Content:
- Tooth enamel: general characteristics and properties:
- Possible reasons:
- What to do if your child’s baby teeth are brown.
1.1. Maturation of enamel.
2.1. Plaque. 2.2. Enamel hypoplasia. 2.3. Fluorosis. 2.4. Caries. 2.5. Other reasons.
Regardless of its cause, such a problem is a mandatory indication for comprehensive diagnostics. Moreover, we are talking not only about visiting the dentist, but also about consulting a pediatrician and highly specialized specialists, since brown plaque on children’s baby teeth can be the result of either a banal lack of hygiene or any diseases.
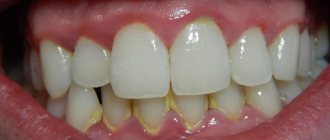
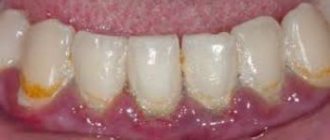
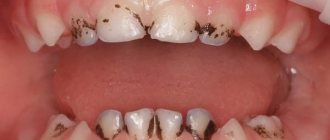
Plaque turns brown
But, if hygiene procedures are neglected for long enough, it comes to the appearance of a brown coating. This stage is the stage of tartar, which can only be removed in the dentist’s office.
This plaque forms for one reason: the acid that gets on the teeth settles on the teeth. In this case, we can also often talk about the presence of dysbacteriosis or dental hypoplasia in the child.
Other reasons that may provoke the formation of such plaque:
- the presence of worms in the child’s body;
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system;
- a fungal infection that develops in the oral cavity.
To defeat a disease, you must first accurately determine its causes and development factors. Only a doctor can do this.
Tooth enamel: general characteristics and properties
This is the hardest and most durable tissue in our body, its thickness on the outer surface reaches almost 2 mm. It consists of many layers formed at various stages of mineralization and has a crystalline structure. The chemical composition is represented predominantly by apatites, calcium and phosphorus predominate from inorganic compounds, and proteins, lipids and carbohydrates from organic compounds.
The main function is to protect dentin from external factors: mechanical, chemical and temperature stimuli. Thanks exclusively to this tissue, teeth can fulfill their main purpose - grinding and chewing food.
Despite its extraordinary strength, enamel is permeable to water and many organic and inorganic substances contained in saliva. It has been found that the degree of permeability for much-needed connections depends on several factors. If we talk about temporary occlusion, this is:
- condition of the oral cavity;
- nutritional features;
- long-term treatment with certain medications (in particular, tetracycline antibiotics);
- features of intrauterine development.
Enamel maturation
The composition of the protective tissue covering dentin is constantly changing, which is associated with age-related characteristics. Throughout the year after teething, there is an active accumulation of calcium and phosphorus, and during this period it is extremely important to receive all the necessary elements with food or multivitamin preparations. It has been proven that a sufficient content of microelements prevents the development of caries.
Brown plaque in children of the first year of life
But what to do if a brown plaque appears in a child who has never eaten solid food before? After all, this problem can also occur in children under one year old.
In such a situation, children's doctors - both pediatricians and dentists - talk about the so-called “bottle caries”. Its cause is drinking sweet milk from a bottle before bed. At night, salivation decreases and becomes less than during the day. Therefore, the remains of milk remain on the teeth for a long time, undergo oxidation and lead to the fact that the baby’s milk teeth are covered with plaque, which quickly transforms into caries.
In addition, some parents have the habit of licking the pacifier before letting their baby suck on it. It would seem that this is a very harmless manifestation of parental care, but it also leads to plaque, because bacteria from the adult’s mouth enters the child’s mouth. And adults have much more bacteria in their mouths than children.
It must be remembered that during this period - when the child is especially defenseless - the health of his oral cavity depends on his parents. First of all, you need to constantly check the condition of your baby’s baby teeth. If plaque has already formed on them, it is recommended to purchase special rubber brushes for infants and use them to clean off the plaque.
You can also resort to a more budget-friendly option - wrap the tip of your finger with a gauze bandage and use it instead of a brush. The main thing is that plaque is regularly cleaned from the baby’s teeth.
Possible reasons
The white color of the enamel layer indicates not only the absence of serious problems with the oral cavity, but also the normal state of health of the child as a whole. Brown baby teeth are an abnormal phenomenon that requires mandatory diagnosis and consultation with a pediatric dentist. Sometimes such a problem “goes away” along with a change in bite, but in many cases such a violation becomes the cause of numerous pathologies in the already permanent dentition.
