Hypertonicity in a child is an excessive overstrain of the flexor muscles. It is due to the fact that for a long time the muscles of an unborn child are in constant tension: in the uterine cavity, the arms are clenched into fists, and the legs are pressed to the body, and the chin is to the chest. In the womb, fetal movements are limited and not varied. It is more comfortable for newborns to maintain the fetal position, this way they feel more protected and calm.
The tension in the muscles of the baby's head and neck in the mother's belly is quite strong, so after birth the head is slightly tilted back, and the limbs are bent and pressed close to the body. In nine cases out of ten, children in the first months of life experience muscle tone, which goes away on its own. As the child grows and adapts to living conditions outside the womb, the muscles relax and voluntary movements appear. However, in some infants the state of tone persists even after 3 months, which may indicate deviations from the norm and the need for treatment. Most often this is due to the fact that during intrauterine development or during childbirth (immediately after it) the child’s nervous system was damaged. The central nervous system is not able to fully transmit impulses to the muscles for their proper functioning due to damage to the neurons of the brain.
Do not be afraid of this diagnosis, since the child’s nervous system is not fully formed, and its condition can be influenced. The main thing is to pay attention to the baby’s well-being and behavior in time, consider the deviation and seek help from a specialist.
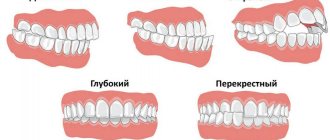
Doctors distinguish the following types of hypertension:
- general, that is, the whole organism;
- only upper or lower extremities;
- according to hemitype, that is, the tone of the limbs on one side: right or left.
Types, levels and forms of speech dysarthria in children
Table of types of disease by location of the lesion
| Name of the pathology form | Peculiarities |
| Cerebellar | Occurs when the cerebellum is involved in the process. Speech is drawn out, slurred, slow, the volume constantly changes, the child’s tongue trembles, he speaks with shouts, as if chanting slogans. Additional symptoms: poor balance, unsteady gait. |
| Bulbarnaya | It is caused by paralysis of the articulatory muscles, as well as the nerves - vagus, glossopharyngeal, ternary, sublingual and/or others. Children lack some reflexes, sucking and swallowing, facial expressions are impaired, and it is difficult for them to chew solid food. There is also increased salivation, simplification (all consonants “merge” into one fricative) and slurred sounds, a nasal, hoarse sound of the voice, sometimes its absence. |
| Pseudobulbar | Occurs with centralized paralysis (spastic) of muscles and their hypertonicity. Speech becomes monotonous, it is difficult for the child to lift the tip of the tongue, move it to the side, or hold it. There is increased salivation, soreness, and swallowing disorders (increased reflex). Speech is slurred, nasal, the pronunciation of hissing, whistling and tone sounds is sharply impaired. |
| Extrapyramidal | It occurs when the function of the subcortical nuclei is disrupted, and therefore received a second name – “subcortical”. Speech is slightly nasal, slurred, and slurred. There are involuntary muscle movements, facial expressions, and articulatory spasms. The timbre and strength of the voice changes, the pace of conversation is disrupted, and there are occasional guttural cries. |
| Cortical | Damage to those areas of the cerebral cortex that are responsible for articulatory muscles. Children pronounce words correctly in structure, but with impaired pronunciation of syllables. There is difficulty breathing during conversation and voice. |
| Cold | Manifests itself as one of the symptoms of myasthenia gravis (fatigue and weakness of striated muscles). Speech disruptions occur when the air temperature in the room where the child is located increases or decreases. |
Classification according to the degree of development of pathology:
- I (erased) - only a speech therapist can identify incorrect pronunciation during examination and examination, almost complete recovery is possible;
- II – pronunciation is clear, but defects are noticeable;
- III – the child is understood only by close people, strangers rarely;
- IV – even relatives do not understand the pronunciation or there is no speech, most often considered within the framework of cerebral palsy.
