From this article you will learn:
- why the gum moves away from the tooth,
- what disease does this indicate?
- what to do if the gum on a tooth has receded.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
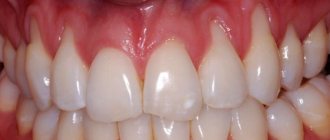
If the gum has moved away from the tooth, this indicates destruction of the attachment of the gum to the necks of the teeth. In this case, the destruction of the periodontal attachment is inflammatory in nature and is one of the symptoms of the development of chronic periodontitis. Such patients usually have additional complaints - bleeding, redness or cyanosis of the gums, and sometimes tooth mobility (Fig. 1).
But, if your gums are receding and your teeth are exposed, this condition, firstly, may also be associated with inflammation of the gums during periodontitis (since inflammatory resorption of the bone around the teeth leads to the fact that the gums sink down). Secondly, there are a number of non-inflammatory reasons, for example, receding gums can occur - 1) due to a traumatic bite, i.e. occlusal trauma, 2) after correcting the bite with braces, 3) due to the thin biotype of the gum, 4) due to the peculiarities of attachment of the lip frenulum to the gum, as well as other reasons.
In Fig. 1 you can see that the patient’s gums have moved away from the teeth (due to the destruction of the dentogingival attachment and the formation of periodontal pockets between the gums and the roots of the teeth) - against the background of gum inflammation.
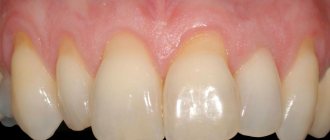
In Fig. 2 you can see “gum recession” (in the area of the central lower incisors) - this is the term dentists use to describe the condition when the gums recede and the surface of the tooth root is exposed.
Why do gums recede?
Gum loss, or recession (in scientific terms), is very rarely an independent disease. Usually this is a consequence of other diseases and pathological processes in the body, which in one way or another affect the condition of the oral mucosa. The main reasons that provoke poor circulation, atrophy and gum loss are:
- inflammation of periodontal tissues with accumulation of pus and plaque in periodontal pockets;
- poor hygiene, accompanied by the formation of tartar. Gradually, this leads to drooping of the moving part of the gum;
- mechanical, thermal and chemical injuries;
- errors during orthopedic and orthodontic treatment, due to which the gums are injured;
- improper hygiene;
- malocclusion;
- pathologies of the structure of the mucous membrane (the gums are initially thin and weakened) and/or the cortical layer of the bone is too thin, which impairs blood circulation;
- general diseases of the body that affect blood circulation and the functioning of the immune system;
- old age, when gum atrophy may occur.
What is the problem?
Because the part of the tooth that is not covered by enamel is exposed, the risk of developing root caries increases. In this case, it is difficult to cure, since ensuring a high-quality fit of the filling material to the root tissues is very problematic due to their hydrophilicity. Over time, teeth can become loose because there is not enough tissue available to hold them in place.
In addition, gum recession is an aesthetic problem, especially when the disease is advanced. People suffering from the disease develop complexes, which leads to social isolation.
Symptoms and forms of the disease
Today, when diagnosing the severity of the disease, the Miller classification is used, which involves 4 stages of gum recession.
- Visually, gum loss is hardly noticeable (or completely unnoticeable) and appears only in the area of contact between the tooth and gum.
- The defect appears slightly in the area of contact between the gum and the neck of the tooth (the level of the attached gum decreases by 1-2 mm). The gums between the teeth remain at the same level.
- The gums recede by 3 mm or more. The necks of the teeth are slightly exposed, but the bone level does not decrease. At this stage, the gums often recede and bleed.
- The most severe stage, when the gums recede by 5 mm or more, the roots of the teeth become visible. Mobility of the teeth is observed, which at this stage of the pathology is often generalized and involves several teeth.
At advanced stages, pathology can be noticed visually, especially when the gums on the front teeth recede. If the pathology is at the beginning of its development, a number of additional symptoms help to detect it.
- Inflammatory process, bleeding.
- Formation of periodontal pockets.
- The sensitivity of the enamel has increased.
- The presence of a thick layer of dental plaque.
- Unhealthy whitish tint of gums.
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis (using modern technologies), so if you have at least one symptom, you should not postpone your visit to the clinic. Of course, everyone is interested in the question of what to do if the gums on a tooth have receded and what treatment should be chosen. There are two directions: therapeutic and surgical. The choice depends on the severity of the pathology and the underlying disease that led to soft tissue atrophy.
Classification
Depending on the preservation of gum tissue, there are 4 stages of gum recession:
- In the first stage, only the attached part of the gum decreases. The decrease in tissue volume is insignificant.
- The area of the attached gum is destroyed, but the bone and gum tissue are preserved, and tooth sensitivity increases.
- In the third stage, the outer surface of the tooth is exposed, and tooth sensitivity becomes painful.
- The tooth is exposed around the perimeter, including in the interdental spaces.
Receding gums are a gradual process. In most cases, it is caused by a specific dental disease. The gums become thinner and smaller, resulting in tooth mobility and loosening, which can lead to their loss.
Therapeutic treatment
Conservative treatment is prescribed in the mildest cases, when it is necessary to stop the inflammatory process and potential gum loss due to periodontal diseases (periodontitis or periodontal disease). Usually, the matter is not limited to one procedure: the doctor prescribes a complex treatment, which may include several techniques.
- Professional cleaning.
Removal of hard dental plaque is a basic procedure that precedes the main treatment. - Cleaning periodontal pockets.
To remove pathogenic microorganisms, the closed curettage technique is used. It can be carried out with standard instruments, as well as with the help of a laser and the Vector device (and its analogues). - Rehabilitation physiotherapy.
