The problem occurs several weeks before the eruption of a baby or permanent tooth. The appearance of a cyst is indicated by a bluish-purple spot (hematoma). This is due to difficulty in tooth eruption.
An eruption cyst is a type of soft tissue benign tumor that appears when a tooth has already begun to erupt through the gum. Scientists and doctors have not agreed on why it occurs. The most likely causes: infection, trauma, improper development of teeth, which causes a lack of space for the “newbie”. In addition, it may be a consequence of caries and improper care.
Eruption cysts occur during the growth of baby teeth or, more often, at 6–9 years of age, when permanent teeth emerge. The fact is that, due to its anatomical structure and location, the chewing group of teeth is the most difficult to erupt.
If you notice a large formation in your baby’s mouth, in the place where a tooth should appear, consult a doctor. Do not resort to self-medication under any circumstances. Infusions, rinses and even strong antibiotics most likely will not help, but ruining a child’s health in this way will cause serious harm.
If you contact a specialist, treatment can follow one of two scenarios. In the most favorable option, the doctor will advise giving the child toys, special teethers, crackers - everything that the baby can chew. This will help break through the mucous membrane.
In difficult situations, surgery may be necessary. Then the surgeon will cut the gum under local anesthesia. This will make teething easier.
It is forbidden to try to cut or tear the mucous membrane on your own; you can cause a serious infection or injure your baby.
Where does the abscess come from and what is its danger?
In the vast majority of cases, an abscess on the gum is associated with a tooth, often with a milk tooth. The most amazing thing is that the tooth may appear healthy from the outside, it may have a beautiful filling, and the tooth may not hurt. Why does pus still appear?
Baby teeth are less resistant to infection than permanent teeth; they are designed for a short service life, although they, like permanent teeth, have a nerve and roots. However, the roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve after five years. Caries in such teeth spreads much faster. Within three months, a cavity can form in the tooth, reaching the nerve. If caries is not treated, all pathogenic bacteria enter the dental nerve, and then, through the nerve, the microbes enter the bone. Bone is quite comfortable for microbes. They multiply there, dissolve the bone, which is accompanied by the formation of pus. If the tooth is open, there is a hole in it, pus comes out into the oral cavity. If food particles, fragments of destroyed enamel get into the tooth, or the tooth is covered with a filling without adequate treatment, pus can no longer flow freely. If the pus cannot flow out through the tooth cavity, it begins to look for another way out. The pus melts the bone and comes out under the gum. The outer covering of the gum, under which the pus has come out, swells and takes the form of a lump. Over time, the lump may burst and pus leaks out.
Once the pus is released, the lump may disappear and the gums may heal until the pus collects in large quantities again. The danger of such “bumps” is as follows:
- there is always an infection in the body (you should never forget that the abscess is not just on the gum, but in the head);
- the pus that is in the jaw dissolves the bone and can damage the growing permanent tooth.
The disappearance of an abscess next to a tooth never means recovery.
Symptoms that appear along with an abscess
- redness on the gum;
- tooth pain (optional);
- There is a hole in the tooth or there may be a filling on it;
- enlarged lymph nodes (dense “balls” appear under the lower jaw).
Sometimes a lump is discovered by chance, and the child may not be bothered by anything at all. The parent should periodically examine the child's mouth independently.
Complications with cyst growth
Tooth trauma, advanced caries, nasopharyngeal or periodontal disease, dental malformations - one or more of these factors can lead to the development of a cyst. The danger is that the cyst grows unnoticed. It usually does not hurt and at the initial stage does not cause discomfort or reaction of the lymph nodes. With further development, suppuration and various unpleasant sensations may appear. But even if there is no pus, the cyst is very dangerous. Therefore, do not delay treatment.
A cyst can lead to intoxication of the body due to the fact that waste products of harmful microorganisms enter the blood. The consequence of this can be headaches, high fever and, in the worst case, sepsis.
