Periostitis translated into Russian means periosteum. Periostitis is inflammation of the periosteum. Usually it begins in its inner or outer layer and then spreads to the remaining layers. Due to the close connection between the periosteum (periosteum) and the bone, the inflammatory process easily passes from one tissue to another (osteoperiostitis).
According to the clinical course, periostitis is divided into acute (subacute) and chronic; according to the pathological picture, and partly according to the etiology - into simple, fibrous, purulent, serous, ossifying, tuberculous, syphilitic.
Simple periostitis
- an acute aseptic inflammatory process in which hyperemia, slight thickening and infiltration of the periosteum are observed. It develops after bruises, fractures (traumatic periostitis), as well as near inflammatory foci, localized, for example, in bones and muscles. Accompanied by pain and swelling in a limited area. Most often, the periosteum is affected in areas of bones that are poorly protected by soft tissue (for example, the anterior surface of the tibia). The inflammatory process for the most part quickly subsides, but sometimes it can lead to fibrous growths or the deposition of calcium salts and new bone formation (development of osteophytes), i.e. turns into ossifying periostitis.
Content:
- What is periosteum
- Signs of the disease
- Diagnostic measures
- Classification
- Treatment of the disease
- Prevention
Some dental diseases lead to severe inflammation due to untimely treatment.
As a result, periosteal tissue is included in the pathological process. If qualified dental care is not received at this stage of the disease, osteomyelitis or other dangerous pathologies may develop. Inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth should not be allowed. It is difficult to treat and may require surgery.
Causes of tire splint
- Weak and clogged foot stabilizer muscles;
- high impact load.
High impact loads may be caused by:
- overweight;
- structural features of the foot - hyperpronation, high rigid arch of the foot;
- shoes with low cushioning;
- hard surface for running;
- hard contact with the surface (excessively high tension of the feet upon contact);
- acceleration or running down an inclined surface;
- running on uneven surfaces.
Moreover, you can clog up your muscles one day, for example, during a workout in the park, and damage the periosteum during the next workout while running on your usual hard surface, simply by shortening the muscles.
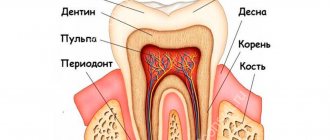
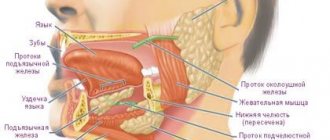
What is periosteum
Other names for this dense connecting structure are periosteum, pericranium. This is a dense shell that covers the outside of all the jaw bones. It is not present only at the articular ends.
It serves as a connecting link between the bone and its surrounding formations. Participates in the processes of bone formation. Responsible for the enlargement of bones in childhood and adolescence, making the healing of fractures possible.
The pericranium includes two layers:
- outer;
- interior.
The first is formed by connective fibrous tissue. It has many nerve endings, lymphatic and blood vessels. The internal one consists of tendons and ligaments. It is needed for the tightest fit of the inner layers to the bone.
The peculiarity of the pericranium is that it is easily involved in various kinds of inflammatory processes. As soon as you start a diseased unit or affected periodontal formations, it immediately becomes inflamed. Most often, inflammation of the bone tissue of the tooth causes the development of periostitis.
Signs of the disease
If the tissue is damaged, acute pain occurs in the area of the affected tooth, the mucous membranes swell, and a white coating appears on the tongue. Other symptoms of the disease include:
- an increase in the size of the cervical lymph nodes;
- swelling of the cheek;
- increased body temperature;
- deterioration in physical well-being, weakness, decreased performance;
- decreased jaw mobility;
- separation of pus from the gums.
Pain during periosteum can radiate to the ear, chin, temple, and neck. If the disease occurs in a purulent form, after the abscess breaks through and the necrotic masses come out, the pain symptoms disappear almost immediately. But this does not mean that the inflammation has passed. It just went into a “calm” phase for a while. If a person continues to put off visiting the doctor, he may lose a tooth.
How to treat inflammation of the periosteum of a tooth before visiting a doctor?
Self-medication for any purulent processes is very dangerous, so it is recommended to consult a dentist at the first symptoms of the disease. However, before visiting a doctor, the patient can alleviate his condition somewhat by applying cold to the cheek on the affected side and rinsing his mouth with an antiseptic solution at room temperature (chlorhexidine soda-saline solution, chamomile or sage decoctions). Here's what you absolutely can't do:
- Apply warm compresses and drink hot drinks.
- Apply any bandages yourself or use medications without a doctor’s prescription.
- It is better not to take analgesics before visiting the dentist.
- If you are undergoing surgery (opening an abscess), you should not take aspirin, since it changes the rheological properties of the blood and can cause bleeding.
Diagnostic measures
The doctor conducts an examination. It is not difficult to understand that a bone is damaged. This is indicated by external signs:
- redness of the gums;
- pain when pressing;
- the presence of a cushion containing pus;
- mobility of the incisor, canine, molar (noted if the disease is advanced).
To determine the stage of the disease and the depth of damage to bone formations, the doctor performs an X-ray or radiovisiography of the jaw.
