diseases of the ENT organs in this area are pharyngitis, laryngitis and tonsillitis.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an infection of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and lymph nodes. As a rule, pharyngitis occurs against the background of an acute inflammatory disease of the upper respiratory tract. More often, pharyngitis is caused by viral-bacterial flora or fungal infection; other causes include injuries and allergic reactions. With prolonged inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa, the disease can become chronic. Frequent colds, pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, smoking, drinking alcohol, exposure to chemicals and living in unfavorable environmental conditions can contribute to this. Exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis can be facilitated by other infectious diseases, decreased immunity, hypothermia, stress, and increased physical activity.
The main symptom of pharyngitis is pain when swallowing. The disease may also be accompanied by dryness, burning, itching, general weakness and headaches. Pharyngitis is dangerous because the infection from the pharynx can move to the middle ear and cause deterioration and even hearing loss, or go down to the larynx and cause laryngitis and tracheitis.
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is an inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the larynx. It can occur either independently or against the background of other inflammations of the nasopharynx. There are catarrhal and phlegmonous forms. The first is characterized by the spread of inflammation only to the mucous membrane of the larynx, the second - to the submucosal layer, ligaments and muscle tissue. Laryngitis can be triggered by hypothermia, contact with people with ARVI, inhalation of irritants, smoking (including hookahs and electronic cigarettes - steam generators).
A distinctive symptom of laryngitis, in addition to changes in voice, is a “barking” cough that irritates the throat. Just like other similar throat diseases, hoarseness is a characteristic symptom here; pain when swallowing, difficulty breathing, and inflammation of the lymph nodes may also be present. Among the most serious complications of laryngitis are infiltration of the epiglottis, abscess, damage to the vocal cords, up to complete loss of voice.
Angina
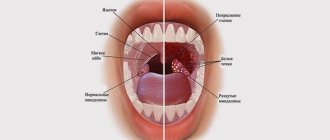
Sore throat is an acute infectious disease characterized by damage to the tonsils, which is caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi. In this case, pathogens can either enter the body from the outside or already be in the body and become activated when immunity decreases. A sore throat begins acutely with a sharp deterioration in well-being and an increase in body temperature to 38-39° C. It is important not to confuse this with a common cold. A sore throat is characterized by severe sore throat, swollen lymph nodes and aching joints. When examining the patient, pustules are observed on the tonsils.
If you suspect a sore throat, you should immediately consult a doctor, because improper treatment is fraught with the development of complications in the form of abscess, otitis, meningitis, sepsis and many other life-threatening conditions.
Why does there be a feeling of a foreign body in the throat?
Acute infections
The sensation of a foreign body is provoked by swelling, inflammation, accumulation of sputum, and plaque formation. It is detected in infectious diseases such as:
- ARVI.
The manifestation is insignificant, disturbing at the initial stage of the disease, complemented by weakness, weakness, moderate redness of the throat, general hyperthermia, and muscle pain. - Measles.
The symptom occurs with the onset of the first wave of fever and is more pronounced in children. The pharynx is hyperemic, the posterior wall of the pharynx is granular. The face is swollen. After 3-5 days, the condition improves and characteristic rashes form on the skin. - Diphtheria.
Accompanied by the formation of fibrinous plaque first, then a dense smooth coating. With widespread damage to the oropharynx, involvement of the larynx and trachea, breathing disorders and the development of diphtheria croup are possible. - Scarlet fever.
The throat is bright red, painful, sometimes there is involvement of the tonsils and enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes. A little later, the tongue and lips also become bright red, a pinpoint rash appears on the face and upper body, spreading to the limbs.
Inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs
In acute inflammation, the symptom does not have a clear localization, occurs suddenly, quickly reaches a significant degree of severity, and disappears after a few days. Chronic inflammatory processes are accompanied by periodic moderate or slight sensation of a foreign body, which is more disturbing during periods of exacerbation.
- Tonsillitis.
The tonsils are hyperemic, enlarged in volume, covered with superficial films, multiple small yellowish-white foci or loose plaque. Sore throat, general hyperthermia, and symptoms of intoxication are observed. With chronic tonsillitis in the acute phase, all symptoms are smoothed out. - Pharyngitis.
