Dental problems
Dental diseases
With deep caries and its complications - pulpitis, periodontitis - the pain radiates to the jaw in the area of the affected tooth.
Infectious and inflammatory processes of the soft tissues surrounding the tooth - periodontitis, abscess - cause swelling, which, by squeezing the nerve endings, provokes the appearance of painful sensations in the jaw.
With increased tooth sensitivity, eating hot, cold, spicy, sour or sweet foods and drinks, and brushing your teeth cause acute pain that spreads to the jaw.
When third premolars - wisdom teeth - emerge, complications often arise: pericoronitis, inflammation of the periosteum, one of the symptoms of which is severe pain in the jaw.
Dental treatment procedures associated with violation of tissue integrity - implantation, prosthetics, tooth extraction, installation of fillings, professional teeth cleaning and whitening - contribute to the appearance of pain in the jaw.
Bruxism
With bruxism, involuntary grinding of teeth at night significantly increases the load on the masticatory muscles, which leads to their prolonged spasm. In this case, the correct occlusion of the dentition is disrupted with the development of pain in the jaw when chewing.
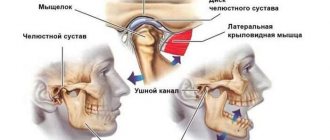
Temporomandibular joint problems
If pain occurs in the jaw when opening the mouth, this is a symptom of temporomandibular joint pathology.
Pain in the projection of the jaw is often accompanied by pain in the ear, head, and face. The causes of joint dysfunction are injuries, malocclusions, incorrectly installed dentures, arthritis, arthrosis, and hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles.
Tumors of the lower jaw
Pain in the jaw area is characteristic of benign and malignant neoplasms. Benign tumors are characterized by slow growth and lack of invasion into adjacent tissues and organs.
Malignant neoplasia rapidly progresses, pain intensifies with irradiation into the eye, temporal region, ear, jaw.
How to get rid of unpleasant symptoms
The choice of method for eliminating pain depends on the cause that caused it. Do not self-medicate: warm, rinse or take pills without consulting a doctor. The insidiousness of pain syndrome is that it is characteristic of different diseases. In some cases, you can alleviate the condition before visiting a specialist.
Ear pain due to caries
You can relieve the pain a little with the help of anti-inflammatory tablets. In such cases, nimide or ibubrofen are recommended. The drugs should be taken after meals in the indicated dosages for no more than 5 days. Fans of traditional medicine use a natural antiseptic – garlic. It is crushed and applied to the diseased tooth.
What to do with pulpitis
The pain with this pathology is often unbearable. Therefore, patients with this disease usually strive to see a doctor as quickly as possible. Treatment can be carried out using biological and surgical methods. In the first case, the tooth is treated conservatively, in the second, the pulp is completely or partially removed. Once the cause is eliminated, the ear pain stops.
How to treat alveolitis
All treatment methods are aimed at eliminating inflammation in the socket. The process is stopped by taking anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and desensitizing agents. The treatment method is determined by the dentist after an x-ray.
Elimination of post-filling pain
The appearance of ear pain after installing a filling is a reason to remove it. The tooth is treated and filled again. In case of an allergy to the substance from which the filling is made, the doctor selects another material.
Pain after wisdom tooth removal
Damaged tissues and nerves need time to recover. Therefore, pain is a common reaction to intervention. To reduce it, dentists recommend taking painkillers. If the pain not only does not go away, but also intensifies, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics and recommend a special rinse.
Causes of jaw pain not related to dental disorders
Neuralgia
When the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for the sensitivity of the face and oral cavity, is damaged, the pain is strong, sharp, reminiscent of the pain of pulpitis. Often patients with trigeminal neuralgia undergo unnecessary dental treatment with depulpation or tooth extraction, but the pain syndrome persists.
Sialolithiasis
Salivary stone disease is characterized by the formation of stones in the ducts of the large salivary glands. Since the salivary glands are located in the mouth, pain during their inflammation also affects other nearby organs of the oral cavity, in particular the jaw.
Sinusitis
When the mucous membrane of the maxillary cavity becomes inflamed, increasing swelling and accumulation of exudate cause pain spreading to the upper jaw area from the side of the affected sinus.
Otitis
Sometimes the symptoms of otitis media are similar to toothache. With inflammation of the middle ear, pain often radiates to the jaw. The pain is sharp, shooting, aggravated by chewing and swallowing.
Submandibular lymphadenopathy
Enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes is observed in diseases of the tonsils, acute respiratory viral infections, stomatitis, and oncological tumors. Pain under the jaw is often accompanied by limited range of motion - it is difficult for the patient to bend and turn his head, or open his mouth wide.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Irradiation of pain into the lower jaw can be observed during an attack of angina and myocardial infarction. A characteristic symptom of coronary heart disease is burning, pressing pain behind the sternum. But with an atypical course of a heart attack, retrosternal pain may be completely absent, only reflected pain comes to the fore: in the left arm, in the neck, in the face, in the jaw.
Symptoms of TMJ dysfunction
- Pain in the jaw, increasing when opening the mouth, chewing, speaking, yawning;
Clicking in the joint of the lower jaw, the jaw “jams”, it does not open, does not close, or has begun to close differently;- Pain in the temples, in the eye area, visual impairment, photophobia (sensitivity to light);
- Pain, ringing and noise in the ears, in the ear area, feeling of pressure in the ears;
- Frequent headaches, dizziness, migraines;
- Sleep disorders, insomnia, anxiety, depression;
- Pain in the neck, in the lower part of the skull;
- Tooth pain from sweets, hot, cold.
