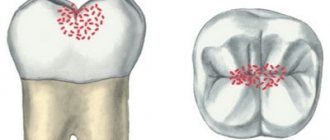
Why do teeth hurt during pregnancy?
Very often, the cause of toothache lies in the exacerbation of existing diseases - caries, periodontitis, gingivitis, pulpitis. A cutting wisdom tooth or tartar can also cause pain.
However, sometimes toothache is directly related to pregnancy.
There is such a thing as gingivitis in pregnant women - rapidly developing gum disease against the background of toxicosis and changes in hormonal balance, in which inflammation occurs more intensely than usual.
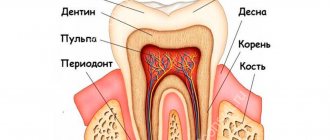
Another reason why pregnant women’s teeth literally begin to “crumble” is the formation of bones in the fetus and their active growth. If there is a deficiency of calcium, vitamins D3 and K in the body of a pregnant woman, the fetus has nothing to “build” a skeleton from, so it begins to “pull” the substances it needs from the mother’s body. And the depots of calcium and phosphorus are teeth and bones. Therefore, if the expectant mother’s diet does not have enough calcium, then the teeth will begin to decay very quickly.
Many pregnant women do not associate their toothache with calcium deficiency, since the expectant mother receives quite a lot of calcium - it is also found in milk, cheese, other dairy products, fish and even in some plants, for example, chia seeds. But in order for calcium to be absorbed, the body must have vitamins D3 and K, but a pregnant woman’s diet may not have enough of them, unless she takes specialized vitamin-mineral complexes. The fact is that the main sources of these vitamins are not very popular products. Thus, a person can get vitamin D3 from animal fats (fish oil, margarine), and their consumption during pregnancy is reduced so as not to gain excess weight. The main sources of vitamin K are spinach, cauliflower and nettle leaves, and its content in other vegetables and fruits is low. But vitamins D3 and K are consumed in huge quantities during pregnancy.
Also, early toxicosis of pregnant women greatly affects dental health: frequent vomiting oxidizes the environment of the oral cavity, provoking the development of diseases that already exist, but previously did not bother the woman, and pass without any special external manifestations. Nausea forces pregnant women to carefully choose food, often not paying attention to its nutritional value, only to the absence of irritating smells and tastes. Thus, the body may not receive vitamins, the lack of which provokes even more severe attacks of toxicosis.
But the reasons listed above do not mean at all that toothache is an obligatory companion for the expectant mother. Let's see what can be done to prevent toothache during pregnancy.
Caries in pregnant women: causes
There is a widespread belief among women that rapid tooth decay during pregnancy is associated with the fetus’ increased need for calcium and phosphorus.
But the increased need for calcium is compensated by the mother’s body not by leaching it from the teeth, but primarily by increasing its absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and reducing its loss in urine and sweat. This mechanism is hormonally determined. But besides this, the body has another mechanism that maintains a constant concentration of calcium in the blood of any person (including pregnant women). Maintaining normal calcium concentrations in the blood occurs due to slow osteoporosis of bone tissue. But the teeth do not suffer, and here's why. The fact is that mineralization of tooth enamel with calcium occurs due to calcium ions contained in saliva, the concentration of which in saliva is strictly tied to the concentration of calcium in the blood. And since, due to osteoporosis of bone tissue, its concentration in the blood is normal (and, accordingly, in saliva too), then the mineralizing function of saliva also does not suffer.
What then stimulates tooth decay in pregnant women?
Firstly, during heartburn and after vomiting, a large amount of gastric juice enters the oral cavity, i.e. hydrochloric acid, which helps wash out calcium from tooth enamel. Therefore, in case of heartburn and after vomiting, first of all you need to rinse your mouth with a soda solution (this will neutralize the acid), and it is not recommended to brush your teeth immediately. Immediately after exposure to acid, the surface layer of tooth enamel becomes porous and can be easily removed with abrasives.
Therefore, after heartburn or vomiting (as well as after drinking wine, fruit or fruit juice), it is recommended to brush your teeth with a soft toothbrush only after 30-40 minutes, using toothpaste with fluoride. Until this point, it is better for you to use a soda rinse, and after it you can immediately use a fluoride rinse. The second very important point is that studies show that 90% of pregnant women have worse oral hygiene (compared to the period before pregnancy).