Plaque
It is a dense formation consisting of proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and inorganic substances, which are an excellent environment for the development of bacterial flora. It is predominantly concentrated in the cervical region (in the place where the dentin comes into contact with the gum), in the fissures of the molars. Dealing with this problem is simple: all you need to do is follow the rules of daily hygiene. Otherwise, a brown coating appears, and it is not always possible to remove it yourself.
Enamel hypoplasia
It develops due to disturbances in the metabolic processes of formation and mineralization, often even before eruption and even during intrauterine development. The etiology of the disease may be associated with:
- severe infections suffered in infancy;
- rickets;
- nutritional dystrophy;
- endocrine disorders;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
The disease most often affects canines and premolars and is accompanied by the appearance of spots, depressions, and grooves of various shapes and sizes. In severe cases of the disease, the child complains of pain during hygiene procedures and reacts to the temperature of food.
Fluorosis
Fluoride is necessary for the full formation and development of both temporary and permanent teeth. But its excessive intake into the body (as a rule, this occurs due to the increased fluoride content in drinking water - up to 1.2–1.5 mg/l or more), especially with a concomitant calcium deficiency in food, leads to the opposite effect - gradual destruction of the enamel coating. This is what causes brown baby teeth to appear.
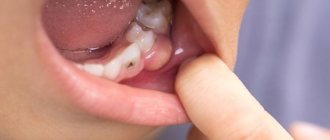
Caries
It develops against the background of gradual “dissolution” of enamel and damage to dentin by microbial flora. Recently, caries is diagnosed much more often. Experts explain this by the action of various unfavorable factors that prevent the maturation and resistance of the enamel coating. These include:
- changes in the composition of the oral microflora;
- excessive consumption of sweets;
- decreased secretory activity of the salivary glands;
- unbalanced diet;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules.
Other reasons
- hemolytic jaundice: indirect bilirubin formed during hemolysis of red blood cells and causes brown plaque on baby teeth in children;
- taking certain antibiotics (especially from the tetracycline group), drugs with a high iron content by the mother in the second half of pregnancy or by the child during the formation of the bite;
- chronic inflammatory process of the gums and oral mucosa.
Plaque accompanied by dental caries
Very often, caries and brown plaque accompany each other. At the same time, the first carious cavities can occur in children of two years of age and, in rare cases, even earlier. The more sweets a child eats, the more milk he drinks (especially from a bottle) at night, the worse the situation with nutritional rationing and teeth brushing - the greater the likelihood of developing caries due to plaque on the teeth.
The appearance of caries indicates the beginning of the process of demineralization of teeth and their destruction. As a result, cavities appear inside the teeth. Obviously, the main cause of caries is dental plaque, which is formed due to acids, microbes and bacteria that enter the baby’s oral cavity.
Parents should know how caries differs from plaque in order to be able to contact a pediatric dentist in a timely manner.
When the number of lactobacilli and streptococci increases sharply, the plaque develops into a carious lesion. It begins to rest against the gum tissue and becomes darker and darker. It is under these conditions that anaerobic bacteria can multiply. An inflammatory process develops, which over time - in the absence of therapy - can develop into more serious stages. In addition to the fact that the child will begin to suffer from headaches, he may develop: pneumonia, problems with the digestive system, and even blood poisoning.
Table. Differences between caries and plaque
| Sign | ||
| Depth of process development | Visually, it seems that the process is happening inside the tooth | Visually, it seems that the process takes place outside the tooth - on its enamel |
| Presence of haze | A tooth affected by caries becomes dull on the outside. The surface of the tooth becomes lighter than before | The tooth does not acquire a matte tint |
| Changes in the contours and surface of the tooth | If you take a toothpick and run it over a tooth, you can feel uneven—stepped—edges, roughness, or porosity. | They don't change at all |
However, if there are doubts about whether the child has plaque or caries, it is better if they are dispelled by a dentist.
What to do if your child's baby teeth are brown
The scope and scope of therapeutic measures is determined only by the dentist after an examination. Usually this:
- correction of nutrition, introduction of foods rich in calcium into the diet, limiting the consumption of sweets and baked goods;
- training in oral hygiene rules;
- taking multivitamins;
- the use of rinsing solutions (these can be ready-made medications or self-prepared decoctions of chamomile, calendula, etc.);
- professional plaque removal;
- filling (if the volume of work is large, this procedure is sometimes performed under general anesthesia).