In addition, complications are caused by local problems - phlegmon, abscesses, osteomyelitis. These complications are inflammatory in nature and often occur when the cyst suppurates. The spread of pus can lead to destruction of the jaw bones, damage to the internal organs of the digestive system, liver, and heart.
It is impossible to avoid the appearance of a cyst, but if you properly care for baby and permanent teeth and treat infections in a timely manner, you can reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. In addition, periodic visits to the dentist will allow you to notice the problem at an early stage, when treatment will be as simple and easy as possible for the body.
Never do
You should never heat your gum or cheek, no warm compresses or salt or other “folk remedies”! It’s better not to do anything at all before going to the doctor. After warm compresses, pus may spread not only in the jaw, but also in the cheeks, throat, and neck. Situations arise that are dangerous not only to health, but also to life.
Contraindicated
- refusal to brush teeth;
- independent opening of the abscess;
- taking medications without the consent of a doctor (except for painkillers).
Do baby teeth all change?
The child has 20 baby teeth. In an adult, the number of teeth can range from 28 to 32. Which baby teeth fall out? Everything! Normally, by the age of 14 they should change to permanent ones. Some teeth initially emerge as permanent teeth.
The order of loss corresponds to the order of appearance of baby teeth - the incisors change first, then the first and second premolars, and the canines change last.
The first molars grow permanently before the teeth change. Second molars appear in empty spaces created by jaw growth. Third molars (wisdom teeth) have lost their functionality and in many people do not grow back at all.
Treatment
Depending on whether a permanent or baby tooth caused a lump on the child’s gum , the doctor carries out appropriate treatment. If a permanent tooth is damaged, seek help immediately while there is a chance to save the child’s tooth. The doctor will have to remove the nerve and fill the canals. In this case, adult dental treatment is a necessity, because if high-quality treatment and appropriate treatment are not carried out, the child may lose a tooth.
Milk teeth are removed immediately - their root system has not yet had time to form, and it is impossible to properly fill the canals. In addition, if a diseased tooth is left, the molar may grow back with defects (stains, damage.
At the Family Dentistry Center, you can remove a child’s tooth without pain or fear. All procedures in the clinic are performed under medical sedation. While the baby is sleeping peacefully and does not feel pain or discomfort, the doctor can carry out all the necessary procedures. Being able to treat your teeth while you sleep is a great way to cope with dental phobia.
Treatment of blue teeth
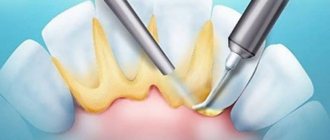
If during diagnostics it is determined that the cause of blueness of all teeth is the use of special products, the dentist or hygienist may prescribe a professional cleaning of the oral cavity. Quite often the patient requires enamel polishing; this allows for the best results.
If after such manipulations the blue discoloration does not disappear, you can try other methods.
First of all, the doctor should send the person for an X-ray examination of the jaw, this will make it possible to make a correct diagnosis, as a result of which the treatment will be as effective as possible. It may also be necessary to remove previously installed fillings and caries-infected hard tissues. If necessary, treatment of the annals and root system of the tooth will be prescribed.
There are several methods to restore the original whiteness of your teeth. One of the most common options is the installation of a composite filling, that is, direct artistic restoration of a row. A more expensive procedure is the production of an artificial crown or special onlays - veneers (indirect restoration).
Prevention
There are no special unique ways to prevent dental disease in children. Ulcers on the gums are the result of untreated caries. Therefore, all preventive measures are aimed at preventing caries:
- oral hygiene (make sure your baby brushes his teeth properly);
- balanced diet;
- rinsing your mouth every meal;
- preventive procedures (remineralization, fluoridation; fissure sealing);
- timely dental treatment;
- preventive examinations at the dentist 2 times a year (some experts recommend once every 3 months if the baby already has treated teeth).
Timely dental treatment for children and proper hygiene will help avoid many dental problems. Teach your child to take care of the health of their teeth and beautiful children's smiles will delight you every day!
