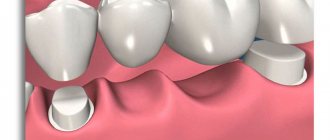
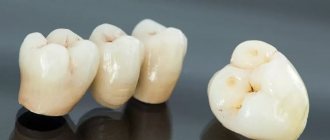
Installing crowns is one of the most effective ways to restore teeth. How can you determine that the prosthesis is of adequate quality and that the fixation procedure was carried out according to all the rules? It’s very simple: artificial teeth should not be visually different from real teeth. By and large, such a result can only be achieved if two conditions are met: the doctor installing ceramic crowns must be a true professional, and the structure itself is made of solid ceramics. Andrey Nikolaevich Karneev, leading orthopedist at the German Implantology Center, spoke about what a ceramic crown on a tooth is.
What are the advantages of a ceramic crown?
Today, ceramic dental crowns are the most aesthetically pleasing orthopedic structures installed both in the smile area and on chewing teeth. Ceramics is biologically inert and indifferent, is not perceived by the body as something foreign, does not absorb foreign odors, pigments and bacteria, does not emit harmful substances, and is also very durable. High-quality dentures cannot be distinguished from natural teeth.
3 main advantages of ceramic crowns
- Superior Aesthetics
- Hypoallergenic
- Reliability
What types of ceramic crowns are there?
Pressed ceramic crown
The most advanced type is the pressed ceramic crown. The design is highly durable, more accurately reproduces the color of natural teeth, and to install the prosthesis there is no need for strong grinding of the teeth, as is required for fixing structures made from other materials. The last advantage is extremely important, since the service life of the prosthesis depends on the amount of preserved natural dental tissue.
The most famous types of dentures made of pressed ceramics are created using E-max and Empress technologies.
- The E-max ceramic crown is made of lithium disilicate, that is, glass ceramics, which has a high degree of strength and is ideal for prosthetics in both the anterior and chewing regions.
- The Empress ceramic crown is made from the same material, but with the addition of leucite crystals, a mineral of igneous origin. The structures have excellent aesthetic characteristics, but are not able to withstand heavy loads, so they are installed only in the smile area.
Ceramic zirconium crowns
Often, prostheses made of zirconium are classified as metal-free ceramic crowns, which is fundamentally incorrect. Zirconium dioxide is the same metal, only white. Unlike ceramics, it does not have sufficient transparency, and its color palette is very limited. But, on the other hand, this material has good strength. Which crowns are better – ceramic or zirconium? Zirconium dioxide ceramic crowns are more suitable for restoring chewing teeth. In the frontal section, preference should be given to designs made of metal-free ceramics.
Ceramic crowns on a zirconium dioxide frame
A crown on a zirconium base, coated with a layer of ceramics, is the latest development in prosthetics. The white material, unlike metal, does not shine through the porcelain shell, which allows you to achieve excellent aesthetic results with high strength and wear resistance of the structure. In addition, the biocompatibility of a ceramic crown on a zirconium frame eliminates the risk of allergies and periodontal inflammation.
Methods for making metal-free crowns
There are 2 methods for making ceramic dentures:
- hot pressing or Empress - it is used to make crowns from pressed ceramics;
- milling or CAD/CAM technology – used for IPS e-max CAD glass ceramics and zirconium dioxide.
Prostheses obtained by different methods differ not only in manufacturing technologies, but also in their area of application.
How does the pressing method work?
Thermal pressing technology is the easiest way to produce metal-free prostheses. It is as follows:
- Based on the impressions obtained, first a plaster model is made from the impression masses, and then a wax model of the prosthesis;
- a wax model and a ceramic blank are placed in a casting mold and sent to the furnace, where the future prosthesis is melted at high temperature (about 800°C);
- the ceramic blank is moved into a press oven, where the crown is formed;
- the frame is polished with diamond burs and given the desired shape;
- the finished base is covered with porcelain masses, glazed and fired again in the kiln - this step is not used when processing IPS Empress CAD Multi ceramics.
Process of making ceramic crowns
What is CAD/CAM modeling and its stages?
CAD/CAM or automatic milling technology is the best. The prosthesis or its frame is made on a computer-controlled machine. This eliminates errors and reduces manual work to a minimum.
