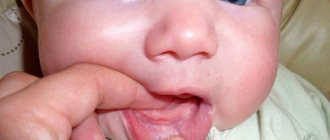
An acute inflammatory process, which, usually starting from the labia minora or majora, gradually spreads to the clitoris and vagina, is called vulvitis in medical practice. This pathological condition is accompanied by acute symptoms, which can manifest in the fair sex, regardless of age.
Vulvitis requires immediate consultation with a specialist, as it can lead to adhesions in the mucous membranes of the external genitalia, which subsequently causes serious problems in the intimate area, and in the case of the disease in young women, becomes a cause of infertility.
Causes of inflammation of the clitoris and labia
Most often, the pathology is of an infectious-inflammatory nature. Depending on the cause of the development of vulvitis, there are two main forms of the disease.
- Primary vulvitis. This inflammation is somewhat less common than secondary inflammation, and usually affects either patients of a younger age category or women in the postmenopausal period. The cause of the development of primary inflammation of the labia and clitoris is the following factors: failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene, too tight synthetic underwear, allergic reactions to shower gel or other hygiene products, mechanical damage to the external genitalia and hormonal imbalances. Little girls may experience similar inflammation if they have helminthiasis - infestation with worms.
- Secondary vulvitis . The most common form of inflammatory processes of the clitoris and labia resulting from infectious infection. Nonspecific pathogens of vulvitis include all representatives of opportunistic flora, which are normally natural inhabitants of female microflora - Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci, yeasts, etc. Specific infections include sexually transmitted infections. Secondary vulvitis occurs more often in young patients of childbearing age, as they are sexually active.
Causes of white vaginal discharge
Physiological factors
The appearance of discharge from the genital tract (leucorrhoea) is caused by the secretion of glands located in the vestibule of the vagina, the cervix. They produce a small amount of transparent mucus without a specific odor, but under the influence of sex hormones, the color and consistency of the secretion changes - it becomes light milky and viscous. If such discharge bothers you constantly or white discharge with a subjectively unpleasant odor occurs, you should seek medical help. The most common natural causes of whitish secretion from the vagina:
- Second half of the menstrual cycle
. A few days before the start of menstruation, scanty white, thick, odorless discharge, similar to glue, is observed. Leucorrhoea usually has a light milky color, less often a slight yellowish tint is noticeable. - Sexual intercourse
. To facilitate penetration into the vagina during sexual arousal, a large amount of viscous white mucus is produced. This secretion has a specific aroma, which is not considered a sign of a painful condition. - Pregnancy
. After 12-13 weeks of gestation, changes occur in the mucous membrane of the reproductive organs, the epithelium is renewed, and therefore white discharge is observed. A sour smell indicates pathological causes of the symptom.
Vaginal candidiasis (thrush)
With vaginal candidiasis, women notice a copious discharge of heterogeneous consistency with a sour odor, which in appearance resembles grains of cottage cheese. An increase in the amount of discharge is caused by sexual intercourse and water procedures. In the chronic process, patients complain of scanty cheesy discharge about a week before menstruation; with the onset of menstruation, the white discharge stops. A typical symptom is a combination of redness of the skin of the labia majora and minora, perineal itching, pain, and pain when urinating.
Genital tuberculosis
White discharge with a faint odor may indicate damage to the fallopian tubes and other parts of the reproductive system by Koch's bacilli. The discharge is scanty, thick, its appearance is not associated with the menstrual cycle. For most women, the interval between menstruation lengthens; young patients complain of the inability to become pregnant. White discharge in genital tuberculosis occurs against a background of mild nagging pain in the lower abdomen and low-grade body temperature.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
A common cause of whitish discharge with an unpleasant odor is taking medications that reduce local immunity in the vagina (antibiotics, corticosteroids). Vaginal discharge appears 5-7 days after the start of antibiotic therapy. White discharge is combined with itching in the vagina and perineum, painful sexual intercourse. Pathological secretions are associated with disruption of the vaginal flora and intensive proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. The causes of leucorrhoea during treatment with glucocorticoids are immunosuppression and activation of opportunistic flora.
