Anatomy of the larynx
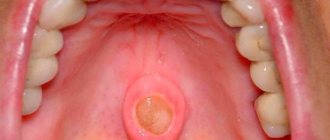
In an adult, the larynx is located at the level of the IV-VI cervical vertebrae along the midline of the neck. At the top it comes into contact with the hyoid bone, at the bottom it passes into the trachea, at the back it is covered with fiber and communicates with the pharynx. The anterior surface of the larynx is covered with muscles, fascia and skin.
The organ has a complex anatomical structure - it contains cartilage, ligaments, many muscles and joints. The large thyroid cartilage, also called the Adam's apple, is palpated on the neck and protrudes significantly forward in men.
Functions of the larynx:
- respiratory – regulation of external respiration, its depth and rhythm;
- insulating (protective) - protection of the respiratory tract from food entering during swallowing, harmful impurities from the air (for this, a spasm of the larynx occurs), evacuation of foreign particles trapped in the respiratory tract by coughing;
- vocal (phonatory) - the formation of vowels and parts of consonant sounds when air passes through the glottis.
Laryngeal cancer is a malignant neoplasm, most often developing from squamous epithelium. Localized in all parts of the organ.
Morbidity statistics
Laryngeal cancer accounts for 2.6% of all cancers. It is in first place in terms of incidence among head and neck tumors. In 95% of cases, malignant lesions of the larynx are squamous cell carcinoma, 2% each are glandular cancer and basal cell carcinoma, and 1% are rare types of cancer.
Men are more susceptible to the disease - they are diagnosed 9-10 times more often than women. 80-95% of patients are men from 40 to 60 years old. Most of them are heavy smokers.
The survival prognosis directly depends on the stage at which the cancer is detected and its location. If the tumor is detected at stage I, the five-year survival rate is 85%, at stage II – 70%, at stage III – 60%, at stage IV it decreases to 20%.
When chemoradiotherapy is started in the early stages, stable remission is achieved in 85-95% of cases, in late stages - in 30-40%.
Neoplasms of the upper part of the larynx give metastases to regional lymph nodes in 35-45% of cases, of the lower part - in 15-20%. In the area of the vocal cords, the lymphatic network is less developed, so the tumor in this area metastasizes rarely and late.
Prevention
Cancer can be prevented by following a number of recommendations from experts. First of all, it is important to properly care for your oral cavity and visit the dentist in a timely manner. The doctor keeps your teeth clean and monitors the condition of your gums and soft tissues twice a year.
Since HPV is a significant factor in the development of oropharyngeal cancer, it is important to reduce the risk of infection. To do this, it is necessary to exclude promiscuity and get a vaccine.
Experts recommend giving up bad habits and completely quit smoking. Immediately after eating, you should rinse your mouth and brush your teeth twice a day. A balanced diet is the key to health, so you should consume more vegetables and fruits every day, eat whole grain bread, and it is better to avoid processed meat, legumes and chicken.
Bibliography:
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer: Screening. 09/2017. Accessed at www.cancer.net/cancer-types/oral-and-oropharyngeal-cancer/screening on February 21, 2022.
- National Cancer Institute. Oral Cavity, Pharyngeal, and Laryngeal Cancer Screening (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version. February 9, 2022. Accessed at www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/hp/oral-screening-pdq#section/_1 on February 21, 2022.
- International Union Against Cancer (UICC). Lip and Oral Cavity. In: UICC TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, 7th Edition. 2009:328.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®), Head and Neck Cancers, Version I. 2022 - February 15, 2022. Accessed at www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/head-and-neck .pdf on February 21, 2022.
- American Cancer Society. Facts & Figures 2022. American Cancer Society. Atlanta, Ga. 2022.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2022. Atlanta, Ga: American Cancer Society; 2022.
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Oral Cavity and Pharynx Cancer. April 2022. Accessed at https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/oralcav.html on February 22, 2018.
- National Cancer Institute. Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer Treatment (Adult) (PDQ®)–Patient Version. January 29, 2022. Accessed at www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/patient/adult/lip-mouth-treatment-pdq on February 22, 2022.
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: new avenues of treatment? // Braunschweig1 , A. Lewandrowski1 , D. Smeets1 , MV Bolotin2
- Bolotina L.V., Vladimirova L.Yu., Dengina N.V., Novik A.V., Romanov I.S. Practical recommendations for the treatment of head and neck tumors. Malignant tumors. 2022.
Causes and risk factors
Laryngeal cancer, like other cancers, develops from mutated cells of normal tissues or benign tumors. Cell malignancy, or malignancy, occurs under the influence of external factors; there are also diseases that have a high risk of degeneration.
External factors that provoke the occurrence of laryngeal cancer:
- smoking and chewing tobacco;
- drinking alcohol;
- occupational hazards - dust, high and low temperatures, benzene vapors, petroleum products, phenol resins.
