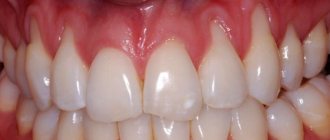
Teething in a child is one of the important stages of its development. Milk teeth not only allow you to gradually switch from liquid to solid food, but also indicate the baby’s health status.
Despite the fact that this process is physiological, the period of teething often causes discomfort to the child and causes a lot of anxiety and worry in parents. What should young mothers be prepared for at this time? Let's explain everything in order.
Children, when teething, pull their toys into their mouths; the desire to chew something alleviates the unpleasant sensations.
Symptoms of periodontitis
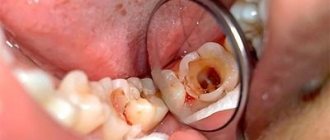
Let's start with the fact that in the initial stages the disease occurs without symptoms, and it can only be detected at a dentist's appointment; this will require an x-ray. Symptoms appear in the stage of acute periodontitis or as a result of exacerbation of the chronic form. Among the signs of the disease:
- sharp or aching pain;
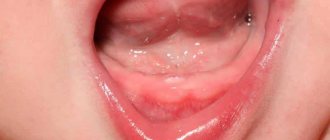
- swelling of the gums in the affected area;
- feeling as if the tooth has become taller;
- temperature increase;
- sleep disturbance;
- tooth mobility;
- tissue redness;
- pain when touching a tooth or chewing food.
If at least two symptoms occur, contact your dentist.
Hyperesthesia (increased tooth sensitivity) - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of hyperesthesia is aimed at reducing the speed of fluid flow in the dentinal tubules. This can be achieved in the following ways:
- blockage of enamel micropores with the help of desensitizers - drugs that reduce tooth sensitivity;
- reducing the size of micropores using mineralizing agents, for example, gels with a high content of fluoride and calcium. These include gels ROCS Medical Minerals, GC Tooth Mousse;
- closing or narrowing of dentinal tubules using a laser [14];
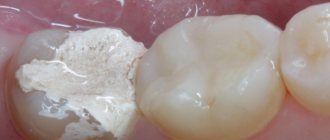
- preparation and filling of teeth for carious lesions;
- surgery on the gum when it recedes as a result of periodontal disease;
- correction of the bite.
In 1935, dentist L. Grossman identified the main properties of an ideal remedy for combating hyperesthesia [12]. In his opinion, it should act quickly and be effective for a long time, not irritate the pulp, not provoke pain and not change the color of the teeth. There are quite a lot of such drugs now. Desensitizing agents (reducing tooth sensitivity) are produced in the form of gel, toothpaste, rinse, varnish, etc. Toothpastes are most often used.
For mild hyperesthesia , as a rule, applications of various solutions are sufficient.
The drug Remodent in the form of a 3% aqueous solution for applications is applied to areas of hyperesthesia for 15-20 minutes. For the course of treatment to be effective, it is necessary to make 8-28 such applications (one 2 times a week) until a positive result is achieved. Sometimes a 3% solution of remodent is used as a rinse (4 times a week). The full course includes about 40 procedures.
Strontium chloride is used in the form of a 25% aqueous solution and 75% paste. When rubbing the paste, stable compounds of strontium appear with the hard tissue of the tooth. This remedy is a good prevention of hyperesthesia after tooth preparation and removal of dental plaque.
To eliminate hyperesthesia, a 30% aqueous solution of zinc chloride is also used. After this, an application is carried out with a 10% solution of potassium ferrocyanide. It seals the tubules with the resulting sediment. The duration of the applications is one minute. The use of a paste containing alkalis is also indicated: sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium, magnesium. It attracts dentinal fluid, which is contained in the micropores of the enamel, and reduces tooth sensitivity.
A modern treatment for hyperesthesia is bifluoride-12, a special colorless varnish containing fluoride, and fluocal, a dental gel containing sodium fluoride. They are carefully applied to the teeth with a brush or foam swab. Both products create a coating that saturates the enamel and dentin with fluoride ions, which leads to a decrease in sensitivity. Fluocal can also be used in the form of an application solution. Typically, a course of treatment with such applications includes only 2-3 procedures. Varnish is usually used as an auxiliary method that enhances the effect of the main drug [15].