The third reason is that insufficient hygiene is aggravated by eating disorders, i.e. constant snacking between main meals (anything containing flour, sugar and starch is especially harmful). Naturally, after snacking, people are not accustomed to brushing their teeth at all, and as a result, cariogenic bacteria in the oral cavity receive constant 5-6 meals a day, while constantly producing organic acids that destroy teeth. At the same time, after the next snack, it is absolutely not enough to simply rinse your mouth and chew gum, because... this does not allow removing plaque, as well as food debris that has accumulated between the teeth.
How to save teeth during pregnancy
First of all, even if the teeth were in perfect order before pregnancy, the expectant mother should remember about prevention:
- brush your teeth not for twenty seconds, but for three minutes, thoroughly and regularly;
- use dental floss, preferably after every meal;
- use suitable gentle toothpastes, avoid whitening pastes;
- change your toothbrush once a month;
- try not to eat food that injures the gums and mucous membranes.
The second important point: take vitamins and minerals, especially vitamins D3 and K. It is most convenient to choose a vitamin and mineral complex for pregnant women, which will also contain other micronutrients necessary for the proper formation and development of the fetus.
In addition, some complexes for expectant mothers help reduce the symptoms of toxicosis (nausea and vomiting, which affect the acid-base balance in the oral cavity), especially if they contain vitamin B6. For example, the Pregnoton Mama vitamin and mineral complex (designed so that it can be taken by women before, during and after pregnancy) contains vitamins B6, D3 and K, as well as other vitamins and minerals necessary for the body of a pregnant woman in precisely calculated doses . The fetus will not take them from the mother’s body, and toxicosis will minimally affect the acid-base balance, without provoking the development of caries, periodontitis and gingivitis.
As for calcium intake, as a rule, calcium is included in vitamin-mineral complexes for expectant mothers purely nominally, that is, in too small dosages. Therefore, discuss with your doctor whether you should take calcium supplements separately, or whether you need enough calcium in your diet.
Unfortunately, often expectant mothers do not think about prevention and “remember” their teeth when they have already become a source of trouble. So what to do if your teeth hurt, are loose, and your gums are red, painful or itchy?
Prevention of tooth decay
To strengthen tooth enamel, you need to:
- comply with oral hygiene standards;
- consume less sweets, rinse your mouth regularly after sour or spicy foods;
- Be sure to come for preventive examinations at the dentist twice a year, have professional cleaning and strengthening procedures;
- monitor your diet;
- stop smoking and bad habits (do not bite hard objects and nails);
- Drink only clean drinking water.
Is it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy?
The modern level of development of dentistry makes it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy. Of course, we are not talking about prosthetics or bite correction. But the dentist will be able to cope with caries, tartar or pulpitis. It is important to inform your doctor about your pregnancy, as this will help you choose the safest pain reliever that does not contain adrenaline.
The second trimester of pregnancy is traditionally considered the most appropriate time for dental treatment. This period is, in principle, the most stable of all nine months of gestation. But if a woman suffers from acute pain or the disease develops quickly, regardless of the trimester, she should consult a dentist and have the aching tooth treated.
Any inflammation takes away the body's strength, makes you experience pain and worry. All this affects both the woman and the unborn child, therefore, if a tooth hurts badly during pregnancy, there is no need to wait and hope that everything will go away on its own, it is better to consult a dentist as soon as possible.
Sources
- Kiselnikova L.P., Popova N.S. Dental status and prevention of dental diseases in pregnant women // Clinical dentistry. – 2011. – No. 1.
- Kuzmina E. M. Prevention of dental diseases in pregnant women and young children. Guidelines. – M., 1999. – 36 p.
- Ubertalli James T., Hingham, MA Gingivitis // MSD Handbook. The version is available at: https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru/home/oral-and-dental diseases/periodontal diseases/gingivitis
THIS IS NOT AN ADVERTISING. THE MATERIAL WAS PREPARED WITH THE PARTICIPATION OF EXPERTS.
When can caries be treated during pregnancy?
When is the best time to treat caries during pregnancy? If a woman did not have time to sanitize her oral cavity before conception, she will now have to wait until 3 months of pregnancy and try to complete treatment before the 6th month of fetal development.
