Materials Manufacturing of removable dentures Manufacturing of fixed dentures Service life
The absence of teeth affects not only the function of chewing and speech, but also the emotional state, socialization and self-esteem. Prosthetics restores physiological functions, equalizes the emotional background, and increases self-confidence.
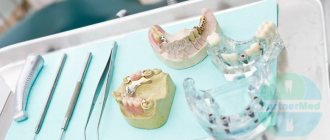
Making dentures is the result of a joint effort between a dentist and a technician. Each stage of work affects the final result. The manufacturing process depends on the type of structure and materials used.
There are the following types of restorations for restoring the dentition:
- Removable
. They are divided into full and partial. Full ones are used for edentia, when there are no teeth left at all. Partially removable ones are attached to the remaining teeth, which serve as support. - Fixed
. Unlike removable structures, inlays, crowns and bridges are fixed in the mouth for the entire period of use. They are removed only to replace them with new ones. - Conditionally removable
. Such dentures can be removed, but under certain conditions. The removable jaw is fixed on implants. You will not be able to remove the restoration yourself. The dentist will do this without difficulty, and after the necessary procedures, he will put it back.
Materials for the manufacture of prostheses
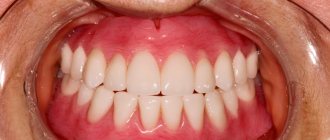
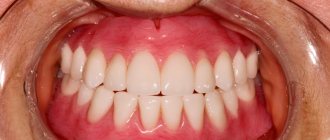
For permanent restorations, metals, ceramics and zirconium dioxide are used. Metal-ceramic crowns consist of 2 layers: a metal base, which is lined with a ceramic composition. Thick double walls require strong turning. Zirconium crowns are very durable, so the teeth need to be prepared minimally for them. New ceramic compositions, such as E-max, are quite durable and at the same time make it possible to choose the color of teeth of any shade.
The same materials can be used for conditionally removable prosthetics.
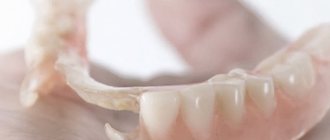
For removable dentures, the most important element is the base. The base is made from:
- Acrylic
- Acry Free
- Nylon
The hardest material is acrylic. Its disadvantages are microporosity and rapid wear. Acrylic contains substances that cause allergies. Pros: low cost and ease of processing.
Acry Free is a material that contains no allergens, it is softer and thinner than acrylic. It is easier to get used to such a product.
Nylon restorations fit comfortably in the mouth and do not cause allergies, but do not distribute the chewing load well enough due to their softness.
Metals and plastics are used for fastening elements of partial removable structures. And for the base - the same acrylic and plastics based on acrylic resins.
The service life of acrylic restorations is about 3 years, Acry Free and nylon restorations are 5 years. Dentures are replaced for several reasons. This could be a breakdown, an allergy, or a desire to replace an old design with a more modern one. The main thing is that removable structures do not stop bone loss. The relief of the oral cavity changes, the gums sag, and the restoration no longer fits.
Advantages and disadvantages
Removable prosthetics has a number of advantages, including:
- Easy maintenance of the structure;
- Aesthetic appearance of the prosthesis;
- Making a complete removable denture is the optimal solution for completely edentulous patients;
- Moderate cost of prosthetics with a reasonable production time.
At the same time, you should be aware of the disadvantages of removable prosthetics:
- The structure is not firmly fixed in the oral cavity, and during a conversation or when chewing food it can go beyond the jaw. The use of a fixing agent helps to correct this situation;
- Due to the transfer of chewing load to the mucous membrane of the upper (supporting for dentures) part of the jaw, a gradual narrowing of blood vessels occurs, blood flow worsens, and edematous phenomena are observed;
- The low thermal conductivity of materials used in the manufacture of removable dentures on implants, plate or clasp structures causes a temperature difference under and outside the structures, which, in combination with food particles accumulated in the pores, can lead to inflammation and an unpleasant odor.
Manufacturing of removable dentures
The process of manufacturing restorations is called clinical-laboratory because it is carried out in close cooperation between the clinic and the laboratory. There are 4 clinical stages in the technology of removable dentures. Between them they carry out work in the laboratory.
First clinical stage
It is performed by an orthopedic dentist. Work begins with collecting anamnesis. The doctor collects information about health status, allergic reactions, and working conditions.
Then the dentist carries out:
- General examination
of the patient. The orthopedist pays attention to the bite, the structure of the jaws, and the condition of the prosthetic bed. The level of preservation of the remaining teeth, if any, is determined. - Special examination
. This includes motor and speech tests, registration of chewing and swallowing characteristics. An X-ray examination is performed and a tomography is performed. - Drawing up a treatment plan
. At this stage, the type of restoration and material for production are determined. - Taking impressions
. Using an orthopedic spoon, the doctor makes anatomical casts of the jaws. In simple cases, this is enough. For complex defects, individual spoons are made. The impressions are sent to the laboratory, where a technician gets to work.
Based on the plaster models, the technician makes an individual spoon. To do this, he uses plastics, thermoplastics or wax. After finishing the work, he hands the spoon to the doctor.
A custom tray is used by the orthopedist to obtain a functional impression. This method is used when:
- severe atrophy of bone tissue;
- some anatomical features (folds on the palatine bed, for example);
- with single-standing teeth, in the case of partial structures.
Second clinical stage
Determination of central occlusion (places of contact when closing the jaws).
Denture manufacturing techniques include casting plaster models and casting wax bases with occlusal ridges. Using them, the doctor determines the central relationship of the jaws. To do this, a wax model is placed in the mouth and height measurements are taken. The orthopedist places marks on the rollers to secure the teeth. At this stage, the color for future crowns is selected.
