Indications for relining Correction methods Relining materials Where to do it?
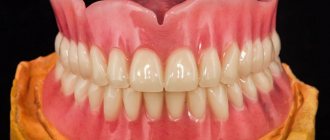
The basis for comfortable use of removable orthopedic systems is a reliable fit to the jaw. But gradually the fixation of the structure weakens, functionality decreases, and discomfort appears when eating and talking. Relining a denture (partial, complete) – involves eliminating inaccuracies, preventing damage to the base of the structure, restoring precise contact with the gums and supporting dental units. Depending on the clinical case, such a procedure is performed in the dentist’s office or in a laboratory setting.
When is denture relining necessary?
After fixing the new orthopedic system, after the first 1-3 months
wearing, relining the denture is necessary to correct the accuracy of its fit to the mucosa. Because the teeth were missing for some time, the jaw joint was rebuilt. After installing the prosthetic structure, the load on the jaw tissue changes. It begins to gradually atrophy, the gums sag, and the bite begins to change. The prosthesis becomes uncomfortable and the occlusion is disrupted.
Relocation shown:
- if the structure does not hold well in the mouth, falls out during conversation, eating, or puts pressure on the gums;
- in the presence of defects in the prosthetic system due to violations of technology during impression taking or manufacturing;
- deterioration of the aesthetic characteristics of the structure;
- the prosthesis has been damaged or has flaws;
- the shape of the alveolar process has changed, which caused instability of the orthopedic structure;
- an atypical change in the height of the lower part of the face was detected (even if the deviation is minimal from the original parameters).
Correction is needed not only for removable models, but also for conditionally removable structures supported by implants. Mostly, these are single-stage protocols with instant load (all-on-4, all-on-6). After implantation of implants and installation of a prosthetic system, the load on the bone increases. This leads to enhanced regeneration of bone tissue and an increase in its parameters, which requires correction of the orthopedic apparatus. That is, if the bite changes, the position of the prosthetic system changes.
Some tips for wearing new dentures
- Chew food alternately on both sides! This will help the prosthesis take its place and minimize the risk of the prosthesis being thrown off the valve area.
- When you bite off solid food using your puller, it is better to use the canines and premolars rather than the incisors, biting as if sideways. Most often, the lateral teeth are located in a more central position in the prosthesis, and the dental technician moves the incisors slightly forward for greater beauty. This is more beautiful, but when biting, tearing moments occur and the prosthesis pushes out of its place.
- At first, avoid eating apples, carrots, and generally solid foods.
- Diction will change; at first, some sounds will not be pronounced. You need to give your tongue time to get used to the changes in your mouth. It is possible that some words and sounds will sound strange when spoken, especially the sounds of the letters “n”, “r”, “z”. But as you well know, only practice makes perfect! The more often you talk or read out loud, the faster you will start talking like you used to.
- To clean dentures, use tooth powder and a denture or hand brush. They are longer and wider, the bristles are denser, and cleaning the prosthesis will be quick. You can, of course, use a toothbrush, but its cleaning effect for plastic is insufficient, cleaning two dentures will take a lot of time, do not forget that you also need to clean the oral cavity.
Caring for removable dentures to prevent complications such as chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane
First of all, dentures should be thoroughly cleaned of all kinds of deposits. Oddly enough, most of the dentures in patients who complained of redness of the gums and pain had plaque on the dentures. Nobody is saying that people don't brush their artificial teeth. But, obviously, they do it quite quickly, as a routine procedure.
Meanwhile, it should be noted that the surface of the prosthesis is curved and has depressions. A protein film accumulates in them, which hardens over time, and then begins to grow in thickness and area. It is very difficult to remove hardened deposits from plastic; sometimes you have to do this with a carborundum head, grinding through each depression, and before doing this, soak the dentures in hydrogen peroxide. But it is this plaque that causes gum inflammation.
Therefore, the patient must independently ensure that this protein film does not form. Once a week, the denture should be carefully inspected, especially the recesses where the cleaning brush may not penetrate. If plaque is found, you need to remove it with a gauze cloth with a cleaning agent and tooth powder or soda. You need to rub quite vigorously, and fix the result by polishing with toothpaste.
