You always want to cure stomatitis as quickly as possible, because mouth ulcers cause severe pain and make it difficult to eat. Often, for the treatment of stomatitis, doctors prescribe not the advertised expensive drugs, but the well-known Fukortsin. Can such a cheap drug really be a worthy alternative to expensive drugs and how quickly can it help?
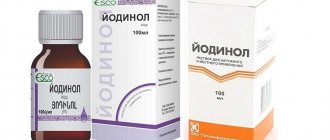
Fukortsin for stomatitis
What is Fukortsin used for?
The pronounced antimicrobial effect allows Fukortsin to be used as a local antiseptic that fights potential infection of wounds and abrasions. In addition, the drug has a fungicidal effect, which means it can prevent the proliferation of fungus. The main purposes of Fukortsin are:
- purulent wounds;
- superficial damage to the skin;
- erosion;
- abrasion;
- deep cracks;
- fungal infection of the epidermis.
Diagnosed streptoderma is treated with the timely use of Fukortsin.
Symptoms of otitis media in adults
With external otitis, the most common complaints are:
- pulsation in the ear, sharp pain radiating to the neck, eye or teeth;
- increased pain when chewing food, talking, closing the jaw;
- redness of the ear canal and auricle;
- hearing loss if there is discharge of pus into the ear canal area.
Acute otitis media begins with a rise in temperature along with shooting pain inside the ear.
It increases as mucus and pus accumulate in the cavity; after 2–3 days, the membrane ruptures, pus flows out of the ear and the condition improves. The temperature drops and the pain subsides. Then the rupture of the membrane heals without a trace. In the chronic form, mesotympanitis may occur - inflammation is localized in the area of the Eustachian tube and the lower, middle part of the tympanic cavity. A hole is formed in the membrane, but the membrane itself is stretched.
Key complaints:
- hearing loss;
- periodic appearance of pus from the ear;
- noise in the ear;
- dizziness;
- during exacerbation - pain and fever.
With the development of epitympanitis, a sharp decrease in hearing occurs, the release of foul-smelling pus, pressure in the ear, pain in the temples, and dizziness. Periods of exacerbation are followed by remissions, but hearing does not improve completely.
Fukortsin for herpes on the face
The drug does not have the ability to affect the herpes virus. However, when applied to the ulcers that it causes, Fukortsin dries them out, prevents them from growing and significantly reduces the area affected by the virus. Therefore, the drug is used as an additional remedy in the treatment of herpes.
A cotton swab is moistened in the solution and Fukortsin is applied to the herpes blisters. It is recommended not to simply spread the solution on the skin, but to hold the moistened cotton swab on the affected area for 1-2 minutes.
What is stomatitis?
This disease manifests itself as multiple ulcerations in the oral cavity, which cause pain. The sores can turn into open sores, making eating very painful. With proper treatment, the wounds heal, and crusts form in their place.
Stomatitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses (particularly herpes) or fungal flora. To select an effective treatment, it is very important to correctly determine the type of pathogen. In many cases, treatment tactics involve the use of Fukortsin.
Attention! The main cause of stomatitis is decreased immunity.
Stomatitis on the upper lip
How to take Fukortsin for stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, which is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers and abscesses. The disease usually occurs most often in children between one and three years of age. And this is due to the fact that during the period of teething, the child takes accessible objects into his mouth, some of which are unclean. Dirt entering the inflamed gum causes infection, which leads to the spread of ulcers throughout the oral cavity.
Adults, paying little attention to dental health, provoke the spread of infection. Stomatitis makes it impossible to eat normally, since any substances that get on the ulcer cause severe pain. Stomatitis is treated by rinsing with decoctions of chamomile or oak bark. And you need to treat wounds with Fukortsin, after moistening a cotton swab or swab in the solution.
Under no circumstances should Fukontsin be used as a mouth rinse. Tissues and mucous membranes have a high degree of absorption. During rinsing, a large percentage of boric acid and phenol will be absorbed into the blood, which will certainly cause general intoxication of the body
Treatment of stomatitis in children
After a medical diagnosis of stomatitis in children under one year of age, a specialist prescribes highly effective drugs to combat the existing type of disease. Experts recommend that parents, at the first suspicion of stomatitis in a child, increase the amount the child drinks to irrigate the oral mucosa and remove toxins from the body. Clean drinking water without gas, fruit drinks or compotes that are not too sweet or sour; herbal teas are perfect for this. During this period, it is worth refusing to drink the child from concentrated juices and drinks with gas in order to avoid irritation of the mucous membrane.
After this, the specialist begins medical manipulations to cure stomatitis in the child.
Anesthesia
The first step is to numb the mucous membranes so that the child can eat and drink properly and generally reduce the child's stress level. Choline preparations with salicylate or lidocaine are commonly used as pain relievers in children. For this purpose, medications to facilitate teething, for example Kamistad or Dentinox gel, are suitable. Gel products are preferable for children because they are almost instantly absorbed into the mucosal tissue. Prepare with lidocaine in the form of a spray should not be used in children under one year of age - this may lead to bronchospasm.