In the laboratory, the technician places the model in the occluder, selects the size, color and shape of the artificial teeth in accordance with the recommendations of the orthopedist and distributes them into the jaw. He then checks all structural elements.
When making clasp restorations, at this stage the frame is cast. It is ground and polished.
Third clinical stage
Fitting. The goal is to eliminate errors, check aesthetics and conduct speech tests. The doctor makes the adjustment himself; to eliminate complex errors, the product is sent to the laboratory.
After adjustment, installation is carried out. The moment the patient receives the restoration is considered the final clinical stage of the work.
The production of dentures in the clinic’s own laboratory helps the orthopedist and the technician to interact on an ongoing basis and clarify certain issues during the production of the restoration. In addition, working directly in the clinic, the technician is more interested in how the denture is made; the reputation of the clinic depends on his qualifications. This increases responsibility, which affects the quality of structures and ease of use.
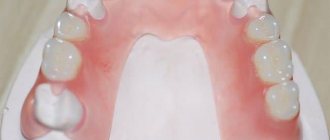
Clasp dentures - a modern type of removable dentures
The clasp removable denture is compact, durable, and easy to get used to, as evidenced by the reviews of the patients themselves.
In the clasp denture, instead of a plate, a fairly thin arch , made of high-strength metal alloys. Artificial teeth are fixed to the arch. A clasp denture is more physiological: the load during chewing is evenly distributed on the gums, jaw and remaining teeth (in a plate denture, the entire load falls on the bone tissue of the jaws).
Clasp removable dentures are compact, durable , and easy to get used to, as evidenced by the reviews of the patients themselves.
The clasp denture has a very reliable fixation, and if during its manufacture locks were installed instead of clasps, then it will be impossible to guess that the patient is wearing a removable denture.
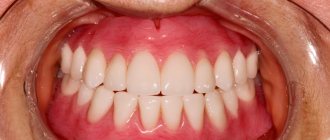
Fixed dentures
Fixed restorations include inlays, veneers, crowns and bridges. The manufacturing scheme differs only in small details. For example, let's take the manufacture of a bridge structure.
Preparation for the manufacture of a fixed denture begins with collecting anamnesis, making a diagnosis and preparing the teeth. The first clinical stage ends with the taking of impressions.
First laboratory stage
The impression technician makes a plaster cast and wax base with occlusal ridges. The model is then handed over to the doctor to determine the central occlusion. After this, the model goes back to the technician.
Second laboratory stage
The technician places the model in an articulator (a dental apparatus that simulates the closure of the jaws) and prepares models of ground teeth. Models crowns on abutment teeth and artificial teeth between them. Depending on how the denture is made, the technician makes metal crowns by casting, ceramic ones by pressing, and grinds zirconium crowns on a milling machine. The bridge is transferred to the orthopedist.
The dentist tries on the crowns and adjusts them. Notes any imperfections and sends them to the technician for final processing.
Third laboratory stage
The structure is polished and ground. In the case of metal ceramics, the metal base is processed and a ceramic coating is applied to it. The finished bridge is sent to the orthopedist, who fixes it on the patient’s teeth.
The production of dentures for the upper jaw follows the same protocol as for the lower jaw.
There are two significant disadvantages to the clasp prosthesis:
- To install it, you need to have your own (at least several) teeth;
- It is more expensive than its LP counterpart.
However, there is good news for patients of the professor’s clinic: prices for dental and orthopedic services in the clinic are affordable, and consultation with the head physician is free . We offer favorable conditions for prosthetics using modern materials, technologies and equipment.
Date of publication: September 20, 2020 Last update: September 22, 2022 © 2020 Professorial Dentistry “22 Century”. All rights reserved.
Repair and service life
Most removable plate dentures can be easily repaired - especially acrylic models. But, for example, nylon ones cannot be repaired, or they will quickly become unusable after repair. The reasons for structural failures are as follows:
- poor quality manufacturing,
- non-compliance with operating rules: if, for example, the patient chewed hard foods, seeds, etc.,
- shocks, falls from a height: the product may crack or break when transported in a box that is too wide without holders, or if it hits a sink, table or tiled floor,
- features of the material: acrylic is quite hard, so it cracks more often. Nylon is flexible and soft, so it is more difficult to break - however, it stretches greatly and does not return to its original size.
REPROSTHETOSIS WITH ACRYLIC PROSTHETICS - RUB 180,000!
Re-prosthetics with an acrylic bridge on a metal frame (all included) up to 12 units.
Call now or request a call
As for the service life, a repaired product will last less than one that was used without breakdowns. The average service life is 2.5-3 years, provided that the plate prosthesis has to be frequently adjusted and repositioned due to bone subsidence and gum loss. With good care it will last up to 5 years.
When is removable prosthetics required?
Removable dental prosthetics is a very common method of restoring the chewing and aesthetic functions of toothless jaws. Unlike fixed prosthetics, removable prosthetics are less demanding on the stability of the teeth on which future dentures will rest. Contraindications to their installation are minimal, but more on them later.
Main indications for removable prosthetics:
- End defects of the dentition;
- Included defects of the frontal and lateral zones;
- Lack of chewing teeth on one side of the jaw;
- Complete edentia;
- Pathologies of periodontal tissues (periodontitis, periodontal disease).
Completely edentulous
Types of removable prosthetics
Complete - prosthetics in the absence of teeth.
Partial is a way to restore chewing efficiency after the loss of one or more teeth.
Conditionally removable - temporary structures that are fixed using claws, clasps and special cements with the ability to be removed by a doctor in the dental office.
Immediate prosthetics are temporary removable structures.
The main types of such prostheses:
Plate prostheses
Plate:
- Partial and complete;
- Acrylic and nylon .
Clasp:
- With clasp fastening;
- With lock fastening.
- On telescopic crowns.