CAD/CAM is the only way to make prosthetic structures from zirconia: this material is too strong and cannot be processed manually.
CAD/CAM technology includes 2 components:
- CAD (Computer-Aided Design) – computer modeling and design;
- CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacture) – automated manufacturing.
The production of fixed dentures using the CAD/CAM technique proceeds as follows:
- An intraoral camera scans the oral cavity and transmits data to a computer.
- An orthopedic dentist uses a special program to develop a three-dimensional model of the patient’s jaws, and then a future design. Moreover, immediately, on the monitor screen, you can try on the electronic prosthesis and see how it will fit in the future. At this stage, the technician plans the shape of the product: a simple framework (for conventional zirconia blocks) or a fully finished crown (if pre-colored or translucent materials are used).
- A virtual model of the structure is transferred to an automatically controlled machine; on its basis, a computer installation will create a prosthesis.
- The resulting prosthesis is baked in an oven at high temperatures. If only the frame is made, it is lined with porcelain masses and fired again - this stage is skipped when using translucent and pre-painted zirconium blocks.
- At the final stage, the structure is glazed, giving it the final color.
CAD/CAM is the only method for making zirconia crowns
Ceramic crowns for front teeth
Many experts believe that ceramic dental crowns can only be used for prosthetics of the front teeth. Meanwhile, new generation pressed ceramics make it possible to make not only highly aesthetic, but also highly durable structures. The absence of a metal frame in such prostheses is not a sign of fragility or unreliability. Ceramic crowns for chewing teeth also have a place in dental practice.
Advantages of anterior dental prosthetics
In addition to metal-free dentures, defects in the smile area can also be eliminated using metal-ceramic crowns and bridges or composite restorations (made from light-curing filling materials). But both of these methods are inferior to ceramic products.
So, compared to metal-ceramic crowns, prosthetics of the front teeth with ceramics have the following advantages:
- thin walls: the wall thickness of zirconium and porcelain crowns is 0.3-1.2 mm, and metal-ceramic crowns are 2 mm, i.e. Under ceramics, a smaller volume of enamel and dentin is removed, which allows preserving the neurovascular bundle (pulp) and extending the life of the tooth;
- there is no cyanosis of the gums: it always occurs in patients with metal-ceramic dentures from the contact of the metal edge of the crown with the mucous membrane, this disadvantage can be avoided by making a metal-ceramic structure with shoulder mass, but its cost will be close to the price of restoration with ceramics;
- excellent marginal fit: this eliminates inflammation of the gums, their recession (drooping) and exposure of the edge of the prosthesis;
- preparation above the level of the mucosa: this technique allows you to avoid injuries to the gingival margin and the circular ligaments in which the tooth is held.
Another drawback of metal-ceramics is that it is impossible to make veneers or ultraneers from it.
Veneers and lumineers are also made from ceramics.
The only thing in which metal-ceramic crowns are superior to ceramics is price. On average, they cost 5-7 thousand rubles, but you can find prosthetics made from cheap materials from 4,000 rubles.
If you compare ceramics with composite restorations, you will find the following advantages:
- high strength: ceramics are less susceptible to chips and cracks;
- stability: zirconium and ceramic fixed dentures are resistant to external factors, and composites have a porous structure, which contributes to the accumulation of bacterial plaque, absorption of dyes and nicotine resins - all this leads to darkening of the restorations;
- longer service life: filling materials last on average 5-7 years (at the same time they change color after 2-3 years), and ceramic ones - at least 10;
- more possibilities: with the help of ceramics you can restore severely damaged teeth or restore missing units.
How are ceramic crowns placed?
Installing a ceramic crown involves the following steps.
- Preparation. The patient undergoes a visual examination, X-ray diagnostics, canal treatment and gentle grinding of the tooth - the specialist removes much less dental tissue than for crowns made of other materials. An additional advantage is that removal of the nerve is not a prerequisite for attaching a ceramic prosthesis.
- Making a ceramic crown. The doctor takes impressions of the jaws and sends them, along with x-rays, to the laboratory, where a plaster model is made to create an orthopedic structure using one of two technologies:
- hot pressing with layer-by-layer application of ceramics;
- computer modeling CAD/CAM and milling.
