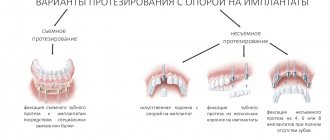
- Materials
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Manufacturing and installation
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Care
- Life time
- Alternative Methods
- Advantages of the ROOTT Clinic
- Prices
- Work examples
- Doctors
- Reviews
- When to use:
any group of teeth - Material:
KHS, gold, silver, palladium - Installation time:
2 to 5 days - Features:
minimal tooth grinding, low price, short service life - Service life:
up to 3 years - Anesthesia:
local
Stamped dental crowns are the oldest in the family of single metal dentures. For a long time, stamping was the only method for manufacturing orthopedic systems. Today, such structures can confidently be called a relic of the past. Structurally, they do not differ from similar prostheses; they are made in the form of a steel cap, 0.2-0.3 mm
, which is fixed to the prepared dental unit.
The production of stamped crowns does not require complex technology. Dentures are created manually, from cylindrical metal caps - factory blanks, sleeves. The dental laboratory has steel sockets of different diameters and thicknesses. The technician selects a blank suitable in diameter and begins stamping the crown. Typically, prosthetic structures are gray or golden in color (depending on the material). At the request of the patient, the prosthesis is coated with gold, titanium nitrite, and lined with plastic or ceramic mass for better aesthetics.
Design information - type and features
Stamped crown - what is it? In terms of its purpose, it does not differ from other similar prostheses. This is a cap that covers the tooth from above and restores its apex (i.e., the crown part). The internal parts - the stump and roots - are protected from infection from the oral cavity. The prosthesis restores chewing function and removes “extra” load from neighboring teeth.
South Korean implant Osstem - from 35,000 rubles.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and lock in promotional prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
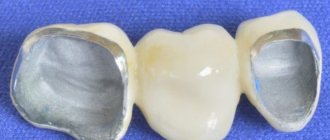
The design is made in a simple, one might even say primitive, way - almost the entire production process is done by hand. As a rule, the products are gray or golden in color, less often white, and the thickness ranges from 0.2-0.3 millimeters. What stamped crowns look like is shown in the photo.
Errors
When installing stamped products, unpleasant circumstances may occur that must be eliminated immediately.
Let's consider the main ones:
- If the edge of the gum turns pale during installation, then the product puts too much pressure on the gum tissue, and it is shortened with a bur or scissors.
- If the crown cannot be placed on the stump, it is too large and should be prepared.
- When the product cannot be put on due to its own problems (if the internal part has interfering areas), as well as in the case of a large diameter of the neck of the crown, which hangs on the stump, it is sent for alteration.
- A short product that cannot fit into the gum groove is unsuitable. In this case, the preparation for installation is repeated from the very beginning.
Materials for production
In most situations, stamped crowns are made of metal only. More precisely, from metal alloys of base metals. But noble alloys can also be used here. All materials are intended specifically for dentistry and must meet certain requirements - strength, low susceptibility to corrosion, ease of processing, lack of toxicity, low weight. The following materials (metals and alloys) are used for the manufacture of stamped crowns:
- iron-based alloys (stainless steel, chromium-nickel alloys) marked X18N9: has good ductility, satisfactory corrosion resistance, is inexpensive,
- gold-based alloys (900 or 750 standard): have excellent ductility, do not cause allergic reactions, but are much more expensive than steel,
- alloys based on silver and palladium: almost identical in their characteristics to the previous type, only they have a silver color rather than gold. The price is also considered high.
What materials are used to create the product?
Such crowns are created from special steel or gold, but the latter option is rarely used today, since the material is quite expensive. In general, the stamping method is outdated, so it is currently used only in rare cases.
So, to create such products one of the following types of steel can be used:
- stainless steel – characterized by increased malleability and a sufficient degree of ductility,
- alloy 1Х18Н9Т – a budget option, characterized by relative lightness.
To create crowns, two types of materials are used.
