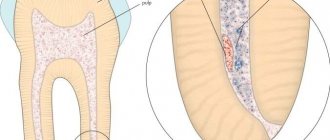
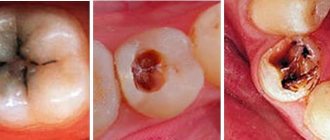
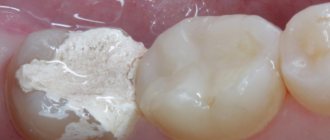
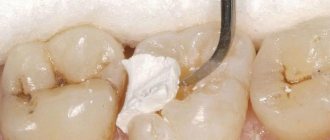
Why do you need to fill teeth?
The main task that fillings solve is to prevent the development of carious tooth decay. After high-quality cleaning of the damaged cavity and filling it with a filling, the risk of secondary caries will decrease to almost zero. This allows a person to lead a normal lifestyle and not experience any discomfort. In addition, fillings allow you to restore the aesthetics of your teeth.
Fillings are also used in case of tooth damage due to mechanical stress. This could be a chip from an impact or abrasion of a large layer of enamel.
Types of fillings by service life
Depending on the period during which the fillings are in the tooth cavity, they are divided into two types - temporary and permanent. They differ from each other in the material from which they are made, and also have different appearance.
Temporary
Temporary tooth fillings are used when treatment is carried out in two stages. At the first of them, the doctor cleans the cavity from caries. Next, it is necessary to place special medications into the tooth that disinfect the tissues or promote the death of the dental nerve. This approach is needed in case of deep caries damage or the presence of its complications, for example, periodontitis.
Temporary fillings are also needed if additional time is needed to make a permanent one. Certain types of fillings are made in a laboratory using impressions that are taken from a cleaned cavity. At the same time, at the first appointment with the doctor, a temporary material is installed, and at the next one he can install a permanent one.
Permanent
Permanent fillings are installed during one-stage treatment of caries. In this case, at the first appointment, the doctor cleans the affected cavity and places a permanent filling in it. This method is suitable if we are talking about superficial or medium caries.
Non-metallic fillings
Cements for filling teeth
Cements are widely used for the manufacture of a wide variety of fillings. They are included in permanent fillings in adults, these materials are used to fill baby teeth in children, and cements are used to make insulating linings.
- Phosphate cements cannot act as an independent material for making fillings, since they tend to decrease in volume after installation. Therefore, to prevent gaps from appearing between the tooth and the filling, and to avoid a loose fit of the filling, zinc phosphate cements are used only as a spacer when installing other fillings, and they are also used to fix crowns.
- Silicate cement is used to fill a tooth after a layer of phosphate cement has been installed on the pulp. The fact is that silicate material is not able to independently provide the necessary permeability, and it can have a pathogenic effect on the pulp. In addition, this cement will dissolve under the influence of saliva and has toxic properties, which is why modern dental clinics do not use silicate cement.
- Combined silicate-phosphate cement has absorbed all the best qualities of the two previous cements. It does not stick to the walls of the dental cavity, while it is as hard as silicate cement and has the necessary transparency. Another advantage of this cement filling is that it does not conduct heat. The disadvantages of fillings made from silico-phosphate cements are: not very high aesthetic qualities, low strength and poor resistance to the environment in the oral cavity, as well as toxicity to the pulp, and therefore it is necessary to use an insulating lining. It is these fillings that are most often installed in free dental offices, as they are low in cost.
- Glass ionomer cement is another modern cement that is characterized by increased strength and durability. This cement adheres well to the tooth and is not toxic. In addition, in the process of wearing such a filling, fluoride is released from it, which contributes to additional protection of the tooth from carious destruction. However, this modern material also has disadvantages. It is fragile and, like all other cements, has increased abrasion. In this regard, glass ionomer cement is used as insulating linings and for securing dental inlays.
Plastic fillings
In dentistry, plastic is used as a material for making temporary fillings.
Their advantages:
- High hardening speed;
- Resistance to chemical agents;
- No oral irritation.
There are many more disadvantages of plastic fillings than positive qualities:
- Reducing the volume of the filling during operation;
- Subsidence of the filling;
- Quick change of original color;
- Tooth destruction as a result of deformation of the filling.
Plastic fillings include acrylic oxide and carbondent.
Acrylic plastics are produced by a domestic manufacturer and have the following advantages:
- High adhesion (adhesion to tooth tissue);
- Tight fit to the walls of the cavity, negligible shrinkage;
- Easy to dispense powder and liquid;
- Resistance to external irritants;
- Long-term preservation of the original color.