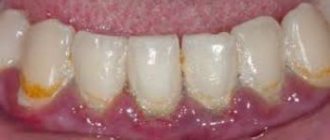
Blue gums
Another common phenomenon, especially in young children, is blue discoloration of the gum tissue. It often occurs during the eruption of the first, baby teeth. During this process, inevitable damage occurs to tissues penetrated by a huge number of blood vessels of different sizes. As a result, blood can enter the soft tissue, leading to the formation of a small hematoma.
That is why, if a baby has a hematoma or bruise in a place where a new tooth is expected to appear soon, there is no cause for concern. However, in all other cases it is recommended to show the child to the dentist. The cause of blueness may be an inflammatory process. It is usually preceded by diseases such as gingivitis or stomatitis.
It is important that such complications usually occur in children with weakened immune systems. Also, the health of teeth and gums is greatly influenced by compliance with the rules of daily care. Due to the abundant accumulation of plaque and stone, most ailments appear; this is especially dangerous at an early age, when the enamel is not yet strong enough.
Memo for parents. Actions for trauma to temporary and permanent teeth in children
• In summer, the physical activity of children and adolescents is especially high - jumping, running, cycling, skateboarding and roller skating, playing outdoors and visiting rope parks sometimes lead to falls and injury to temporary and permanent teeth.
• Unfortunately, many parents do not immediately seek dental treatment for children due to injury, but only after the development of inflammatory complications or in order to eliminate aesthetic problems. Often, some injuries to the children's dental system are completely ignored by adults.
• There is a misconception that an injured temporary tooth will still be replaced by a permanent one, so it is not necessary to show the child to a pediatric dentist. Meanwhile, if a temporary tooth is injured, not only its root can be damaged, but also the germ of the permanent tooth. This subsequently leads to the development of complications such as underdevelopment of permanent tooth enamel (enamel hypoplasia), disruption of its formation, and even death of the permanent tooth germ. In the latter case, the absence of a tooth in the dentition can lead to malocclusion and the need for orthodontic treatment.
• Dear parents! Experienced pediatric dentists at the Jasmine Clinic have prepared for you a memo on the sequence of actions in case of trauma to the dental system in children and adolescents.
• Immediately after the injury occurs, it is necessary to reassure the child and not show your confusion and excitement. Set your child up in a positive way, convincing him that you know how to act correctly in such a situation.
• Try to get an appointment with a pediatric dentist as soon as possible. Call your loved ones or friends who will urgently begin searching for a qualified pediatric dentist, followed by making an appointment as soon as possible.
In such a clinical situation, the doctor will try to make a diagnosis as quickly as possible and begin measures to save the injured tooth. If the damage is serious, you need to inquire about the availability of not only a therapist, but also a surgeon in the clinic, since tooth extraction and/or suturing of soft tissue may be required.
• Ask the child whether his general condition has changed after the injury - whether there has been any memory impairment (does he remember what preceded the fall or hit an object and what happened after that), whether dizziness, flickering of “spots” before the eyes occurred, nausea, vomiting, headache. Chipping and dislocation of teeth can be accompanied by a concussion, therefore, if there is a change in the general condition, a mandatory examination by a neurologist is necessary, along with actions to save the injured or dislocated tooth.
• Examine the child's oral cavity to understand what happened to the teeth during an impact or fall. After all, even minor injuries such as chipped enamel or a bruised tooth do not go away without consequences. It is very important to see your dentist on time! Pay attention to the preservation of the soft tissues of the lips adjacent to the injured tooth, bleeding of the dentogingival groove of the injured tooth, and its displacement outside the dentition. The cause of tooth injury is usually a blow to it. And, nevertheless, injuries are different: tooth bruise, tooth dislocation (complete or incomplete), tooth fracture (at the level of enamel, dentin, dental pulp or longitudinal tooth fractures), tooth root fracture, tooth germ injury and combined injuries. The simplest of the above types of injuries can be identified immediately by a number of symptoms. If it is a tooth bruise: the child may experience pain, especially in the first hours after the injury, which intensifies when biting. If this is a dislocation of a tooth, then significant pain, which intensifies when biting, is combined with its mobility. Diagnoses of “tooth fracture”, “tooth root fracture”, “tooth germ injury” can only be made by a dentist after an X-ray examination.