In this case, steel structures can be coated or without it. In the latter case, the product turns out to be shiny and silver in color. Titanium nitride is usually used as a coating material, which gives the crown a golden color. If we talk about gold structures, then 900 ductile gold with additional 750 karat solder is used to create them.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of these prostheses are quite few. In principle, only two can be distinguished - low cost (if you do not take gold for production) and ease of manufacture. Stamped crowns have many more disadvantages; they look like this:
- low manufacturing precision: therefore, the product does not fit very tightly - a small gap remains between the metal and the gum. Here food remains are retained, plaque and tartar build up - as a result, inflammation or caries begins,
- rapid abrasion, change in shape: opposing teeth (antagonists) can be injured or neighboring ones can be overloaded,
- short service life: the prosthesis quickly loses its fixation due to the destruction of the cement under it,
- low aesthetics: even for lined structures, the color will differ from the general shade of the smile, because plastic is porous - it quickly absorbs dyes and does not bleach well,
- high risk of deformation of the edge of the prosthesis in the area adjacent to the gum or deformation of the apex,
- allergic reactions to base metals are possible: irritation and rashes on the gums occur,
- the gums may acquire a “bluish” tint,
- there is a risk of galvanosis (galvanism): this is the name given to the appearance of an electrical impulse between prostheses made of dissimilar metals (if the patient, for example, already has a crown or bridge made of a different alloy in his mouth)
What are the pros and cons?
The main advantage of a stamped crown is its low price. This is the cheapest option for a single restoration, except when using gold as the base material. In most situations, the product is obtained with a thin wall thickness, so that the tooth does not have to be ground down too much. The materials used are easy to process. In addition, this option can save a situation when it is impossible to use any other type of prosthetics.
However, such crowns have much more disadvantages. Here are the main disadvantages characteristic of stamped products:
- low level of aesthetics due to silver or gold color,
- insufficient strength due to the thinness of the walls of the product,
- short service life - the crown wears off quickly,
- the risk of developing allergies or galvanosis - electric current,
- insufficiently accurate reconstruction of the anatomical shape of the tooth,
- negative effect of the material on hard tissues and gums, which is explained by the loose fit of the product to the tooth.
Such products have rather poor aesthetics.
Dental cement used to fix the structure has a porous structure. It creates a favorable environment for the active proliferation of bacteria, which is why caries and inflammatory processes often begin to develop under such a crown, and the cement itself quickly dissolves.
Indications for prosthetics
The main indication for installing a stamped crown is severe tooth decay, when it is no longer useful to install a filling or restorative inlay. Additionally, the following indications for prosthetics can be identified:
- frequent occurrence of caries on the causative tooth,
- pathological abrasion of enamel,
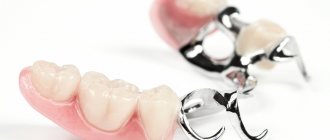
- for inclusion in bridges, clasp and acrylic removable dentures,
- abnormal shape of the tooth apex,
- for fixation of maxillofacial and orthodontic appliances,
- for splinting: in case of a jaw fracture or mobility of teeth I-II degrees,
- for prosthetics of primary molars (chewing teeth).
Read on the topic: ceramic inlays - why are they the best replacement for fillings?
Contraindications
Relative
the procedure can be carried out with extreme caution
- Bite defects;
- increased abrasion of the enamel of the antagonist tooth;
- gum pathologies (atrophic, inflammatory);
- pregnancy;
- allergy to anesthetics;
- acute infections;
- mental disorders;
- exacerbation of a chronic disease.
Absolute
the procedure is strictly prohibited
- Severe periodontitis with tooth mobility grade III-IV;
- malignant processes of the oral cavity;
- allergy to prosthesis material;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus.
Preparation and preparation before prosthetics
Before prosthetics, you need to undergo sanitation of the oral cavity - cure dental diseases (caries, gingivitis, etc.). It is imperative to undergo X-ray diagnostics to identify hidden pathologies - for example, cysts under the roots. Then the orthopedic dentist prepares the tooth for a stamped crown - the enamel is ground down by approximately 0.3 mm. This creates the most suitable stump shape for the prosthesis, which will correctly distribute chewing pressure. If necessary, the dental nerve is removed and the root canals are filled. They can also be further strengthened with pins. After this, you can proceed to taking impressions and making a prosthesis.
Dentists against stamped products
Despite the fact that stamped crowns have been used for quite a long time, many modern dentists are against their use due to a large number of shortcomings and imperfections, and prefer more modern types of products.
The result of unsuccessful installation of a stamped product may be the following:
- gradual dissolution of cement due to incomplete adhesion;
- Pieces of food that rot accumulate near the stump;
- caries affects the enamel, and then dentin, sometimes even their complete dissolution;
- The tooth is destroyed and can no longer be restored; it has to be removed.
In addition, the monotonous production of stamped crowns resists the necessary repetition of all the cusps on the tooth surface. A sleeve is taken, which is then shaped by tapping with a special hammer.