Direct treatment of stomatitis
After anesthesia, you can begin treating your baby’s stomatitis. Firstly, all rashes and wounds must be treated with a special preparation, depending on the type of disease. Antiviral drugs are used for herpetic stomatitis, antibiotics and antiseptic drugs for bacterial stomatitis, antifungal drugs for candidal stomatitis. Not only the affected area, but also adjacent areas must be treated - this will stop the spread of the pathogenic process.
An important condition for eliminating infection is thorough and timely oral hygiene. The surface of the child's tongue and teeth should be brushed twice a day; experts recommend rinsing the mouth after every meal or drink. For young children, hygiene procedures are carried out using a piece of gauze or a silicone fingertip.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis
If a specialist has identified the presence of allergic stomatitis or severe swelling of the oral cavity is observed, then the drugs Fenistil, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine are used.
Treatment of viral stomatitis
For herpetic stomatitis, antiviral agents should be used in the form of ointments containing acyclovir - Gerpevir, Virolex, Acik, Viferon, oxolinic ointment.
For relapses of viral stomatitis, experts recommend a general strengthening of the immune system with the help of Immunal, Interferon, Viferon in suppositories. The duration of treatment and dosage of the drug is determined by the doctor. Often, medical experts recommend using the drug Cholisal in gel form. Perfectly relieves swelling, inflammation, pain, fever, eliminates pathogenic microflora. The drug does not contain sugar, has no taste and has a light anise aroma. To treat stomatitis in a child under one year old, it is necessary to rub a strip of gelatin preparation no more than 0.5 centimeters long into the palate, gums and inner surface of the cheeks, teeth, 2-3 times a day after brushing the teeth.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis
For candidal stomatitis, the doctor uses antifungal drugs in the form of an ointment, for example, Clotrimazole, Candida, Candizol, and often prescribes soda rinses.
This helps create an alkaline environment in the oral cavity, harmful to pathogenic fungal microflora. Procedures with soda are especially effective in the treatment of candidal stomatitis in children under the age of one year, because at this age most drugs are contraindicated. To treat the oral cavity, you need to dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water, then wrap a piece of gauze around a clean finger and wipe the palate, inner surface of the cheeks, gums and sublingual space of the child, periodically dipping your finger into the solution. The procedure should be done after every child eats or drinks. Older children can rinse their mouths with baking soda themselves.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
With aphthous stomatitis, the first priority is to unload the affected area and speed up the healing of the poop. An aqueous solution of blue (methylene blue) has long been used for this purpose. It is not recommended to use a blue alcohol solution for this, since the ethyl alcohol in its composition will cause poisoning or burn the baby’s mucous membrane.
Wounds are treated with a blue cotton swab 3-6 times a day.
Treatment of traumatic stomatitis
According to experts, traumatic stomatitis most often occurs in children 1-2 years old. This type of disease is accompanied by bacterial microflora, so the use of medicinal and antiseptic agents will be required. For children under 2 years of age, use Cholisal, Solcoseryl, Actovegin gel, and also wipe the oral cavity with a solution of chlorhexidine or soda.
Treatment of bacterial stomatitis
For the treatment of bacterial stomatitis, drugs such as Tantum Verde, Orasept and Hexoral in the form of a spray, Doctor Theiss and Septolete in the form of lozenges and many others are effective. Experts do not recommend using lozenges to treat children under 6 years of age due to the risk of asphyxia, and sprays are suitable for treating bacterial stomatitis in children over one year of age. Antiseptic rinses and gel preparations with metronidazole are also effective.
Among solutions with an antiseptic effect, the drug Miramistin is especially recommended, as it promotes the regeneration of the affected mucous membrane and eliminates most pathogens. The aerosol can is convenient for treating children under one year of age. To do this, you need to make 3 injections and rinse your mouth with them for several minutes 3-4 times a day. Babies under the age of one year are treated with gauze soaked in the drug.
Fukortsin or brilliant green for chickenpox
With chickenpox, treating blisters on the body has a special meaning. Chickenpox is a type of herpes virus that causes a rash all over the body. Doctors do not recommend getting the affected areas of the body wet, which means the patient should not wash during the entire period of illness, which can last up to 14 days. The patient is considered infectious as long as new lesions of the rash appear on his body. As soon as the rash stops appearing, make a mark on the calendar and count another 5 days, after which the patient with chickenpox can return to the team.
Zelenka, like Fukortsin, in addition to drying out sores, preventing a secondary infection from joining, serves as a kind of marker for a previously appeared rash. The absence of uncolored bubbles will indicate that the disease is receding.
The child, reacting to the itching that often accompanies the chickenpox rash, tries to scratch it, breaking the tightness of the ulcers. Dirt and infection can quickly get into a torn wound, which will cause suppuration and other complications. Fukortsin, like brilliant green, does an excellent job of disinfecting. What color the patient will be after treatment is a decisive factor influencing the choice between the two drugs. Both brilliant green and Fukortsin are difficult to wash off from the skin.