• If a tooth or part of it is missing, try to find it as quickly as possible, enlisting the help of others.
• If you find a tooth or its fragment, get to the nearest pharmacy as quickly as possible, buy a test container, saline solution and miramistin. You can use milk instead of saline solution.
• Place the tooth or its fragment in a container with saline solution or milk.
• Treat the child's oral cavity with miramistin.
• If a child, in addition to a dental injury, has suffered a bruise with damage to soft tissues (hematoma, bitten wound of the lips), buy a briquette with frozen meat or minced meat at the nearest grocery store, wrap it in a napkin and apply it every 2-3 minutes with the same breaks to the skin in projections of damage. Under the influence of low temperature, the vessels will contract, bleeding, swelling and pain will decrease.
• If a tooth is dislocated (complete or incomplete), it is important to consult a dentist as soon as possible - within 1 hour! This will give you a good chance of saving your child’s tooth. There are cases when informed parents bring in their hands a child’s tooth that has fallen out due to an injury. If the condition of the bone tissue at the root of the tooth allows, then an experienced dentist, after X-ray examinations and special preparation of the oral cavity, will be able to put the tooth back into the socket and splint it, that is, strengthen it to the neighboring teeth. A successful manipulation, with full compliance with all the recommendations of the dentist, allows you to save the injured tooth for a long period.
• If you consult a doctor within the next 2 hours after injury, the tooth also has a chance of being saved. With each subsequent hour, these chances decrease significantly. When contacting 6 hours after injury, the likelihood of saving the tooth after its reposition is very low. A permanent tooth that has been completely dislocated from its socket can and must be returned to its place as quickly as possible, but not on your own! This should be done by a doctor.
• Primary teeth cannot be repositioned. If, as a result of a fall in 2-3 year old children, the front temporary tooth has penetrated deep and disappeared under the gum, after 2-3 weeks it may come out on its own. But an urgent consultation and examination by a dentist, as well as systematic monitoring of a child’s injured tooth, are strictly necessary!
• A high-quality diagnosis before dental treatment in case of injury to the dentoalveolar system is the first thing a dentist does. The standard set of studies is a targeted (using a radiovisiograph) or panoramic (orthopantomograph) image, 3D diagnostics depending on the nature and severity of the injury, as well as electroodontodiagnostics (EDD) to check the viability of the dental pulp. To exclude a fracture of the root of an injured tooth and to identify the integrity of the adjacent bone tissue, targeted radiovisiographic images are necessary, and for sufficient information in case of chipped teeth, not one image is needed, but several, taken in different projections. Splintered fractures of the crowns of the anterior teeth can be accompanied by the penetration of small fragments into the soft tissues - the adjacent areas of the lips. To exclude this complication, an X-ray examination of soft tissues - lips - is also performed.
• For 2 weeks after treatment, it is necessary to follow a gentle diet (purees, soups, cereals) with the exception of hard foods.
• To prevent inflammatory complications, high-quality systematic oral hygiene using a soft toothbrush, as well as toothpaste and herbal rinse is important.
• A patient with dental trauma should be under dynamic observation and examined by a dentist after 2 weeks, 1, 3,6.9 and 12 months, and then 3 times a year.
• As a rule, children with malocclusion are susceptible to injury because protruding teeth are damaged when they are hit or fall. Early detection and timely treatment of malocclusion pathology is the prevention of traumatic dental injuries in children.