How structures are made
The technology for making stamped crowns is very simple - it only requires the skills of a dental technician1, consumables, hand tools and 2 dental machines. Let's take a closer look at the laboratory stages of prosthetic manufacturing:
- Stage 1 – taking impressions (in the orthopedist’s office): for this, alginate impression material is used, less often - gypsum,
- Stage 2 – creation of a plaster model (in a dental laboratory): a plaster model is cast based on the impression. It is being finalized - a small depression is formed in the gum area (approximately 0.5 mm). Then hot wax is applied on top to increase the internal diameter of the prosthesis - otherwise there will not be enough space for the cement “glue” when fixed to the support. Afterwards, the plaster “tooth” is cut out from the cast and placed in plaster - the result is a detachable mold with a hole,
- Stage 3 - casting the workpiece : liquid low-melting metal (melting point about 130 degrees Celsius) is poured into the resulting mold - this is how 2 metal tooth models are made,
- Stage 4 – working with a metal sleeve (pre-stamping): 1 metal model of the tooth is taken from the previous stage and its crown part is placed in a metal sleeve (it can be called a “bucket” or “cap”). Next, stretching occurs in the SAMSON apparatus - this is how the standard sleeve takes on a more anatomical shape. After this, the sleeve is fired at a temperature of 1100 degrees and cooled. Then the cap is tapped with a hammer - while the sleeve is compared several times with the 2nd metal tooth (obtained at stage No. 3), because The dental technician needs to recreate the shape very accurately. Next, a metal model of the tooth is melted from the formed sleeve, and the sleeve is fired,
- Stage 5 - second stamping : the sleeve is placed on the second metal tooth and again tapped with a hammer. The workpiece is placed in a device (“press gun”) and compressed under a pressure of 3-5 tons. After this, the workpiece is again tapped with a hammer so that there are no sharp corners, and cut to the level of the gums,
- Stage 6 – finishing (only for single crowns): the workpiece is bleached in an acid solution, ground and polished - since initially it does not look aesthetically pleasing (black, matte). You can also do spraying or cladding. All that remains is to transfer the design to the orthopedic dentist, who will fix the prosthesis to the patient using cement.
If the stamped crown is planned for inclusion in a bridge or removable denture, then after the 5th stage it is transferred to the orthopedist. Next, the doctor fixes the structure to the patient and again takes impressions - this time for the manufacture of an extended prosthesis.
There are also soldered stamped crowns. To make them, the cap sleeve is first cut into 2 or 3 parts, each is modeled by tapping with a hammer, and then all parts are joined into one product by soldering. This method is used when it is not possible to process a solid sleeve on a model.
Kinds
There are several types of metal structures:
- Dentures are installed in the presence of a destroyed tooth fragment, when it is not possible to install a filling or inlay
Stamped - made on the basis of caps (sleeves) with subsequent giving the workpiece the anatomical shape of the patient’s tooth;
- Cast - the manufacturing process includes casting molten metal into a prepared mold, this makes it possible to obtain precise parameters of the prosthesis and a high-strength product;
- Brazed - the manufacturing technology resembles a stamped one, but the sleeve is first cut into 2-3 parts, after tapping it is joined together by soldering (this method is used in cases where it is not possible to give an anatomical shape to the whole sleeve).
How long does adaptation take?
How long does it take to get used to stamped crowns? As a rule, adaptation takes very little time - a day or two. It all depends on how well the structure is made and how long the patient walked with a damaged tooth. Since the product follows the anatomical shape, there is no particular discomfort when getting used to it.
Complex on 4 OSSTEM implants with delayed loading - from RUB 170,000.
Complex implantation Osstem (South Korea) with delayed loading after 4-6 months.
Guarantee for the doctor’s work - unlimited Call now or order a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
How to avoid shortcomings?
During installation, it is important to ensure that the stamped crown meets the following requirements:
- tightly covered the dental neck to prevent gum atrophy;
- did not descend more than a third of a millimeter into the gum groove, which can provoke marginal periodontitis;
- restored the functionality of the tooth;
- repeated the anatomical features of a living tooth;
- contributed to the preservation of the interalveolar height of the opposite tooth, eliminating the risk of permanent injury.
Caring for new teeth
Oral care is also not particularly difficult. As before, you need to take a responsible approach to oral hygiene - brush your teeth morning and evening. Dentists also recommend rinsing your mouth with clean water after every meal. What is best not to do is chew something hard (seeds, candies, nuts) or chewy (taffy, chewing gum), or open lids with your teeth. This can cause the denture to become damaged or fall off the tooth.