If the tooth tissue is severely damaged and there is no reliable base for the prosthesis, a stump inlay is first placed under a ceramic crown. More recently, under similar circumstances, a ceramic crown was installed on a pin, but today the method is outdated and is practically not used in clinics.
- Fixation of a ceramic crown. The procedure is carried out using a special cement or primer, which is polymerized by light. A ceramic crown, like any other, can be placed correctly only by an experienced orthopedist. Poor quality prosthetics leads to inflammatory processes in the gum tissue, tooth destruction and loss of the structure.
What are the differences between crowns, veneers and ceramic inlays?
5 types of prostheses are made from metal-free ceramics:
- veneers – ceramic plates (onlays) up to 0.7 mm thick, which cover defects in incisors and canines;
- Lumineers are a type of veneers with a thickness of 0.3 mm, they are also called ultraneers or Hollywood veneers;
- restorative inlays are analogues of fillings; they restore premolars and molars that are destroyed by 40-50%;
- crowns – hollow caps used to restore severely damaged units (60% or more);
- Bridges are structures consisting of several crowns (3 or more) to replace extracted teeth.
Veneers, ultraneers and inlays are classified as microprostheses. They are used to close minor defects. But in case of severe damage and missing teeth, only crowns and bridges will help.
The doctor decides which type of ceramic or zirconium dioxide prosthesis to use. It is based on the scale of the defect and the overall clinical picture.
What is the service life of a ceramic crown?
Metal-ceramic crowns are fixed with dental cement, which breaks down after about 5 to 7 years. However, ceramic dentures are attached to a particularly strong adhesive material, which increases their service life to 10 years.
As for strength, ceramic crowns can easily withstand the required chewing load. If a ceramic crown chips for some reason, it can be easily restored. Since the metal-free structure does not have a frame, almost any minor damage to it will be invisible. If more or less serious damage occurs, the all-ceramic crown can simply be polished.
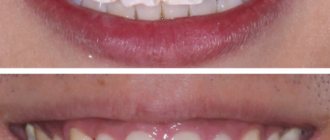
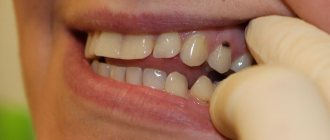
Photos before and after installation of ceramic crowns at the Research Center. Works by Karneev A.N.
Restoration of ceramic crowns
Despite the strength of modern ceramic dentures, the query “The ceramic has broken off from the crown, what should I do?” found on the Internet quite often. Typically a defect occurs for the following reasons:
- injury - blow or fall;
- defects in the work of a dental technician;
- malocclusion, bruxism;
- strong mechanical impact on the structure during chewing.
There are two possible solutions to the problem - replacement and restoration.
- Replacement of prosthesis. The crown is removed from the mouth, and the entire prosthetic process is repeated from the moment the impressions are taken until the new structure is attached.
- Restoration. The chip on the ceramic crown is polished to the optimal shape, and a light-curing composite material is placed into the cavity. After hardening, the specialist models the coating, forms bumps and fissures, and grinds uneven edges to the desired size.
The advantages of repair are short time and low cost; chipped ceramics on the crown can be restored in an hour in the dentist’s chair. However, even the use of the most modern materials does not provide the quality that is obtained when making a prosthesis “from scratch” in a dental laboratory. If the cause of the chip was carelessness when chewing hard food, after repair the denture will last for many years. Malocclusions and other pathologies of the dental system reduce the service life of the restored crown several times.
Restoration
No matter how good the ceramic and zirconium dioxide prostheses are, it is impossible to avoid chipping the facing porcelain. They occur due to:
- excessive chewing load (crunching nuts, removing lids with teeth, etc.) or its improper distribution due to malocclusions and bruxism;
- injuries - falls, blows;
- errors during the work of an orthopedist or dental technician.
Serious damage to the crowns cannot be eliminated - the structures will have to be completely changed. But chipped cladding can be restored for a couple of thousand rubles. They do this in two ways:
- polishing - in case of microscopic damage, simply polish the surface of the crown;
- composite restoration - chips and cracks are covered with light-curing polishing materials.
A restored metal-free prosthesis is inferior in strength to a structure made from scratch - new chips will not keep you waiting. Although, with careful handling, the crown will last for several more years.
Before and after dental restoration