Modern pediatric dentistry allows you to painlessly and without unnecessary stress cope with the problem of brown baby teeth and prevent damage to an already permanent bite.
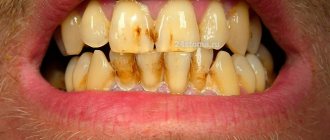
Why do teeth darken?
When a child develops dark plaque, this indicates the proliferation of pathogenic microbes that are deposited on the tooth enamel.
Black deposits may be a sign of:
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes mellitus;
- helminthiasis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- immunity disorders.
Dark plaque on a child’s tooth enamel appears due to dental pathologies:
- tartar;
- caries;
- mineral deficiency;
- enamel hypoplasia;
- malocclusion.
The cause of tooth discoloration may be the effect of dyes, a disorder in the intrauterine development of the child, or a genetic predisposition.
Treatment methods: dentist recommendations
Attention! Only a qualified doctor can determine the exact cause of brown plaque on teeth. If there is no caries in the oral cavity, then a teeth cleaning procedure will be prescribed.
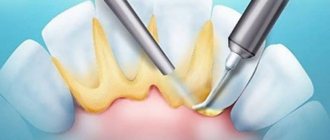
Cleaning methods:
- It is possible to clean the enamel using a manual instrumental method. It is used in cases where jet or ultrasonic cleaning cannot be used due to contraindications. In this case, the child’s teeth are cleaned with special instruments. The procedure takes from half an hour to two hours.
- Ultrasonic cleaning occurs using a scaler. It transmits sound vibrations to replaceable tips, with the help of which plaque is removed. The session is carried out under local anesthesia. Duration: about an hour, but can last two. This procedure is not performed on very young children.
- Blasting used in the case of removing plaque caused by food dyes (Coca-Cola, tea, Pepsi-Cola, candy, some juices, etc.). This method uses fine abrasives and is called “Air Flow”. Plaque is removed from teeth using a directed flow of air, sodium bicarbonate and water. The procedure is contraindicated in the following cases:
- the presence of any damage or inflammation in the oral cavity;
- age 0-7 years;
- existing chronic diseases such as asthma, bronchitis or emphysema.
Attention! Before any procedure, the child must be examined. The doctor should be warned about the presence of existing diseases.
For young children, doctors treat baby teeth with silver or fluoride. This method is relevant if there is no caries, gum damage or inflammation. Silver disinfects germs and protects tooth enamel, and fluoride strengthens it.
Teeth affected by caries should be treated without fail. The doctor will clean the carious cavities and fill them. If some teeth cannot be saved, they will be removed.
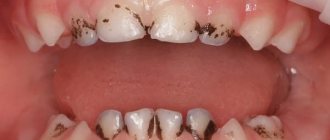
Why do baby teeth turn black?
When starting a conversation about why baby teeth turn black, let us remember that children’s teeth have some differences from “adult” (“permanent”) teeth. The structure is fundamentally the same: crown, neck and root. But the enamel is thinner, and the pulp chamber of baby teeth is larger than that of permanent teeth. As a result, children's teeth are more susceptible to pathogenic effects.
Perhaps the most common cause of blackening of baby teeth (dark spotty formations appear on the teeth, sometimes quite extensive, often covering the area above the gum) is caries. Regarding baby teeth, the expression “bottle caries” is known. This name is associated with night feedings or with the baby’s habit of falling asleep while sucking on a bottle, for example, with formula milk. In this case, tooth enamel is greatly exposed to negative/aggressive factors, and conditions favorable for the progression of the disease appear. Since the enamel of children's teeth is quite thin and has little resistance, caries spreads quickly and affects a large part of the tooth.
A lack of vitamins and minerals in the child’s body can contribute more to this pathological process.
In addition, from an early age it is necessary to pay due attention to proper oral hygiene (insufficient or incorrect hygiene will almost certainly lead to the appearance of carious lesions).
Adults remember from their childhood that sweets are harmful to teeth. First of all, this phrase is completely true; secondly, it does not lose its relevance. When consuming sugary foods or drinks, the most favorable environment for caries is formed; Accordingly, you should not overindulge in sweets.
Other possible causes of darkening of baby teeth (less common):
- A similar phenomenon can occur as a result of traumatic damage to a tooth;
- The appearance of stains on teeth, which subsequently darken, may be due to exposure to some substance (for example, fluoride - for fluorosis, or antibiotics);
- As a result of the course of chronic diseases of other organs.