It is important to regularly visit your orthopedist for a medical examination so that the doctor can promptly notice the onset of complications - displacement of the prosthesis on the support, exposure or darkening of the gums. It is advisable to go to the dentist 3-4 times a year.
Features of care
Special care for crowns made from stamped metal is not required. The main measures include regular hygiene procedures and thorough cleaning of the oral cavity after eating food.
The list of recommended products includes:
- paste and brush with medium-hard bristles;
- rinse balm;
- dental floss.
After smoking cigarettes or drinking coffee, you need to rinse your mouth with a special liquid; in extreme cases, you can get by with water.
Every six months you need to visit the dental clinic to monitor the integrity of the prosthesis and for thorough cleaning of the oral cavity, which can only be provided by professional cleaning.
Such measures will help prevent the formation of plaque and the growth of stones. Also, based on a number of signs, a specialist can promptly identify the problem and prescribe treatment.
Adequate alternatives to “stamping”
The best alternatives to a stamped crown are modern cast (solid) and milled ones. What is the difference? The differences between stamped and cast are that they have different manufacturing technologies. Cast, as the name suggests, is made by casting. This allows the use of stronger and more durable metal alloys (for example, with cobalt). Cast dentures are precise - they fit better to the support and to the gums, do not wear down over time, and last about 10 years. They can also be coated with a ceramic veneer to enhance aesthetics.
“The doctor dissuaded me from having a stamped crown because it’s a thing of the past. Although it is cheap, it is from the category of “the miser pays twice.” It’s better to immediately make normal metal ceramics, which will last a long time and pay for itself. Somehow I don’t want to go for a new prosthesis every 2-3 years and finish off the tooth with new drillings.”
Ruslan, review from the website stomatology.rf
Another type of dentures is milled. They are modeled in a computer program and manufactured using a computer-controlled milling machine. This ensures the highest precision - the prosthesis fits onto the support without the smallest gaps, which eliminates the risk of microbial penetration. Titanium, aluminum and zirconium dioxides are suitable for milling - the latter are metal-free ceramics and last 15-25 years.
What is a crown and what is it for?
A crown is a permanent dental prosthesis, which, due to its shape, is difficult to distinguish from a real tooth.
Crowns are used when the tooth root is preserved and it is necessary to restore the functionality of the tooth, as well as the attractive appearance of the dentition, while preventing subsequent destruction of the dental organ.
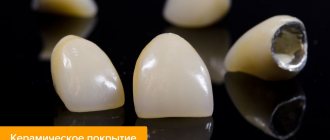
The material used to make crowns varies. Depending on it, these prostheses are divided into: metal, plastic, ceramic and metal-ceramic. Metal products are used extremely rarely, especially for visible teeth in the smile area. After all, they look completely unattractive.
Crowns made of ceramics or zirconium are the most expensive, because they look as close as possible to natural teeth, and even in the smile area they look very attractive.
Plastic products most often play the role of a temporary prosthesis. After all, they can crack or break and will not last long. Their cost is the lowest.
Metal-ceramic crowns are durable and aesthetic. Their practicality makes this type the most sought after and popular.
In addition to the material used to make crowns, the criterion for dividing them into types is the manufacturing method. Thus, crowns can be either solid or stamped.
Cost of dental restoration
Stamped crowns for teeth made of base metal alloys (steel, for example) are relatively inexpensive - about 1500-2000 rubles. If the prosthesis is coated - an acrylic “white” coating will be applied on top, then the price will increase by another 500-1000 rubles. In the case when the prosthesis is made of gold, the price increases significantly, because 1 gram of the noble alloy costs about 5,000 rubles. That is, the cost of such a solution is close to the cost of a solid-cast metal-ceramic crown.
Don't know what type of prosthetics to choose?
We will help in the selection, advise where to read more information and compare types of prosthetics.
Consultation with an orthopedic doctor in Moscow clinics is free! Call now or request a call
Working hours: from 9:00 to 21:00 - seven days a week
Possible errors and ways to fix them
In order for the prosthesis to fit the patient perfectly, it is necessary to strictly adhere to technology during its manufacture. But even in this case, errors are possible that will require correction.
- If during the installation of the crown the edge of the gum begins to turn pale, the structure needs to be shortened slightly using a bur and scissors.
