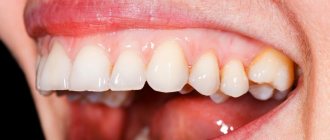
Hyperplasia as the main cause of pathology development
Why does this phenomenon occur when gums grow on a tooth? Most often this is due to the proliferation and enlargement of its cells. Scientifically, this process is called hypertrophy or hyperplasia (i.e. proliferation and increase in volume of tissue). The problem in most cases occurs against the background of an inflammatory process occurring in the oral cavity or metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalances in the body.
On a note! Hyperplasia or hypertrophy is a pathology in which soft tissue cells begin to grow uncontrollably, and the gums themselves can become inflamed and increase in size, they can begin to “crawl” onto the crown, partially or even completely (in the most advanced situations) block it.
Prerequisites for the development of hyperplasia
Various reasons can serve as prerequisites for accelerated and enhanced cell division:
- excessive accumulation of hard tartar and bacterial plaque above and below the gums,
- malocclusion: in such a situation, some teeth and, accordingly, the soft tissues and mucous membrane that surrounds them are subject to increased stress and pressure, they are constantly injured. The nutrition and blood circulation of tissues is disrupted, as a result of which their cells can begin to grow rapidly,
- endocrine diseases,
- genetic predisposition and heredity,
- long-term use of steroid hormonal drugs, antidepressants, anticonvulsants,
- hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, after childbirth, during menopause in women, changes in hormonal status in adolescents during puberty1,
- acute vitamin deficiency: hyperplasia often occurs due to a lack of vitamin C,
- traumatic damage to the mucous membrane due to incorrectly installed fillings, artificial crowns or braces,
- teething,
- leukemia
Causes
Exposed necks indicate periodontal damage. Most often the problem occurs for the following reasons:
- Genetic predisposition. When exposed to this factor, a person can very diligently monitor the health of his smile, but will still periodically encounter unpleasant dental symptoms.
- Mechanical and thermal damage. The habit of gnawing on foreign objects, eating too hot food, using a hard brush are all provocateurs that contribute to irritation.
- Poor oral hygiene. If the patient neglects basic hygiene rules, a lot of plaque is deposited on the crowns. Pathogenic microorganisms spread in it. The gums become irritated, turn red, and bleed. Gradually they begin to move away from the teeth. It is important to use a brush and paste twice a day, and undergo professional hygiene at the dentist’s office annually.
- Poorly performed prosthetics or mistakes made during filling. It is necessary that the dentures fit as tightly as possible to the bases and do not fall under pressure, otherwise the gums will be constantly injured and inflamed.
- Curvature of the bite, problems with teething “eights”, uneven edges of the crowns. All this causes the gums to move away from the tooth.
- Unbalanced diet. If a person eats only soft foods and sweets, he does not actively chew food. As a result, blood circulation in the oral tissues slows down, less saliva is released, and periodontal deposits are actively formed. These are the prerequisites for a recession.
- A large amount of tartar. Despite the fact that dentists recommend removing stones annually or even more often, many patients do this very rarely. You shouldn't wait until a serious problem arises. It is easier and cheaper to prevent it than to treat it later.
- Hormonal imbalance. Most often, this reason concerns women, for example, during pregnancy, menopause, and breastfeeding. With hormonal fluctuations, the mucous membranes become especially vulnerable. Even minor mechanical impacts cause recession.
Don't forget about the negative effects of tobacco smoke. According to statistics, smokers are much more likely to suffer from gum disease and exposed necks. They accumulate plaque faster. Therefore, if you want to have a healthy smile and visit the dentist less often, stop smoking.
Main diseases characterized by tissue hyperplasia
Fibrous or hypertrophic gingivitis
Between the teeth there are gingival papillae, which during the development of fibrous gingivitis begin to gradually increase in size, they become denser and grow. In this case, the mucous membrane remains painless for a long time, and there is no bleeding.
Read more about all types and symptoms of gingivitis in a separate article on the website.
The disease develops against the background of poor oral hygiene and the accumulation of a large amount of plaque; it can appear due to poor-quality prosthetics and constant trauma to the mucous membrane. People who have hormonal imbalances or gastrointestinal diseases also encounter fibrous gingivitis. The disease often occurs in both adults and children.