Used to improve cell health and better restore blood circulation in soft tissues (laser therapy, electrophoresis, current therapy, etc.). - Taking vitamins
, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and preventive therapy.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
Traditionally, diagnosis begins with a history taking. During a conversation with the patient, the doctor establishes the duration of the disease, studies working conditions and lifestyle, bad habits, and dietary habits. Next, they move on to examining the oral cavity. In addition to receding gums, bleeding gums, bad breath, ulcerative and necrotic lesions and other characteristic symptoms may occur. In order to establish the severity of the disease and assess the extent of damage to all tissues, clinical diagnostic methods are used, which include:
- Schiller-Pisarev test.
- Panoramic or targeted x-rays of teeth.
- Assessment of the resistance of gum capillaries.
- Determination of tooth mobility.
- Measuring the depth of the periodontal pocket.
- Microscopic examination of the biopsy specimen.
- Bacteriological research.
It is not always necessary for a doctor to use all of these methods. Based on the patient’s complaints, clinical picture and general condition of the body, a specific examination regimen is prescribed, which helps confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Surgery
In case of severe gum loss, the only effective way to restore it is soft tissue surgery. Today, several surgical techniques are actively used.
| Methodology | Description |
| Flap reconstruction | Gum plastic surgery, when its deficiency is compensated with the help of a donor flap, which is taken from neighboring areas. If the patient’s gums have dropped slightly (by 2-3 mm), this method can be used to quickly restore its previous level. Disadvantages of the technique are traumatic and aesthetic defects (there may be a discrepancy in color between the donor and native areas) |
| Tissue regeneration using plasma lifting and PRF membranes | A more modern technique that does not require taking donor tissue. Injections of plasma and/or installation of fibrin membranes are made into the affected area. This starts the process of tissue regeneration. The treatment is longer compared to the first method, but it is effective and less traumatic |
| Installation of a collagen implant | A minimally invasive technique that is effective for tissue restoration after periodontal disease or age-related gum atrophy. Such implants contain an analogue of connective tissue, which helps restore gums |
| Classic implantation | What to do if the gums have receded, the tooth root is exposed, and the doctor says that tooth extraction is no longer possible? The best solution in this case would be bone grafting and the installation of dental implants. This is the only way to effectively replace lost teeth. In some situations, additional soft tissue plastic surgery may be required. |
In case of mechanical damage, receding gums can be raised using classic surgery with sutures. This is only possible if there are no serious injuries that require additional measures. It is important that surgical treatment is also aimed at eliminating visual defects. To deal with the root cause, comprehensive treatment is required, especially in cases where periodontal diseases develop against the background of problems with the functioning of other body systems.
Content:
- Causes
- How does pathology manifest itself?
- How is the treatment carried out?
- Surgical techniques
- Additional treatments
- Preventive measures
If the gums have become detached from a wisdom tooth or any other unit, you need to visit a doctor as soon as possible.
When the soft tissues subside, the neck remains unprotected and exposed. It is not covered with a thick layer of enamel, so it immediately begins to react sharply to temperature changes. The situation is aggravated by the fact that food debris gets into the formed periodontal pocket. They accumulate there and serve as an ideal breeding ground for pathogens. If such a pocket is not cleaned in a timely manner, it will increase in size. Then it will come to edentia.
The gums are receding - what can I rinse with and what ointments should I use?
Unfortunately, it is impossible to cure gum recession (recession) with home remedies or conservative methods, i.e. with the use of medications. To correct the situation, procedures in a dental clinic are always necessary.
But, since one of the reasons for receding gums is an inflammatory process, the dentist can select anti-inflammatory home care products for the patient. These include medicinal pastes, which can only be used as prescribed by a doctor, as well as gels, ointments, rinses, etc.
Quite often, the following are used to treat inflammation in the oral cavity:
- Cholisal
is a gel based on choline salicylate, which has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect that lasts 3-8 hours, - Metrogyl Denta
- includes the antibiotic metronidazole and the antiseptic chlorhexidine, especially effective at the initial stage of inflammation, - Solcoseryl
- ointment heals wounds, improves nutrition of injured tissues, and is often used after operations in the oral cavity.
Anti-inflammatory rinses work due to chlorhexidine, herbal components (extracts of geranium, sea buckthorn, hawthorn, sage and chamomile) or a combination thereof. There are a lot of such products on the market, and it is best to consult a dentist before purchasing. It is also important to remember that you should not prescribe any medications to yourself - this may not improve the situation, but rather make it worse.
Prevention of receding gums
To prevent gum recession, your doctor may recommend the following measures:
- Timely, regular visits to the dentist: it is important not only to undergo an examination, but also to carry out professional hygiene twice a year. This will prevent the accumulation of plaque and the formation of hard deposits.
- Timely correction of bite, treatment of inflammatory gum diseases, replacement of fillings, careful selection of orthopedic structures.
- Individual selection of oral hygiene products, especially in the presence of periodontal tissue diseases.
- Using dental floss and irrigator. It will not only improve the quality of hygiene and help remove food particles from the interdental spaces, but will also serve as a kind of gum massager, stimulate blood circulation and maintain the health of the mucous membranes. It is important to consult a doctor about the advisability of use, however, modern irrigators provide mild modes of exposure.
- Avoiding mucosal injuries: avoiding uncomfortable orthopedic structures, using special wax when wearing braces.
- Quitting smoking: this bad habit impairs the blood supply to the tissues of the oral cavity and contributes to the formation of a large amount of plaque on the teeth.
You can learn more about treatment and prevention, as well as get quality help if you have gum recession, from the doctors at the STOMA clinics. Experienced periodontists are highly qualified and have a whole arsenal of modern treatment methods: we are ready to offer comprehensive assistance in diagnosis and treatment. You can make an appointment by phone or through a special form on the website.