Recommendations during treatment
Treatment of stomatitis should be carried out comprehensively - local therapy, taking medications appropriate to the type of disease, and strengthening the immune system. During the treatment period, you must adhere to the following recommendations.
- Compliance with the diet - you need to exclude from the diet spicy, salty, sour, too sweet, smoked, hot, cold and any dishes that are traumatic to the mucous membranes.
- Maintaining oral hygiene . To maintain it, it is necessary to use antiseptic agents that you regularly rinse your mouth with.
- Taking vitamin-mineral complexes that strengthen the body's protective functions.
If the doctor has diagnosed the presence of candidal stomatitis, then you should not drink milk or consume fermented milk products, which activate the activity of pathogenic fungi.
Any medications should be used only as prescribed by a doctor. Especially antibiotics.
It is important to know! It is not recommended to cauterize emerging ulcers with pure alcohol solutions. The only thing that is allowed is treating the lesions with a weak solution of iodine or potassium permanganate.
Adverse reactions
Sometimes, if the solution is abused, inflammation of the treated areas of the skin may occur, accompanied by burning or itching. A similar effect is achieved by prolonged contact of the epidermis with the active substance. Treatment of adverse reactions is symptomatic:
- Wash off excess solution from skin using soap and running water.
- Apply a cream containing dexpanthenol to the skin, excluding the wound itself.
- Stop using Fukortsin.
Causes of otitis media in adults
The most common causes of otitis externa are injuries, infections of the skin and underlying tissues in the ear canal area.
Chemical trauma to the ear, irritation and inflammation due to wax plugs, water getting into the ear, and the formation of boils are also possible. Otitis media is the most common form of the disease. It is usually provoked by bacterial infections, less commonly by viruses, pathogenic fungi, and mixed infections. The most common pathogens:
- Pneumococcus;
- hemophilus influenzae;
- influenza virus;
- various pathogens of ARVI.
In recent years, cases of fungal otitis media have become more frequently reported.
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of otitis media include sniffing and excess mucus in the nasopharynx. pressure difference when diving, diving to depth. Often, otitis media becomes a complication of a cold, ENT pathologies (adenoiditis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis). The risk is higher in people with immunodeficiencies.
special instructions
It is highly not recommended to treat large surface areas of the skin with Fukortsin, as this will lead to intoxication with phenol, which is part of the drug, which will cause weakness, surges in blood pressure, respiratory distress and dizziness.
Before handling the bottle, it is recommended to wear rubber or polyethylene gloves to protect your hands from accidental contact of the dye with your skin. Like brilliant green, Fukortsin can stain objects that receive random drops while unsealing the bottle. Therefore, it is better to cover the table or cabinet on which the bottle will stand with a waterproof napkin.
From real life
From the reviews, some conclusions can be drawn about the effectiveness or ineffectiveness of Fukortsin in the context of the treatment of stomatitis.
At the age of 6, my daughter fell ill with stomatitis. Ulcers and pustules appeared. The baby was in pain. The doctor prescribed Fukortsin.
Gently lubricated the wounds with the solution for five days. Already on the second day it was noticeable that the ulcers began to dry out. A good drug, fast acting, inexpensive.
Elena, 21
After suffering from ARVI, my oral mucosa became inflamed. Mom advised me to cauterize the pustules with Fukortsin, which I did. The drug helped very quickly. True, at first there was a slight tingling sensation, but everything was tolerable. I would not use it on the skin, as the medicine has a bright pink tint. But for the mucous membrane - just what you need!
Lilia, 34
What antibiotics are effective for otitis media?
“Systemic antibacterial therapy is indicated in all cases of moderate and severe acute otitis media,” says otolaryngologist Svetlana Kovaleva, “as well as in patients with immunodeficiency conditions.
If otitis is mild (no pronounced symptoms of intoxication, pain, hyperthermia up to 38 ° C), you can refrain from prescribing antibiotics. However, if there is no positive dynamics within 48 hours, antibiotic therapy should be resorted to. For otitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed that are effective against typical pathogens: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus.
The drug of choice is Amoxicillin.
Alternative drugs for allergies to β-lactams are modern macrolides (Josamycin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin). In case of ineffectiveness, as well as in patients who have received antibiotics for a month, for patients over 60 years of age, it is advisable to prescribe a complex - amoxicillin + clavulanic acid. Alternative drugs are II-III generation cephalosporins (Cefuroxime axetil, Ceftibuten) or fluoroquinolones (Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin).
For mild to moderate cases, oral antibiotics are indicated. In severe and complicated cases of otitis, begin with intravenous or intramuscular administration of the drug, and then continue treatment orally.
The duration of antibacterial therapy is 7–10 days. For complicated otitis – 14 days or more.
You should not use antibiotics on your own; you should consult an otolaryngologist. Otitis media can be caused by fungal flora or herpes infection. The use of antibiotics in this case can worsen the course of the disease.