Important! A growth over a tooth is not always associated with hyperplasia; it can be nothing more than a gumboil, abscess, fistula or cyst, indicating advanced dental diseases. Most often, such manifestations are very painful, they are white in color, because... pus accumulates in them.
Fibromatosis
This is a hereditary disease and therefore often manifests itself in childhood. It is characterized by the growth of individual areas of the gums and proceeds very slowly. The color of the affected tissues is usually no different from healthy ones; they are painless.
The disease occurs mainly in the frontal area of the smile, and soft tissues can grow so much that they cover the crowns by more than 2/3. If fibromatosis is not treated, it is fraught with destruction of interdental septa, osteoporosis, and a severe violation of the aesthetics of the smile.
Fibropapilloma
If the gums have grown onto the crown, then a disease such as fibropapilloma may be to blame. This is a benign tumor. The tumor is hard to the touch, but painless. Its appearance in childhood is more dangerous, because can lead to disruption of the formation, growth and eruption of permanent elements.
Epulis
Epulis, like fibropapilloma, is a benign formation. It has a mushroom shape, because the tumor grows on a stalk. Appears as a result of chronic irritation and tissue injury. The most common location is the area of the incisors or canines. If the tumor is not removed, it can lead to pathological mobility and tooth loss.
Causes and risk factors for gum recession in children and adolescents
Dentists are faced with many reasons that cause degenerative processes in the gums. The development of pathology in childhood and adolescence is most often associated with the following problems:
- malocclusion: improper closure of teeth leads to uneven distribution of load and tissue degeneration;
- crowded teeth;
- insufficient oral hygiene, accompanied by the deposition of large amounts of plaque and tartar;
- tissue injuries (including those associated with overly aggressive brushing of teeth);
- short frenulum of the lip.
The list of risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing gum recession in children and adults includes:
- hormonal changes during puberty;
- chronic diseases of the cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive systems;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- decreased immunity;
- vitamin deficiency, lack of microelements, unbalanced nutrition in general.
Why does the problem appear in children and when should you see a doctor?
The situation when gums grow on a child’s tooth most often occurs during the period of teething, as well as the change from a primary bite to a permanent one. During eruption, the mucous membrane swells and increases slightly in size, because it is irritated, blood circulation increases in it, but in this case we are not talking about hyperplasia. However, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the child’s oral cavity over time.
You should consult a doctor in the following situations:
- if 2-3 months after the crown “hatched”, it did not come out completely, and most of it remains under the gum or soft tissue hangs over it, partially covering it,
- the baby tooth did not fall out during the change of bite, but gums are growing on it: perhaps a permanent element is “hiding” under the formed tubercle, which did not have enough space, and it began to make its way in a different direction or into the second row,
- the growth is filled with white contents, and the child has a bad smell from the mouth: perhaps we are talking about the presence of advanced dental diseases, which are complicated by a fistula, abscess or cyst.
Prevention measures
It is impossible to completely guarantee protection against the gradual separation of the gums from the tooth, because this will happen naturally with age, but you can slow down this process. Experts in the field of periodontology and dentistry have identified several basic recommendations, following which you can minimize the risk of gum recession:
- The first thing you need to do is systematically visit the dentist 2-3 times a year as a preventative measure.
- You need to give up bad habits or reduce them to a minimum.
- Enrich your daily diet with fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Perform hygiene procedures at least 2 times a day, in the morning and before bed. If desired, you can supplement brushing with dental floss.
- If you suspect or have any symptoms of any oral disease, consult a doctor immediately.
Regular dental checkups are something that most people neglect. Therefore, you need to develop a habit that will help keep your teeth healthy.
It is important to know! If your gums are your weak spot, you need to brush your teeth very gently, using a soft toothbrush and mouthwash. A hard brush can harm the gums and cause them to separate over time.
Gum recession is not just an aesthetic problem. This phenomenon signals the presence of a more serious disease or ongoing pathological processes in the soft tissues of the gums. Any deviation from the normal state should alert you and cause a visit to the dentist.