Dear parents! The pediatric dentists at the Jasmine Clinic are always ready to respond to a call for help and choose the best restorative treatment option for your child if an injury suddenly occurs. Let our little patients receive only pleasant emotions and a charge of vivacity, being in constant motion, surrounded by our common care and attention!
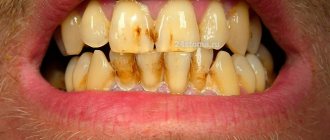
Causes of blue gums in adults
The reasons may be different, the most common include:
- problems with the cardiovascular system;
- thyroid diseases;
- kidney pathologies;
- stomatitis;
- inflammatory periodontal diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis or periodontal disease;
- caries and its complications;
- improper orthodontic treatment;
- incorrectly selected or incorrectly manufactured orthopedic design.
- a consequence of surgical intervention (blue discoloration of the periodontium can occur after tooth extraction);
- chemical (exposure to the mucous membrane of an aggressive substance used in the treatment of root canals) or thermal burn (exposure to high temperatures on the gums).
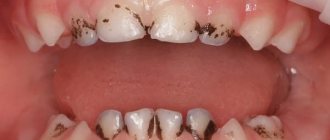
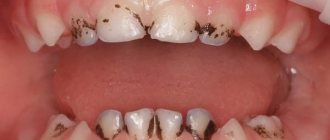
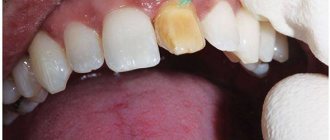
Causes of black spots on gums
If your baby is under three years old, there is a chance that the formation that has alerted you is an erupting tooth. Its appearance is accompanied by swelling and redness of the gums, sometimes it can darken significantly. You can gently touch the lump with your finger after washing your hands. When pressed, it feels like
then under the relatively soft gum there is a hard formation. This is a new tooth being felt.
It is believed that teething is a physiological process and does not require consultation with a dentist. However, if the gums are very swollen, have a bright red or bluish color, and the child reacts to manipulations in the mouth extremely painfully, this is a reason to consult a specialist.
Black spots on a child's gums may be evidence of a disease. With insufficient oral hygiene, weakened immunity, diseases accompanied by the consumption of medications that reduce the body's resistance, a pathological process may develop in the mouth, for example:
- gingivitis. This is a disease of the gums in which they become inflamed, swollen, and change color. There may be an unpleasant odor from the baby's mouth. Symptoms of gingivitis are unpleasant for a child - itching, burning sensation and soreness of the gums. Possible refusal to eat. The disease requires consultation with a doctor! He will prescribe treatment that is appropriate for the baby’s age and condition.
- stomatitis. The disease's symptoms are similar to gingivitis and also manifests itself as a white coating on the oral mucosa. It can be caused by either a fungus (“thrush”) or bacterial or viral agents. Precisely because there can be several causative agents of the disease, consultation with a pediatrician is mandatory - he will prescribe a medicine that will act specifically on the cause of the disease.
If a dark spot appears on the gum of an older child, one can also assume the traumatic nature of the formation. Ask him if he hit his face on something, perhaps got into a fight with someone, causing a “bruise” on his gum.
How to make teething easier
While the teeth are just getting ready to appear, the baby experiences a lot of unpleasant sensations, which, of course, causes a lot of trouble for the parents. During this period, the child needs care and affection, as well as plenty of fluids. It is recommended that infants be breastfed more often, and children on artificial nutrition should be offered more warm water.
There are many ways to relieve discomfort. Two most popular:
- Give your child special teethers - these are soft silicone toys filled with liquid. Cool the toy slightly in the refrigerator before use. This will help relieve swelling and reduce pain. The textured surface of the teether will give the baby the opportunity to thoroughly massage and “scratch” the gums. The bright design of the toy will attract attention to it and amuse the child.
- Use topical medications - pain-relieving gels and ointments for gums, designed specifically for children. These remedies act very quickly and help the child forget about discomfort for several hours.