Denture cleaning tablets are sold.
However, both tablets and hydrogen peroxide do not remove the protein film itself, but only discolor and inactivate it. [email protected] Samara, Industrial district st. Novo-Vokzalnaya, 269 +7
Correction methods
Relining a complete removable denture, as well as restoring a partial structure, is carried out by two methods - clinical (in the dentist's office) and laboratory. If the design does not fit well enough, the doctor will be able to adjust it in front of the patient; this takes a minimum of time. If there is a significant violation of the fit, or a decrease in the height of the bite, additional equipment will be needed; correction is carried out in a laboratory. How dentures are relined depends on the complexity of the work and the type of prosthetic system.
Clinical method
The procedure includes the following stages of prosthesis relining:
- assessment of bite, occlusion, compliance of the orthopedic design with the jaw relief;
- adjusting the structure, filing edge elements (lengthening, shortening);
- removal of polishing from the orthopedic system, preparation of the polymer mass;
- distribution of the polymer composition onto the treated surface of the prosthesis;
- installation of an orthopedic system for the patient, with complete closure of the teeth of the upper and lower jaw (assessment of central occlusion);
- removal of excess polymer mass from the structure, polymerization of plastic (if there is a metal base, a layer of the corresponding metal is sprayed onto the inner surface of the prosthesis, then a plastic mass is applied to the metal base);
- immersion in hot water for final polymerization, improving adhesion strength;
- modeling of the edge segment, finishing polymerization.
The clinical method allows you to immediately eliminate all shortcomings and achieve a tight fit of the prosthetic system to the gums. The technique is not used in the presence of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa or allergies to plastic.
Laboratory method
Relining the prosthesis base in the laboratory allows you to avoid the negative impact of the plastic composite on the mucous membrane, but you will have to wait several days for the result.
- The doctor assesses the condition of the prosthetic structure, takes an impression of the patient’s teeth and sends everything to the laboratory;
- a thin layer of plastic is removed from the orthopedic system, the polishing is removed from the edge segment;
- the required amount of plastic is applied to the structure, its boundaries are formed, ground, polished, and the closure in the position of central occlusion is checked;
- the finished orthopedic system is returned to the doctor, who installs it for the patient.
Among the advantages of the technique are high aesthetics of the prosthetic system, maximum adhesion of materials (base, relining polymer), and absence of allergies to the plastic composite. Relining plate dentures in the laboratory takes 2 days or more
. There is no adaptation to the adjusted orthopedic device, since the patient has already used it before.
Complications after dental prosthetics
- Sores and chafing after installation of dentures;
- Inflammatory process on the gums under dentures. Stomatitis;
- Diseases of supporting teeth (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, etc.);
- Allergy to materials used to create prostheses;
- Galvanic syndrome;
- Loosening the fixation of removable structures;
- Changing the position of the cheeks and lips.
Let's look at each of the complications in more detail.
Sores and chafing after installation of dentures
A common phenomenon, especially typical for removable structures.
Symptoms
- Unpleasant sensations, pain while eating;
- Feeling of a foreign body in the mouth;
- Profuse salivation.
Treatment
The next day after the installation of a removable structure, there is always a follow-up appointment at the dentist's office. Regardless of the presence or absence of unpleasant sensations, it is necessary to come to the clinic for an examination, otherwise, if this is not done, bedsores will form .
If necessary, the doctor will correct the prosthesis and set a date for the next visit. At least two amendments are required for everyone.
During the first two to three weeks, you get used to the dentures, and discomfort is completely normal. Full adaptation usually occurs by the end of the third week.
Prosthetic stomatitis
Prosthetic stomatitis
One of the most common complications.
Symptoms
- In the first time after installing the prosthesis, in addition to discomfort, excessive pressure on the mucous membrane and pain are felt. Redness of the gums appears, and possibly the formation of pustules on the mucous membrane. Small blood vessels are pinched, and the blood supply to the tissues is disrupted at the site of contact - bedsores form;
- The fixing elements of partial dentures can also irritate the surrounding periodontal tissues and contribute to their inflammation.