Treatment of hyperesthesia with laser has been shown to be the preferred treatment method. It is aimed at narrowing the dentin tubules by combining the proteins of the dentin fluid, partially melting the hard tissues and relaxing the internal nerve receptors. Laser therapy has no side effects [15].
Treatment of generalized hyperesthesia is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, so it not only relieves symptoms, but also affects the course of the disease. Treatment must be comprehensive. In addition to treating the main cause of hyperesthesia, it is necessary to restore the mineral composition of enamel and dentin, and normalize the content of phosphorus and calcium in the body. For this purpose, calcium glycerophosphate, clamine or phytolon, as well as multivitamin preparations are prescribed. Taking phosphorus-calcium drugs throughout the course of treatment provides a good prognosis. Otherwise, restoration of normal sensitivity will take a long time.
To eliminate pain at the beginning of treatment, in addition to using toothpaste with phosphate, electrophoresis with a 2.5% solution of calcium glycerophosphate is required. The course of such physiotherapy is 10 sessions. In case of hyperesthesia against the background of impaired neurological status, the use of a galvanic collar according to Shcherbak is indicated (also at least 10 sessions).
Studies have shown that the effect of complex treatment of hyperesthesia occurs quickly and lasts for quite a long time. The content of phosphate and calcium in the dental tissues increases, the level of calcium and phosphate in the blood normalizes.
During the treatment of hyperesthesia of any degree it is necessary:
- select personal hygiene products;
- control bad habits (do not bite nails, pencils);
- adjust your diet (exclude soda, sticky sweets, consume vegetables, fruits and dairy products more often);
- wear a mouth guard at night (for bruxism) [14].
Stages and forms of the disease
Periodontitis is divided according to the general principle into chronic and acute. Chronic cannot be completely cured. It is only possible to eliminate local inflammation and stop further exacerbation of the disease. Chronic periodontitis is asymptomatic and does not bother the carrier, but in case of exacerbation of the disease, symptoms begin to appear. In a calm state, a small fistula may appear on the gum from time to time, and slight discomfort may occur when chewing food or mechanical impact on the area of inflammation. If left untreated for a long time, the risk of tooth loss is high.
Treatment of acute periodontitis has an end result. But even after complete recovery, control over the oral cavity is necessary to avoid re-inflammation. In acute periodontitis, all of the listed symptoms are characteristic, only 2-3 of them may appear, and this is already a signal to visit the dentist. Purulent periodontitis is especially pronounced. In this case, the pain is acute, body temperature rises, and gumboil formation is possible.
Forms of periodontitis:
- Fibrous. In this case, periodontal tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue. It is often asymptomatic and can be detected by external signs: changes in enamel color, bad breath, pulp death.
- Granulating. It leaks quickly and destroys bone tissue. It is characterized by painful sensations when pressing on the gums or chewing food. A pulling or bursting pain may be observed without mechanical impact on the tooth.
- Granulomatous. This is a dangerous type of disease because it is asymptomatic, while destructive processes take place inside the periodontium, which are accompanied by the appearance of cysts and granulomas. If left untreated, the tooth may simply fall out. An infection locked in a granuloma or cyst can “explode” under the influence of the slightest irritant: provoke inflammation (for example, sepsis).
- Apical. The simplest form, easy to treat. It occurs as a result of untreated pulpitis and is localized in one place near the root.
When does a child start teething - table
From 4 to 7 months is the age when most children develop their first teeth. The sequence of their eruption is visible from the table.
| Name of teeth | Period of eruption, months. | |
| 1. | Incisors (central and lateral) | 4-12 |
| 2. | First molars | 12-19 |
| 3. | Fangs | 18-24 |
| 4. | Second molars | 24-32 |
The appearance of all 20 baby teeth occurs by the age of 3. But this process is individual, so small deviations in one direction or another should not cause anxiety in parents. If you are still concerned about early or late teething, then check this point with your pediatrician.
Factors influencing the timing of eruption:
- the nutritional pattern of the expectant mother;
- water quality;
- baby food ration;
- climatic living conditions;
- heredity.
There is usually nothing wrong with teething. But still, most children at this time experience discomfort and become restless.
Treatment methods for bruxism in adults
Treatment of the disease involves the complete elimination of the factors that provoked its occurrence. For this, high-quality diagnostics is necessary.