Gum massage during teething
Since drug treatment cannot be considered completely safe, you should try more moderate options first. We have already talked about one of them above - these are teethers. In addition to these, other measures can be taken. For example, switch to chilled food and drink. This will help reduce the discomfort a little.
Gentle gum massage will also be an effective solution. Be very careful, since your baby's gums are very delicate, if you overdo it, there is a risk of increasing the pain. Therefore, you should approach massage wisely and with balance. And most importantly, with full knowledge of the methodology.
The massage consists of three main stages:
- Preparation.
If you decide that you will massage your gums with your finger, you need to trim your nails well, rinse thoroughly, and disinfect. It is very important to get rid of any dirt on your hand. But since this is quite difficult, there is a simpler and more convenient option - use special finger pads or napkins. They can not only massage your gums, but also gently clean your first teeth of food debris. Wet wipes "ASEPTA BABY" from 0 to 3 years help reduce pain during teething, effectively cleanse the oral cavity of food debris, and reduce the risk of inflammation. Each napkin is individually packaged; when using, you do not need to rinse your mouth with water. So you can have a massage not only at home, if necessary. Place the napkin on your finger, now you can proceed directly to the massage itself. - Massage.
Both infants and older children need to move massage movements from the edges of the disturbing areas to the site of eruption. Lightly rub the gums, stroke or apply a little pressure. All these movements can be combined. Watch your baby's reaction and choose the option he likes best. You don’t have to worry that you won’t be able to reach all the places; the soft fibers of the finger napkin will help you massage hard-to-reach areas. Remember that the procedure should be carried out only where the roots of the teeth are. There is no need to massage the eruption site itself, as this can worsen the child’s condition, cause discomfort and make it difficult for the tooth to emerge. - Hygiene.
As early as six months, you can accustom your child to the need for daily oral care. At this time, it is already recommended to use a special children's brush instead of a finger napkin, as well as toothpastes intended for children. For example, ASEPTA BABY paste, made on the basis of plant extracts. This product does not contain resin or abrasive substances, so it is excellent for newly erupted baby teeth that are still fragile. The paste has a pleasant taste, which will make the cleaning process more enjoyable. At first, watch the cleaning, and when the child grows up, he can do everything on his own.
Teething massage is an effective procedure that can not only reduce discomfort, but also reduce the use of medications. But it is very important to be extremely careful when performing a massage, both for infants and older children. Babies' gums are much more tender than those of adults. But if you do everything correctly, then after a fairly short time you will notice that the baby has become more comfortable, he has calmed down, and the teething itself is faster and easier.
Signs of teething
Most often, the first teeth appear at the sixth to eighth month, but in some babies the incisor may emerge as early as four months or, conversely, teething will be delayed for six months. All this is quite normal for a healthy little organism.
Since the tooth literally needs to cut through soft tissue to appear, the first symptoms will be redness and slight swelling of the gums in this place. In addition, the following symptoms may indicate the rapid eruption of the first teeth:
- Increased amount of saliva.
Over the course of a few weeks, you may notice that drool is dripping and even leaking from your mouth - this is normal during the teething period. - Itchy gums.
The tooth that is preparing to appear irritates the gums, causing itching and unpleasant pain. The child, trying to reduce discomfort, more often puts toys and pacifiers, various other objects and his hands into his mouth. - Appetite and sleep disturbances.
Unrelenting itching prevents the child from falling asleep and prevents him from eating properly. - Heat.
Some children experience an increase in temperature during this period; be careful; if the fever does not subside for more than two days, consult a doctor. - Stool disorder.
Diarrhea often accompanies the appearance of the first teeth, but you should also be very careful with it. If it intensifies, is too intense, or lasts more than two days, or is accompanied by a change in the color and smell of the stool, be sure to tell your doctor. - Symptoms of ARVI.
Since a cutting tooth causes inflammation in the oral cavity, it is quite logical for a runny nose and cough to appear. The main thing is not to confuse these symptoms with a real disease.