However, despite the strength of acrylic oxide, it is chemically toxic and will eventually lead to the development of an inflammatory reaction under the filling.
Compared to acrylic oxide, carbondent is denser, less toxic, but very fragile and quickly darkens.
Ceramic fillings
Ceramic fillings have a number of advantages, including:
- Increased hardness;
- Resistance to original color;
- Maintaining the original size, no shrinkage;
- Excellent aesthetic qualities.
Ceramic fillings are made as an inlay, that is, according to a pre-made impression of a treated tooth. The configuration of the ceramic filling makes it possible to evenly distribute the load throughout the entire tooth during the process of chewing food. There are several types of ceramic fillings: from pressed ceramics, from metal ceramics, with zirconium oxide included in their composition. One and perhaps the most significant disadvantage of a ceramic inlay is its high cost compared to fillings made of other materials.
Light-curing composite fillings
Light-curing fillings are those that harden as a result of exposure to light of a certain frequency. They are as close as possible to the appearance of a person’s own teeth, almost invisible after their installation, durable and initially look perfect. The advantage of these materials is that they are highly polishable, and their high aesthetic qualities make it possible to use these fillings for the treatment of anterior teeth. However, over time, such fillings need to be replaced, as they will still shrink.
Types of fillings according to materials used
The materials used to make fillings can vary from precious metals to modern polymers. They may differ in their appearance, wear resistance and price.
Cement based
Cement tooth fillings have been around for a very long time. Their use was most common before the advent of various modern materials. This is due to the low cost of the components that make up them.
Other advantages of such fillings include:
- low shrinkage;
- tight fit to the tooth, which prevents the possibility of falling out or the appearance of secondary caries;
- long service life.
As for the disadvantages of these fillings, the main one is the unnatural color of the material, which often differs from the surface of the tooth, as well as the likelihood of its pigmentation under the influence of coffee, food coloring, etc.
Plastic
Plastic fillings are used quite rarely. Most often they are used to close small cavities, and are also used in pediatric dentistry for filling baby teeth. Plastic fillings are often used as temporary fillings in multi-stage treatment. Like the previous option, they are low cost.
Among the disadvantages of such fillings are strong shrinkage of the material and the presence of a porous structure, which can cause secondary caries, since it does not properly protect against bacteria.
Amalgam
Amalgam are tooth fillings made of metal alloys with different compositions. It may contain mercury, tin, gold, etc. One or another option should be chosen depending on personal preferences and the available budget, since some of them are very expensive. A significant disadvantage of such a filling is its unnatural color, which differs significantly from the shade of tooth enamel.
The main advantage of this type of filling is its durability. Amalgam fillings have one of the longest lifespans and are often chosen for placement in posterior teeth.
Ceramics
Ceramic fillings are among the most expensive. Their advantages:
- they have natural shades and are therefore invisible on the teeth;
- do not change color under external influences;
- have a long service life.
The downside is that such fillings must be made separately, so the treatment process always takes place in several stages.
Light-curing composites
One of the most modern and high-quality types of fillings are light-curing composites. They are highly durable and aesthetically pleasing, since the doctor can always choose the most suitable shade that will not differ from the patient’s natural tooth enamel. The main advantage of this material for fillings is that it hardens only under the influence of a special lamp, so the doctor can regulate this process and adjust the shape of the tooth filling before its final hardening.
Glass ionomer cement material
Glass ionomer cement is a material that combines the properties of silicate and polyacrylic systems. Such fillings are used extremely rarely, although they have high adhesion to tooth tissue and other materials. This ensures the durability of the filling and its good fit. However, this material has mild toxic properties, so it is gradually being abandoned in dentistry.
Types of dental filling materials
The tooth is filled at the final stage in curing teeth from carious plaque and possible problems after it. The filling helps restore the drilled part of the tooth and returns it to its original appearance. If the filling material is chosen correctly, it will last a long time and will not cause any complaints. If the doctor did his job “carelessly”, without individually selecting the material for filling the tooth for the patient, then even the most expensive and high-quality filling may fall out the next day.
To avoid such a situation, it is not necessary to look through a bunch of material on the topic of dental fillings on the Internet, or ask a lot of friends which dentist they treated their teeth with. In order to know what filling materials exist, and which of them are used most often in dentistry, read our article, we will tell you all the nuances of this process. We hope that after reading, you will have a better understanding of the topic and you will not have any questions about it.
Types of materials for fillings
Materials for fillings are classified according to the content of components, features and method of use.
Initially, they were divided into three groups - temporary and permanent fillings and gaskets.
