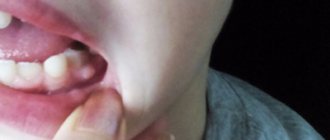
In cases where pulsating sensations are accompanied by aching pain in the gums, we can talk about one of the most unpleasant dental problems, since even painkillers are usually powerless.
There is no single answer to the question why the gums are pulsating: it could be the result of the dentist’s careless work (a mistake made when filling a tooth) or a consequence of pathology.
This article is about the possible causes of pulsation in the gums and recommendations regarding actions that are advisable before seeking dental care.
What does pulsation in the gums indicate?
Pulsating sensations in the gum against the background of its swelling and pain are a clear signal of the presence of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane associated with injury to soft tissues and the penetration of infection into them (the strength and frequency of attacks are important in diagnosis).
In addition, the symptom may be a consequence of various pathological processes. The most frequently diagnosed are:
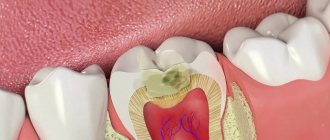
- progressive caries short-term attacks of pulsating pain are possible with carious destruction of the middle and deep stages, most often provoked by external irritants - such as a reaction to cold/hot, sweet/salty.
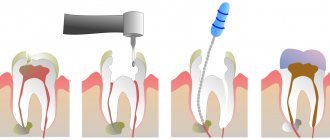
- acute pulpitis is a complication of caries associated with the penetration of harmful microorganisms deep into the dental tissues: upon reaching the pulp, they provoke a serious inflammatory process, accompanied by severe painful sensations, which usually intensify at night.
- periodontitis is a consequence of untreated pulpitis (or, alternatively, the result of poor-quality treatment of dental canals), accompanied by the formation of a purulent abscess at the root of the tooth.
Other factors can also provoke pulsating pain in the gum tissues; only a specialist can determine the real cause of the problem, therefore, if you feel pulsation in the gums, do not delay your visit to the dentist!
Help with inflammation after removal
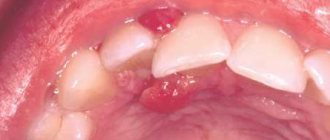
Due to their inaccessible location, full or partial impaction, and large tooth sizes, removal of third molars is often painful and traumatic. If after surgery to remove figure eights there is severe swelling, and it is accompanied by increasing pain for more than three days, this may be a sign of a disease called alveolitis. It occurs due to the entry of bone fragments, pathogenic bacteria into the wound formed after extraction, or due to the blood clot being washed out of the hole too quickly.
Signs of alveolitis are sharp pain in the wound area, redness of the gums, swelling of the extraction site, absence of a blood clot in the first week after the removal procedure, purulent discharge, fever, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, general weakness.
It is very important to treat alveolitis immediately. This condition, without proper help, can cause tissue necrosis, abscess, phlegmon and osteomyelitis. In addition, alveolitis can lead to blood poisoning. If there are any signs of this problem, an urgent visit to the dentist is indicated.
Swelling of the gum tissue around the wisdom tooth is the first signal about the development of complex and dangerous dental diseases. Therefore, it is important not to rely on self-medication, but to consult a specialist in time.
Pulsation without pain
Pulsating sensations in the gums without significant pain are the most likely symptom of the development of apical periodontitis: the process of releasing space for purulent exudate that accompanies the problem causes the sensation of a distinct pulse within the jaw.
As a rule, there are no unpleasant sensations at rest, but they appear under any stress (during hygiene, when eating food, when applying pressure). The symptom is characteristic of any inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues, as well as in the initial stages of the formation of a hilar cyst.
Gum diseases
There are 3 gum diseases that can cause pain. These include:
- Gingivitis.
- Periodontal disease.
- Periodontitis.
The main cause of gum inflammation is poor hygiene and the formation of stone and plaque, which activates the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Inflamed gums begin to swell, turn blue or red. In advanced cases, tooth mobility appears, which can later cause tooth loss.
Gingivitis
Gums with gingivitis
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, which most often causes pain between the teeth. It is superficial in nature, and at an early stage a person experiences the following symptoms:
- Redness and swelling.
- Bleeding.
- Itching.
- Unpleasant smell.
- The pain intensifies after eating.
As it progresses, small ulcers may form on the gums, which are particularly painful. Subsequently, the gum tissue decreases, which leads to exposure of the tooth root. There is severe discomfort while eating.
