Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes various changes. She ceases to be the same as she was before the child was conceived. Such updates occur in her that change her entire usual state. The hormonal background changes, a hormonal surge occurs. At this time, “sores” may appear that the expectant mother had no idea about before. One of the probable diseases may be stomatitis. According to statistics, this disease is detected to one degree or another in every second pregnant woman.
Stomatitis is a common mucosal disease. This inflammation is common in both adults and children. According to statistics, during the period of bearing a child, stomatitis occurs in every second pregnant woman due to hormonal changes and weakened immunity in the pregnant woman.
During this period, for stomatitis to appear, only minor exposure to factors promoting the proliferation of infection on the oral mucosa is sufficient. Because of this, inflammation and ulcers subsequently appear.
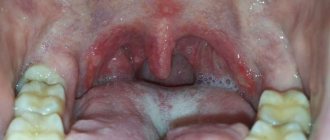
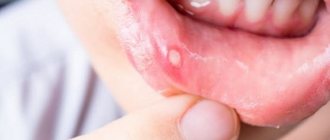
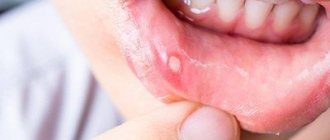
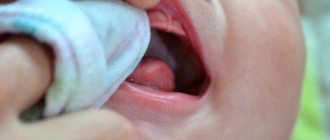
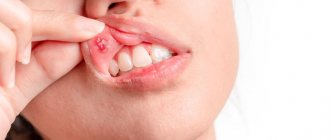
During pregnancy, stomatitis manifests itself in the same way - the mucous membrane in the oral cavity becomes inflamed, redness of the lips, palate and cheeks becomes visible, which then turns into erosion and ulcers (white spots with a red border and plaque).
Do treatment methods for stomatitis depend on the timing of pregnancy?
First of all, we must keep in mind that the first, second and ninth months are the most undesirable in terms of any intervention. Therefore, it is better not to treat stomatitis during these periods. The methods depend on the form of the disease: candidal stomatitis is treated with antifungal drugs, viral - with antiviral drugs, bacterial - with antibiotics, and in the allergic form of stomatitis, contact with the allergen is excluded or antihistamines are prescribed. Whatever method is used, the dentist takes into account the patient’s condition and selects exclusively harmless means of therapy.
Consequences of stomatitis for the expectant mother
If stomatitis is not treated promptly, it can lead to serious complications. For example, an increase in body temperature in a pregnant woman can negatively affect the fetus. Some experts argue that an advanced form of the disease can affect the development of stomatitis in a baby. A viral variant that is not treated in a timely manner can also negatively affect the child.
Painful sensations cause severe discomfort to the expectant mother, and the inability to chew food normally can provoke vitamin deficiency.
What should be the prevention of stomatitis during pregnancy?
The most important thing is to take good care of your oral cavity. Ask your dentist to recommend a suitable antibacterial toothpaste. Be sure to use mouthwash and dental floss. A healthy diet is also of great importance: balance your diet, do not get carried away with sweet carbohydrate foods (bacteria love them very much). Take vitamins - they will help support the body during the difficult period of bearing a baby.
Stomatitis during pregnancy: before and after photos
Experts' opinion
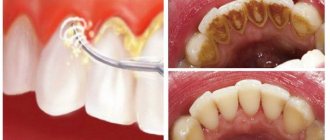
The effectiveness of ASEPTA rinses has been repeatedly proven by clinical studies. For example, according to A.K. Iordanishvili, Doctor of Medicine Sc., professor, North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov, based on a study of 46 people suffering from gum inflammation, it was found that the use of mouth rinses “ASEPTA PARODONTAL ACTIVE” and “ASEPTA PARODONTAL FRESH” (JSC “VERTEX”, Russia) allows not only to improve oral hygiene and reduce inflammatory processes in the gums by 55.37%, but also reduce the number of relapses of localized periodontitis by 21.36%.