Laser gingivotomy - surgical treatment of complex forms of periodontitis
The roots of the teeth are exposed - what to do and how to treat them
Splinting teeth for periodontitis with fiberglass and tape
Catarrhal and hypertrophic gingivitis symptoms and treatment in adults
Open and closed curettage of periodontal pockets
Treatment of generalized moderate and severe periodontitis
Gum growth on wisdom teeth
There are situations when gums have grown on a wisdom tooth. And this is not related to the phenomenon of hyperplasia. If the third molar has only recently begun to erupt outward, one of its cutting edges has already appeared, and suddenly you feel pain, bad breath appears, and upon examination, inflammation, swelling of the soft tissues and their overhang over the tooth are discovered, then you probably have pericoronitis began.
Pericoronitis is an inflammation of the gingival hood over the third molar. The disease develops due to the fact that small pieces of food begin to get into the gap between the gum and the “eight” that has not fully penetrated, which rot because they are difficult to remove.
For more information about what pericoronitis is and how it is treated, read the feature article on the website.
Symptoms of receding gums
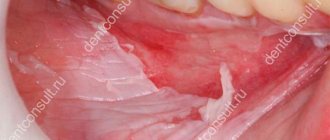
The condition in which the gums recede may be accompanied by other symptoms. Depending on the extent of the pathological process, recession is observed in a limited area, one side or the entire jaw. As a result, the neck of the tooth may be exposed, and with severe loss, part of the root.
This cannot but be accompanied by increased sensitivity of the teeth - increased susceptibility to hot and cold, sour, sweet foods and even mechanical stress. This symptom leads to difficulties while eating.
It is important to understand that some symptoms may indicate concomitant pathologies. So, if recession is observed against the background of whitish, pale gums, we can talk about periodontal disease. Bleeding and red gums often develop with periodontitis and gingivitis.
What will happen if left untreated?
Lack of timely treatment for gum recession can be fraught with more than just aesthetic problems. If there is a gap between the gum and the tooth, food debris and plaque get into it, and this can cause an inflammatory process. As the tissues become thinner and sagging, the following consequences of recession may appear:
- Hyperesthesia, or increased tooth sensitivity, difficulty chewing.
- High risks of caries development, and in the least protected and more vulnerable areas - in the area of the exposed necks of the teeth. At the same time, carious lesions in this area proceed faster and are more quickly complicated by pulpitis and periodontitis due to a thinner layer of enamel.
- Increased risk of developing a non-carious lesion - a wedge-shaped defect.
- High risks of inflammation, swelling of the gums, and the formation of periodontal pockets.
- An increase in the amount of plaque at the roots, which further aggravates the condition.
Complications can result in serious consequences such as loosening and loss of teeth.
Diagnostic methods
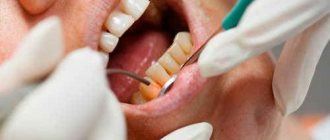
If the gum is moving away from the tooth, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible: in the early stages, recession is faster and easier to treat. Diagnosis involves collecting anamnesis, analysis of symptoms and complaints, examination and instrumental examination if necessary. During the examination, the doctor will assess the width and nature of the gum damage. A periodontal probe can be used for diagnosis - it is inserted into the periodontal pocket to assess the depth of the lesion.
An assessment of the degree of gum damage is calculated by calculating the recession index using the following formula: the number of affected teeth is divided by the total number of teeth and multiplied by 100%. This is how the severity of the disease is determined: less than 25% is a mild recession, 26-50% is moderate, and from 50% is severe.
For diagnostics, a microscope is used, and binocular magnifying glasses are used. The thoroughness of diagnostic measures allows you to accurately select an effective treatment method. In addition, before starting treatment, it is very important to find out the causes of the disease: to determine whether recession is an independent disease or a symptom of another pathology.
Therefore, differential diagnosis with other periodontal diseases in which the gums rise is necessary. To do this, the doctor may prescribe a targeted or panoramic X-ray to assess the condition of bone tissue and detect hidden concomitant diseases.
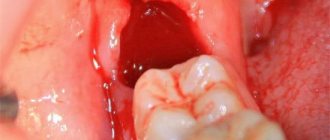
If a broken tooth is healed
Situations where a tooth broken at the very root is overgrown with gums are not uncommon. It can break due to injury or collapse due to advanced dental disease. After this, many people are in no hurry to remove the root, and in some cases it gradually grows over from above (this process can last several years), and then does not bother or hurt for a long time. However, sooner or later, unpleasant sensations still appear: it becomes painful to chew, overgrown tissues swell and are constantly injured.