- Pocket in the gum between the teeth - how to treat
Important! The main cause of gingivitis is the formation of plaque due to poor hygiene.
Treatment is carried out by a dentist and depends on the severity of the gingivitis. Initially, plaque removal is required, and hygiene products are selected individually. In severe cases, overgrown gum tissue is removed.
Types of gingivitis
The standard treatment regimen includes the use of:
- Anti-inflammatory gels (Cholisal, Mundizal-gel, Kamistad).
- Paste (Lacalut fitoformula, Parodontax F, PresiDENT exclusive).
- Rinse aids (Lacalut “aktiv”, Paradontax, President profi).
- Vitamins (B1, C, A, E).
Treatment lasts 10 days. Treatment of gums with gels is carried out 2 times a day. Rinse aids are used after meals. During treatment, it is necessary to use a soft brush to avoid further trauma to the gums.
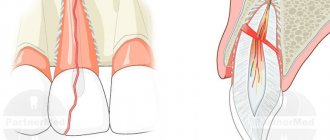
Periodontitis
Inflammatory gum disease, which is characterized by damage to periodontal tissue. It is a consequence of untreated gingivitis.
Gums with periodontitis
The symptoms are similar to gingivitis, but other unpleasant signs appear:
- Severe swelling and suppuration.
- Pain when touched.
- Gaps between teeth and their loosening.
Periodontitis can be caused by failure to comply with hygiene rules, deficiency of vitamins and beneficial microelements, and improper bite and tooth shape. The treatment regimen coincides with therapy during gingivitis. After removing plaque and stone, a person needs to carefully maintain hygiene for 2 weeks.
Stages of periodontitis
Important! Advanced stages of periodontitis require cutting the tissues surrounding the tooth and removing deep stone.
Local treatment includes the use of anti-inflammatory gels (Acepta, Cholisal, Mundizal-gel). If tooth mobility occurs, the installation of temporary splints is required, which can be replaced with a prosthesis if necessary.
Periodontal disease
Damage to periodontal tissue. Pain occurs not only between the teeth, but also around them. The disease occurs rarely - no more than 8% of dental patients. Leads to increased tooth mobility and does not relate to inflammatory pathologies. Symptoms:
- Bleeding.
- Exposing the neck of the teeth.
- Severe pain.
- Tissue atrophy.
Periodontal diseases
The main reason is poor circulation in the periodontal tissues. Periodontal disease is often a consequence of systemic diseases of the body (diabetes, atherosclerosis, hypertension). It can occur in people with a hereditary predisposition.
- Caries between teeth - why I have it and my neighbor doesn’t
The treatment is long-term, and at the first stage includes the removal of tartar. Severe stages require the use of gels, ointments and rinses with an anti-inflammatory effect. If there are carious teeth, they are treated.
Local treatment includes:
- Rinse with 0.05% Chlorhexidine solution.
- Applications "Cholisal gel".
Dental gel Cholisal
The average duration of treatment is 10 days. Rinsing with Chlorhexidine solution should be done in the morning (after breakfast) and in the evening. Then the teeth and gums are dried with a cotton swab and the gel is carefully applied to the marginal part of the gum. After using medications, it is not recommended to eat for 2 hours.
Discomfort under the filling
Unlike the previous case, pulsation in the gum under a recently filled tooth does not always indicate a mistake by the dentist. It is important to distinguish the stage of treatment here:
- When installing a temporary filling, pain and pulsating sensations are acceptable during the first few days, since temporary filling is most often carried out with the addition of a devitalizing agent to destroy the neurovascular bundle. The killing of the pulp occurs gradually, but a visit to the doctor is justified if the discomfort persists for more than 2-3 days.
- If discomfort is felt under a permanent filling, it is advisable to get dental care as quickly as possible. The causes of pain can be different; a competent diagnosis based on an X-ray examination of the problem tooth is necessary.
First aid
Before going to the dentist, you can relieve pain at home using certain pharmaceutical products.
- Drink a painkiller drug - Nimid, Nice, Analgin, Ketanov, Paracetamol, Tempalgin.
- Place the turunda on the swollen area with a special ointment or gel - Kamistad, Dentinox, Metrogyl-Denta, Cholisal.
- Rinse the mouth with antiseptic solutions - Miramistin, Chlorhexidine and Furacilin.