When examining the pharynx, swelling and diffuse hyperemia are revealed. The general condition remains normal, sometimes there is weakness and an increase in temperature to low-grade levels. In the chronic form, one part of the pharynx is predominantly affected: the oropharynx, nasopharynx or hypopharynx. - Laryngitis.
The patient complains of scratching, soreness, and tickling in the lower parts of the throat. The voice becomes hoarse; in severe cases, the patient speaks in a whisper. There is a paroxysmal dry cough. The symptom is more noticeable in phlegmonous and infiltrative forms. Chronic laryngitis is manifested by coughing, the need to periodically clear the throat, and rapid voice fatigue.
Laryngeal sore throat is accompanied by the same symptoms as acute laryngitis, but is characterized by a more severe course. The pain in the throat is so severe that patients refuse to eat and take a forced position.
Purulent processes
Abscesses in the throat area occur with sore throat, and less often result from rhinitis, pharyngitis, or sinusitis. Sometimes they develop with otitis media, mastoiditis, mumps, and are formed against the background of acute infections or carious teeth. The sensation of a foreign body has a clearer localization than in inflammatory pathologies, appears on the side or in the central part of the throat, and is accompanied by significant hyperthermia and severe intoxication. Detected under the following conditions:
- Peritonsillar abscess.
It manifests itself as sharp, rapidly intensifying pain when swallowing. The pain becomes tearing and radiates to the ear and lower jaw. There is a tilt of the head towards the affected area and a putrid odor from the mouth. Possible trismus. - Retropharyngeal abscess.
It is accompanied by extremely intense pain, forcing patients to refuse food. When the abscess is located in the upper part of the pharynx, nasal breathing disturbances and nasal sounds are observed; in the middle and lower parts - difficulty breathing and hoarseness. - Epiglottitis.
Signs of a purulent process are combined with breathing problems. The patient complains of pain in the lower part of the throat. Hoarseness and muffled voice, wheezing, cyanotic lips and nasolabial triangle, and tachycardia are detected.
Ludwig's angina is one of the most common purulent processes. The sensation of a foreign body appears when the pharynx is involved, accompanied by severe fever, swelling of the neck, breathing problems, loss of voice, and drooling.
Sensation of a foreign body in the throat
Traumatic injuries
The sensation of a foreign body in the throat may indicate the presence of a foreign object or injury caused by the object as it passes through the throat. The cause of the symptom is fish bones, crackers, fruit and berry seeds. Children sometimes swallow inedible objects with sharp edges, such as building blocks. With thermal and chemical burns, discomfort in the throat occurs due to swelling and damage to the mucous membrane.
Tumors
The symptom is included in the typical clinical picture observed with benign neoplasms of the pharynx and is combined with a sore throat, nasal voice, and difficulty in nasal breathing. Slowly builds up over a long period of time. It is detected with papillomas, fibromas, and hairy pharyngeal polyps. It is noted for angiomas, neuromas, and pharyngeal cysts. With benign neoplasia of the larynx, complaints of the sensation of a foreign object are less common, and voice changes prevail.
In patients with pharyngeal cancer, the sensation of a foreign body is the first symptom of the disease. Later, pain, choking, difficulty swallowing, and sensitivity disorders occur. Manifestations quickly progress, complemented by general signs of the oncological process - weight loss, weakness, intoxication. The symptom is also characteristic of laryngeal cancer, affecting the upper parts of the organ.
Allergy
The symptom is observed in allergic reactions accompanied by swelling of the throat. It appears suddenly. The patient is bothered by sneezing, nasal congestion, lacrimation, sore throat, itchy skin. In the spring-summer period, allergies are provoked by contact with plant pollen, throughout the year - with wool, dandruff, feathers of animals and birds, house dust, and food products. The most striking picture is observed with Quincke's edema.
Thyroid pathologies
The thyroid gland is located near the upper part of the trachea, its enlargement causes irritation of the receptors, causing the sensation of a foreign body. The symptom is detected in the following pathologies:
- Iodine deficiency conditions
: diffuse euthyroid goiter, nodular goiter. - Mainly hyperthyroid conditions
: diffuse toxic goiter, thyroiditis (subacute, autoimmune, others). - Benign and malignant tumors
: adenomas, cysts, lymphomas, thyroid cancer.