Diseases prone to malignancy:
- long-standing papillomatosis;
- fibroma with a wide base;
- leukoplakia;
- pachydermia;
- dyskeratosis;
- ventricular cysts;
- chronic inflammatory processes.
Causes of development of malignant tumors in the respiratory tract
As mentioned above, the main causes of the development of respiratory tract cancer are unfavorable factors of long-term exposure - smoking (active passive), polluted air, the presence of chronic diseases, etc. Moreover, scientists have proven that the development of lung cancer can be caused by microorganisms that affect the cell cycle and promoting uncontrolled cell division:
- human papillomavirus;
- JC virus;
- simian virus;
- BK virus;
- cytomegalovirus.
Even the presence of several factors does not always cause cancer; moreover, no one can guarantee that you will not get it, even if you follow all precautions.
According to scientists, having good immunity plays a big role in reducing the risk of respiratory tract cancer; the chances of a tumor appearing significantly increase in people who have a high susceptibility to diseases. According to statistics, men suffer from lung cancer 10 times more often.
Symptoms of laryngeal cancer
The first signs of a tumor are nonspecific, they are similar to the symptoms of many inflammatory diseases, and it is difficult to suspect an oncological process from them and, even more so, to determine its location.
Early symptoms:
- low-grade fever;
- weakness, fatigue, general malaise;
- drowsiness.
Late signs vary depending on where the neoplasm develops.
Supraglottic cancer is characterized by:
- dryness and sore throat;
- discomfort and pain when swallowing, radiating to the ear on the side of the tumor, choking;
- sensation of a foreign body in the larynx;
- dull voice.
Symptoms of a neoplasm on the vocal cords:
- change in voice, loss of sonority and melody;
- hoarseness and hoarseness.
- When a tumor develops in the subglottic region, patients complain of:
- paroxysmal dry cough;
- voice disorders.
In the late period, when cancer of any localization grows into the lumen of the larynx, difficulty breathing, attacks of suffocation, putrid breath, and cough with blood clots appear. Due to discomfort when swallowing, the patient limits food intake, and exhaustion develops.
The sooner a person seeks help, the more effective the treatment will be. Even early signs (weakness, fatigue) should be a reason to visit a doctor. In this case, it is possible to diagnose the tumor at an early stage. If you experience coughing or difficulty swallowing, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Diagnostics
After an examination by an oncologist and a dentist, a number of examinations are prescribed:
- blood test for HPV. The study is carried out using PCR, sequencing or enzyme analysis. Confirmation of human papillomavirus changes tumor treatment tactics;
- endoscopic examination of the larynx and oropharynx using laryngoscopy and pharyngoscopy;
- cytological examination. During laryngoscopy, the doctor takes a scraping from the mucous membrane and sends it for analysis. The cellular composition of the tumor is determined;
- biopsy. The removed area is stained with eosin and hematoxylin, and then a reaction to the drug is observed;
- CT/MRI. Tomography clarifies the location and size of the tumor;
- PAT. Shows the spread of the tumor to surrounding organs, as well as metastasis to the chest organs.
Classification
Classification of laryngeal cancer is carried out according to different criteria.
Localization of education
There are three anatomical sections of the organ:
- supraglottic (vestibular);
- middle (vocal cords);
- subglottic
Cancer of the supraglottic region develops most often - from 65% to 70% of all laryngeal tumors. It appears on one side and quickly spreads to the other. Neoplasms in this area are characterized by aggressive growth and rapid appearance of metastases.
A tumor of the middle section is diagnosed in 25-30% of cases. Usually develops on one vocal cord. Less aggressive than in the supraglottic. Voice disorders force patients to see a doctor quickly, which is why ligament tumors are often detected in the early stages. Localization of the formation facilitates surgical access to it.
Neoplasms of the subglottic region are the rarest - approximately 2% of cases. At the same time, they are characterized by fairly rapid infiltrative growth, and their location complicates surgical access and increases the risk of injury to the vocal cords during surgery.
Stages of laryngeal cancer, Russian classification
According to the prevalence of the process, malignant lesions of the larynx are divided into four stages - I, II, III and IV, stage III has substages a, b, IV - a, b, c, d.
| Stage | Characteristic |
| I | The formation is limited in size and does not extend beyond the mucous membrane of one anatomical part of the larynx. |
| II | The process completely covers one anatomical part of the larynx (all layers can be involved), does not spread beyond its limits, and does not metastasize. |
| III | a – the tumor extends beyond one anatomical part of the larynx, spreads to adjacent tissues, and causes immobility of half of the larynx. b – in addition to the spread of cancer to neighboring anatomical areas, regional lymph nodes are affected: one fixed or several mobile enlarged nodes are detected. |
| IV | a – spread of the tumor to neighboring organs. b – the formation occupies a significant part of the larynx and penetrates into the underlying tissue. c – fixed metastases are detected in the lymph nodes of the neck. d – tumor of any size, metastasizes to regional lymph nodes and distant organs. |
Growth pattern
Exophytic cancer - grows into the lumen of the organ or outward. The formation usually occurs on the wall of the larynx and grows outward, blocking the lumen of the upper respiratory tract. It has no clear boundaries, the surface of the tumor is lumpy, with papillary growths.