Classification
Dentists classify pathology into the following types:
- Simple. It is the result of bruises and injuries. The lesion is found in close proximity to mechanical action. A person complains of aching pain and swelling.
- Fibrous. A consequence of prolonged irritation of the periosteum, for example, as a result of necrosis. During palpation, a painful thickening of the bone is detected. If the necessary measures are not taken in time, the tumor can greatly increase in size and become malignant.
- Purulent. The result of an infection that penetrated from the outside after damage to the integrity of the mucosa. This form is often found with abscess, osteomyelitis, and phlegmon. Its causative agents are streptococci and staphylococci. Serous exudate is actively released from the abscess. An abscess occurs. Further, several options for the development of pathology are possible. The first is that pus destroys a separate area of the bone structure and breaks into the soft tissue. The second is that pus contributes to the exfoliation of a separate section of the periosteum. Then the bone stops receiving the necessary nutrition and dies. This type of inflammation always manifests itself clearly. The patient's body temperature rises. The cheek swells and an abscess forms in the mouth.
- Serous. May form after injury. A large amount of serous mucus is discharged. It accumulates. As a result, the periosteum may peel off and die.
- Ossifying. Bone tissue gradually grows. The problem occurs due to prolonged irritation of bone structures. For example, chronic osteomyelitis leads to it.
- Tuberculosis. This form is characterized by the formation of fistulas, inside which pus accumulates.
- Syphilitic. Found in patients with syphilis. The bones of the jaw and skull are affected. Pain is the main symptom. It intensifies at night. If fistulas form and break through, your health temporarily improves.
To understand how to treat pathology, it is important to determine what caused the abnormal process. That is why, before starting therapy, the dentist collects anamnesis and conducts diagnostics.
Periostitis in children
In children, the inflammatory process usually develops as a result of untreated caries of baby teeth, infectious diseases or injuries. Due to the peculiarities of the physiology and anatomy of the child’s body, as well as due to the immaturity of the child’s immune system, the pathology develops quickly and rapidly, and the infection quickly spreads through the bloodstream and lymph flow, so multiple lesions can form.
Periostitis of the upper jaw in a child requires special attention, which, when localized in the palate, may not change facial features - swelling forms inside the oral cavity and can only be noticed by the characteristic convex swelling on the palate. The abscess gradually grows, capturing the mucous areas of the pharynx and tongue, which causes pain when swallowing and chewing. If a child develops symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, or painful swallowing, it is imperative to check whether such a condition is caused by developing gumboil.
Treatment of the disease
The therapeutic regimen is always selected on an individual basis. If the disease has recently developed, it is usually possible to manage with conservative methods. The patient is prescribed:
- anti-inflammatory;
- antibiotics;
- antiseptics.
Sanitation of the oral cavity is mandatory. If there are indications for removing destroyed units, they are pulled out and replaced with dental prostheses. Physiotherapy helps speed up the healing process.
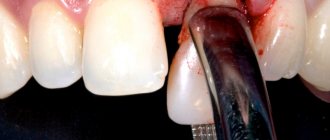
In advanced cases, surgical treatment is performed. In this case, the treatment plan looks something like this:
- The doctor examines the condition of the mouth and determines the cause of the disease.
- A local anesthetic is injected into the affected area. As soon as it takes effect, an incision is made in the gum with the abscess.
- The opened lesion is cleaned of purulent exudate and washed. If necessary, install a drainage tube. It is necessary so that necrotic masses do not again begin to accumulate in the existing cavity.
- The doctor treats the tooth, if it is possible to save it. Fills the canals and installs a seal. If the unit cannot be cured because the roots are severely damaged, removal is carried out.
- The patient is prescribed antibiotics, painkillers, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
It is important that after treatment the patient comes for follow-up examinations. They are needed to prevent relapse of pathology and create optimal conditions for rapid regeneration.
Examples of work “Before” and “After”
Metal-ceramic crowns and stump inlays
Case: destruction of the anterior teeth (11 and 21).
Restoration of front teeth with ceramic veneers (May 2012)
Case: I went to the clinic with a complaint about the unsightly shape and position of the central incisors on the upper jaw.
Aesthetic restoration of anterior teeth - lumineers
Case: the patient complained about the unsatisfactory aesthetics of his smile (he was not satisfied with the color and shape of the teeth), since the teeth were not affected by caries, the curvature was small, the patient chose the most non-traumatic restoration option - installing lumineers without grinding and depulping the teeth.
Prevention
Since periostitis is most often a consequence of advanced caries or injury, you need to be as careful as possible about the health of your teeth and gums. Prevention comes down to:
- hygiene in the morning and evening;
- rinsing the mouth after every meal;
- timely and competent treatment of emerging dental diseases;
- using dental floss on a regular basis;
- wearing protective mouthguards while engaging in traumatic sports;
- visiting the dentist once a year;
- annual professional hygiene in the dentist’s office.
If your tooth starts to hurt or your gums turn red, you should immediately make an appointment with a doctor. When an abscess forms, it is unacceptable to open it yourself. Such actions aggravate the course of the disease and lead to serious complications.