Symptoms of inflammation of the clitoris and labia
The symptoms of the pathological process are vivid, so it is impossible not to notice it, and includes the following signs:
- itching, burning and soreness of the affected area;
- tissue swelling;
- hyperemia (change in color) of the skin;
- development of small ulcerative lesions;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse.
All of the above symptoms usually intensify during urination and during intensive walking. Lack of rational and timely treatment can lead to the spread of an infectious and inflammatory process to the tissue of the inner thighs and vagina.
Treatment
After confirming the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. The prescription of medications depends on the type of infectious agent. Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Let's consider the principles of therapy depending on the cause of the pathology:
- The accumulation of smegma does not require special medical intervention. It is enough to correctly follow the rules of personal hygiene.
- If hormonal imbalances are detected, the endocrinologist prescribes specialized medications. After adjusting the hormone levels, the plaque disappears.
- Genital herpes has common treatment principles with any herpetic infection. The drugs Acyclovir and Zovirax are prescribed. These medications have a general (tablets) and local effect (creams, ointments). Immunomodulatory medications are added to antiviral therapy. During treatment, it is important to strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene. After water procedures (washing), wipe the damaged areas dry, do not rub. Wash your hands after touching an infected area to avoid spreading the infection.
- Bacterial vaginosis is treated with topical antibiotics. Metronidazole is prescribed in the form of suppositories. Drugs that restore the natural microflora (Lactofiltrum) are added to therapy.
- Thrush caused by a fungus of the genus Candidiasis is difficult to treat. Self-medication is unacceptable; it can lead to a chronic process. There is local and general treatment. Local products include suppositories and vaginal tablets of various effects:
- Pimafucin – causes the death of fungi;
Clotrimazole, Antifugon, Canesten - the components of these drugs destroy the candida membrane;
- Isoconazole disrupts the permeability of the cell membrane and is involved in the elimination of itching;
- Terzhinan, Polizhinaks - moisten before using them.
Along with vaginal products, general medications are used. Complex therapy allows you to achieve maximum effect in the shortest possible time. These medications include: Ketoconazole, Fluconazole, Natamycin, Miconazole.
Diagnosis and treatment of inflammation of the external genitalia
The diagnosis can only be made by a gynecologist. At the same time, no special diagnostics are needed at the first stage. The doctor will immediately notice inflammation during a routine gynecological examination. Next, the doctor determines the cause of the inflammation, after which a treatment regimen is selected.
Depending on the cause of the development of the pathology - an allergic factor, injury, incorrectly selected underwear - it is enough to simply limit the direct contact of the provoking agent with the organs and apply symptomatic therapy (local treatment that relieves unpleasant symptoms). You can easily identify this cause by donating blood for allergies. The analysis will show the cause due to the presence in the blood of special antibodies that are formed only during allergic reactions.
When diagnosing the infectious nature of the disease, microbiological culture is carried out on nutrient media in order to identify the causative agent and the correct selection of antibiotic therapy. To do this, the gynecologist takes swabs from the genital tract and sends them to the laboratory.
There, they first determine the type of infection, and then test different drugs on the samples. Since almost all pathogens of sexual diseases easily adapt to medications, choosing pills that will help you completely recover is not easy. Sometimes specialists go through up to a dozen different medications.
Unfortunately, inflammation is rarely caused by a single pathogen; more often, the cause is a whole bunch of infections, starting with thrush and ending with gonorrhea. In such cases, it will not be enough to simply take smears - the examination will continue further. You will have to donate blood for syphilis, hepatitis and undergo a pelvic ultrasound, as the process quickly spreads through the genital tract, affecting internal organs.
Diagnostics
For any discomfort in the intimate area, it is recommended to consult a doctor; white plaque on the labia is no exception. The gynecologist examines for the presence of plaque on the labia majora and minora. If there is a suspicion that the problem is infectious, appropriate tests are taken.