- If the stump is too large in diameter, the doctor will need to sharpen the tooth so that the crown fits tightly on it.
- If the prosthesis is made poorly, the doctor sends it to the laboratory for revision.
- If the crown is too short, it cannot be used. It also cannot be corrected. In this case, it is necessary to make a new design that will suit the patient in all respects.
During the installation of the crown, it is possible to adjust the product for the best contact. If the crown is not made correctly, it is sent to the laboratory for revision.
User Questions
QUESTION Tell me, I have a gray crown on a molar that seems to be stamped. I noticed that the gum area around me was very red. Does this mean it’s time to change the crown or what? Sergey Anatolyevich
ANSWER Hello, Sergey Anatolyevich. Here you need to look at the situation - it is advisable to go to an orthopedist and get an x-ray. It is possible that food gets stuck under the gum, which is why it becomes inflamed. It is also possible that you have an allergy to metal. Perhaps some diseases have appeared under the roots, or cement has dissolved under the crown - and microbes penetrate into the resulting niche. After diagnosis, the dentist will make a verdict - whether the gum can be cured without removing the crown or not.
1Haug S. Correct modeling, 2006.
Author: Sambuev B. S. (Thank you for your help in writing the article and the information provided)
Prices for stamped crowns
Our LeaderStom clinic employs only highly qualified doctors. They have extensive experience working with complex dental cases, and positive results show the high efficiency of our specialists.
When using a stamped crown for prosthetics, an individual approach to each patient is important. This is the key to a positive outcome after treatment.
In our dental clinic, the price for this service is very favorable in the modern dental services market. Compared to competing clinics, this is the most optimal price-quality ratio.
Our specialists will provide you with:
- Providing highly qualified medical care from the most experienced dentists with extensive experience;
- Individual approach;
- Comfortable treatment conditions;
- Minimizing complications;
What teeth are they placed on?
Since the technology for manufacturing steel crowns is significantly outdated and has low aesthetics, it is rarely used when correcting defects in the anterior row of teeth. Such microprostheses are used if tooth decay is 70% or higher, when the use of other methods (filling or extension) to restore chewing function is no longer possible. These can be either pulpless or dead teeth after removal of nerves.
Metal microprostheses are installed in cases where the dentition has suffered serious damage as a result of severe carious lesions or injuries. Experts also recommend this solution if it is necessary to correct the pathological process of incorrect taste.
Such designs allow you to fully restore the chewing function of teeth.
Patients' opinions
Reviews from patients who had stamped crowns installed.
As a result of deep caries, which led to complications, several distant teeth had to be removed at once. As a result, severe discomfort appeared when eating and chewing.
The dentist recommended installing stamped crowns coated with gold. After all the tissue had recovered, I went to the doctor to have these products installed.
The procedure is of course long, but in principle tolerable. Two weeks later I had a crown installed, which I quickly got used to. I've been wearing it for about a year, and overall I'm happy with it.
Ivan, 45 years old
I engage in professional winter sports, namely skiing. During the next race I fell hard and hit my jaw area. After some time, I discovered severe pain in my tooth and immediately decided to see a dentist.
Upon examination, it was discovered that I had a crack in my tooth. The doctor treated everything, installed a filling, but recommended additionally installing a crown.
I chose a stamped crown with a plastic veneer; it is practically no different from a real tooth. Of course, the installation took a long time, but now I know that the damaged tooth is protected from negative effects.
Sergey, 36 years old
After I gave birth, my teeth just fell out one after another. As a result, I lost almost 5 chewing teeth. At first I wanted to get implants, but they are quite expensive.
The dentist advised me to use stamped crowns. I chose crowns with plastic lining and spraying. Still, it is much cheaper than implantation.
Perhaps in the future I will be able to save up money for implants, but for now I’m happy with it this way.
Irina, 33 years old
Installation of stamped crowns
This is where the work of the dental technician ends and I, the orthopedic doctor, get down to business. First, the finished crown is checked on the prepared tooth in the oral cavity and if the fitting process went well, then the stamped crown can be fixed using special cement. Since our clinic uses only the highest quality materials, the service life of the orthopedic structure is extended several times. And the skill and professionalism of me and my colleagues allows us to minimize all unpleasant sensations during the treatment process and extend the life of your tooth. But you shouldn’t rely only on fate and wait for this design to go out of service. It is enough to regularly visit a dentist and check the integrity of the structure, and if necessary, replace it with a new one in time.