Endophytic (infiltrative) cancer - grows inward, into the tissue of the organ. It looks like an infiltrate with ulcerations, without clear contours. Penetrates into the thickness of adjacent tissues.
Mixed - combines the features of exo- and endophytic growth.
Histological structure
Most often, laryngeal cancer arises from squamous epithelial cells. Glandular cancer, basal cell carcinoma and other rare types of tumor are diagnosed much less frequently. Some types are further subdivided:
- Squamous cell carcinoma : non-keratinizing – arises from non-keratinizing epithelium, grows quickly, has a high risk of metastases;
- keratinizing – develops slowly, metastases appear after a long period of time.
- poorly differentiated - it is difficult to determine the type of cells and tissues that make up the neoplasm, the tumor is characterized by a high degree of malignancy, grows quickly and metastasizes;
Recovery after treatment
Full recovery from CyberKnife treatment usually occurs within a few hours or days. A visit to the clinic is not required.
After the classic operation, the patient is left in the hospital under the supervision of a doctor, if necessary, taught to swallow, eat and speak again, and care for the stoma.
If you need a second opinion to clarify your diagnosis or treatment plan, send us an application and documents for consultation, or schedule an in-person consultation by phone.
Expert opinion
Diagnosis of laryngeal cancer
During the initial visit, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the patient’s life and illness, asks him about the presence of provoking factors, conducts a visual examination, palpation of the neck, indirect laryngoscopy - examination of the larynx with a mirror on a long curved handle.
If there is still suspicion of a tumor formation, the patient is prescribed direct laryngoscopy . This is an invasive diagnostic procedure during which the larynx, trachea, and bronchi are examined using a laryngoscope (rigid method) or a flexible fiberscope. As a rule, during direct laryngoscopy, a biopsy of the neoplasm is performed - biomaterial is taken for cytological and histological analysis.
of tumor markers SCC and CYFRA 21-1 is considered an effective diagnostic method . To analyze tumor markers, venous blood is taken from the patient.
To assess the degree of tumor invasion, damage to the lymph nodes, and the presence of metastases in distant organs and tissues, additional procedures are used: CT or MRI , PET scan , biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes , scintigraphy , radiography .
Primary diagnosis for suspected tumor in the throat
An examination for throat cancer begins with an external examination, during which the doctor carefully palpates the neck area, determining the presence of lumps and/or soreness. In addition, during the initial consultation, the specialist examines the oral cavity using conventional ENT instruments.
In some cases, it is possible to detect throat cancer, obtain material for analysis under a microscope, and draw the first conclusions about the stage of the disease even with these simple manipulations. However, more often than not, additional examination is required to clarify the diagnosis.
In particular, the primary diagnosis of throat cancer includes a detailed examination of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx using endoscopic equipment. If during such an examination suspicious areas are detected, tissue fragments are taken from them for biopsy.
Various devices can be used for endoscopic examination of throat cancer, including:
- Rigid laryngoscope. The use of this device makes it possible to examine the ligaments, subglottic region and trachea, as well as obtain material for biopsy analysis. Classic laryngoscopy is performed under general anesthesia.
- Nasopharyngolaryngoscope. This is a flexible and thin device that is inserted into the patient's throat through the nose. This procedure is quite comfortable and low-traumatic, so it is usually performed on an outpatient basis. Using a nasopharyngolaryngoscope, the doctor is able to examine areas of the larynx that are inaccessible when examined with a rigid laryngoscope.
If there is a lump in the neck area, a needle biopsy may be prescribed. This method makes it possible to detect throat cancer in cases where it does not grow in the cavity of the pharynx or larynx, but grows into the surrounding tissues. In addition, puncture can be used to determine whether there are tumor cells in nearby lymph nodes. This procedure is performed using a long and thick hollow needle, which is inserted through the skin and muscles into the problem area after preliminary anesthesia. The accuracy of the method increases control using ultrasound, CT or other imaging methods.
Treatment methods
For laryngeal cancer , radiation chemotherapy (rarely), targeted therapy , and surgery . A single method or an integrated approach can be used, depending on the stage of the tumor, its location, degree of aggressiveness, growth pattern, and extent of the process.
