Bruxism and hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles are inextricably linked processes. Bruxism is a condition when the muscles of the jaw involuntarily spasm, as a result of which a person begins to grind his teeth. There is an increased tone of the masticatory muscles.
Very often, this problem becomes a serious obstacle to dental procedures, such as implantation, prosthetics, and installation of veneers. Bruxism can interfere with quality orthodontic treatment. Increased tone of the jaw muscles overloads the implants, and dentures are destroyed much faster.
Bruxism also has a negative effect on “native” teeth. The enamel is damaged and worn away, and the teeth become loose. Therefore, if such a problem arises, it is necessary to look for ways to solve it. Thanks to modern medicine, you can get rid of bruxism for a long time.
Symptoms of bruxism and the main causes of hypertonicity:
- the surface of the teeth grinds down, they become flatter;
- the enamel is damaged, fillings fall out, teeth begin to loosen, their integrity is violated, the gums become raw and bleed;
- crunching and clicking appears in the jaw when opening and chewing;
- teeth grinding occurs when a person sleeps;
- it is difficult to open and close your mouth, you feel tired and overstrained masticatory muscles;
- you often unconsciously clench your jaw, most of the time they are tense;
- malocclusions appear;
- the lower part of the face takes on a square shape;
- posture worsens.
Causes of hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles
As a rule, tension in the masticatory muscles is an expression of general mental stress. Remember the expression “gritting your teeth.” Endures, gritting his teeth or makes his way through obstacles, gritting his teeth, etc. And also: grinding, grinding his teeth out of anger or powerlessness.
The jaw clenches in situations involving the need to defend or compete. But in case of psychological shock, confusion, experience of failure or loss, the muscles relax. In such cases they say: “the jaw dropped.”
Daily stress associated with work, business, family matters, etc., can cause hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles.
On the other side:
joy, smile and laughter, pleasure and love relieve tension by relaxing the jaw.
Changes in other parts of the body also provoke hypertonicity , most often this is a pathology of the cervicothoracic spine.
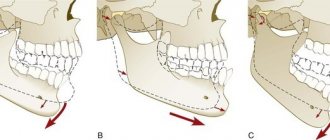
The incorrect position of the cervical vertebrae disrupts the symmetry of the face, the chin moves forward, which causes compensatory tension in the masticatory muscles . Malocclusion, treatment at the dentist, etc.
A temporary increase in tone can occur as a result of muscle fatigue during prolonged dynamic or static load.
For example, after running or being in an uncomfortable position.
Tension of the muscles of the eyes and neck during prolonged work at the computer also involves the masticatory muscles in this process. Prolonged and frequently repeated exercise can cause hypertension.
Botulinum therapy as a method of treating bruxism
Botulinum therapy is effectively used to relieve overstrain in the masticatory muscles, fights bruxism and can relieve involuntary teeth grinding at night.
In medicine, as in cosmetology, botulinum toxin type A is used. It is able to immobilize a muscle or relieve tension in it, acting locally. This effect lasts only for a certain period of time. But during this time the body manages to get used to the new state, and the overstrain disappears completely.
Botulinum toxin type A is a neurotoxin produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. It is capable of blocking impulses from the central nervous system sent to the muscles. In fact, botulinum toxin paralyzes them, breaking the connection between muscle fibers and the brain.
The drug is injected into the required areas, so it has an effect exclusively on the desired areas. Dosages of butolotoxin are completely safe, and its effect is reversible. After six months, it is completely eliminated from the patient’s tissues.
Reasons for jaw reduction
Spasm of the facial muscles can be associated with internal or external factors.
Internal:
- physical condition of the body;
- diseases of organs and systems (oncology, musculoskeletal disorders, mental disorders, etc.).
External:
- pathological conditions of the oral cavity;
- consequences of unsuccessful dental treatment;
- jaw injuries (dislocations, fractures);
- arthritis of the jaw joint;
- neuralgia;
- inflammatory processes;
- abscesses;
- periosteum.
At risk are people suffering from bursitis, who are also exposed to constant stress and overstrain of the nervous system.
Main stages of treatment
The first step is preparation for the procedure. It's simple. For a few days, it is necessary to eliminate alcoholic beverages from the diet, and also reduce caffeine consumption. Before the procedure, you should not take antibiotics or blood thinners.
The second step is the introduction of butolotoxin. The procedure lasts about twenty minutes. The required dose is divided into three to four injections. The injection needles are very thin, so the procedure is virtually painless.
The third step is the rehabilitation period. Butolotoxin acts instantly, but gains its full strength after two weeks. After injections, it is not recommended to overheat or cool the treated areas. Sports and facial massage should be excluded.
Diagnostics
Several conditions can cause jaw clenching. The doctor or dentist will review the person's medical history and ask about symptoms. Imaging tests can help diagnose inflammation and structural abnormalities that are causing the jaw to tighten. Some of these tests include:
- Radiography;
- CT scan;
- MRI.
When to see a doctor
If a person experiences the following symptoms, they should consult a doctor:
- severe pain in the jaw, which increases with movement or chewing;
- difficulty opening your mouth or swallowing;
- headache.
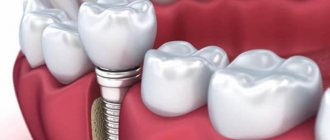
Implantation for bruxism
Implants can be placed if an integrated approach has been taken to the procedure. In cases where the dental system has not worked correctly for a long period of time, dentists perform treatment using complex implantation.
If excessive tension in the jaw muscles was caused by a reason such as psychosomatics, then the patient is referred for examination to a specialized specialist. Only then can you begin to restore your teeth.
Causes of jaw muscle tension
Stress or anxiety
Stress and anxiety are common causes of muscle tension. A person may clench their jaw or grind their teeth without noticing it when they are stressed, which can lead to muscle tension over time. Stress or anxiety can also cause a person to clench their fists and lead to tense shoulder and neck muscles.
TMJ dysfunction
TMJ dysfunction affects the lower jaw joint as well as the surrounding muscles. TMJ dysfunction can cause:
- bodily injury;
- grinding or clenching of teeth;
- inflammation from infections or autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms of TMJ dysfunction depend on the cause and severity of the condition and may include:
- soreness in the jaw, ear, face, or neck;
- difficulty chewing or opening your mouth;
- a jerky or clicking sound when moving the jaw;
- headache.
Tetanus
Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused by the bacteria Clostridium tetani. The pathogen produces toxins that cause painful contractions of the neck and jaw muscles. The infection can limit a person's ability to open their mouth and swallow. Fortunately, vaccines can prevent tetanus. Vaccination recommendations:
- DTP vaccination for children aged 2 months to 6 years;
- Tdap booster vaccine for adolescents aged 11-12 years;
- Td vaccine every 10 years for adults.
Grinding of teeth
Bruxism is the medical term for unconscious clenching or grinding of teeth. This can happen while you are awake or asleep. Chronic stress or anxiety can cause a person to grind their teeth. Certain medications and nervous system disorders can also cause bruxism.
Symptoms of Bruxism
- stiffness or soreness in the jaw and surrounding muscles;
- tooth pain;
- clicking in the temporomandibular joint;
- headache.
In some cases, bruxism can lead to tooth fracture.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints. Approximately 50% of people with RA also experience symptoms in the TMJ. RA can cause the following symptoms:
- jaw clenching;
- joint pain, inflammation and stiffness;
- low-grade fever;
- weight loss;
- lumps under the skin of the finger joints and elbow joint.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) develops in people over 65 years of age. Although OA typically occurs in the joints of the hands, knees and hips, it can also affect the TMJ.
Prevention of bruxism
Preventive measures for hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles of the jaw imply measures that can prevent bruxism. Treatment of this disease without diagnosis and examination by a qualified specialist can be hazardous to health. As soon as you notice the first signs of this pathology, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. He will prescribe diagnostics that will help identify a possible problem and effectively eliminate it.
The patient may need to be examined by specialists such as a neurologist or psychotherapist. Increased tone of the masticatory muscles has different etiologies. Doctors in these areas can prescribe various treatments, such as physical therapy, magnesium-based medications. All this is decided on an individual basis.
Preventative measures may help if approved by the patient's physician. You can easily massage the cramped areas. There is a set of exercises that can reduce the manifestations of bruxism. They must be done daily before going to bed.
Stressful situations must be avoided. You should rest more, get enough sleep, and spend a lot of time outdoors. Avoid caffeine and take baths with herbs that have a sedative effect. These measures will be an excellent prevention of muscle spasms, and will also enhance the effect of complex treatment.
Contact the Denta-Labor dental laboratory for solutions to issues regarding the protection of your teeth during bruxism.
Measures to prevent trismus
To prevent trismus, it is important to sanitize the oral cavity in a timely manner: remove teeth that cannot be restored, treat caries and inflammatory gum diseases. If prosthetics are necessary, you should contact only qualified specialists, and orthodontic structures should be replaced in a timely manner. The presence of neurological diseases requires constant monitoring by a neurologist.
If you have trismus, you can get advice from dentists at STOMA clinics. If pathology of the temporomandibular joints is detected, experienced specialists will prescribe an additional examination and give recommendations aimed at eliminating the causes of the disease. You can make an appointment for an examination by calling the specified phone number or using a special form on the website.
How to treat trismus of the masticatory muscle?
Treatment involves the following steps:
- jaw immobilization;
- elimination of the disease or condition that caused trismus;
- taking medications with a relaxing effect (neuropsychic stimulants);
- taking antibiotics;
- the patient takes sedatives;
- Physiotherapy is recommended.
If trismus is caused by an inflammatory process in the mouth, the dentist sanitizes the lesion (for example, opens an abscess), cleans the hole and, if necessary, removes the tooth along with the root.
The main causes of trismus
Often the causes of trismus are diseases that are localized near the jaw:
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- inflammatory process of masticatory muscles;
- jaw injuries;
- periostitis;
- advanced caries, extensive carious damage to teeth;
- inflammation of the gum tissue;
- acute stage of pulpitis;
- inflammation of the periosteum of the lower jaw;
- abscesses.
Compression can also occur in the background:
- neurosis;
- brain inflammation;
- cerebrospinal meningitis;
- epileptic seizures;
- paralysis;
- cerebral hemorrhages;
- rabies;
- muscle cramps;
- tetanus;
- tumor processes;
- hysteria.
Sometimes the disease can occur due to a direct blow to the jaw area, due to an unexpected dousing with cold water. Often a spasm occurs after an animal bite (one of the consequences of rabies).