Cones (tubercles, nodules) on the body are compactions of a predominantly round or oval shape in the form of a subcutaneous bulge, in most cases having clear contours. Lumps on the back can appear for various reasons, for example, as a result of injury or inflammation in the spine or surrounding soft tissues. Less commonly, compactions are of a tumor nature and are neoplasms or cystic protrusions in the form of sac-like cavities filled with exudate.
Lump on the back
If lumps or dense balls appear on your back, you should show the formation to a specialist, even if it does not cause discomfort or pain . Emergency medical attention is required in cases where the lump itches, hurts when pressed or touches clothing, has a mobile structure, or the skin around the lump is covered with scales or changes color.
Lump under the skin on the back
Hematoma
Description
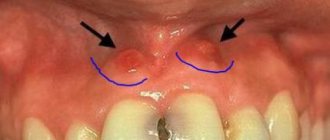
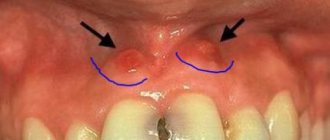
If there is a swollen lump on the gum filled with blood, most likely it is a hematoma. This tumor occurs as a result of an incorrectly removed tooth or injury. Such a lump on the gum above the tooth, as a rule, does not hurt.
Treatment
Dissolves on its own. But if the lump hurts, consult your dentist for advice. The doctor will prescribe painkillers.
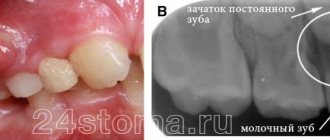
Lump at the base of the tooth after installing a permanent crown
If the prosthetics are carried out correctly, the doctor did not make mistakes, no neoplasms should appear in the mouth. If, after the end of treatment, the gums swell and a painful blister forms on it, it means that something did not go according to plan.
Most likely, the doctor poorly prepared the unit for prosthetics. Depulpation must be carried out extremely carefully. There should be no air bubbles in the canals to be filled. Under no circumstances should you leave fragments of dental instruments in them. Poor depulpation creates conditions for the development of an infectious process and subsequent periodontitis.
It is also possible that the lump was formed due to shortcomings that were made at the time of fixation of the artificial unit. Then the glued structure begins to put pressure on the mucous membranes and rub the tissue. Abscesses, growths, and purulent lumps form. To eliminate these unpleasant symptoms, you need to adjust the shape of the prosthesis.
If the crown is installed correctly, it will never interfere. This needs to be understood. Only in the first hours after its fixation may an unusual sensation of a foreign body in the mouth persist. But then the person stops noticing the structure altogether.
Epulis
Treatment
The lump on the root of the tooth is attached to a stalk and is either red or gum-colored. It affects the lower jaw and occurs as a result of malocclusion, permanent mechanical damage, and poor quality dentures. Often observed in women with hormonal imbalance.
Treatment
It is removed by one of three methods: scalpel, diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction. The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia.
Trigger points for myogelosis
Myogelosis (Schade-Lange disease) is a pathology of muscle tissue in which painful lumps called trigger points form in the muscles. These compactions provoke myofascial pain, which is significantly aggravated by mechanical irritation, such as pressure. There are four types of trigger points, classified according to the degree of pain response to external influence.
Myogelosis of the neck and back
Table. Types of myofascial trigger points on the back.
| Variety | Conditions preceding the onset of pain |
| Active | Pain is chronic and can occur both under the influence of negative and provoking factors, and in the absence of visible and significant stress (at rest). |
| Passive (latent) | Pain syndrome is detected only with physical irritation of the trigger point, for example, during palpation. |
| Primary | The cause of the primary trigger syndrome is chronic muscle overload or a single power or dynamic load that does not correspond to the degree of training of the muscle fiber. |
| Secondary (associative) | The mediator of pain is usually trigger points from nearby muscles or excessive loads of the compensatory type (compensate for the insufficient functioning of another muscle). |
Clinically, myofascial syndrome with myogelosis is manifested by painful sensations in the back associated with physical, static or dynamic load, as well as the appearance of small subcutaneous lumps in the area of the affected muscle. Lumps with myogelosis are not painful, have clear boundaries, and do not have mobility.
Periodontitis
Description
A hard lump on the gum, an abscess formed at the base of the tooth root. In the absence of therapy, it transforms into a benign tumor.
Treatment
If such compaction of the gums under the tooth appears, contact your dentist. The teeth are unfilled and root canals are cleaned. After removing the exudate, oral baths with medicinal herbs or soda solution are prescribed. Treatment for periodontitis may require multiple visits to the doctor.