“My gums have grown on my back tooth, which broke off three years ago. I completely forgot about him, because... It didn’t give me any trouble, only sometimes after cleaning it would scavenge, but I didn’t attach any importance to it. All this was revealed during an examination at the dentist, when I went there with a completely different problem. In principle, the doctor decided everything quickly: he opened this growth and removed the root, then put stitches, but then it healed for a very long time and painfully. It was also very disappointing to hear that if I had contacted him immediately after the tooth was chipped, it could have been restored, but I immediately decided for myself that it was lost. That’s it!”
Varvara, review from 32top.ru
Remember that if a tooth is broken, then either its timely removal or restoration and prosthetics is necessary, because a serious inflammatory process can begin under the overgrown tissues or at the root, which can spread to the jaw, cheek, can develop deep into the body, lead to periostitis and osteomyelitis.
How long does the gum “grow” and the stages of development of hyperplasia
Pathology can develop slowly if it is caused by fibromatosis, epulis or fibropapilloma. And it can develop more rapidly if it occurs against the background of gingivitis.
As for the stages of development of hyperplasia, doctors identify the following:
- first stage: the gingival papillae thicken and thicken, while there are no other alarming signs,
- second stage: soft tissues grow and can cover up to half of the crown. Due to the volume, tissues are easily injured during oral hygiene and when chewing food, they can begin to bleed,
- third stage: the most rare stage. The tissues grow so much that they can even cover the cutting area of the crown. Granulations appear on the affected areas.
If you break off a tooth, gum growth may take several years.
The gum has moved away from the tooth: treatment
If the gum has moved away from the tooth, treatment will largely depend on the severity of the inflammation. For example, if a patient seeks help at a fairly early stage of inflammation (when the depth of periodontal pockets does not yet reach 3 mm and there is no tooth mobility), significant success can be achieved in the treatment of periodontitis and the process can be completely stopped. Advanced cases of gum inflammation will require much more complex treatment and serious financial costs. Next we list the main stages of treatment.
1) Consultation and x-ray diagnostics –
It is necessary to begin treatment with a consultation with a periodontist and a panoramic photograph of the teeth, which will allow you to create an optimal treatment plan taking into account the condition of your teeth and gums. The image will allow you to determine the amount of destruction of bone tissue around each tooth, the location and depth of periodontal pockets, and will help guide the patient in the need for splinting of mobile teeth, the need for prosthetic replacement of missing teeth, and make the correct diagnosis.
An example of a panoramic image of a patient with periodontitis –
Looking closely at the image, you may notice that the level of bone tissue (the bone looks in the image as fine-mesh looped tissue and normally should reach the necks of the teeth) is reduced in different teeth by 1/4 to 4/5 of the length of their roots. The patient has decayed teeth that need to be removed, as well as carious teeth that require treatment (24stoma.ru). The level of bone tissue is most reduced in the front teeth of the upper and lower jaw, which in this case was the result of not only inflammation of the gums, but also the absence of the chewing group of teeth.
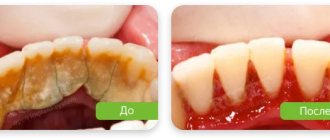
To treat gums, it is best to contact not ordinary dental therapists or hygienists, but periodontists. These are the dentists who specialize in gum treatment. The first and most important stage of treatment will be ultrasonic teeth cleaning. Next, a course of anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out, which in most cases can be successfully carried out at home.
2) Removal of dental plaque –
First of all, it is necessary to remove the cause of inflammation - microbial plaque and dental deposits. They are removed from the teeth using an ultrasonic scaler (Fig. 15), usually over several visits. It is simply impossible to remove all dental deposits in just 1 visit in a patient with periodontitis, because... It takes a lot of time to remove subgingival dental plaque, which is localized in periodontal pockets below the gum level.
It is subgingival dental plaque that poses the main danger for further progression of inflammation, so sometimes it is necessary to prescribe the patient even 3-5 times. Learn that without professional cleaning, all other stages (for example, anti-inflammatory therapy, splinting) will be completely meaningless.
Most dentists and hygienists won't bother with finding and removing subgingival calculus...as experience has shown. Therefore, it is very important to find a competent specialist. Anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed immediately after 1 session of removing tartar, and within the first 24 hours you will be able to notice changes in the appearance of the gums. In parallel with the reduction in gum swelling, their volume will also decrease, which will allow you to see new portions of dental plaque and remove them during subsequent visits.
