Effective treatment of stomatitis in adults
Treatment of stomatitis in adults largely depends on the type of this disease, as well as concomitant diseases that provoke the appearance of ulcers and inflammation in the mouth. The most interesting thing is that the diagnosis of stomatitis is still carried out visually: the patient undergoes tests only if other, more serious diseases are suspected. Effective therapy for stomatitis is possible, but only if the type of disease is correctly determined. Recovery usually occurs within one or several weeks, but there are also more severe forms when long-term rehabilitation is required for complete recovery. Let's look at the main types of disease and drugs for the treatment of stomatitis in adults.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
Treatment of stomatitis after detection can be carried out many times (once a year or more often), since once settled in our body, the herpes virus remains there for life. Herpes stomatitis is characterized by the accumulation of reddish transparent blisters on the lips and inside the mouth, so it is quite easy to detect. Especially often, herpetic stomatitis manifests itself against the background of decreased immunity, vitamin deficiency, hypothermia and stress. Remember that herpetic stomatitis in adults is contagious, so you should avoid tactile contact.
Types of drugs
- Antiviral agents.
- Immunostimulants (as a preventative measure).
- Ointments (including to eliminate visual manifestations of the disease).
Which doctor should I contact for stomatitis?
If you notice the first signs of damage to the oral mucosa, you should immediately consult a dentist. After differential diagnosis of the disease and an accurate diagnosis, it is possible to observe it with a general practitioner or other specialized specialist, for example, an allergist.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis
A type of stomatitis that is caused by a special type of fungus – Candida albicans. Very often, candidal stomatitis begins with glossitis, which is why its second name is stomatitis on the tongue. Treatment in this case requires fairly prompt treatment, since in adults it is quite painful and is accompanied by a burning sensation in the mucous membrane and sore throat. On the inner surface of the lips and cheeks, as well as on the tongue, characteristic foci of inflammation appear, covered with a white cheesy coating.
Treatment methods
- Treatment of common diseases (if detected).
- Antimicrobial therapy.
- Preventive rinses.
What is stomatitis?
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. According to statistics, about 20% of the population of our planet faces it. In adults and children, it can take the form of an independent disease or act as a symptom indicating pathologies of the body. In both cases, treatment is carried out comprehensively and under the supervision of a doctor.
What does the disease look like?
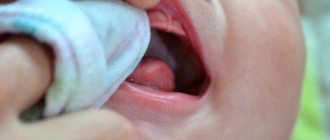
Stomatitis is not difficult to recognize. The initial stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of mild swelling of the oral mucosa. It becomes redder, drier and shiny. A plaque may appear on its surface, and at the site of future lesions the patient feels an unpleasant itching or burning sensation.
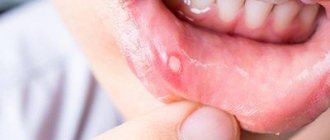
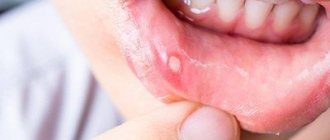
As the disease develops, small ulcers and wounds appear on the mucous membrane - painful oval or round lesions. Their location may be the inside of the lips, cheeks, palate, tonsils, or mucous membrane under the tongue. Their appearance can be seen in the photo at the end of our article.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis
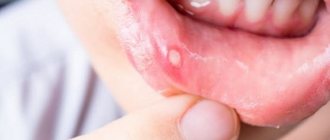
A distinctive feature of this type of stomatitis is the appearance of so-called aphthae on the oral mucosa. These are small round ulcers with redness at the edges, the touch of which causes unpleasant painful sensations. Often occurs as a result of the activity of microorganisms (in particular, staphylococcus). Treating aphthous stomatitis at home is only recommended if it is not caused by a more severe illness. Often aphthous stomatitis occurs with problems with the immune system, liver and gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment methods
- Allergy therapy.
- Antiseptic therapy (treatment of aphthae with anti-inflammatory solutions, gels and ointments).