Digestive system diseases
Foreign body sensation is sometimes accompanied by GERD. Patients complain that they want to drink water or cough to get rid of a foreign object. The symptom is provoked by constant irritation of the receptors with acidic contents thrown into the upper parts of the digestive tract during reflux. A distinctive feature is the increase in discomfort when lying down. With dyskinesia of the esophagus, the symptom appears due to a violation of the passage of the food bolus due to a disorder in the motility of the organ.
Dental diseases
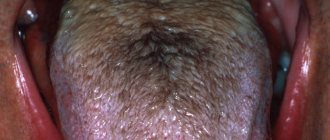
Patients with certain tongue pathologies complain of a feeling of a foreign body in the throat: black hairy tongue, papillomatous form of rhomboid glossitis. In the first case, there is a significant increase in taste buds in the posterior and middle thirds of the tongue, coloring the affected area in black and dark brown shades. With rhomboid glossitis, pale pink growths appear on the tongue.
The symptom accompanies benign and exophytic malignant tumors of the oral cavity if they are located on the root of the tongue or in the palate. In addition, the sensation of a foreign body occurs with the stylopharyngeal variant of stylohyoid syndrome.
Neurosis of the pharynx
Initially, the sensation of a coma (foreign body) in the throat was described as a typical symptom of hysteria. Currently, along with hysteria, the causes of pharyngeal neurosis include astheno-neurotic syndrome and severe stress. Pathology can also be observed in cervical osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, spondylolisthesis, and certain diseases of the nervous system (neoplastic tumors, stroke, multiple sclerosis).
Throat examination
For what changes in the throat should you call an ambulance?
Some throat diseases pose a threat to the lives of patients, especially in childhood. Calling an ambulance is necessary in the following cases:
- When examining the larynx, a narrowing of the lumen is observed. It becomes difficult for a person to breathe. This condition may indicate laryngeal stenosis, which can be fatal, especially for children.
- The throat is strewn with ulcers, ulcers, rashes, and the body temperature is higher than normal.
- Vessels bleed on the back wall of the larynx. The patient has signs of intoxication, vomiting, fever.
Features of laryngitis
Types of inflammation of the throat include laryngitis, which occurs in acute or chronic form. The diagnosis of this throat disease itself is rarely made; it manifests itself against the background of influenza, ARVI, scarlet fever, whooping cough, etc. Hypothermia, prolonged singing, oratory, smoking - all this becomes a provoking factor for the occurrence of laryngitis.
The distinctive symptoms of laryngitis are a dry cough at the beginning, dry mucous membranes, soreness and hoarseness of the voice. In more complex cases, the voice may disappear completely. On the 3-4th day, the sputum begins to disappear, the cough becomes periodically wet, but more often it is still dry. Upon visual examination (laryngoscopy), swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membranes are clearly visible.
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the nature of the throat disease, but patients should definitely refrain from drinking hot drinks, smoking, and try not to talk, much less scream or sing.
Chronic laryngitis is associated with atrophic or hypertrophic changes in the mucous membranes, although various types of throat infections are often the causes. In any case, the first symptom of laryngitis is a hoarse, barely audible voice.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is one of those types of throat diseases that rarely occur in isolated form. More often it is a consequence of influenza, ARVI or other infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Pharyngitis can develop on its own with prolonged smoking and bad habit abuse, or prolonged inhalation of cold air, i.e. when the irritant acts directly on the mucous membrane of the throat.
A throat disease such as pharyngitis is distinguished by the appearance of a feeling of rawness in the throat, while severe pain is usually absent. Painful sensations appear mainly when swallowing saliva. The temperature with pharyngitis is usually low-grade, and the patient’s general condition suffers slightly.
We have looked at what types of throat diseases there are: the types of sore throat can be different, but timely treatment, including effective medications for the treatment of throat diseases, helps prevent complications and eliminate all unpleasant symptoms!