Important! The erased form is characterized by difficulty chewing solid food. Parents should not change their child's diet because of this. It is necessary to gradually accustom him to chew on the same basis as other people. Source: E.F. Arkhipova Erased dysarthria in children: a textbook for university students // M.: AST: Astrel: KHRANITEL, 2006, p.319
How to treat hypertension in infants
Hypertonicity in infants is very common. When examining a child, a pediatrician and neurologist can easily identify it. In some cases, the increased tone goes away on its own by 3–4 months. In addition to the main symptoms, doctors rely on the following reflexes of the child, which, with normal development, should disappear by the 3rd month of life:
- step reflex. With the body in a vertical position, the baby begins walking movements on a flat surface;
- support reflex. On the floor, the child places his foot on the entire foot, and not on the toe;
- symmetry/asymmetry reflex. When the baby lies on his back and presses his chin to his chest, his legs extend and his arms bend. When tilting the head to the left, the left limbs bend; when tilting to the right, vice versa;
- tonic reflex. In the position on the stomach, the arms and legs are bent; in the position on the back, they are straightened.
In addition to pediatrics and neuropathology, osteopathy is widely popular and effective in treating tone in children. This is the main alternative to traditional treatment: massages, physiotherapy, aromatherapy, therapeutic exercises, drug treatment, which in most cases only relieves symptoms. The main task of the osteopath in this case is to find the cause of abnormalities in infants and eliminate hypertonicity.
The doctor collects a detailed medical history and asks how the pregnancy and childbirth proceeded. For osteopathy, the human body is a single whole, all its organs and systems are inextricably linked with each other. The specialist has very sensitive fingers, and all the manipulations he performs are extremely soft and gentle.
Disorders of the nervous system, which causes muscle tone in infants, are treated by an osteopath with a special massage. These procedures do not cause pain or discomfort in children, therefore they are absolutely safe. The positive effect will be noticeable after the first sessions. The child experiences an improvement not only in muscle tone, but also in appetite, sleep, and digestive processes. The osteopathic doctor triggers the necessary mechanisms in the baby’s body, aimed at correcting the functioning of the brain centers and metabolic processes between them.
Parents should listen to the doctor’s recommendations, but self-medication is unacceptable, since the osteopathic doctor performs extremely delicate and gentle manipulations with the child, requiring certain knowledge, skills and qualifications. The duration of therapy is different for each patient, so return visits to the clinic may be repeated after one to two weeks.
Causes and symptoms
The disease is provoked by a number of harmful factors:
- viral diseases of the expectant mother;
- pathologies of the placenta at the stage of intrauterine development;
- Rhesus conflict;
- fetal hypoxia;
- very rapid or slow labor with cerebral hemorrhage in the child;
- some birth injuries;
- prematurity;
- infections of the brain and its membranes, such as meningitis;
- Cerebral palsy (up to 85% of cases of dysarthria);
- TBI;
- hydrocephalus;
- severe intoxication;
- encephalitis. Source: L.I. Belyakova, Yu.O. Filatova Diagnosis of speech disorders // Defectology, 2007
Why is hypertension dangerous?
As mentioned earlier, infant hypertonicity can be caused by disorders of the nervous system. It is obvious that such deviations will worsen and develop if measures are not taken. At first, motor disturbances in the baby will be noticeable, and subsequently deviations in fine and gross motor skills, coordination, and speech will appear. Possible problems with gait and posture, developmental delay. All of the above suggests that the problem of increased tone in infants requires special control, primarily from parents. Timely detection of disorders, their causes, as well as subsequent proper treatment is the key to the health and normal development of a little person.
Symptoms and treatment
The main symptoms include the following:
- incomprehensible, slurred speech;
- spastic manifestations in the articulatory muscles (neck, lips, face, tongue are constantly tense, articulation is limited, lips are tightly closed);
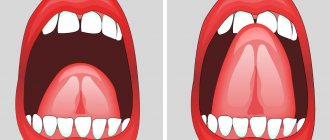
- hypotonia of the articulatory apparatus (lips do not close, tongue lies motionless in the mouth, mouth is slightly open, increased salivation);
- dystonia of articulatory muscles (when a child tries to talk, his muscle tone goes from low to high);
- slurred pronunciation;
- in difficult cases, the child misses sounds, replaces them or pronounces them distorted; Source: O.Yu. Fedosova Features of sound pronunciation of children with mild dysarthria // Speech therapist in kindergarten, 2005, No. 2, pp. 36-41
- slowness of conversation;
- inability to speak (in severe forms);
- nasal voice without signs of a runny nose;
- change, omission, replacement of some sounds with others;
- fading of a phrase towards the end of its utterance, rapid breathing during a conversation due to lack of air;
- very high, almost “squeaky” voice;
- a fast or very slow flow of words, while the child cannot change the tone.