Pus in the gums with periodontitis -
Very often, the patient’s complaints that his gums near the tooth are festering are not associated with inflammation at the apex of the tooth root during periodontitis, but with the formation of periodontal pockets in local or generalized forms of periodontitis. With periodontitis, there is destruction of the attachment of the gingival margin to the necks of the teeth, destruction of the alveolar bone around the teeth, as well as periodontal fibers, with the help of which the tooth is attached to the bone tissue.
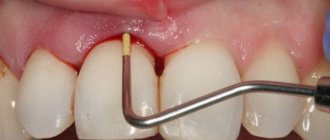
All this leads to the formation of so-called periodontal pockets between the gum and the surface of the roots of the teeth (Fig. 14). They create good conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the development of chronic inflammation. When one of the periodontal pockets becomes too deep, this can lead to disruption of the discharge of inflammatory serous-purulent exudate through the lumen of the pocket. As a result, an abscess forms in the projection of the periodontal pocket on the gum, which dentists call the term “periodontal abscess” (Fig. 15-16).
You can immediately suspect that gum swelling is associated with periodontitis, and not with periodontitis, if the tooth is completely intact (i.e., externally healthy and does not have a filling, crown or caries), if it has mobility, and mobility was present in this tooth and before the gums become suppurated, and also if, with slight gentle pressure on the abscess, pus comes out from under the gums (as in Fig. 16).
The differences between local and generalized periodontitis are that they are caused by completely different reasons and, accordingly, the treatment will also be different. With local periodontitis, the inflammatory process occurs only in the area of 1-2 teeth - due to exposure to a traumatic factor. For example, a pocket may appear as a result of trauma to the gum margin by the overhanging edge of a filling or crown. The cause may also be the premature closure of several teeth, which leads to chewing overload and destruction of the bone tissue around them.
But with chronic generalized periodontitis, gum suppuration occurs for other reasons. You can immediately suspect this form of periodontitis if you have symptoms of bleeding and pain when brushing your teeth, swelling, redness or bluishness of the gum margins in the area of most teeth. The cause of generalized periodontitis is soft microbial plaque and hard tartar, which accumulate on the teeth as a result of insufficient oral hygiene.
Bacteria in plaque and tartar produce toxins and various pathogens that trigger an inflammatory reaction in the gums. With prolonged inflammation, first the dental-gingival attachment is destroyed, and then the periodontal fibers and bone tissue around the teeth are destroyed. With this form of periodontitis, pockets are found in almost all teeth, and not just in 1-2 (as with local periodontitis). When the outflow of inflammatory serous-purulent exudate in one of the pockets is disrupted, a periodontal abscess is formed in the gums.
Treatment of local periodontitis –
Based on the examination, the identified amount of tooth mobility, probing the depth of the periodontal pocket and analysis of the x-ray, the doctor will determine the possibility of saving the tooth and the algorithm for further treatment.
If the tooth can be saved, then the first thing to do in case of local periodontitis is to eliminate the impact of the traumatic factor. This means that you need to remove the overhanging edge of the filling or crown, and selectively grind the contacts of the chewing surface of the causative tooth and its antagonists. Next, under anesthesia, the periodontal abscess is opened to allow the outflow of pus and to rinse the periodontal pocket with antiseptics. If pus comes out of the pocket without an incision, but only little by little, then after anesthesia you still need to widen the mouth of the pocket with a stroker. Next, the doctor prescribes systemic antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antiseptic rinses.
Opening of periodontal abscess –
Next, the issue of the need to fill the root canals in the causative tooth is resolved. This must be done if the depth of the periodontal pocket reaches 2/3 or more of the length of the root of this tooth. Removing the nerve from the tooth and filling the canals is required here because infection from a deep pocket very easily penetrates through the bloodstream into the neurovascular bundle (tooth pulp), as a result of which the pulp itself becomes a source of infection. But all this is just initial basic treatment!
The main treatment consists of open curettage of the periodontal pocket. This operation allows you to remove inflammatory granulation tissue (which forms at the site of destroyed bone tissue) from under the gums, as well as fill the periodontal pocket cleared of granulations with bone material, which allows you to partially restore the level of bone tissue around the tooth.
Progress of open curettage operation –
During open curettage, the gums are first moved away from the teeth and bone tissue to create good access to the periodontal pocket. Then the granulations are removed from the pocket, the root surface is polished and the pocket is filled with material based on artificial or bovine bone tissue. Next, the flaps of the gum mucosa are placed in place and the gum is sutured. Figure 19 shows that the bone level differs between radiographs taken before and 4 months after surgery (an increase in bone level of approximately 2.5 mm).
