Have questions?
Viral stomatitis is an inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity caused by a virus.
The disease itself is a reaction of the human body to certain factors. So, most often the cause of the disease is infection with chickenpox, herpes, measles, and influenza.
Typically, infectious stomatitis is manifested by damage to the corners of the lips and mucous membrane of the mouth. Such symptoms are characteristic of the herpes virus and are most often found in children under three years of age. If a person’s immunity is strong and can resist the virus, the disease passes without a trace. In weakened patients, the disease can develop into a chronic form.
Causes of viral stomatitis
The occurrence of the disease is caused by a complication of the primary disease (chickenpox, herpes, etc.). The following may cause signs of the disease:
- poor oral hygiene;
- untreated caries;
- gingivitis, periodontal disease;
- unbalanced diet;
- avitaminosis;
- general weakening of the body;
- long-term antibiotic therapy.
Inflammation in other organs and systems of the body also causes viral stomatitis in children and adults.
Stomatitis - symptoms and treatment
The main goal of treating stomatitis is to prevent the lesion from spreading throughout the entire oral mucosa and to prevent the disease from becoming chronic. First of all, it is necessary to determine the form and stage of the disease, since treatment tactics will depend on this. Treatment is complex: both local and general.
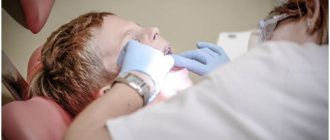
For all types of stomatitis, professional oral hygiene . It is the removal of dental deposits such as tartar and soft pigmented plaque.
Effective drugs for the treatment of stomatitis in adults
Next, it is necessary to eliminate chronic foci of infection and predisposing factors. For painful ulcers, anesthesia of the oral mucosa :
- applications of a 2% solution of procaine (Novocaine);
- applications of 2% lidocaine solution [7].
The affected mucous membrane is treated with antiseptics (0.02% Furacilin solution; 0.06% chlorhexidine solution; 0.1% Dimexide solution).
Applications of collagen films with various medicinal substances, for example, corticosteroid drugs, Diphenhydramine, and anesthetics, are also used. This film attaches to the erosion and has anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects, after which it dissolves on its own. To accelerate the healing of the mucosal epithelium, an oil solution of vitamin A, rosehip oil, and dental adhesive paste with solcoseryl are used.
How can you rinse your mouth for stomatitis?
When treating stomatitis, it is very important to identify the cause and eliminate it. Rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions (0.02% Furacilin solution, 0.06% Chlorhexidine solution) or herbal decoctions will reduce swelling and inflammation, but this is not the main method of treatment.
General treatment
Includes adherence to a diet (it is not recommended to consume spicy, spicy, rough foods, alcoholic beverages), as well as the use of antihistamines, antivirals, antibacterial, antifungal drugs (depending on the form of stomatitis) and sometimes glucocorticosteroids (GCS) - analogues of natural hormones of the adrenal cortex [6 ].
Desensitizing therapy : orally “Tavegil”, “Diphenhydramine”, “Suprastin”, 1 tablet 2 times a day for a month.
Antifungal therapy is carried out for candidal stomatitis: tablets “Nystatin”, “Nizoral”, “Diflucan” [9].
For viral stomatitis, antiviral drugs are prescribed: Lavomax, Valtrex, Bonafton. In severe forms of stomatitis, corticosteroids can be prescribed: prednisolone 15-20 mg per day, the dose of the drug is reduced by 5 mg per week from the moment of epithelization of erosions and ulcers.
For stomatitis, restorative therapy . Vitamins of group B, C, PP. Imudon tablets have an antiseptic effect, normalize microflora, and increase local immunity [11].
From the first day of the patient’s treatment until complete epithelialization, physiotherapy : ultraviolet irradiation, helium-neon laser, laser biostimulation of blood.
Laser treatment of stomatitis
Laser in the treatment of stomatitis is especially effective if the oral mucosa is affected by bacteria, viruses or fungi. The laser beam is targeted specifically at the affected area of the mucous membrane without damaging healthy tissue. The method allows you to destroy microbial cells, reduce pain and swelling, improve microcirculation, which promotes healing. The procedure is painless and safe.