This diversity in symptoms, which often makes it difficult for doctors to diagnose, is explained by the fact that the joint is connected to many important organs and parts of the body (eyes, ears, neck, head) and errors in its functioning can affect everything at once, or they can only affect something one. It is usually possible to determine that the problem is in the temporomandibular joint only in a complex manner.
In most cases, TMJ dysfunction is manifested by pain in the face, joints of the jaw, neck, shoulders, ears, crunching and clicking. Complaints of dizziness, difficulty chewing food, speech and hearing disorders, difficulty opening the mouth, “jamming” of the jaw, or even the appearance of swelling and fever are also common.
Diagnostics
When there is pain in the jaw, the patient first seeks advice from a dentist.
A dental examination includes the following steps.
- Clarifying patient complaints and collecting anamnesis. Since the main complaint is pain in the jaw, the time of its appearance (at night, during the day), the nature of the pain (sharp, dull, pulsating, aching), and duration (constant, paroxysmal) are specified.
- Examination of the oral cavity with assessment of the condition of the mucous membrane, tongue, gums, determination of the type of bite.
- Examination of the surfaces of all teeth using a probe and mirrors, identifying the integrity of the dentition, detecting defects in the hard tissues of the teeth.
- The percussion method is used to determine caries complications.
- Thermodiagnostics is used to identify pain reactions.
Diagnostics and x-ray of the temporomandibular joint
Diagnosis of TMJ when it is dysfunctional is difficult due to the variety of clinical complaints. This leads to the fact that the patient can undergo examination by different specialists for a long time, wasting time. A full examination is carried out by dentists
(primarily an orthopedist or orthodontist) and neurologists.
Diagnosis with the naked eye is difficult, and TMJ problems can only be directly noticed if the malocclusion is clearly visible. Most often, dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint is associated precisely with disorders of bite and jaw closure.
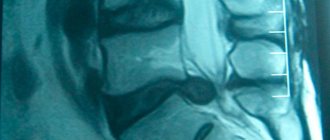
The most reliable and effective way is to conduct x-ray diagnostics and orthopantomogram
jaws. In some cases, an MRI may also be done.
If the cause of pain is a problem with bone tissue
Pain emanating from the bone and joint structures of the jaw can spread to the ear area.
Bone fractures
During accidents and other types of incidents, head injuries can occur, which cause fractures of the facial bones of the skull and jaw.
The most common injury accompanied by jaw pain is a jaw fracture. It occurs due to the great force of the blow applied to the face, which is why pain is felt in the jaw in the ear area.
This type of fracture can be identified by symptoms:
- hematoma at the fracture site;
- pain when trying to open your mouth and chewing;
- swelling of the tissues; with a severe fracture, severe swelling is possible, spreading to the face;
- With complex fractures, bones are displaced and the soft tissues of the oral cavity are damaged.
Important: after a strong blow, dislocation of the jaw joint is also possible, in which case pain will be observed during chewing movements.
Osteomyelitis of the jawbone
This disease is characterized by damage to the bone tissue of the jaw. It occurs under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the bone through the root canals of diseased teeth. This disease is considered a consequence of neglected dental problems and not timely treatment of pulpitis.
In addition to pain in the jaw and ear, symptoms include:
- increased body temperature, feeling of chills;
- swelling of facial tissues and the appearance of its asymmetry;
- lymph nodes increase in size.
This disease is very dangerous and requires qualified treatment.
Important: prolonged pain of a nagging and aching nature requires mandatory consultation with a doctor, because these symptoms are typical in the presence of neoplasms.
If the cause of pain is an inflammatory process of the ENT organs
If your ear and jaw hurt, you may also have a sore throat
Sinusitis
Pain in the ear and jaw often bothers a person who has inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. The pain has a right-sided or left-sided localization.
The areas that become painful are:
- upper jaw;
- ear;
- eye;
- the area where the sinus is located, away from the nose.
Patients often suffer from headaches. Unpleasant sensations increase significantly at night and when the body is tilted.
Important: inflammation of the sinuses is very dangerous due to its complications due to their close location to the brain.
If a person suspects he has sinusitis, he should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
Tonsillitis
Inflammation of the pharyngeal tonsils causes severe pain in the throat, which can spread to the lower jaw and ear. Such severe pain prevents a person from eating, drinking, or talking. The temperature rises, the symptoms of intoxication of the body increase. Inflammation from the tonsils spreads to surrounding tissues.
Otitis
With inflammation of the outer and middle parts of the ear, there will be a sensation that the jaw under the ear hurts. In case of inflammatory processes of the outer ear, there may be a lump in the area around the auricle or the lump will be located directly on the auricle.
If inflammation of the middle ear has developed, the pain will be stronger. It spreads to nearby tissues, the jaw, teeth, eyes. The pain feels sharp and shooting. The body temperature increases, the patient looks lethargic and broken.
Important: inflammatory processes in the ear must be treated by a doctor; in the event of complications, inflammation may spread to the inner part of the ear, which can cause hearing problems.