- Dental treatment and sanitation of the oral cavity (after dental treatment, stomatitis occurs less frequently than in the presence of carious lesions).
- Immunotherapy.
- Diet.
Causes of stomatitis
The mechanism of stomatitis is not yet fully understood. But scientists are inclined to believe that the root cause of its development is the reaction of the human immune system to various irritants. At some point, the immune system ceases to recognize the potential threat of internal and external factors, which causes its atypical reaction, as a result of which “aggressive behavior” of lymphocytes is observed. The attack of lymphocytes against irritant molecules leads to lesions of the oral mucosa.
A variety of factors can provoke an atypical reaction of the immune system. The most likely of them are the following irritants:
- Pathogenic microorganisms that live in the mouth.
- Improper oral hygiene.
- Various damage to the mucous membrane, for example, burns from eating too hot food or mechanical injuries from seeds, nuts, crackers and other hard foods.
- General dehydration due to high fever, blood loss, vomiting, diarrhea, or thirst.
- Poor quality treatment of teeth and gums.
- An allergic reaction to dental structures in the mouth - braces, implants, crowns, bridges, etc.
- Long-term use of medications.
- A diet depleted of beneficial vitamins and elements.
- Smoking.
- Malignant formations of the oral cavity, respiratory organs or undergoing a course of chemotherapy.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body, for example in pregnant women or children during puberty.
- The presence of chronic diseases or allergies.
- Severe stress.
Interesting to know! Frequent stomatitis in adults can be caused by the use of toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate, a substance added to oral care products to form a thick foam. According to recent studies, it dehydrates the oral mucosa and makes it vulnerable to various types of irritants. Patient observation data confirms the fact that avoiding the use of sodium lauryl sulfate paste can reduce the risk of developing stomatitis in adults by 81%.
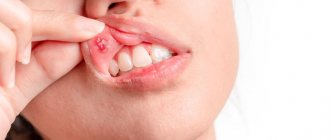
Treatment of ulcerative stomatitis
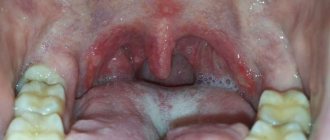
Ulcerative stomatitis very often occurs due to poor oral hygiene and bad habits (especially smoking). Often this type of stomatitis at its onset is confused with periodontitis and gingivitis, since it is characterized by inflammation of the gums, a grayish coating around the teeth and death of soft tissues. Often accompanied by fever and fever. One of the few forms of stomatitis, which often requires treatment by a doctor, and in the most advanced cases, surgical intervention.
Treatment methods
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Antibacterial treatment of affected areas.
- Surgical intervention (in severe cases, removal of areas of dead tissue and gum grafting).
Types of ointments
The main difference between drugs of this form lies in their composition - it is the properties of the main component that determine the ability of the drug to destroy one or several different pathogens. Based on this principle, four types of ointments have been developed against different types of this disease:
- for the treatment of herpes stomatitis resulting from damage to the body by a virus;
- against aphthous stomatitis associated with poor oral hygiene (considered the most common form of the disease);
- for the treatment of candidal stomatitis, which is often found in children and has another common name - “thrush”;
- universal drugs suitable for eliminating all types of stomatitis.
However, to decide what to apply to a child’s stomatitis, knowing only the main effect of the main component is not enough. Therefore, to choose the right ointment, you need to familiarize yourself with the most popular ones.
Holisal
Cholisal is a universal ointment suitable for the treatment of all types of stomatitis, including fungal. It is capable of providing local analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. Prescribed primarily for children over 1 year of age.
- Ingredients: Cetalkonium chloride and Choline salicylate.
- Application : apply 2-3 times a day after meals, as well as at night. To treat a child, squeeze 5 mm of ointment onto a clean finger and rub it into the affected areas of the oral cavity.
- Contraindications : intolerance to salicylates and other components. Not recommended for treating children under 1 year of age.