Moreover, if an abscess on the gum occurs near a moving tooth, then in addition to all of the above treatment, splinting of the moving tooth may be required. For this purpose, fiberglass and filling material are used, with the help of which the movable tooth is fixed to the adjacent stable teeth. Detailed information on curettage and splinting in the articles:
→ How the open curettage operation is performed, → Teeth splinting technique
Treatment of generalized periodontitis –
With generalized periodontitis, periodontal pockets occur not in 1-2, but in almost all teeth. Typically, this form of periodontitis has a sluggish chronic course. Common complaints from patients include bleeding gums and inflammation of the gingival margin. In severe cases, tooth mobility, changes in the position and inclination of teeth, and suppuration from periodontal pockets occur.
Against the background of decreased immunity, an exacerbation of chronic inflammation may occur, and then abscess formation (i.e., the formation of purulent abscesses) may occur in the area of one or more periodontal pockets. Treatment of the generalized form of periodontitis is very complex, and we have devoted a separate article to this topic, which you can read at the link above. We hope that our article on the topic: What to do if your gums are swollen turned out to be useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook” ( Borovsky E.).
Flux (periostitis)
Description
An inflammatory process of bone tissue, which is accompanied by pain, elevated body temperature, enlarged lymph nodes, and swelling of the oral mucosa. The seals have purulent contents. The cause is an infection of the oral cavity resulting from untreated caries.
Treatment
A visit to the doctor is required to treat the lump. The dentist opens the tooth, places special medications in the cavity, and closes it with a temporary filling. If treatment does not bring positive results, the tooth is removed.
Inflammatory processes
Pus-filled, painful bumps on the back can also be boils or carbuncles. These are purulent-necrotic inflammatory processes in the hair follicles, sebaceous and sweat glands, which often involve the surrounding connective tissue. One of the main reasons for the occurrence of boils and carbuncles is lack of personal hygiene (irregular showering) and microtrauma of the skin, through which microbes and bacteria enter the hair follicle. In 60-70% of cases of furunculosis, the causative agent of the inflammatory process is Staphylococcus aureus, so treatment of boils and carbuncles may include antibiotic therapy.
What does a boil look like?
You can understand that a purulent lump on the back is the result of an inflammatory process by the following signs:
- the presence of red erythema around the formation and a purulent core in its center;
- severe pain even with mild exposure to external irritants (for example, upon contact with clothing);
- Predominant localization - on the back, back of the head and neck;
- rejection of necrotic tissue with subsequent scarring.
"Flemoxin"
Boils are treated comprehensively. To eradicate the infectious pathogen, penicillin antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Flemoxin) are used. If the abscess has opened, a bandage with a hypertonic solution is applied on top. This is the name of a solution with a higher concentration of dissolved substances and a higher osmotic pressure. After draining the wound, dressings with tetracycline or erythromycin ointment are used topically. If the boil has just appeared, the use of physiotherapeutic methods (dry heat, ultra-high frequency therapy) and ichthyol ointment, which has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and disinfectant effect, is indicated.
Erythromycin ointment
If you want to know in more detail what types of pain-relieving ointments for the back there are, and also consider the composition and application, you can read an article about this on our portal.
Fibroma
Description
Benign tumor of epithelial cells. Initially, the bumps on the gums above the tooth are small in size and do not hurt. However, mechanical stress and other negative factors can lead to the transformation of fibroma into a malignant tumor.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out surgically. The doctor excises the tumor, applies stitches, and prescribes rinses. Further follow-up visits may be required to monitor the recovery process.
Cyst
Description
A hard, bone-like compaction of gums under a tooth, up to 1 cm in diameter. Occurs in people with weakened immunity, genetic predisposition, as well as due to acute infectious diseases, mechanical damage to the soft tissue of the oral cavity.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in the same way as for fibroma - by excision. After surgery, mouth rinses and baths are necessary, as well as repeated visits to the doctor to monitor recovery.
Gum cancer
Description
A rare dangerous disease. It is characterized by the formation of a dense lump on the gum at the root of the tooth; it can develop asymptomatically for several months.
Treatment
Requires serious medical intervention, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, long-term recovery and follow-up.
Gum cancer, if detected early, is curable, otherwise it ends in death. Red and white bumps on the gums appear in both adults and children. Only a doctor can correctly identify the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. The sooner you see a dentist, the greater the chances of a quick recovery.
Don't self-medicate! If a ball is inflated on your gum and you don’t know what to do, contact a dentist in Odintsovo. The doctor will conduct a full examination of the oral cavity, accurately diagnose the disease, and prescribe effective treatment.
You can make an appointment for a consultation, as well as find out the cost of admission and treatment by calling the clinic in Odintsovo.
Tumors on the back
Lumps and bumps on the back can be a symptom not only of inflammatory, degenerative and traumatic processes, but also of tumor diseases, including severe forms of cancer. If a tumor in the spinal area or in the surrounding soft tissues has a malignant etiology, timely diagnosis is of great importance to form a relatively favorable prognosis for future life and treatment, so any compactions and formations should be examined by specialists .
The most common types of tumors found on the back are: