A problem that many people face is dental plaque. It is deposits located at the border of the tooth and gum, in the spaces between the teeth. Plaque includes food debris, bacteria and their metabolic products, as well as substances contained in saliva. Deposits form constantly; if you pay due attention to oral hygiene, most of them can be removed yourself. If hygiene procedures are ignored, soft deposits mineralize, turning into dense tartar, which cannot be treated at home.
| Prices for plaque removal | |
| Air Flow Plaque Removal | from 3000 R |
Plaque forms at any age, both in adults and children. Its amount depends on the type of food consumed. The largest amount of deposits is formed among lovers of sweets and starchy foods. In the process of chewing hard foods, in particular vegetables and fruits, part of the plaque is mechanically removed. If deposits are not removed within 24 hours, they become saturated with calcium salts contained in saliva and transform into tartar.
Symptoms, how to determine the presence of deposits
The formation of dental plaque cannot be tracked, since this process occurs at the cellular level. But its quantity must be controlled and not allowed to turn into hard stone, since this is fraught with the emergence of many problems. The following are symptoms that will help detect the presence of deposits in the oral cavity:
- yellow or white plaque that is located on the surface of the teeth, between them, as well as along the entire length of the gingival margin,
- teeth become rough if you run your tongue over them,
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth,
- As plaque turns into stone, bleeding gums appear, mucous membranes can move away from the surface of the teeth, change their color to bright scarlet or even bluish.
There are two types of dental plaque in terms of their localization, i.e. locations:
- superficial, that is, supragingival: visible to the naked eye, has a white, yellow or even brown color,
- subgingival: can be detected during an examination by a dentist, because is located under the mucous membranes and often the patient does not see or feel it (especially if the amount is small). It has a darker shade, even brown. It is impossible to remove it at home.
How does plaque form?
During the formation process, plaque goes through three phases:
- 1st phase (lasts for 1.5-3 hours after cleansing teeth with toothpaste). At this stage, up to 1 million different bacteria and microorganisms may be present in the oral cavity, for example, staphylococci, lactobacilli, streptococci. During the specified time, these microorganisms actively multiply;
- 2nd phase of plaque formation (lasts about 3-6 hours after cleansing teeth with toothpaste). During the specified time, the teeth are covered with a thin film of plaque, which is invisible to the naked eye. By this time, there are already about 10 million microorganisms in the oral cavity;
- 3rd phase (5-6 days after the last toothpaste cleansing). After this phase of plaque formation, several hundred billion pathogenic bacteria already live in the oral cavity. The plaque is fully formed and has distinct contours. The resulting plaque already contains bacteria of infectious etiology.
Causes of plaque and tartar
The main reason for the appearance of plaque and tartar is associated with the accumulation of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity. In general, this is a normal process, but deposits must be removed independently and several times a day. If this is not done, their number will increase significantly, which will lead to various complications - diseases of the teeth and gums.
In addition to poor hygiene, there may also be other factors that cause increased plaque formation on teeth. These include:
- smoking and drinking alcohol,
- unhealthy diet - eating a large amount of carbonated drinks and sweets, focusing on soft foods and avoiding hard foods, which have a cleansing effect on the enamel (especially a diet without vegetables and fruits),
- taking certain antibiotics and medications that disrupt the composition and quantity of saliva,
- diabetes mellitus, hormonal disorders.
Types of Tartar
Tartars on teeth are classified according to where they are located:
- supragingival - they are visible to the naked eye during a routine examination. They look like dark or yellowish deposits above the gum level. This type of stone is easier to remove;
- subgingival - what this type of tartar looks like can only be determined by a doctor. This type of deposit is located under the gum, below its level, so it is impossible to see it. However, there are indirect signs of the formation of such stones: redness, swelling or cyanosis of the gums, bleeding, and possible outflow of pus from the periodontal pocket.
The second type of hard deposits is more dangerous because it is indirect evidence of periodontitis and periodontal disease. The stone is formed due to the destruction of the attachment of the gum to the surface of the tooth, its detachment. The next stage may be a structural change in the tissues that hold the tooth, loosening and its loss.
Possible complications
Plaque is the #1 cause of gum inflammation (gingivitis and periodontitis). Therefore, in the long term, this problem can even lead to tooth loss. In addition, deposits are localized on the teeth, and the bacteria that make them up lead to the destruction of enamel, the appearance of caries and other dental diseases.
The aesthetics of a smile are also disturbed, an unpleasant and even putrid odor from the mouth occurs, which affects a person’s psychological comfort. Another consequence is disruption of the digestive tract, since plaque is bacteria and, along with food, they also enter the stomach.
Causes of tartar
So, we have figured out the mechanism for the appearance of solid deposits. What causes tartar and what contributes to its rapid formation? There are several factors:
- Ignoring hygiene, improper brushing of teeth. An increase in the volume of bacterial plaque leads to rapid mineralization and proliferation of the stone;
- consumption of carbohydrates (sweets, baked goods), preference for soft foods (lack of natural mechanical cleaning with solid foods);
- changes in the composition of saliva, its acidity or increased salivation as a result of metabolic disorders lead to rapid saturation of soft deposits with calcium salts;
- internal diseases, inflammatory, infectious, which causes a large number of pathogenic bacteria;
- rough surface of the teeth - “simplifies” the formation of soft and hard plaque;
- bite defects, which makes it impossible to properly clean some areas (for example, when teeth are crowded);
- taking certain medications that help change the composition of saliva.