Oxolinic ointment
A drug based on oxoline (0.25%) is an effective remedy for getting rid of stomatitis caused by herpes viruses, influenza and adenoviruses. It is especially often prescribed to neutralize this disease in a child.
- Composition : Oxolin.
- Application : a certain amount of ointment is rubbed into the affected areas of the oral cavity 2-3 times a day.
- Contraindications : oxolin-containing products are prohibited for use in the presence of any drug allergies.
Bonafton
This drug has an antiviral effect and is intended to combat stomatitis caused by the Herpes simplex virus and adenoviruses.
- Ingredients : Bromonaphthoquinone.
- Application : a small amount of the product should be applied to the affected areas 3-4 times a day and left for a maximum of 5-10 minutes.
- Contraindications: the drug is contraindicated for use if the child has a hypersensitivity to its components.
Acyclovir ointment
It is one of the drugs prescribed for the treatment of herpetic stomatitis in a child.
- Composition : thymidine nucleoside analogue of synthetic origin.
- Application : acyclovir ointment should be rubbed into the surface of the affected areas every 4 hours. The duration of treatment is determined by the pediatrician individually.
- Contraindications : the presence of individual intolerance to the constituent ingredients.
Tebrofen ointment
It has antiviral properties and is prescribed to combat stomatitis caused by various types of viruses.
- Composition: Tetrabromotetrahydroxydiphenyl.
- Application : a certain amount of 2% ointment is applied to the inflamed areas 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 1 week.
- Contraindications: increased sensitivity to the components of the ointment.
Treatment of bacterial stomatitis
This type of stomatitis is also called prosthetic stomatitis, since it occurs due to unsatisfactory care of the orthopedic structure, when many pathogenic microorganisms accumulate in the area of contact between the prosthesis and soft tissues. After treating foci of inflammation, it is necessary to carry out complete cleaning and antibacterial treatment of the prosthesis or replace it. This type of stomatitis should not be confused with allergic stomatitis, which develops against the background of an allergy to the prosthetic material. In this case, the prosthesis must be changed to a hypoallergenic one.
Treatment methods
- Anti-infective therapy.
- Mouth rinse.
Treatment of allergic stomatitis
This type of stomatitis is caused by the body's immunological response to contact with an allergen. The role of the latter can be played by anything: food products, new oral hygiene products, dentures, animal hair and much more. At risk are patients who are predisposed to allergies or suffer from various autoimmune diseases. A distinctive feature of allergic stomatitis is the acute onset of the disease, accompanied by an increase in temperature, severe pain and putrid odor from the mouth, which does not disappear even after thorough brushing of the teeth.
Treatment methods
- Identifying the allergen and eliminating it (or minimizing contact).
- Antihistamine therapy.
- Relief of inflammation with corticosteroids.
- Taking analgesics to relieve pain.
- Local antiseptic drugs
- Diet.
Signs and symptoms in infancy
The main symptom of stomatitis is aphthous rashes on the surface of the mucous membranes, which can be single or have multiple courses. If the number of ulcers exceeds 20, the child is diagnosed with a severe form of stomatitis, requiring treatment in a hospital. Almost all babies experience an increase in the activity of the salivary glands and an increase in the production of salivary secretions - hypersalivation. Drooling can occur at any time of the day and does not depend on food intake. If you examine the oral cavity, you can see signs of an acute inflammatory process: redness of the soft tissues, fluid accumulation, swelling and bleeding of the gums.
Fungal stomatitis
Other signs of stomatitis include:
- What causes stomatitis?
- itching and soreness of the gums (the child puts everything into his mouth, making chewing movements that help relieve the soreness);
- temperature rise to +38°C;
- a dense coating of milky or dirty yellow color, having a creamy or curdled consistency;
- bad breath.