Removing dental plaque with ultrasound: video
You can see in the following photos what happens when subgingival tartar is removed poorly. The first photograph shows that the gums are visually in good condition, although a periodontal probe revealed the presence of a periodontal pocket about 5 mm deep. The second photograph was taken after the gums were detached from the teeth, and it shows a very large amount of destruction of bone tissue, which arose due to the presence of small subgingival tartar on the surface of the tooth root.
3) Anti-inflammatory therapy –
The course of anti-inflammatory therapy usually lasts 10 days. In most cases, it is carried out by the patient himself at home, after doctor’s prescriptions and patient education. However, if the patient has deep periodontal pockets with purulent discharge, the doctor may additionally prescribe washing the periodontal pockets, which is done using a syringe and antiseptic solutions. In some cases, antibiotic therapy may also be prescribed for periodontitis.
Anti-inflammatory treatment regimen - usually a complex is prescribed, consisting of an antiseptic mouth rinse and application of gel to the gums. The procedures are carried out 2 times a day (morning and evening, after meals and subsequent oral hygiene), for 10 days. Most often, a complex of the following drugs is prescribed:
- rinsing with Chlorhexidine (instructions)
- “Cholisal-gel” applications (instructions)
In patients with periodontitis, the correct choice of treatment agents is very important. For example, a standard 0.05% solution of chlorhexidine, sold in pharmacies for 40 rubles, is advisable to use only for superficial inflammation of the gums (gingivitis), but for periodontitis it is better to use a 0.2-0.25% concentration of this antiseptic. It is a big plus when such a solution contains not only a good concentration of chlorhexidine, but also other active ingredients (for example, aluminum lactate for bleeding gums or extracts of medicinal plants).
Antiseptic mouth rinse is carried out after breakfast and oral hygiene, rinse your mouth for 1 minute. After this, the gums need to be dried with a dry gauze pad to remove excess saliva, and an anti-inflammatory gel should be applied to the gum edge. The gel is applied in front of a mirror using a finger, and usually only on the front side of the teeth. After such treatment, it is not recommended to eat for 2-3 hours, and also not to drink for 30 minutes. There are a lot of remedies for treating gums, and we hope that our next articles will help you understand their diversity -
→ The best antiseptics for mouth rinsing, → Rating of the best gels for treating gums.
4) Oral hygiene training –
If you have not yet forgotten the beginning of the article, then remember that the cause of periodontitis and destruction of the dental-gingival attachment is unsatisfactory oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of microbial plaque and tartar on the teeth. Therefore, in addition to the basic treatment that we described above, it is very important to constantly maintain high-quality oral hygiene.
Good hygiene doesn't mean just brushing your teeth twice a day, that's not enough. Good oral hygiene includes brushing your teeth after every meal, not snacking on cookies or candy between meals, and regularly using dental floss. You can read about absolutely all the recommendations in the article at the link above. Below, you can watch the video on how to properly use a toothbrush and dental floss.
How to use dental floss and brush correctly -
In the presence of periodontal pockets and mobile gingival margins, it is important to carry out hygiene below the gum level. This can be done using special devices - home irrigators. Special attachments allow you to rinse at home not only areas of the oral cavity that are difficult to reach for hygiene, but also periodontal pockets below the level of the gingival margin. Irrigators can use both ordinary boiled water and special medicinal solutions.
Signs and symptoms of hyperplasia
Those who have this problem rarely experience pain right away. But almost all patients notice a visual violation of the aesthetics of a smile, because the gums become voluminous and loose, which, as a rule, is the reason for visiting a doctor.
Discomfort and pain appear after the tissues have grown significantly, and they involuntarily have to be constantly injured during hygiene procedures and eating food. Another sign is the appearance of bad breath, which does not go away after careful hygiene or quickly returns again.
Consequences and complications if the pathology is not treated
Many patients see overgrown gums as only one problem – a significant disruption to the aesthetics of their smile. However, this is not so: if the pathology is not eliminated and it is allowed to progress further, then this is fraught with serious complications for the health of the oral cavity and the body as a whole.
If left untreated, the patient may develop degenerative diseases of periodontal tissues, leading to the destruction of the interdental septa and supporting ligaments that hold the teeth in the sockets. You may lose your teeth much earlier than you would like.