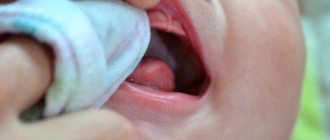
How to cure stomatitis in a child
The principles of treating stomatitis in children and adults are similar, but it is important for the doctor to take into account the age of the child and correctly calculate the dosage of drugs. Another feature is that young children will not be able to rinse their mouths or use mouth baths. Therefore, antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity is carried out by parents with a finger wrapped in several layers of gauze and soaked in an antiseptic solution.
Treatment of stomatitis at home
If symptoms of stomatitis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-diagnosis and treatment with folk remedies often aggravate the disease.
Features of the clinical picture
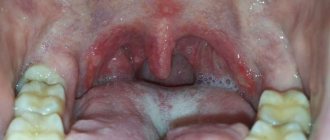
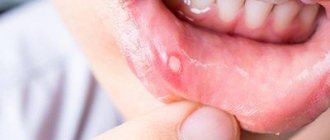
The symptoms of viral stomatitis at the initial stage of its development are easily confused with the symptoms of a common cold. The patient's body temperature rises and a headache appears. Gradually, the oral mucosa becomes very swollen and red, making it difficult for the patient to chew and swallow.
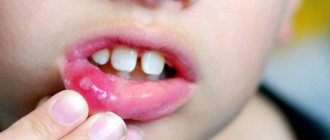
A few days after the onset of the inflammatory process, rashes characteristic of the disease appear:
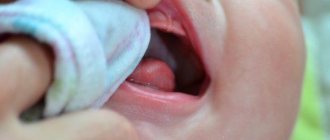
- ulcers on the inside of the cheeks, palate, gums and tongue;
- groups of bubbles with clear liquid inside;
- “cold” on the lips, on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and in the nose;
- erosions that itch and hurt.
A whitish coating appears in the mouth of a sick person. The patient is concerned about general malaise, lack of appetite, bad breath and swollen lymph nodes.
How to treat candidal stomatitis?
Candidal stomatitis
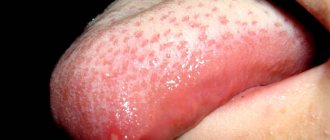
The causative agent is the candida fungus, which attacks the body's cells with weakened immunity. It is rare in a healthy person, mainly at risk are young children, those who have recently had ARVI and influenza, diabetics and people suffering from tuberculosis. Externally, the disease manifests itself as multiple white deposits on the tongue and upper palate; there may not be severe pain, but swelling of the lips and cheeks is almost always present.
After a comprehensive diagnosis, courses of treatment are prescribed, which include:
- Levarin, daktarin and analogues of antifungal agents.
- Nystatin ointment or miconazole gel - instead of or as an addition to tablets.
- Iodinol or Lugol - treat the entire affected area and adjacent tissues.
- For at least a week, switch to a light diet - steamed vegetables, chicken fillet, it is advisable to give up flour products, fatty, spicy and salty foods.
How is viral stomatitis treated?
Often, treatment of viral stomatitis is based on local exposure to damaged areas of the mucous membrane and skin. Ulcers and erosions are treated with an antiseptic and painkillers, the dentist prescribes applications (application of the drug) with anti-inflammatory and wound-healing compounds. To strengthen the immune system, the patient is prescribed medications based on echinacea and vitamins.
It is also important to follow a diet during therapy. All products consumed must be neutral in taste, pureed, and not hot.
You cannot self-medicate: without the help of a doctor, the disease can develop into a chronic form.
It is advisable to reduce home treatment of viral stomatitis in adults and children only to procedures that will speed up the healing process of lesions. The doctor will recommend rinsing with decoctions of herbs and oak bark.
Is stomatitis transmitted?
Allergic stomatitis
– one of the most common and intractable types of the disease.
The cause is an allergy, but what exactly is allergy is to be determined first. Allergens can be both food and medicine, as well as materials for dentures installed in the oral cavity. The typical course of stomatitis - the occurrence of painful ulcers - can be further complicated by difficulty breathing and swallowing, typical of allergies. Allergic stomatitis is not transmitted
except through hereditary means.