Stomatitis in a child
If you try to remove plaque from the surface of the gums or tongue using gauze or a napkin, underneath it there will be injured mucous membrane that will bleed and hurt. In very rare cases, a pinpoint rash of pale pink color may appear on the mucous membranes - this picture indicates the allergic nature of the disease.
Child's tongue is white
Treatment of stomatitis in children
Treatment of childhood and adult stomatitis follows the same methods. At the same time, some drugs used for adults are replaced with those that are better suited for the child’s body. First of all, we are talking about antibiotics, antiseptics and drugs to enhance immunity. Children are often prescribed more gentle methods, which include the use of herbs and natural tinctures for rinsing. At an early age, dentists recommend preventing stomatitis using traditional medicine.
| Age | Type of disease |
| From 0 to 3 years | Candidal stomatitis, or childhood oral thrush. This type of stomatitis is especially common in infants. |
| 1 – 4 years | Aphthous and herpetic stomatitis caused by external infections and mechanical trauma to the oral cavity. |
| Children of primary and secondary school age | Allergic and aphthous stomatitis. |
Treatment of stomatitis at home
I would like to immediately note that treating stomatitis with folk remedies at home is possible, but you need to understand that in many cases it is impossible to do without a visit to a specialist and the use of antibiotics. Ignoring these points can lead to worsening of the disease and longer rehabilitation. In addition, on the Internet you can find a whole lot of “revolutionary” recipes for stomatitis, so you need to be able to separate the wheat from the chaff and understand which remedies can really help, and which are the fruit of the inflamed imagination of “couch healers”. Below we publish the most common methods of preventing and treating stomatitis with folk remedies, but please note that only an experienced specialist can draw up an optimal treatment plan.
In the case of children, treatment of stomatitis with folk remedies at home is used quite often. This is especially justified as a preventive measure, since the child’s body is more susceptible to the influence of the external environment. The most popular remedies are considered to be all kinds of decoctions, for the production of which chamomile, calendula, burdock, propolis and blackberry leaves are used. A homemade ointment is also used to treat stomatitis, which is made from novocaine, egg white and honey. Be that as it may, if your child shows signs of stomatitis, it is best to immediately take him to a specialist who can make the correct diagnosis and plan treatment.
How many days does treatment last?
Correct, competent treatment of stomatitis significantly speeds up the healing process. Depending on the type of disease, it lasts for 3 to 7 days. If after 1 week of treatment the signs of the disease have not disappeared or worsening is observed, then the patient most likely has complications. The following factors may be the probable reasons for its development.
- The patient self-medicated or did not follow the doctor's instructions.
- Decreased immunity.
- The presence of chronic diseases of the body.
- Regular injury or infection of the oral mucosa.
- Undiagnosed allergy.
- Having bad habits - smoking, chewing, etc.
- Depression or frequent stress.
- Improper oral hygiene.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- The use of oral hygiene products containing sodium lauryl sulfate.
Returning to the question - can stomatitis go away on its own - it should be noted that a seemingly harmless disease can turn into serious problems for the patient. Therefore, you should remember three “don’ts” - don’t
engage in self-medication,
do not
put off visiting a specialist and
do not
ignore the recommendations of your doctor.
How to understand that stomatitis has passed?
Very simple! A complete cure is indicated by the absence of lesions in the oral mucosa. There are no small ulcers, wounds or plaque on the cheek, palate, lip, tongue or tonsil area. The mucous membrane looks healthy, is well moisturized, does not cause pain and does not create discomfort during eating, talking, smiling and performing hygiene procedures.
Treating stomatitis with home remedies
| Facilities | Description |
| Hydrogen peroxide | Rinsing with a solution of hydrogen peroxide helps reduce discomfort and has an antiseptic effect. |
| Baking soda | Treatment of stomatitis in adults with soda is recommended when the disease is detected in the initial stages. A solution of the substance (a spoon in a glass of water) is recommended for rinsing. |
| Decoctions of chamomile, rose hips and calendula | They have disinfecting properties and contain vitamins and nutrients to maintain oral health. |