A smear is prescribed on the flora of the vagina and surrounding tissues, which is necessary to identify the pathogen. Normally, lactobacilli are contained (90% of the total number of identified microorganisms), representatives of the genus Candida can be found in single quantities. The sample is viewed under a microscope. The microflora is inoculated onto nutrient media. This allows you to determine the type of fungus and determine sensitivity to medications.
There is also another research method - colposcopy (a colposcope is used).
Sakania Luiza Ruslanovna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist
Ask a Question
The gynecologist applies Lugol's solution to the vaginal walls. If white spots the size of semolina appear against its background, then a diagnosis of thrush is made.
If a patient is suspected of having sexually transmitted diseases, the doctor prescribes an appropriate examination. If candidiasis is provoked by a chronic pathology, the doctor refers the woman to the appropriate specialist.
Diagnosis of vulvar leukoplakia
Diagnosis of vulvar leukoplakia, in some cases, is difficult and requires some experience. The lack of experience among antenatal clinic doctors is associated with the rare occurrence of leukoplakia.
Diagnosis of vulvar leukoplakia and diagnosis are often carried out already in the later stages of the development of the disease.
For an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS of vulvar leukoplakia, gynecologists refer to the Women's Health Resort Clinic and women from many cities of Russia, near and far abroad, independently apply.
There is EXPERIENCE, there are RESULTS, there are ways of SUCCESSFUL treatment.
- Colposcopic examination (examination through a colposcope - a special microscope for examining the cervix and vagina WITHOUT PAIN). The Women's Health Resort Clinic uses ULTRA-modern Olympus colposcopes (Japan).
| Photo of cervical leukoplakia. Leukoplakia is defined as a white area at 12 o'clock on the dial |
- SCHILLER'S TEST (test with Lugol's solution for uniform staining of the mucous membrane of the cervix). Areas of leukoplakia on the cervix and vagina are not stained and are visible to the naked eye.
| Photo of cervical leukoplakia. The same case. After Schiller's test, the true size of the leukoplakia area is determined at 12 o'clock on the dial | |
| Photo of cervical leukoplakia. After the Schiller test, a large, unpainted area of cervical leukoplakia with transition to the vaginal vault is determined |
- Vulvoscopy (examination through a vulvoscope - a special microscope for examining the vulva WITHOUT PAIN).
| Photo of kraurosis and leukoplakia of the vulva, stage 2. The skin of the labia majora and pubis with white spots, roughened, with numerous microcracks |
- Test with special dyes and examination of the vulva, vagina and cervix in green light.
- BIOPSY - collection of a piece (fragment) of suspicious tissue with subsequent histological examination of the surgical material. At the Women's Health Resort Clinic, a biopsy is performed using a non-contact radio wave method WITHOUT PAIN.
- MICROSCOPIC examination of the flora of a smear from the urethra, cervix and vagina.
- CYTOLOGICAL examination of scrapings of the cervix and cervical canal for atypical cells.
- ASPIRATION of the contents of the uterine cavity followed by microscopic (cytological) examination of the aspirate. Aspiration of the uterine cavity in our Leukoplakia Treatment Clinic is performed using a thin, elastic probe WITHOUT PAIN.
- If necessary, separate diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal and the uterine cavity, followed by histological examination of the obtained material.
- Clinical blood test.
- Immunogram.
Diagnosis of vulvar leukoplakia in our Clinic during a full examination is 100% accurate.
| ONLINE about vulvar leukoplakia at BOOK ONLINE for leukoplakia treatment here. BOOK online for leukoplakia treatment here. Buy coursework for treatment by phone or here. |
Booking a course
Curdled discharge in women, causes of white curdled discharge
In women, vaginal discharge is as normal and natural as the production of gastric juice, saliva and other physiological secretions. In normal condition, the vaginal glands play a very important role for a woman’s body - with their help, the genital tract is cleansed, in addition, they prevent various kinds of infectious agents from getting inside.