Sources:
- Prevention of recurrence of localized periodontitis in young A.K. YORDANISHVILI, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov, Military Medical Academy named after. CM. Kirov, International Academy of Sciences of Ecology, Human Safety and Nature.
- Report on clinical trials to determine/confirm the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: mouth rinse "ASEPTA PARODONTAL" - Solution for irrigator." Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Head. Department of Preventive Dentistry S.B. Ulitovsky, doctor-researcher A.A. Leontiev First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry.
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Causes of aphthous stomatitis
Not all causes of aphthous stomatitis are fully understood. The mechanism of aft formation is often associated with activation of the local immune system - immune cells begin to destroy the epithelium of the mucous membranes, which leads to ulcers.
Local reasons include the following:
- allergic reactions;
- pathogenic microorganisms;
- mechanical damage (biting mucous membranes, injury from sharp edges of fillings or orthopedic, orthodontic structures);
- temperature or chemical influences.
Systemic causes of aphthous stomatitis:
- menstruation, pregnancy in women;
- sudden cessation of smoking;
- enteropathy, celiac disease, malabsorption;
- blood diseases;
- diseases of the immune system;
- lack of vitamins;
- other systemic diseases (lupus erythematosus, Crohn's disease, HIV infection, etc.).
Acute gastritis
In case of acute gastritis, you should consult a doctor.
This form consists of inflammatory processes that involve the upper parts of the mucosa or penetrate into its deeper layers.
The main difference between the acute form is the high rate of development of pathology. Maximum – several days, more often – several hours.
In this case, unpleasant signs suddenly appear, the provocateur is alcohol intake, consumption of foods, medications that irritate the mucous membrane, and being in a nervous environment.
With acute gastritis, all the usual signs of this disease are observed, to which flatulence may be added. Appetite may disappear completely. If there is pain or other unpleasant sensations in the upper abdomen, you cannot ignore them.
An examination is required that will help to identify the pathology in time and correct the condition. Most often, discomfort in this area is caused by gastritis. The depth of damage in acute gastritis and the intensity of inflammation are the main indicators on which the classification of acute gastritis is based.
- Catarrhal. In this form, the inflammation is superficial and is therefore considered mild. To normalize the condition in this form, special medications cannot be taken. The pathology develops quickly, but also quickly passes without much intervention. It is difficult to confuse this form with other diseases, because the symptoms are clearly expressed. All dyspeptic symptoms are present, including diarrhea. The condition is aggravated by general malaise, lethargy, fever, and heart rhythm disturbances.
- Erosive. This form is distinguished by the characteristics of mucosal damage. Small ulcers appear on it - erosion. Such ulcers cause serious consequences. In addition to discomfort in the abdominal area, severe pain occurs, and bleeding inside the stomach may develop.
- Hemorrhagic. This form is accompanied by inflammatory processes and deep erosive lesions of the mucous membrane, which lead to bleeding. Since quite a lot of blood is released, the stool becomes black. This is what is considered the defining feature in diagnosing this form.
- Phlegmonous. With this type of gastritis, the inflammation is purulent in nature, resulting in destruction of the gastric wall. Fortunately, this form is rare. But this does not mean that you do not need to be vigilant. Indeed, with the phlegmonous form, death is common. This form can be recognized at an early stage by the usual signs of gastritis, accompanied by an increase in temperature.
How to get rid of heartburn during pregnancy, watch the video:
How to treat stomatitis in pregnant women?
Treatment of stomatitis in pregnant women is complicated by the fact that most medications for expectant mothers are prohibited. Restrictions are especially strict in the first trimester of pregnancy. And gentle therapy in the form of rinsing with herbal decoctions and more thorough oral hygiene is often ineffective.
That is why, at the first symptoms of stomatitis, the expectant mother should run to see a doctor. Firstly, the initial stage of the disease is treated faster and easier. And secondly, only an experienced specialist will be able to select therapy so that it does not harm the unborn baby, but at the same time copes with the disease.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
Medications
For any type of stomatitis, repeated treatment of the oral cavity with local antiseptics - furatsilin or chlorhexidine - is prescribed. Their task is to suppress pathogenic microflora.
