The vast majority of the adult population of the planet is familiar with toothache. It can manifest itself in different ways, including when pressure is applied to a tooth, when a person cannot bite even soft food.
| Causes of pain and accompanying conditions | Methods for eliminating toothache |
| Increased sensitivity of the tooth in the absence of external damage, pain occurs even with slight pressure | At home: rinsing with herbal decoctions, soda solution When visiting a doctor: remineralization (treatment with preparations containing calcium and fluoride), in some cases - building up new enamel |
| Damage to enamel (cracks, chips - including microscopic ones invisible to the eye), the appearance of severe pain when exposed to any factor | It is recommended to consult a doctor |
| Inflammation of the gums: pain occurs when pressing on a healthy tooth precisely because of the condition of the gums | At home: rinse with a water-soda solution, sea buckthorn oil lotions. If there is no effect, you should consult a doctor. |
| Inflammation of the upper part of the tooth (periodontitis), accompanied by independent, precisely localized pain and a general deterioration of the condition | Treatment at home is impossible; you need to see a doctor. During the first week after removal: rinse |
| Removal of the nerve: after depulpation, pain may persist due to injury to the fibers (the reason is unskilled intervention that led to tissue necrosis due to insufficient asepsis of the canals) | The persistence (especially the intensification) of pain requires immediate contact with a doctor in case of a medical error |
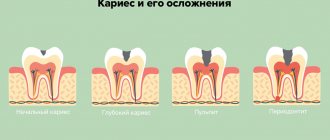
| A complication of caries is pulpitis, intense pain that intensifies when chewing, discoloration of tooth enamel (graying) | requires immediate medical attention; if delayed, tooth loss may occur |
Pain when pressing on a tooth after treatment
Pain when pressing on a treated tooth is an absolute norm: any dental intervention has a traumatic effect on the gum tissue, recovery takes some time, but every day the pain weakens.
In patients with increased tooth sensitivity or a low pain threshold, the recovery process may take 1-2 months.
To alleviate the condition during this period, it is recommended:
- Thorough brushing of teeth using dental floss;
- rinsing (starting from the fourth day after treatment);
- use of painkillers.
Pulsating pain in a tooth can be caused by non-dental problems.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Unbearable, throbbing pain covers the teeth on one side (on the upper and lower jaws on the right or left). At the same time, half of the head hurts, “shoots” in the ear, eye and under the jaw. In severe cases, the tongue becomes temporarily numb, the patient complains of tingling of the face and twitching of facial muscles. The pain usually appears at night. During the day, an attack can be triggered by eating, talking, brushing your teeth, combing your hair, and even yawning. Without treatment, the patient's condition worsens due to the destruction of the protective myelin sheath of the nerve. If you have the slightest suspicion of trigeminal neuralgia, consult a neurologist.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Pulsation of teeth without pain may indicate a dysfunction of the liver, diseases of the stomach and intestines. Characteristic signs of gastrointestinal pathology are a coated tongue, bad breath and an unpleasant taste in the morning, abdominal pain, flatulence, constipation or diarrhea. After successful treatment of the underlying disease, discomfort in the mouth disappears.
Sinusitis
Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is manifested by prolonged nasal congestion, discharge of purulent mucus and headache. The patient breathes through his mouth, his face is puffy. Often, a nagging pain in the area of the maxillary sinuses radiates to the cheekbones and provokes pulsation in the teeth. An ENT doctor treats sinusitis.
Why complications arise
Deformation of tissues (even minimal chips of enamel) causes various complications, which is associated with the penetration of infections into the depths of the tooth. Among the most serious complications:
- abscess (can spread to several teeth or cover half the jaw);
- sinusitis, pharyngitis, sepsis;
- inflammation of the jaw bone;
- development of phlegmon (with damage to the facial muscles).
All these infections are fraught with penetration into the blood and disruption of the general condition of the body.
The most common complication is the development of caries, which, in the absence of adequate treatment, leads to complete destruction of the tooth with the need for its removal.
Throbbing after dental procedures
Throbbing pain in a tooth can occur after the installation of a filling, tooth extraction, crown fixation and orthodontic treatment.
Throbbing pain occurred after tooth extraction
Painful sensations after the end of anesthesia and tooth extraction are a normal reaction of the body to a traumatic procedure. To eliminate “twitching”, painkillers are allowed in the first 1-2 days. The intensity of the pain gradually, the discomfort goes away within 3-4 days. After the removal of wisdom teeth and molars (6th, 7th and 8th teeth), the gums hurt and pulsate a little longer.
Increasing pain after removal of a dental unit may indicate the development of alveolitis. Inflammation of the dental socket develops due to the left fragment of granuloma (periodontitis) or root fragment. However, in most cases, alveolitis is caused by premature washing out of the blood clot and infection of the wound.
Important! It is prohibited to actively rinse your mouth after tooth extraction.
Tooth pulsates after filling
The dentist placed a nerve-killing drug into the root canal and installed a temporary filling. Do not panic if you experience throbbing pain from time to time for 3-4 days. However, if discomfort lasts longer, it is necessary to visit your dentist unscheduled. It is possible that the medication under the filling caused irritation to the surrounding soft tissue.
There may be several reasons for tooth pulsation under a permanent filling:
- insufficiently thorough cleaning of the carious cavity,
- poor quality filling installation,
- radiating pain from a neighboring tooth.
To exclude infection of the filled tooth and re-development of caries, it is necessary to take an x-ray.
Tooth pulsates after nerve removal
A filled tooth with a removed nerve should not hurt. The exception is when the dentist cleans out a root cyst and installs a temporary filling. After cementing the cystic cavity and filling the canals, the tooth may pulsate (without pain!) for several days.