By its nature, natural vaginal discharge completely depends on many factors: what age is the woman, what is the degree of her sexual activity, what is her hormonal status, etc.
Normally, vaginal discharge has the following characteristic features: - the discharge is either colorless or has a mild whitish or yellowish tint; - discharge is not abundant; - the consistency of the discharge is mucous or watery; — the smell is barely noticeable, sourish or completely absent.
However, in some cases, vaginal discharge is a sign that there is some kind of pathology in the woman’s genital area; in addition, they are the first symptoms of various gynecological diseases. If the consistency of the discharge has changed, a non-standard color or a foul odor has appeared, then this is a clear sign that some destructive process is taking place in the female body. One of the types of pathological vaginal discharge is white discharge with a cheesy consistency. In most cases, the presence of such discharge is a clear sign of the presence of candidiasis, or thrush - the most common fungal disease, during which the internal tissues of the genital tract, as well as internal organs, are affected.
Curdled discharge in women is the main sign of candidiasis
Genital candidiasis is one of the most common gynecological diseases. According to medical statistics, about 75% of women of reproductive age have encountered its manifestations. The cause of genital candidiasis is a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida, which normally is always present in the natural microflora of the internal tissues of the female genital organs. Thrush occurs when fungi begin to multiply faster, which leads to disruption of the normal environment of the reproductive tract.
The fungus can begin to actively multiply for the following reasons: - decreased immunity of the female body and, as a result, resistance to all infections; - long-term or uncontrolled use of a number of medications containing hormones or antibiotics; — signs of intestinal dysbiosis; - any stage of pregnancy; - wearing very tight underwear or synthetic underwear; - unreasonable or very frequent douching; - unfavorable external factors, for example, staying for a long time in rooms with high levels of humidity and temperature.
Signs of candidiasis are not only abundant milky-white discharge with a cheesy consistency, but also the following symptoms: - burning, irritation or itching in the vulva area. These sensations may intensify during sleep, as well as after a warm bath and urination; - painful sensations during sexual intercourse, as well as increasing irritation; - redness of the internal tissues of the vagina affected by the disease, the appearance of a pathological plaque on the epithelial tissues, which looks like cheesy white films.
Genital candidiasis is a disease that does not threaten women’s health in particular and her life in general, but its manifestations are very unpleasant, and this entails disturbances in both the psycho-emotional and intimate spheres. In addition, the appearance of candidiasis may be a sign that a woman has a more serious disease in her body, for example, diabetes mellitus or HIV infection.
With the help of modern treatment methods, curing candidiasis is not difficult. To treat mild forms of thrush, as a rule, local medications are used, for the treatment of aggravated forms - drugs that have a general effect. For local treatment of candidiasis, vaginal tablets, capsules, suppositories and ointments are used, which contain antifungal drugs: nystatin, pimafucin, clotrimazole, ketoconazole, miconazole. Fluconazole and itraconazole are used as general medications for the treatment of thrush.
During treatment of candidiasis, one should not forget about proper nutrition. With thrush, a woman should not eat foods that provoke yeast-like fungi to multiply. These are sugar, coffee, mushrooms, yeast dough, beer, carbonated drinks, spicy, fatty and spicy foods, sweet fruits, ketchup, mayonnaise, mustard, dairy products. It is necessary to eat boiled fruits and vegetables, lean fish and meat, fermented milk drinks, stale bread, legumes and cereals.
Other causes of curdled discharge in women
Cloudy-white, cheesy vaginal discharge can also appear with other gynecological diseases, for example, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, chlamydia. These diseases occur when pathogenic microorganisms - mycoplasmas and chlamydia - enter the body. If a woman suffers from one of these diseases, then the vaginal discharge has a dirty gray color and a strong, unpleasant odor.
From this we can conclude that if a woman experiences white, cheesy vaginal discharge, she should immediately contact a gynecologist for professional help, regardless of the reason for the discharge. In case of delaying a visit to the doctor, as well as in case of self-medication, you can only aggravate the course of the disease, which will lead to difficulties in the process of its subsequent treatment.