Viral (herpetic) stomatitis
- another popular type of this disease, especially common in small, close groups of people (schools, kindergartens, work groups, camps).
Its cause is the herpes virus, and its features are erosive spread (others may appear next to one ulcer) and the possibility of severe complications with fever, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. This is the most contagious variety; in 80% of cases, this stomatitis is transmitted both by airborne droplets and by contact
.
Aphthous stomatitis
– most often occurs in adults, and is associated with weakened immunity.
That is why outbreaks of aphthous stomatitis occur mainly in spring and autumn. It is characterized by the formation of aphthae - small ulcers, both single and occurring in clusters. This stomatitis is not contagious
and cannot be passed on to other people.
Fungal stomatitis (candidomycosis)
– is characteristic of both children (mainly infants) and adults, and mainly women.
It occurs due to Candida fungi, which multiply in the mouth due to weakened immunity or long-term use of antibiotics. It is characterized, in addition to the formation of ulcers, by a white “curdled” coating on the tongue, palate and inner surface of the cheeks. This stomatitis is contagious
: it can be transmitted through direct contact or through household and hygiene items (towel, toothbrush, dishes). A pathogenic fungus can remain in the body for some time and develop in an environment favorable to it.
Nicotine stomatitis
– as the name suggests, occurs in smokers as a result of a long-term addiction to cigarettes.
Tobacco smoke, affecting the oral cavity, actively promotes the growth of bacteria, and also irritates the palate, the tissues become denser, resulting in the formation of numerous ulcers. This type of disease is especially dangerous: although it is not transmitted to other people
, and generally goes unnoticed for a long time, it can develop into oral cancer.
What is stomatitis
Stomatitis can be either an independent disease, which includes several varieties, or a symptom of another, more serious pathology. All stomatitis is characterized by inflammation of the oral mucosa. This is a fairly common problem that can occur repeatedly and in some cases be transmitted from the sick person to other people. There are no tests for the presence of stomatitis; the doctor determines this diagnosis based on examination data and the patient’s complaints. A smear can be taken afterwards to determine the causative agent of the disease. Having made conclusions, the specialist will give recommendations on how to treat stomatitis.
General symptoms of stomatitis
The main manifestation of stomatitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane, however, depending on the form of the disease, additional different symptoms may occur.
There are 3 main features:
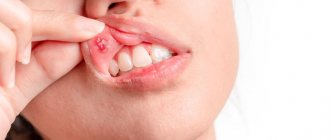
- Hyperemia and redness. Swelling and an unhealthy red color indicate the beginning of a pathological process. immediate treatment at this stage of stomatitis , then small round ulcers may appear in the future. They are usually gray or white, with a red border and film.
- Severe pain and ulcers. At this stage, the surface of the mucous membrane is covered with small ulcers. They can be on the inside of the lips and cheeks and even under the tongue. The patient experiences pain at this time and finds it difficult to eat.
- Fever and headache. The rise in temperature may vary depending on the degree of inflammation. With profuse ulcers, it becomes high, and the headache becomes more pronounced.
Stomatitis should be treated as recommended by your dentist. It is best to consult a specialist at the stage of swelling and redness to prevent further development of inflammation and the appearance of ulcers. However, not everyone pays attention to the first symptoms stomatitis .
Prevention of stomatitis
You can avoid any form of the disease if you follow a few tips from dentists:
- Chew food thoroughly and slowly - the slightest wound after biting will provoke the appearance of multiple ulcers.
- Do not brush your teeth with a brush that is too hard; it is better to choose medium-hard bristles. At your doctor’s appointment, ask which type of toothpaste is best for you individually.
- Maintain hygiene – cleaning should not be limited to morning and evening. If you cannot use a toothbrush, rinse your mouth with warm water at room temperature after each meal. Ideally, buy a compact irrigator.
- For smokers, reduce the number of cigarettes per day, or give up the bad habit forever. Tobacco smoke not only harms the mucous membrane, but also promotes the growth of fungus and pathogenic bacteria.
- Balance your diet - drink scalding hot drinks as little as possible, reduce sour, spicy, salty and fatty foods in your diet. Give preference to dairy products, white meat and fresh, thoroughly washed fruits.
- Visit the dentist at least twice a year for a preventive examination.