If the pulpless tooth still begins to hurt, the dentist probably made a mistake and installed the filling unsealed. A slight painful pulsation will occur after eating. It is possible that the tooth was affected by periodontitis and a fibrous compaction formed on its root. In any case, if discomfort occurs after nerve removal, you should visit a dentist.
Important! To avoid negative consequences, before treating a dental cyst and removing a nerve at the Matiss Dent clinic, the patient is given an X-ray.
The tooth under the crown is pulsating
Painful pulsation after crown installation indicates that a medical error was made during prosthetics:
- tooth root infection occurs,
- the channel is poorly dried,
- the tooth is too ground and the crown does not fit tightly.
The crown will need to be removed, the tooth canal will need to be treated with an antiseptic again and a new prosthesis will be made.
Teeth pulsating under braces
Installation and tightening of braces, especially metal ones, often provokes pulsation in the gums. If the pain does not go away after a few hours, then the arch is too tight. Contact your treating orthodontist. The doctor will adjust the pressure of the braces on the teeth.
How to cope with pain?
Toothache is always a good reason to see a doctor; it’s worth taking the time to avoid complications!
If professional dental care is not possible, first aid is to relieve pain and minimize inflammation.
Analgesics of various effects used in dentistry - tempalgin, ketorol, nurofen; standard dosage regimen - 1-2 tablets every 4 hours; The effect of the drugs begins within the first 15 minutes and lasts up to 6 hours.
What to do if a tooth hurts under a filling, in which there is no nerve, but sensitivity remains
With persistent pain and progressive sensations, the only right decision is to consult a doctor. Only he can remove the pulp completely, even if the nerve endings were left behind, and also determine an additional cause for the symptoms.
Emergency methods of control
If it is not possible to urgently go to the dentist, then it is quite possible to relieve the pain caused by the inflamed nerve residue. To do this, it is enough to drink a strong painkiller or use traditional methods - rinses, lotions. Note that medications need to be dosed, and their compatibility with other drugs must be monitored.
And most importantly, you need to understand that these are only temporary measures that are needed to hold out until the moment when a doctor sees you and provides assistance.
Using medications at home
Even after proper treatment in the dental office, pain is a normal reaction due to irritation of the gums, as well as aching enlarged canals and neighboring teeth. But no one wants to live with constant pain for 7-10 days, so immediately after leaving anesthesia it is recommended to take drugs such as Analgin, Ibuprofen; Ketorol and its analogues are considered the most effective. This will not only remove the symptoms, but also stop the inflammatory process and relieve swelling. You cannot take pills every day. Therefore, if symptoms increase, you should immediately make an appointment with a doctor.
Rinse for painful sensations
Rinses are also widely used - both homemade and pharmacy. For example:
- 100 ml of water, a teaspoon of soda, a teaspoon of soda, iodine - 5 drops. Used to relieve swelling and remove purulent contents
- 1 spoon of sage per glass of boiling water (decoction), anise - 10 drops. Provides pain relief and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- 1 glass of warm water, 1 tablet of furacillin. Powerful antibacterial effect, reducing swelling.
The drug chlorhexidine has a good aseptic effect; so-called dental elixirs can be used to relieve pain.
It is important to understand that all the methods listed above are only first aid for toothache; if you stop there, you will soon inevitably need tooth extraction!
To eliminate pain, it is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of the problem. This can only be done in a dental clinic, where modern equipment ensures comfortable and painless treatment.
Treatment: when the cause of the pain is established
Having established the cause of the pain, the dentist will prescribe appropriate treatment.
The approach to treatment depends not only on the established cause of pain, but also on the neglect of the process (the degree of damage to the tooth and adjacent tissues).
- If increased tooth sensitivity is detected, remineralization or fluoridation is performed.
- The presence of chips and cracks requires composite enamel extension, or, as an option, the installation of veneers or crowns.
- In inflammatory processes, a course of treatment with antibiotics is usually prescribed with the installation of a filling after the source of inflammation has been eliminated.
- If the cause of pain lies in a poorly placed filling, it is polished or replaced with a new one.
- Detection of caries and pulpitis requires dental intervention such as preparation of the upper part of the tooth and opening of the cavity with the placement of medicine. After eliminating the infection, the dental canals are filled and the relief of the dentition is restored.
- Treatment of periodontitis is more complex; a specialist in such diseases is a dental surgeon. Drainage of the purulent cavity is performed, after the capsule is emptied of purulent contents, the canals are cleaned and the tooth is treated; in case of extensive lesions, resection of the root apex of the tooth is required.
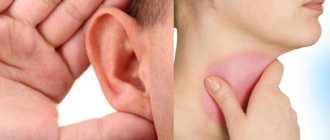
Reasons not related to teeth
With severe toothache, it seems that everything hurts - the ear, throat, head and even the skin on the face. In some cases, a person is not able to determine the source of the sensation and believes that a bad tooth is to blame.
Night pain similar to toothache can also occur in the following cases:
- For inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Characterized by a nagging, severe pain, localized in the area of one tooth or spread throughout the entire jaw. This is explained by the fact that the branches of the nerve are located very close to the roots of the teeth and when they become inflamed, pain occurs that is very similar to toothache.
- For sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis media. Swollen tissues and sinuses filled with purulent contents put pressure on the roots of the teeth. The resulting pain is very similar to toothache. In most cases, it is observed in children who find it difficult to correctly determine the location of pain
- Under stress. Chronic night pain can be considered as one of the factors confirming the stressful state of the body.
Important.
Even if you have such assumptions, you will still have to visit the dentist. This must be done in order to exclude inflammatory diseases of the teeth and oral cavity, correctly diagnose and prescribe the correct treatment.