Hypertrophied tissues are subject to constant trauma, which is why any benign formation can sooner or later become malignant. Another common complication is osteoporosis.
For children, the lack of treatment is fraught with disruption of the formation, as well as the timing of the loss of milk and the eruption of permanent elements.
If a single growth appears on the gum, this may not always indicate hyperplasia or hypertrophy. Some people mistake the growth for a fistula, cyst, or abscess. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner for these pathologies, the purulent contents from these neoplasms can spread throughout the body, causing damage to the cardiovascular and circulatory systems, gastrointestinal diseases, sepsis and even a brain abscess.
About orthodontic treatment to stop gum recession
These can be orthodontic structures: braces, or aligners, or something else - this is what the orthodontist will choose, it is he who determines which technique for correcting the bite in a given case of recession will be best applicable for each specific patient. There are no universal treatments. The only question that is subject to discussion is how long orthodontic treatment will take in one way or another.
As a result of treatment, the orthodontist must place the teeth in a physiological occlusion so that the tooth/teeth do not bear such a load that they experience excessive chewing stress at the time of contacting the doctor.
And then, when the tooth is placed in the functionally correct position, the following happens to the gum. Gum recession stops. And again, if it stops at such a level that closing the recession is possible, then the gums subsequently rise and the recessions close.
And after some intervention, perhaps the gums will return in full.
Cases where orthodontic treatment eliminates recession
We cannot always close all gum recessions with the help of orthodontics. We remove the cause of the recession, that is:
- malocclusion,
- we correct occlusal contacts that lead to this recession,
- eliminating improper stress on teeth,
- We eliminate the lack of load in the case of an extracted tooth and the overload, in turn, of neighboring teeth.
And after the doctor has normalized the patient’s bite and normalized the correct closure of his teeth, we refer him to a periodontist who will perform gum plastic surgery.
In any case, the pathological process of gum loss stops after our treatment; it no longer progresses. And we always wait after removing braces (or other orthopedic structures) from 3 to 6 months
for the gums to recover and calm down. And after this, if necessary, plastic surgery of the frenulum, plastic surgery of the vestibule of the oral cavity is performed - all this is done only after orthodontic treatment.
Why is plastic surgery done AFTER, and not BEFORE, bite correction?
Because a scar is formed inside the operated tissue, which in the future can interfere with the movement of teeth when correcting the bite.
Methods of treating pathology in dentistry
The most common method of removing overgrown tissue is surgical excision using a scalpel or laser. Scientifically, this surgical operation is called gingivectomy. The procedure is performed under anesthesia.
About the indications, types and complications after gingivectomy - in the feature article on the website.
If there are few damaged tissues, then doctors may suggest their removal using cryodestruction, when under the influence of low temperatures they die off on their own over time.
If tissue proliferation is accompanied by an inflammatory process, then electrophoresis and darsonvalization may additionally be prescribed.
In addition to excision of excess tissue, treatment should be carried out aimed at eliminating the cause that provoked the development of the pathology. If the cause is a malocclusion, then the patient needs to see an orthodontist, who will prescribe devices to correct the position of the dentition. If there is a fragment of a tooth inside the overgrown gum, then it is necessary to remove it or use prosthetics, if the situation allows. In case of internal diseases of the body, the patient will be referred to specialized specialists - endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist, etc.
Dentists are required to sanitize the oral cavity and remove hard and soft bacterial plaque.
Additional treatments
Considering that gums become inflamed for various reasons, it is important to try to find out the provoking factor. Then the risk of relapse of dental pathology can be reduced to a minimum.
If the doctor determines that the disorder is related to hormonal levels, it is necessary to select hormonal therapy . In case of malocclusion, consultation with an orthodontist is indicated. If the diet is unbalanced, the patient is told what the diet should be like after recovery.
Often, when fighting gum that has receded from a tooth, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, glucocorticosteroids, and antiseptics are used. It is very important that the patient strictly follows all medical prescriptions and does not engage in amateur activities. An integrated and responsible approach to treating recession is a guarantee of a speedy recovery.
If the tissues become so inflamed that the teeth begin to loosen, splinting may be required. If there is a deficiency of bone tissue, their deficiency is compensated with special compounds.