Infectious causes of white plaque on the penis
They differ according to the type of pathogen:
Candidiasis
This is a fungal infection. Occurs after long-term use of antibiotics or when infected during sexual intercourse. Candida is usually found in a woman's vagina. During intercourse, microtraumas are formed on the skin of the genitals, facilitating the penetration of infection. The plaque looks like white lumps, has a sour smell, and is accompanied by itching. If treatment is not started on time, pain when urinating and ulcers develop.
Bacterial balanoposthitis
Caused by bacteria that normally live on the surface of the skin, most often streptococci and enterococci. White coating on the frenulum of the penis, on the head. It has a creamy density, combined with red spots. Itching and discomfort increase after urination or sexual intercourse. If treatment is delayed, the infection penetrates and affects the bladder, ureters and kidneys.
In the photo: candidiasis balanoposthitis
Gonorrhea
The plaque is concentrated around the head of the penis. In addition, there will be abundant purulent discharge from the urethra, an unpleasant odor, a deterioration in general health, and painful urination. There may be blood in the urine.
Chlamydia
The head of the penis itches, a white coating is located under the head of the genital organ, abundant, translucent. The disease is accompanied by the discharge of yellowish-green mucus from the urethra and pain.
Syphilis
The appearance of a whitish coating on the head is one of the signs of this complex disease. Characteristic rashes and lumps are not necessary and a person may not notice them. Therefore, it is very important to contact a urologist in time and get tested.
Why see a doctor?
The doctor first assesses the nature of the discharge and interviews the patient. A gynecological examination and tests (blood, smear) are prescribed. The absence or presence of swelling, inflammation, and other pronounced symptoms that can be determined during the examination are taken into account. If necessary, a rectal or bimanual vaginal examination is performed.
To avoid the appearance of unusual vaginal discharge, it is first of all important to observe good personal hygiene and not be promiscuous. Attentive attention to nutrition and the use of medications is another step towards women's health. Every woman should visit a gynecologist at least once a year for preventive purposes.
At the Diana Medical Center, each patient can receive professional advice from an experienced gynecologist, undergo comprehensive diagnostics and a course of individually selected treatment. Professionalism, modern equipment and affordable prices are the main advantages of the Diana multidisciplinary clinic.
Types of leucorrhoea
Depending on the place of formation, leucorrhoea is classified into the following types:
- Vaginal
. They usually appear after suffering from inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. Discharge in this case can be the result of transudation (leakage of the liquid part of the blood) into the lumen of the vagina, caused by mechanical or chemical effects on the mucous membrane of the organ. During the oncological process, vaginal discharge can be sanguineous. - Cervical
. Symptoms of diseases of the cervix, endocrine system, tuberculosis. Depending on the origin, they may contain pus or blood impurities. With cervical cancer, leucorrhoea usually has a liquid consistency. - Uterine
. The appearance of uterine leucorrhoea indicates endometritis or tumors. The acute course of endometritis is accompanied by purulent discharge, and the chronic form is watery. With cancer of the uterine body, the uterine discharge is watery, and during the disintegration of the tumor it becomes red-gray in color. - Pipe.
Tubal discharge is usually watery and yellow in color. Tubal leucorrhoea appears due to cancer of the fallopian tube. Their consistency is watery with an admixture of blood. This disease is quite rare and is the result of advanced inflammation of the cervix or fallopian tubes.
White coating on the penis: when is this normal?
Why might a white coating on the penis be normal? Due to the increased production of a special male secretion - smegma. It is produced by tyson (preputial) glands under the foreskin - a type of exocrine sebaceous glands. Smegma facilitates the sliding of the foreskin when exposing the head of the penis. The secretion mixes with exfoliated epithelial cells, forming a white coating on the head of the penis. The problem is more common in men who have not undergone circumcision. Increased secretion of the preputial glands does not require special treatment. But if the rules of hygiene of the genital organs are not followed, it can lead to inflammation (balanitis, balanoposthitis) and oncopathology.