Material for temporary filling
Fillings that are installed for a short period of time are not very strong and not particularly aesthetically pleasing. But these features are not important, because they are installed for only a couple of weeks and do not bring much discomfort to the wearer. But since temporary filling is most often installed while a tooth or gum is healing, it has a high cost. During dental therapy, temporary material also promotes faster healing. Popular temporary fillings are Septopak, Parasept, Tempofot, Koltosol and others.
Treatment pads
Therapeutic pads are used to promote rapid tooth healing. The hydroxide contained in this product prevents tissue inflammation and prevents the transformation of caries into pulpitis. The pads are applied to the bottom of the drilled and cleaned tooth, the top is covered with a separating pad, and then a permanent compound is installed on the tooth. Dentists prefer Deykal, Life, Calcipulp, Pulpomixin and others for their work.
Insulating gaskets
Having touched upon the topic of insulating gaskets above, we also note their beneficial properties. Since fillings are a foreign object, they can irritate the dental pulp. To reduce the likelihood of this action, it is necessary to use insulating gaskets. Before their invention, the pulp was isolated with a phosphate cementitious dental solution. But based on their experience of using it, dentists noticed that this material does not cope with its task very well. Glass polymer insulating gaskets “Copalight”, “Whitebond”, “BaseLine” and others are produced.
Permanent fillings
There are a great variety of materials for conventional dental fillings. All this diversity can be divided into three general classes:
- cements;
- amalgams;
- composites.
Each of these groups is also divided into subgroups, depending on their own individual characteristics.
Cements for fillings
These groups include silicate, polycarboxylate, phosphate and glass ionomer cements. But in today's medicine, these components are used to secure stable dentures. Filling with cements has faded into the background.
Amalgams for permanent fillings
This type of raw material is a durable alloy of metals and mercury. Its use in dentistry has a long history of more than 100 years. Today, silver amalgam with a large amount of copper admixture is used. But amalgams also have their disadvantages - they do not adhere well to the teeth and are a conductor of heat. And the presence of mercury (a radiation and poisonous metal) in the composition is considered a controversial point in the decision to install this particular material.
Composites for fillings
This material is considered one of the most widely used. A composite filling is easy to apply, holds well, and meets beauty requirements. Composites for permanent fillings consist of a combination of only two chemical components. Hardening occurs after the filling is placed on the tooth, as a result of the interaction of the material with air. This is also affected by the main component of the material. Depending on this, it can harden not only due to a reaction to air, but also after complete installation, as a reaction to the light of a special lamp.
When preparing a solution, the dentist mixes a small amount of a catalyst into chemical composite materials, which affects the hardening of the components. If the doctor works for too long, the material may dry out before the work is completed. That is, the dentist must have time to mix the components and catalyst, simulate a model of the drilled tooth for the aesthetic appearance and convenience of the patient, before the composite begins to harden. Otherwise, the work will have to be done again. The disadvantages of a chemical composite also include a small selection of color shades that could be matched to the color of the patient’s teeth.
Light-hardening filling composites are most often used in dental clinics. They are easy to use and aesthetically pleasing. And the dentist can control the hardening of the material independently, after the complete process of modeling the tooth to be filled. This control is carried out using an ultraviolet lamp. For high-quality work, the dentist is provided with a wide selection of shades of this type of composite composition. The doctor can calmly select the shade of the material so that it does not differ in color from the natural teeth, and form a filling for restoration. At the moment, doctors have not found any downsides to this product, but note only its positive aspects - long-term stability, beauty, a large palette of shades. Stability is determined by high-quality fixation of the filling composition with the inside of the tooth and insulating materials.
Take care of your teeth, treat them on time and be healthy!
Chemically cured composites
The main property of chemically cured composites for fillings is their polymerization exclusively when exposed to certain substances. That is, such materials harden evenly after mixing their original components. This makes the filling process more controlled and of high quality, especially when it comes to very deep cavities or extensive carious lesions.
The disadvantages of this material for fillings include the following:
- insufficient resistance, especially under systematic mechanical influence;
- rapid pigmentation and high probability of darkening.
In this regard, such fillings are used less frequently compared to photopolymers.
Installation steps
The process of filling a tooth has a specific algorithm, which consists of the following stages:
- First, the mouth is rinsed for additional disinfection.
- Next, the doctor must isolate the work area from exposure to saliva, which may contain bacteria.
- After this, the immediate cleansing of the affected cavity begins with the help of a special bur.
- If all foci of caries are removed, the tooth cavity is washed with a special solution and dried.
- Next, you can proceed to placing the filling.