Conservative therapy
Almost always, the first stage of treatment is radiation therapy . It is used to treat cancer of the middle section of the larynx, which is highly radiosensitive, as well as for tumors of the upper and lower regions of the larynx of stages I-II. Radiation is sometimes combined with hyperbaric oxygenation - saturating the blood with oxygen in a special chamber. This procedure enhances the effect of rays on degenerated cells and reduces damage to healthy tissue.
Treatment of stage III-IV laryngeal cancer, localized in the upper region of the organ, begins with chemotherapy . Chemotherapy is ineffective for the lower and middle parts of the larynx.
Radiation and chemotherapy can be used in combination.
Targeted therapy is the directed effect of a drug on the epidermal growth factor receptor. In laryngeal cancer, a large amount of the EGFR receptor protein is often found on the surface of tumor cells, which stimulates cell division. The drug Cetuximab, used for targeted therapy of the disease, suppresses the activity of this receptor. The drug is administered intravenously, usually used in combination with radiation, and in later stages - together with chemotherapy.
Surgical treatment
Sometimes, for stages I-II of laryngeal cancer, conservative therapy is sufficient. If it turns out to be ineffective, as well as for tumors detected at stages III-IV, surgical intervention is recommended. Before surgery, radiation therapy is always indicated to reduce the size of the tumor.
For stage I-II tumors, doctors try to perform organ-preserving resection: hemilaryngectomy - removal of one vocal cord, supraglottic laryngectomy - removal of part of the larynx above the ligamentous apparatus.
In the early stages, laser removal of the tumor using an endoscope can be used. The advantage of this method is that it is less traumatic; the disadvantage is that it is not possible to take a tissue sample for histological examination.
In later stages of the disease, it is necessary to resort to radical operations: chordectomy - complete removal of the vocal cords, total laryngectomy. In this case, the patient completely loses his voice.
Auxiliary Operations
In addition to direct removal of the malignant tumor, other surgical operations are performed. When laryngeal cancer metastasizes to regional lymph nodes or there is a high risk of metastases, these nodes are excised along with the surrounding tissue. The operation is called a cervical dissection .
When the larynx is completely removed, the patient needs a tracheostomy , a surgically created hole in the trachea. When creating a tracheostomy, the upper end of the trachea is sutured to the skin of the neck.
If laryngeal cancer makes it difficult to eat, the patient will have gastrostomy tube placed directly into the stomach.
If necessary, after extensive surgery, reconstructive plastic - operations that allow at least partially restoring the functions of the removed organs.
Treatment of respiratory tract cancer
Oncology uses different methods for treating lung cancer; they are prescribed individually after passing all the necessary examinations.
Chemotherapy
Considered the most effective method of treating respiratory cancer, it involves the introduction of toxic drugs into the body that kill cancer cells and prevent their development. The center uses monochemotherapy and polychemotherapy. The treatment regimen is selected by the attending physician.
Surgical method
Includes several options:
- the tumor lesion and other damaged areas are completely removed;
- radical - used as an additional method in the form of radiation therapy, medications;
- palliative treatment - it is prescribed to hopelessly ill patients to relieve pain and provide psychological support.
Radiation therapy
It is prescribed in cases where, for some reason, surgical intervention is not possible. It is highly effective, the effect is only on the affected areas, and is prescribed even to seriously ill patients.
Fractionated radiotherapy
It is highly effective in the fight against respiratory tract cancer, has minimal side effects, the latest generation linear accelerator TrueBeam is used for its implementation, sessions are held daily at any time convenient for the patient, their number can range from 10 to 35, it all depends on the patient’s condition, stages of the disease, etc.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disease depends on how early the tumor is detected. Unfortunately, laryngeal tumors are often diagnosed late due to the nonspecificity of early symptoms.
Newly diagnosed stage III laryngeal cancer is 46.8%, stage IV – 17.0%. The mortality rate in the first year from the moment of diagnosis for lesions of the larynx is 24.2%.
A large number of patients develop resistance to radiation and chemotherapy. When conservative therapy is used, recurrent tumors occur in 20-40% of cases, the treatment of which is only possible through surgery.
Without treatment, laryngeal cancer lasts from one to three years. The prognosis of 85-90% of cases of complete recovery is given only if the tumor is detected early, treatment is started in a timely manner and completely completed.
Prevention of laryngeal cancer
Quitting smoking cigarettes, pipes, hookahs, and chewing tobacco is the basis for preventing the disease. Eliminating alcoholic beverages or reducing their consumption will help prevent not only laryngeal cancer, but also other pathologies.
There is an opinion that red meat and smoked meats increase the risk of cancer. You should reduce their number in the menu, eat fresh vegetables and fruits more often.
It is important to undergo medical examinations on time - medical examinations, medical examinations at enterprises. If you suspect a disease of the larynx, even if general symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.