Treatment
It is necessary to visit your doctor, who will carry out antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity and dentures, prescribe local anti-inflammatory therapy (rinses, mouth baths, ointments, gels), as well as a set of procedures aimed at accelerating tissue regeneration.
Diseases of supporting teeth
In the case of partial dentures, there are teeth in the oral cavity that perform the important function of supporting and securing the denture. Whether the supporting teeth are healthy, covered with crowns or restored with fillings, in any case it is necessary to take care of it and maintain hygiene of the entire oral cavity.
Symptoms
- Visible accumulations of food debris, plaque on teeth, as well as on removable structures;
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth and from the prosthesis;
- Bleeding gums around supporting teeth;
- Painful sensations during meals, from temperature stimuli, night pain.
Treatment and prevention
- Maintain regular and thorough care of dentures and teeth;
- Visit a doctor for professional oral hygiene;
- If pain occurs during chewing, as well as aching, sharp pain, contact your dentist.
Allergy to dentures
Allergy to dentures
An allergic reaction to denture materials can occur when the dentures come into contact with the tissues of the patient's body.
Currently, scientists are trying to minimize the occurrence of such reactions, and today many different materials for the manufacture of removable dentures.
The rate of occurrence of an allergic reaction can vary - from several minutes to several hours, and sometimes days after installation of the prosthesis.
Symptoms
- Rashes on the skin of the face;
- Redness and swelling of the oral mucosa;
- Attacks of bronchial asthma. Suffocation;
- Inflammation of the salivary glands;
- Dry mouth;
- Burning sensation of tongue.
Treatment
- Remove dentures;
- Contact an orthopedic dentist as soon as possible;
- Carry out repeated prosthetics with structures made of a different material.
Galvanic syndrome
This complication after prosthetics is the formation of galvanic current in the oral cavity.
The cause of the occurrence is the presence of dissimilar metals in all structures installed in the oral cavity (for example, used as the base of a prosthesis and as part of crowns) if a particular patient is predisposed to this disease.
In modern dentistry, in the manufacture of dentures, metals and their alloys are used, such as stainless steel, cobalt-chrome, silver-palladium alloys, alloys based on precious metals and others.
It is known that any alloy immersed in an electrolyte solution (in this case, saliva acts as this) acquires a potential unique to it. If metals with different potentials are present in the patient’s oral cavity, then all the conditions necessary for the formation of galvanic current arise.
Symptoms
- Unpleasant sensations while eating;
- Metallic taste in the mouth;
- A bitter and acidic taste in the mouth, especially aggravated when a metal spoon touches the dentures;
- Headache;
- Sleep disorders;
- General malaise;
- Allergic manifestations on the oral mucosa (swelling, erosion);
- Darkening of metal prostheses.
Treatment
- Repeated prosthetics, excluding the presence of dissimilar metals in the oral cavity.
Loosening the fixation of removable structures
Weakening of fixation of removable structures
This complication develops gradually, as the design of lamellar prostheses approaches the end of their service life.
In the case of clasp prosthetics, it is also possible for the plastic parts of the locking prostheses to wear off and the clasps to loosen .
Causes
- Daily use, regular removal from the oral cavity, changes in the anatomical structure of the prosthetic bed (loss of bone tissue with age).
Symptoms
- Sensation of displacement, movement of the prosthesis in the mouth;
- Lack of adherence of the prosthesis to the gums and teeth;
- Loss of structures from the mouth during eating and talking.
Treatment
- Making a new removable denture;
- Using special dental adhesives for fixation.
Correction of fastenings, relining of the prosthesis
Correction of fastenings, relining of the prosthesis
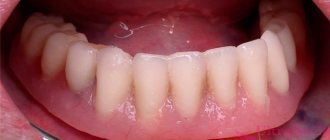
Relining of the prosthesis - correction, restoration of a removable structure in order to obtain a denture base adapted to chewing pressure, clarifying its fit to the prosthetic bed.
Over time, atrophy of the mucous and bone tissue occurs under the base of the removable denture. Atrophy leads to uneven distribution of chewing pressure between the supporting teeth (if any) and the mucous membrane. Failure to reline a removable denture can lead to its breakage and loss of supporting teeth.