Recovery period after surgery
If the gum has grown on the tooth, then now you know what to do - you need to contact a dentist who will prescribe adequate treatment.
Since treatment for hyperplasia involves surgical manipulation, there will be a recovery period after it, taking from 5-7 to 10-14 days. At this time, you need to follow all the doctor’s recommendations: take prescribed anti-inflammatory and wound-healing agents, rinse with antiseptics, and use painkillers as pain occurs.
During the rehabilitation period, it is important to exclude “irritating foods” from the diet: spicy and salty, cold and hot, solid foods. And, on the contrary, you need to diversify your diet with foods rich in vitamins C, E, B, A, calcium and phosphorus.
To care for the oral cavity, you need to use a brush with soft bristles and a non-abrasive toothpaste; you should avoid using an irrigator for a few days.
Surgical techniques
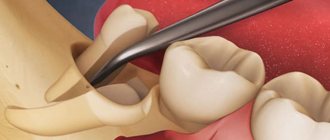
In advanced situations, plaque removal alone is not enough. Then there may be a need for open or closed curettage. It is indicated if the gums are very severely detached from the dental neck and the bone structure is changed.
The dentist-surgeon treats the lesion with an antiseptic, makes a small incision and removes purulent deposits and affected tissue . Then the gum is sutured. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. This means that the patient is conscious and can communicate with the doctor, but does not feel pain.
For a speedy recovery after curettage, antibiotics and mouth rinsing with an anti-inflammatory solution are prescribed. If the pain after surgery is very severe, the patient can use painkillers.
Is it possible to get rid of the problem on my own?
Some people use decoctions of medicinal herbs and plants (chamomile, oak bark, sage and others), as well as solutions to relieve gum inflammation (such as Chlorophyllipt or Stomatophyte) to get rid of the problem. However, you need to understand that hyperplasia cannot be cured by rinsing. This measure will not reduce the volume of overgrown tissue, but will help relieve signs of the inflammatory process and alleviate the condition during teething, and is also well suited as a concomitant therapy after surgical excision of excess gum tissue, which is carried out in a dental office.
Features of treatment of gum recession
There are conservative and surgical methods, with the help of which it is possible to cope with the problem relatively quickly. The development of a treatment program is always individual and takes into account the severity, causes of prolapse, prevalence of pathology and other conditions.
The first step is always professional teeth cleaning. It is necessary to remove soft and hard dental plaque. Sometimes subgingival tartar is removed, which already makes it possible to reduce the depth of periodontal pockets, and in combination with other methods, cope with the problem completely or achieve a significant improvement.
Drug treatment can solve several problems at once:
- eliminate or prevent gum inflammation;
- strengthen gums;
- improve blood circulation;
- speed up recovery processes;
- activate the growth of mucosal cells and gum tissue.
For this, vitamin therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs and local antibiotics, self-absorbing membranes, etc. can be used. The doctor may prescribe medicinal baths, rinsing with certain solutions or application of drugs to the gums, including at home.
Preparations that activate recovery processes are also widely used: products based on hyaluronic acid, regenerating gels with growth factors. The launch of natural regeneration processes allows you to literally “grow” the gum in the place where it subsides.
Another conservative method is the use of the patient's own blood plasma enriched with platelets. This method is called plasma lifting, or APRF technology. Injections into the gums can be used, as well as special membranes that are placed under the gums, but as part of a surgical intervention. This allows you to quickly restore tissue and improve cell nutrition.
As for other surgical treatments for receding gums, the most common are:
- Flap surgery - gum recession is closed with a gum flap, which the doctor takes from the patient's own tissue located nearby. Intervention is performed when the gum defect is minor and there is a sufficient amount of surrounding tissue that can be used.
- Transplantation of a graft from the hard palate/tuberculum of the upper jaw. In this case, part of the gum or a flap of connective tissue is taken from the donor sites and planted in the defect area. Can be used for all types of recession.
- Combined method: the movement of gum tissue is combined with the collection of tissue from the hard palate. The combination of approaches makes it possible to obtain high aesthetic results and close deep recessions. However, if gum loss is more than 5 mm, multiple interventions may be required.
Closure of gum recession is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. The choice of type of operation is determined by the condition of periodontal tissues and diagnostic results. All surgical methods are often combined with curettage - cleaning the space under the gum and removing subgingival deposits, and are also supplemented with growth activators.