What to do if baby teeth start to turn black? The answer here, by and large, is one: go to the doctor. Let's say in more detail why the answer turned out to be so unambiguous.
- First of all, it is the doctor who will accurately determine the cause of darkening of the teeth. And the elimination of a pathological phenomenon must proceed from the cause of its formation.
- If caries has developed, then there is no doubt: you need the help of a dentist, and preferably as early as possible.
- If the blackening of teeth is associated with insufficient oral hygiene, then its correction is required. The dentist’s participation in this issue is also necessary: it is the specialist who will understand what is “wrong” with existing hygiene procedures and give recommendations aimed at correcting the current situation.
- You may need to clarify your balanced diet. But then the question arises: what should constitute a balanced diet in a particular case? And to answer this question, the participation of a specialist is necessary. The same applies to vitamin-mineral complexes. There are many options available in pharmacies now. You can choose the best one only with the help of a specialist.
- If a child is afraid to go to the dentist, he will still have to go. In this case, you can go to the doctor in advance (without the child), explain the situation, and the doctor will tell you how to act in this case. The sooner a child acquires the habit of visiting the dentist, the stronger his correct preventive skills will be in the present and future, and this is the key to “dental longevity.”
If you have questions about children’s dental diseases, you can contact the specialists of the Healthy Smile network of clinics.
Bacterial plaque on teeth: causes
Soft or, as it is also called, bacterial plaque has a soft consistency, so it is easy to get rid of it with the help of an ordinary toothbrush. The main place of its accumulation is the neck of the teeth.
Harder plaque that cannot be removed with a brush is called tartar. It occurs during the mineralization of soft plaque with phosphorus and calcium salts present in saliva.
Why does plaque form?
There are constantly a huge number of bacteria in the mouth, which, firstly , multiply, and secondly , leave behind waste products. Even if you brush your teeth regularly, plaque cannot be avoided: within 6 hours after thorough brushing, you can easily notice, without resorting to the use of specialized equipment, a bacterial mass on the surface of the tooth enamel. A surge in microbial activity is observed immediately after eating: leftover food in the mouth forces bacteria to begin intensive processing.
At the same time, even small pieces of food that are invisible to the human eye are enough for microorganisms: they can feed on a film consisting of carbohydrates and proteins that invariably remains on the surface of the teeth after eating, and on food debris that gets into the spaces between the teeth. In this regard, it is imperative to brush your teeth for 15 minutes after each meal, since the mass of bacterial plaque can increase several times in volume in 1-2 hours. Plaque accumulates especially intensely on the necks of teeth in people who like to snack on a bun or something sweet between main meals.
Almost immediately after the soft plaque appears, the process of mineralization begins, as a result of which it gradually hardens. The period of primary mineralization (i.e., when the plaque, in simple terms, “sets” but still remains loose) is 10-15 hours. When the plaque finally hardens, its surface becomes ideal for the formation of deposits.
How to clean at home?
Most children really don't like visiting the dentist, so you can try to get rid of brown plaque on your teeth at home.
Activated carbon
- You should take one tablet of coal and grind it to a powder.
- Then add a little water and stir thoroughly. You should have the consistency of a paste.
- Apply the resulting mixture to a brush and brush your teeth well with it.
- After this, you need to rinse your mouth to completely wash off the activated charcoal.
Baking soda
- You need to sprinkle a little baking soda on your baby's brush.
- Brush all teeth using gentle movements.
Baking soda is a good bleacher; in addition, it perfectly disinfects the oral cavity and can dissolve tartar.
Strawberry puree
The most “tasty” way that children really like.
- A handful of fresh strawberries should be washed and mashed.
- Apply the resulting puree to your teeth and leave for a while.
The acid contained in the berries should dissolve the brown coating.
Hydrogen peroxide
- Mix a teaspoon of 3% hydrogen peroxide with 200 ml of clean water.
- Soak a cotton pad in the solution and gently wipe the child’s teeth with it.
- After the procedure, rinse your mouth thoroughly.
Orange
This fruit contains acid that can dissolve plaque.
- The orange should be cut into slices and rubbed on the tooth enamel.
- After a few minutes, brush your teeth.
If there is damage to the gums, then this method will not work.
Attention! Any of the homemade cleaning methods should not be used very often so as not to damage tooth enamel. If the brown plaque does not disappear, the child must be shown to a doctor.