Is it possible to perform massage at home?
Experts recommend performing speech therapy massage at home. Firstly, this is a guarantee of continuity of treatment, which affects the effectiveness of correction. Secondly, children, especially small ones, are more relaxed in normal circumstances, but with a stranger it can be impossible to even force their mouth to open. Thirdly, at home you can perform a massage at any time: you don’t need to adjust to your schedule or change your routine, which is a stress factor in itself.
Massage your face with your fingers. You can use teaspoons. Instead of probes, when massaging your tongue, you can also use improvised means: spoons or the same toothbrushes. Kneading with your fingers will also help.
It is necessary that you know how to do a relaxing massage for dysarthria. It is important to do all the movements correctly, to know where to press harder and where it is better to use light touches. You can learn through courses. A speech therapist can also show you the basics. If you combine the procedures with a regular massage, the effect will be many times higher. Just keep in mind that it can be relaxing or tonic.
Incorrect technique can cause deterioration: other types of speech disorders may appear, in addition to dysarthria.
What to do? Treatment methods for the disorder
The child must undergo additional classes with a speech therapist (at home or in a special institution) on:
- development of motor skills;
- forming a conversation;
- honing diction;
- correcting the pronunciation of distorted sounds;
- expanding vocabulary;
- development of phonetic hearing;
- memorizing grammatical structure.
Against this background, drug therapy is carried out using nootropics. Medicines in this group specifically affect brain functions: stimulate mental activity, cognitive functions, increase learning abilities, and improve memory.
The package of measures also includes exercise therapy - articulation gymnastics to strengthen the facial muscles, massage, exercises with the hands and fingers.
Sources:
- E.F. Arkhipova. Erased dysarthria in children: a textbook for university students // M.: AST: Astrel: KHRANITEL, 2006, p. 319.
- L.I. Belyakova, Yu.O. Filatova. Diagnosis of speech disorders // Defectology, 2007.
- 3. O.Yu. Fedosova. Features of sound pronunciation of children with mild dysarthria // Speech therapist in kindergarten, 2005, No. 2, pp. 36-41.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Face massage
The correct sequence for a relaxing massage is as follows: first, apply to the face and lips, then to the tongue.
Facial massage for dysarthria involves rubbing, kneading, and stroking. Before the procedure, remove jewelry and keep your nails short. The first sessions are short, the duration gradually increases.
The classic version begins with kneading movements in the forehead area. The movements are smooth, from the central part towards the temples. Then stroking from the eyebrows to the hairline with the pads of all fingers.
You cannot press hard on the eyelids: all movements should be light, stroking. The direction is circular, clockwise.
In the cheek area, it is necessary to relax the muscles by stretching them from the mouth towards the temples, and from the cheekbones - downwards, towards the chin. After this, we move to the nose, smoothly rubbing the wings up and down, stroking the nasolabial fold in the direction from the nose to the corners of the lips.
Articulatory lip massage for dysarthria involves kneading with vibration movements, then rubbing from the middle of the lips to the corners. Then they rub the chin and stroke the ears.
When a child has facial asymmetry, different muscle tone on the left and right, pay more attention to the affected side to achieve normalization of muscle tone in dysarthria.
Manifestations of hypotension: note to parents
A child’s lethargy is often mistakenly perceived as a calm character, and increased painful drowsiness as healthy, sound sleep. In such cases, it is important not to miss the pathology.
Attentive parents can detect decreased muscle tone by indirect signs:
- While the baby is awake, you should pay attention to his activity and reaction to external stimuli. A child's low activity should alert parents.
- During sleep, in infants with muscle hypotonicity, the arms and legs are straightened (a specific symptom of the pathology), the palms are wide open. If the mother opens her clenched fist to the child, the palm remains open.
- When feeding a baby, the mother should pay attention to whether he takes the breast or pacifier well and how long he eats. Muscle hypotension can be suspected in cases where the baby eats slowly and gets tired quickly during feeding.
As a rule, children suffering from decreased muscle tone lag behind in physical development: they later begin to hold their heads, roll over onto their stomachs, and hold their toys. In addition, babies do not gain weight well.