Since the main cause of teeth grinding at night is nervous tension, it is important to deal with this particular problem. Helpful medical advice can look different.
- Learn to relax muscle fibers. To do this, you can eat food that requires thorough chewing. The muscles will get tired and will be in a relaxed state the rest of the time.
- Organize your workday correctly, avoid stress, and avoid drinks that irritate your nervous system.
- Take a warm bath with herbal decoctions before bed, drink herbal teas.
- Exercise regularly to promote good sleep.
All of the above methods should be used along with medical intervention. If you neglect to go to the dentist or other medical institution, following simple rules will not help in getting rid of the disease.
Psychotherapy
For psychological causes of bruxism in adults at night (during sleep), treatment should be carried out by a psychologist. A visit to a specialist is mandatory if the patient is plagued by depression, neuroses, stress, suicidal thoughts and other dangerous symptoms. During the therapy period, the doctor will provide support and help establish the etiology of mental disorders, including noting hereditary or acquired factors.
During therapeutic sessions, a person with mental disorders will learn to cope with stress, emotions, and problems that have arisen. A competent psychotherapist is able to teach a patient to get rid of fears, grievances accumulated in childhood and adolescence, to let go of anger and other experiences. Psychotherapy will have a beneficial effect not only on oral health, because the patient will stop grinding his teeth and straining his jaw, but also on his overall well-being.
Drugs for the treatment of bruxism
The main goal of drug therapy for this disease is to reduce spasmodic muscle tone. The main groups of medications prescribed by dentists individually can be used either separately or in combination.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. Vitamin B should predominate in them, as well as calcium and magnesium.
- Sedatives and mild solutions (valerian, motherwort, Novo-Passit).
- Muscle relaxants (Detilin, Flexen).
It is worth mentioning botulinum toxin injections separately. When the substance is injected into the trigger point of a toned muscle, the analgesic effect quickly appears. After a few days, complete muscle relaxation occurs (muscle relaxation). The procedure helps to forget about the problem for six months to a year. In any case, only a doctor can prescribe such interventions.
Orthodontics
Occlusal guards not only eliminate grinding, but also protect teeth. These are safe structures made of soft polymers based on an impression of the patient’s dentition. Wearing the accessory does not bring any discomfort.
Kinds:
- Daytime. Indicated for serious stages of pathology, worn throughout the day. They are invisible to others, do not distort speech, and do not interfere with eating.
- Nighttime. They act similarly to those discussed above, but are worn only at night while sleeping.
- Resonating. Doctors prescribe them if the disease is very advanced. They help move the articular head and get rid of spasms.
- On one or both jaws. This depends on the extent of the damage and the need to protect a small or large area.
What is the temporomandibular joint - TMJ
We use this joint while talking, chewing, yawning, laughing - very often. Around it are muscles and tendons that allow the jaw to move in different directions for different purposes.
TMJ problems occur for many reasons:
- violation of the dental system, for example, congenital anomalies of teeth, gums or bone tissue, malocclusions, injuries, poor-quality prosthetics;
- congenital anatomical abnormalities of this joint;
- increased or decreased tone of muscle fibers around the TMJ;
- active conversational load, for example, among actors, singers, speakers;
- central nervous system problems;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- excessive tension of the jaw muscles, for example, due to the bad habit of biting nails.
What is the temporomandibular joint and why do problems arise with it? Detailed and clear - in the video:
Actors and singers with active oratorical articulation are at risk for TMJ arthrosis
How to understand what is bothering you with TMJ: 4 obvious signs
If you feel discomfort while talking, chewing, or yawning, look out for these signs:
- Are there any clicks or popping sounds during jaw operation (only 20% of people who notice this symptom complain of pain, however, this is a reason to suspect arthrosis of the temporomandibular joint and go for a diagnosis);
- Is there a feeling of jamming of the joint (if the fossa and the articular head are not in perfect contact, you have to open your mouth as much as possible, trying to find the right point);
- How severe is the pain (can occur when chewing, radiate to the temples, under the tongue, ears, neck, sternoclavicular region);
- Has your general health changed (headache and dizziness, insomnia, hearing impairment, depression and other uncharacteristic manifestations are possible).
With TMJ dysfunction, some patients develop snoring