Depending on the type of disease, medications also change:
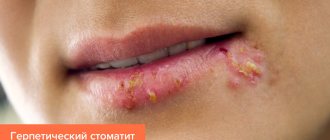
- viral stomatitis
requires the use of antiviral agents (Acyclovir, Gerpevir). But all drugs in this group have an aggressive effect and are strictly contraindicated during pregnancy. Therefore, dentists prefer to make do with gentle local treatment and prescribe vitamins to boost immunity. And after the birth of the child and completion of the lactation process, it will be possible to carry out full treatment; - aphthous stomatitis
brings treatment of the underlying disease to the forefront. And here the dentist can only recommend rinses, pain-relieving ointments, and transfer the prescription of drug therapy to a gastroenterologist, phthisiatrician, venereologist, or infectious disease specialist. They will decide how appropriate antibacterial therapy is. Ideally, it should be postponed until after lactation; - allergic stomatitis
is treated with antihistamines (Loratadine, Cetirizine). But the most important and most difficult thing is to identify the allergen and completely eliminate contact with it. Sometimes allergy tests will be required to detect the pathogen; - advanced candidal stomatitis
is treated only with antifungal drugs (Futsis, Fluconazole). Many of them are safe for the fetus and mother, but, nevertheless, they should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor; - Treatment of catarrhal stomatitis
begins with relief of symptoms with local antiseptics, after which the expectant mother is recommended to undergo full dental treatment, including removal of tartar.
If stomatitis is too painful, the doctor prescribes local anesthetic ointments, sprays and rinses. For example, Hexoral Tabs can be safely used at any stage of pregnancy, as well as during breastfeeding. "Lidocaine Asept" is used in the treatment of stomatitis in pregnant women, but is strictly contraindicated for nursing mothers.
One of the most important tasks for stomatitis is to boost immunity. Therefore, in any case, the expectant mother will be recommended to take multivitamins and, separately, vitamin C, for example, in the drug “Cevicap”. It is important to strictly follow the dosage: in the later stages, excess vitamin C can cause premature birth.
Folk remedies
Treatment of stomatitis in pregnant women is a rare case when official medicine is not only not against traditional methods, but also recognizes their safety and effectiveness. Moreover, you can increasingly see rinses and ointments on sale, which are based on recipes passed down by our ancestors from mouth to mouth for many generations. A striking example is “Sage extract with vitamin C”, Dr. Theiss.
As a rinse for stomatitis, folk wisdom recommends using decoctions and infusions of herbs that have a powerful anti-inflammatory and healing effect.
| 1 | Sage decoction | Take 2 teaspoons of dried sage for half a glass of water, boil, leave to steep for 10 minutes. When the broth has cooled to room temperature, rinse your mouth with it for at least 1 minute. Afterwards, rinse your mouth with clean water. |
| 2 | Chamomile decoction | Take either 1 tablespoon of dried flowers or 1 bag of chamomile tea. Pour a glass of water, bring to a boil, leave to simmer over low heat for 5-10 minutes. |
| 3 | St. John's wort infusion | Pour boiling water over 20-30 g of dry St. John's wort herb. Leave for 2 hours. Afterwards, the broth needs to be strained and diluted with a small amount of warm water. |
| 4 | Yarrow infusion | Only the inflorescences of the plant are used to treat stomatitis! Pour 2 tablespoons of dried flowers into 1 glass of water. Bring to a boil and continue cooking for another 20 minutes. Strain. |
| 5 | Melissa decoction | Pour 1 tablespoon of lemon balm leaves into 1 cup of boiling water. Cook in a water bath for 15-20 minutes. Strain. Use after cooling. |
| 6 | Oak bark decoction | Pour 2 tablespoons of crushed oak bark into 2 cups of poda. Bring to a boil, reduce heat and continue cooking for another 5 minutes. Leave the broth to infuse. When it cools to room temperature, strain. |
You need to rinse your mouth with herbs 4-5 times a day, and before going to bed, it is useful to hold a cotton swab moistened with a decoction or infusion directly on the affected areas of the mucous membrane for 10 minutes. Very important: only freshly prepared decoction and infusion have medicinal properties. Therefore, you need to prepare them daily!