To understand why doctors treat caries in pregnant women at this particular time, you need to know what happens in each trimester of this period:
- From conception to 12 weeks is the most responsible and important time in the development of the fetus, because it is in the first trimester that the most important organs of the child are laid and the placenta is formed. Before the formation of a protective barrier in the form of the placenta, the fetus is still poorly protected and many drugs are contraindicated for use in the treatment of the expectant mother.
- In the second trimester (up to 24 weeks), there is already a placenta around the fetus - this period is ideal for treating caries during pregnancy.
- In the third trimester (from 25 weeks until the birth of the baby), treatment of caries and its complications during pregnancy may already be accompanied by risks. An already weakened body, a greatly distended uterus with increased sensitivity to the effects of drugs and stress - all this can cause untimely onset of labor.
Neither a doctor, nor even a woman would want to risk the baby’s health, but there are situations when a pregnant woman urgently needs emergency dental care. In these situations, it is possible to treat pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontal diseases and even remove teeth, but under the supervision of a whole team of doctors and after careful selection of drugs and preparation of the woman.
In less urgent situations, when there is no acute pain, it is better to postpone treatment of caries during pregnancy until after childbirth. Nursing mothers are also not recommended to use strong painkillers, but during the period of treatment and removal of drugs from the body, you can prepare milk that has been expressed in advance for the baby. Then it will be possible to treat teeth even under the most powerful anesthesia.
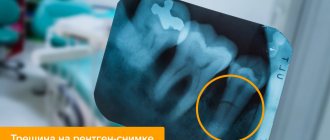
Safe dental diagnostics during pregnancy
Many diagnoses in dentistry can be made only on the basis of a survey and examination of the patient. In controversial cases and in order to distinguish diagnoses with similar symptoms, an X-ray examination is required. To avoid exposing the baby to radiation, pregnant women undergo digital radiovisiography. This procedure has 90% less radiation exposure than traditional radiography.
If this is not possible in the clinic, then exposure can be reduced by using a lead apron.
Nuances of dental treatment for pregnant women
It is possible to treat teeth during pregnancy, but taking into account its duration and characteristics of the course. A competent assessment of the woman’s general health is also important. What besides caries is included in the list of diseases that can be treated by a dentist?
- If treatment of caries in pregnant women is not carried out in a timely manner, it will be complicated by pulpitis, periodontitis, and inflammatory lesions of periodontal tissue. While carrying a child, women can develop stomatitis, glossitis, cheilitis, periodontitis, periostitis, sinusitis, and abscess. In case of accidental injuries, various injuries can occur - chips and fractures of teeth and roots.
- Caries during pregnancy, as in any other period of life, is treated only by preparation (drilling) and filling. The only exception is caries in the initial stage - the spot stage. The dentist is free to use any filling materials except amalgam. Light-curing polymer fillings are not contraindicated for pregnant women, and the light from light-curing polymer lamps is completely safe.
- Any pain is dangerous - it is not only stress, but also increases the likelihood of injury due to fear or reflexive movement. Dental procedures that may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations. Should always be performed only after proper pain relief. Since general anesthesia is practically contraindicated for pregnant women, it remains possible to treat caries and other diseases under local anesthesia.
- Whitening and straightening of teeth, implants and dentures that require preliminary tooth preparation will have to be postponed. Although removable dentures can be made and worn even by pregnant women.
What does caries treatment look like during pregnancy?
A pregnant woman’s visit to the doctor also has some features:
- The dental chair tilts at an angle of 15°. If the woman is already quite advanced in pregnancy, then she is asked to lie reclining on her left side. The patient lies down comfortably and relaxed so as not to overstrain the abdominal muscles.
- The dentist offers the safest procedures, manipulations and medications for the baby and expectant mother.
- If the diagnosis, clinical conditions and the patient’s capabilities allow it, then it is better to treat caries during pregnancy using a non-contact method - laser, ozone or remineralization (at the spot stage).
- For better treatment, the use of a dental microscope is recommended. It increases the intervention area by 30 times, increasing the accuracy of the doctor’s work.
- If a woman goes to the dentist in the last stages of pregnancy, the doctor can recommend a number of preventive measures that will stop the development of the disease and wait until childbirth to carry out full treatment.