The causes of tartar formation can be combined with each other. When visiting a dentist, it is important to find out about them in order to select effective methods of prevention.
Methods of prevention and treatment
Both prevention and treatment come down to careful and thorough oral care. It is necessary to strictly follow the rules in order to protect yourself from the formation of pathological plaque:
- Brushing your teeth twice a day – morning and evening, for at least 2 minutes, and using properly selected products. It is important to use a brush with medium-hard bristles (even if gum inflammation is present); one that is too soft will not cope with deposits,
- using dental floss and irrigator after every meal,
- using interdental brushes to help clean narrow spaces between teeth,
- Visit your dentist every six months for a checkup.
But you should understand that even with careful hygiene, plaque will still accumulate. For example, under the gums. And even if you missed cleaning at least once or were unable to use the product after meals, especially against the background of reduced immunity or hormonal changes, plaque will again accumulate in greater quantities. Therefore, it is very important to periodically seek help from a dentist for professional oral hygiene.
Professional oral hygiene The procedure allows you to quickly and effectively remove plaque and tartar, as well as get rid of subgingival deposits. For this, an integrated approach is used: ultrasound, Air Flow air abrasive device, manual cleaning, chemical destruction of deposits (if necessary), as well as thorough polishing of the enamel and application of a strengthening composition. This is an excellent method of preventing many oral diseases. It is recommended to carry out an average of 1-2 times a year.
Price:
3000 rubles more details about the solution
Treatment with the Vector and Varius apparatus The use of apparatus treatment is advisable in the presence of pathological gingival pockets in which plaque and stone accumulate, and there is also pronounced inflammation of the mucous membranes. These devices allow you to remove stone located deep under the gums due to targeted vertical action along the tooth, unlike conventional ultrasonic scalers.
Price:
10,000 rubles more about the solution
Treatment
There are supragingival and subgingival tartar. The only treatment for both types is surgical removal. There are several types of such intervention:
- Laser. Equipment for such a procedure is expensive, so not every clinic has it. The principle of operation is crushing tartar and completely cleansing the enamel.
- Ultrasound. A completely non-traumatic method - during the procedure, the device attachment does not touch the tooth being treated. The ultrasonic cleaning method has absolute contraindications – the presence of a pacemaker. If the patient has problems with the heart and blood vessels, you need to warn the doctor about this. If the enamel is highly sensitive, tartar is removed with local anesthesia.
- Air Flow cleaning. Typically used as a final procedure after laser or ultrasonic cleaning. During this process, the remaining hard deposits are removed. The teeth are slightly whitened and the enamel is polished. Air Flow cleaning can be used as a stand-alone product only to remove very small and not completely hardened deposits.
Tartar removal
Unlike soft deposits, hard deposits cannot be removed on your own: professional dental care will definitely be required. To do this, the doctor can use the following methods for removing tartar in dentistry:
Ultrasonic cleaning. This technique guarantees complete destruction and removal of tartar. It is used for supragingival and subgingival stones. The doctor uses an ultrasonic scaler - a special attachment connected to an ultrasound source machine. By directing the scaler at the tartar, it destroys it, and the supply of water allows you to remove it from the mouth and prevent overheating. Ultrasound does not have a harmful effect on dental tissue.
Air Flow method. The procedure is performed using a device that supplies a water-air mixture with abrasive particles. It is worth noting that this method is combined with ultrasound, but is not used as an independent method of stone removal - the abrasive may not be enough to destroy solid deposits. However, it perfectly fights soft plaque and serves as a way to prevent stones.
Mechanical removal. The doctor, using a special bur, mechanically separates the stone from the tooth and scrapes the enamel surface. This method does not allow impact on subgingival deposits; moreover, it is more traumatic than modern ones and can cause discomfort.
Laser removal. The doctor acts on hard deposits with a special attachment with laser radiation. He removes the stone layer by layer, crushing it. Removal from the oral cavity is carried out using water and a stream of air. The procedure does not cause discomfort and therefore does not require anesthesia.
Chemical removal. It consists of applying special products containing acids and alkalis to the surface of teeth covered with stone. They help soften the hard stone, and then the doctor removes it mechanically. The only disadvantage of this method is its inability to apply to subgingival calculus. This method is used less frequently because acids can damage the enamel and it is important to ensure there are no risks.
Removal of subgingival hard deposits can be performed surgically - using closed or open curettage operations. Such procedures consist of gaining access and mechanical removal of subgingival stone using curettes and special instruments. They are required for diagnosed periodontal disease and involve the simultaneous removal of granulations from periodontal pockets. Curettage is carried out under mandatory anesthesia, since the doctor’s manipulations can be quite painful. It is important to entrust this procedure to a professional, a periodontist.