Relining can take place either directly in the patient's mouth or in the laboratory.
Method of relining a removable denture in the clinic
- The dentist removes a thin layer of plastic from the surface of the prosthesis adjacent to the mucous membrane of the prosthetic bed and applies an even layer of self-hardening plastic to the treated base. After some time, the prosthesis is inserted into the oral cavity, installed and pressed, after which the patient closes his jaws. Excess plastic is removed with a spatula. After this, the prosthesis is removed and placed in a special apparatus, where the final polymerization of the plastic (hardening) takes place;
- Changing the position of the cheeks and lips.
Causes
- Errors at the stages of prosthesis manufacturing: excessive or insufficient thickness of the base in the frontal region, incorrect determination of the height of the lower third of the face and the centric relation of the jaws, inaccurate placement of artificial teeth in the base of the prosthesis.
Symptoms
- “Failed” or, conversely, excessively protruded lips;
- Biting cheeks with removable dentures;
- Deep nasolabial folds;
- Drooping corners of the mouth;
- The ability to close your lips only with force, while in a relaxed state your teeth are visible;
- Feeling of tightness in the cheeks.
Types of relining material
Correction of removable laminar dentures involves the use of the following materials:
- Hard plastic
– cold-curing acrylics (Protacryl, Redont), hot-curing acrylates (Ethacryl, Ftorax, etc.), polymethyl methacrylate. Solid base plastics are used for rigid fixation of orthopedic systems or laboratory relocation. - Soft composites
– acrylic, silicone elastomers. It is used if the physical parameters of the orthopedic device are normal, but the patient experiences headaches and discomfort. Typically used for relining mandibular prosthetic structures. - Temporary elastics
(conditioners) – polyvinyl chlorides and silicone base materials are highly elastic and are used for soft relining of dentures in case of systematic inflammation of the gums. Elastic materials are characterized by particular softness and are intended to reduce and uniformly redistribute chewing pressure to sensitive areas of the mucosa. Temporary material should be regularly updated, as it reacts negatively to cleaning agents and is susceptible to the accumulation of bacterial plaque.
The cost of relining an orthopedic system depends on several parameters - the technology used, material, type (clasp, conditionally removable, removable), size of the prosthesis, etc.
Doctors' opinions on removable dentures
Modern dentistry has advanced significantly. Today, prosthetics with removable clasp and other types of prostheses are viewed more as a temporary measure. It is advisable to install such dentures even if there are contraindications to wearing fixed products or performing dental implantation.
Doctors advise installing structures for adults and children who have lost teeth in order to prevent the displacement of dental units. In pediatric dentistry, such devices prevent the development of malocclusion pathologies and other problems associated with the premature loss of baby teeth.
Obviously, this type of prosthesis deserves attention in certain clinical cases. Sometimes removable products become the only real opportunity to restore lost teeth, and with them the opportunity to live a full life.
Where to contact
Patients with removable orthopedic devices are recommended to see an orthopedist every 6 months
for relocation of the structure. This must be done for preventive purposes, since due to a violation of the fixation of the orthopedic system in the mouth, breakage of the structure, rapid loosening and loss of supporting teeth (with partial structures) may occur.
To restore a prosthesis in Moscow, it is most convenient to contact the RUTT network of clinics. Relining is carried out using modern cushioning materials from reliable manufacturers, which guarantees precise fit of the restored structure, uniform distribution of the chewing load, and long service life.
Expert of the article Alekperov Roman Borisovich Dentist-orthopedist, doctor of the first category
Work experience24 years
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Main indications for the procedure:
- Complete edentia;
- Loss of chewing units on one side of the jaw;
- Pathological abrasion of teeth;
- Impossibility of installing an implant or bridge due to the characteristics of the jaw system;
- Defects of the dentition (in the end, frontal, lateral areas);
- Diseases of periodontal tissues (periodontal disease, periodontitis).
Main contraindications to the procedure:
- Acute inflammatory process in the oral cavity;
- Tuberculosis in open form;
- Epilepsy;
- Immunodeficiency conditions (HIV, AIDS).
You can find out how much removable prosthetics costs by consulting an orthopedic doctor.