You can use home help methods for three days. Next, the supervision of a professional doctor is necessary. If the pain does not go away and the swelling does not go away, then you should immediately visit a dentist to find out and eliminate the cause of the painful condition. Inflammation during pericoronaritis is relieved by washing the gingival hood with pharmaceutical antiseptic solutions: Iodopharm, Potassium permanganate, Furacilin.
Discomfort in the area of the extracted tooth
Unpleasant sensations, including throbbing pain, after tooth extraction are a natural and inevitable phenomenon, since it takes time to restore damaged tissue.
But after such an operation (especially after the removal of a wisdom tooth), patients should listen very carefully to their feelings so as not to miss the moment of possible complications, such as alveolitis (suppuration of the tooth socket as a result of the loss of a blood clot protecting the wound from infection).
Painful eruption and incorrect position during germination
Periods of active wisdom teeth eruption often cause discomfort. Many people experience pain during this process, swelling and inflammation of the gum tissue. The reason for this manifestation is the absence of the previous milk tooth in the place where the figure eight grew. Third molars are forced to find a path of growth and break through dense bone tissue, which, given the large size of these teeth, becomes the cause of discomfort. Often, the lack of space for the normal position of the figure eight leads to its complicated germination.
In particularly difficult cases, the tooth takes on a dystopic position. It grows in an atypical direction, not upward, but at an angle. It causes injury to neighboring teeth and displacement of the entire dentition, up to bite deformation. A wisdom tooth growing horizontally can injure the cheek, tongue and roots of its “neighbors”.
Waiting for a visit to the dentist: how to relieve pain
It's no secret that toothache appears unexpectedly, and dental care is not always available at the right time. Therefore, we have selected recommendations that will help you cope with pain while waiting for a visit to the dentist.
ethnoscience
The main recommendation is decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage and oak bark): a teaspoon of crushed dry plant in 200 ml of boiling water, infuse, strain and use for rinsing the mouth.
You can also:
- apply cold to the cheek;
- rinse with a soda-saline solution (2 grams of salt and soda per glass of warm water), for acute pain - every quarter of an hour;
- chew propolis (provides slight numbness of soft tissues);
- Apply a cotton wool soaked in eucalyptus or clove oil to the tooth.
Although these recommendations are time-tested, prior consultation with a doctor is advisable.
Pharmacy products
The choice of a pharmaceutical painkiller should be made taking into account the characteristics of the pain syndrome - its intensity and frequency:
- for moderate pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Aspirin, Paracetamol) are suitable, which can reliably alleviate the condition for a couple of hours; if pain increases in the evening, you can add an antispasmodic (Spazmaton, No-shpa)
- with severe pain and pronounced pulsation in the gums, more powerful drugs will be required - such as Nise, Ketorolac, Nimesulide.
It is important to understand that painkillers do not solve the problem; pain relief is only a respite that does not relieve the need for dental treatment.
After eliminating the acute manifestations of the inflammatory process, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
By postponing a visit to the dentist, saving yourself from pain using folk or pharmacy remedies, you risk bringing the situation to a critical point, when saving the tooth becomes impossible!
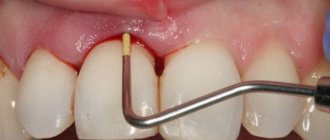
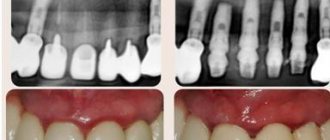
Diagnostics
To identify the cause of gum pain, the dentist examines the oral cavity, evaluates the configuration of the face and the condition of the lymph nodes.
The doctor collects an anamnesis of the patient’s life and illness. To make an accurate diagnosis and choose an effective treatment method, additional examinations are prescribed. Diagnostic methods:
- general blood test - carried out to assess the severity of the inflammatory process;
- in case of periodontitis, measure the depth of the periodontal canals with a special instrument;
- plain x-ray of the jaw;
- orthopantomogram - examination allows you to see how the teeth are located in the jaw;
- cytological analysis.
When a bacterial infection is detected in the oral cavity, an additional analysis is performed to determine the sensitivity of pathogens to antibacterial drugs.
What to do if your gums hurt:
Possible complications
Complications with sore gums arise due to the spread of the infectious process throughout the body.
The most common complications :
- formation of a fistula, sometimes it affects facial tissues;
- loss of teeth due to increased mobility;
- sinusitis, sinusitis;
- sepsis;
- osteomyelitis.
Severe dental diseases require surgical intervention. After them, you have to recover for a long time and follow all the rules of the rehabilitation period.