Getting rid of stones on teeth using improvised means
If there is tartar, how to get rid of it at home? We invite you to study some folk recipes:
- Use toothpastes with abrasive particles and a hard brush for cleaning, then you can get rid of soft plaque and even remove small stones.
- Prepare a decoction of 40 grams of walnut bark or shell and a glass of boiling water. You need to dip your brush in it and brush your teeth, adding a little toothpaste.
Removing dental plaque using folk remedies is a long process; you won’t be able to get rid of tartar in one use, so you will have to be patient and use the product regularly. If folk remedies do not help cope with plaque on the teeth, then you will have to visit a specialist who will quickly and safely return you have a beautiful smile and healthy teeth.
Diagnostics
Pathology can be detected by visual examination. Even with insignificant volumes of deposits, they are indicated by:
- redness and swelling of the gums;
- increased temperature of inflamed tissues;
- tooth mobility;
- pain when pressing on an area with signs of hyperemia.
A periodontal probe allows you to detect the location of the stone. In addition, some of the deep deposits are visualized on an x-ray of the dentition.
What are dental deposits?
Such formations on the teeth appear even in those who regularly and conscientiously brush their teeth and take care of their oral cavity. Deposits on teeth are formed under the influence of various factors. They affect not only the crown of the tooth, but also the surface of the gums. Dental deposits often cause the development of diseases of the gums and teeth. They are irritating to the gums and tooth enamel, as they contain a huge amount of bacteria and their metabolic products. Partially, soft plaque is removed when brushing your teeth. But this is only provided that the oral cavity is cleaned correctly and regularly. If personal hygiene rules are not followed, plaque remains on the teeth, between them and gradually leads to the formation of hard deposits.
How to remove plaque at home
Fortunately, unlike tartar, plaque can be removed without resorting to special procedures performed exclusively in a dental clinic. Of course, this is true if we are talking about the initial stages of deposit formation. If the plaque has hardened, you will still have to see a doctor.
At the initial stages of plaque formation, the following method is effective. The toothbrush must be moistened in a weak solution of soda. Then you need to use this moistened brush to clean your teeth, very carefully and without pressing on the tooth surfaces. The procedure should be carried out once a week. If brushing with soda is done infrequently, it has a beneficial effect on the condition of teeth without damaging tooth enamel.
Whitening toothpastes have a good effect on the tooth surface. Most often, they contain special abrasive substances that cleanse tooth enamel of deposits. But you should not constantly use whitening pastes. It is necessary to alternate them with other types of pastes: classic or with medicinal herbs.
Natural plaque removal is achieved by eating hard fruits. Fruits such as carrots or apples act as a natural cleanser for the teeth. But there is no need to strain your teeth and try to bite off a piece of an apple from a whole fruit. You need to cut the apple or carrot into small pieces before eating. Corn also has cleansing properties.
Diagnosis of dental deposits
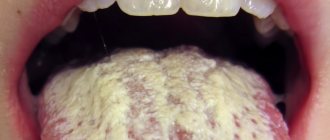
Detecting plaque on teeth is a fairly simple matter. Even if you run your tongue over their surface, you can feel it if there is a coating. The surface of the teeth does not seem so smooth. You can see it in the mirror; such deposits are best visible on the lower jaw from the inside.
Smokers can see the plaque without any problems, since it most often has a brownish color. At the pharmacy you can buy special pastes or tablets that color the plaque a different color, but the most effective way is to visit a dentist, who will determine how much your oral hygiene can be assessed.
What is the raid like?
Depending on the color, there are several types of such film on the teeth: white plaque; yellow; brown; black; green and orange.
White plaque
- the variety that occurs most often. This is simply a film that forms during the day due to food intake and is easily neutralized after brushing your teeth.
Yellow plaque
- These are soft deposits that are most often located close to the gums. It is formed for several completely different reasons:
- insufficiently thorough brushing of teeth;
- excessive consumption of sugar-containing foods, as well as coffee;
- frequent smoking - both cigarettes and hookah;
- nutritional imbalance;
- aging;
- Also, some dentists believe that this may be a hereditary problem.
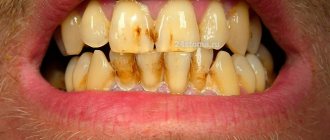
Brown plaque
- a long-standing and serious problem for all experienced smokers. It appears due to the fact that resins linger on the tooth enamel and over time form a durable film. This also indicates the presence of iron in saliva - watch what kind of water you drink.
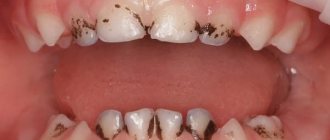
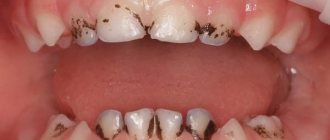
Black plaque
is a problem that can arise for a wide range of reasons. Sometimes teeth turn black due to chemotherapy or hormonal imbalance, sometimes due to intoxication and parasitic infection. Another appearance of such plaque is an individual reaction to antibiotics.
Green and orange plaque
- a common problem for young children. It occurs due to fungal diseases, which can be easily treated by an experienced dentist.