If you don’t have the time or desire to prepare it yourself, you can buy calendula tincture at the pharmacy. For rinsing, you need to dilute it in the following proportion: 1 teaspoon to 100 grams of water.
Alas, if the dentist has diagnosed viral or fungal stomatitis, herbal decoctions will be useless.
A decoction of rose hips and blueberries improves the immune system for stomatitis. Moreover, it is useful to consume the latter in any form: eat fresh berries, prepare mousses from frozen blueberries and brew their leaves instead of tea.
Symptoms
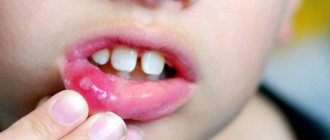
Painful wounds, erosions and ulcers form on the inner surface of the cheeks and lips, on the gums and palate. Visually, they appear as small white spots with a red border ranging in size from 1 to 10 mm. During eating or hygiene procedures, they may bleed and hurt. The disease may be accompanied by increased salivation, bad breath, loss of taste, swelling and pigmentation of the tongue, and high fever.
Stomatitis on the inside of the lip
Diet for stomatitis
In order not to aggravate the situation with stomatitis, you should avoid sweet, spicy and salty foods. It is not recommended to eat mushrooms and legumes. But most importantly, all food should be of a warm, delicate consistency, so as not to further injure the mucous membrane. It is very important that the menu is rich in vegetables and fruits. It is better to stew vegetables and prepare nutritious cream soups from them. And fresh fruits are especially good in the form of smoothies.
In some cases, diet alone will be enough for the expectant mother to forget about stomatitis after 1-2 weeks. But only a doctor can rule out the bacterial, fungal or viral nature of the disease, in which it will not be possible to cope with the disease so easily.
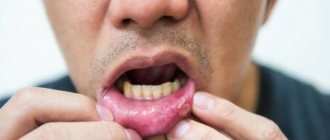
Stomatitis caused by fungi
Candidal stomatitis is a fungal disease caused by fungi of the genus Candida.10 Young children and the elderly are more often affected; people with diabetes and xerostomia (dry mouth), pregnant women and people with weakened immune systems are also at risk. Elderly people wearing removable dentures often get sick.
The main symptom of fungal stomatitis is a burning sensation and the presence of a white, cheesy coating, when removed, a swollen, red mucous membrane appears. The general condition of adults with candidal stomatitis is practically not affected.
Causes of the disease
Gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the gastric mucosa.
Gastritis manifests itself in inflammatory processes that affect the gastric mucosa. This lesion leads to disruptions in the functioning of the organ.
It is believed that most pregnant women experience gastritis if this disease has already visited them before. This rule applies to 75% of girls.
The bacterium Helicobacter pylori that enters the digestive tract is another factor that provokes gastritis.
Usually it ends up in the stomach long before the first signs of the disease appear. Having become infected even before pregnancy, women do not even suspect it, because the symptoms may not be felt for a long time.
An exacerbation begins at the moment when it is provoked by other factors. These include changes in hormonal levels, under the influence of which signs of the disease appear.
Since significant changes occur in the human body during pregnancy, all of them can also become stimulants of gastritis. This includes iron deficiency anemia, disruption of the endocrine system, and infection. There are other reasons for the development of this disease:
- non-compliance with the rules of a balanced diet;
- frequent inclusion in the diet of foods containing refined carbohydrates;
- eating foods containing preservatives, dyes, and harmful flavors;
- eating large amounts of food;
- bad habits;
- experiences, being in a stressful state.