- After it hardens, the doctor removes all excess material and grinds the surface of the filling so that it does not interfere with the patient.
This is the simplest process of installing a filling, which occurs when treating superficial caries. If we are talking about a deeper lesion, then such an algorithm can be supplemented with other stages related to the treatment of the internal tissues of the tooth.
Filling baby teeth
In pediatric dental practice, both phosphate cements and compomers - composites combined with glass ionomers - are used as permanent filling materials.
Both have the ability to enrich tooth tissue with fluoride, but the latter are more resistant to destruction and have high aesthetic characteristics. Some dentists use chemical-curing compounds with colored components to make fillings for children.
What anesthesia is used?
Anesthesia is not necessary during tooth filling. If the lesions are small, the filling procedure can be performed without pain relief. Often it does not cause any discomfort to the patient and is carried out quite quickly.
In cases where the lesion has many lesions or is very deep, the patient may be given local anesthesia. To do this, one or more injections are made into the gum near the diseased tooth.
In some cases, general anesthesia may be used. However, it is used extremely rarely. Usually it is resorted to when it is necessary to carry out treatment in young children or patients who are terrified of such interventions.
Contraindications for filling
There are very few contraindications to filling. Usually they are limited to recommendations for the use of a specific type of filling, since they may be allergic to others.
Other contraindications include the following:
- subgingival destruction, which limits access to the damaged area and also makes it impossible to isolate this area from saliva;
- the presence of bruxism in the patient, which is accompanied by frequent grinding of teeth for no reason, as a result of which fresh fillings are quickly destroyed;
- increased tooth abrasion, which will also quickly render the filling unusable.
In addition, filling is not carried out when more than 1/3 of the tooth is damaged by caries. In this case, the doctor may recommend its removal with further use of the implant. Another solution may be to use a crown, which is placed on a completely cleaned tooth.
Materials for filling root canals of teeth
Root canals are filled when caries reaches the stage of pulpitis. The essence of filling is to fill the tooth canal as tightly as possible with the selected material. Modern dentistry makes this process painless and quick.
The following materials are used for this:
- Gutta-percha is the result of processing a material such as latex. When heated, gutta-percha becomes viscous, and after cooling it hardens. This material has high biological compatibility with dental tissues, has low toxicity, does not dissolve, and does not cause allergic reactions. If such a need arises, gutta-percha can be removed from the dental canal. The disadvantages of the material include the lack of bactericidal properties, the inability of the material to adhere to dentin, and the difficulty of installation.
- Silver pins are used less and less in modern dentistry, as it has been found that they tend to oxidize and provoke a relapse of inflammation.
- Titanium pins do not provoke allergic reactions, are very durable, light in weight and do not corrode. However, they can only be used if the tooth is slightly damaged and there is no nerve in the canal.
- Natural pastes (sealers) contain various antiseptic and antibacterial components that prevent the development of inflammation, they do not cause difficulties in installation and dissolve over a long time. The disadvantages of sealers include the likelihood of developing an allergic reaction and the presence of toxic components. In addition, upon contact with the mucous membrane, they can cause throbbing pain.
- Polymer pastes (sealers) are used more often than natural ones, since they do not stain the tooth, do not dissolve in liquids, and have good attachment to the canal walls. However, they can provoke an allergic reaction, especially for patients prone to such manifestations.
- Cortismol is a powder that helps eliminate pain after it is introduced into the root canal of a tooth, as it contains hormones. However, it cannot be used to fill the front teeth, as it contains coloring pigments.
- Kanason Combipak acts as an antiseptic and antibacterial agent for filling. It isolates the channel perfectly, but the main disadvantage of using it is the long installation time.
- Glass ionomer cement is not suitable for filling dental canals, as it has low strength and allows fluid to pass through. Therefore, it is often used for filling baby teeth.
- Polymethylsiloxane has an excellent ability to fill even the smallest cavities, as it consists of tiny particles. Its main disadvantage is the novelty of the material and insufficient knowledge of its effect on the body.
- Cements are used to fill tooth canals only after applying isolation.
Possible complications
Complications after filling occur if the doctor did not properly clean the tooth cavity of caries. This can lead to a recurrence of the lesion, which will then pass under the filling and go unnoticed. As a result, significant damage to the tooth can occur.
Another complication is associated with breaking off the edges of the tooth after the filling shrinks. To avoid it, the doctor must carefully remove all overhanging edges of the enamel.
Also, in case of poor-quality grinding, the patient may experience overbite, which will lead to significant discomfort. However, this problem can be solved very quickly by visiting the doctor again.
The iOrtho clinic network provides high-quality services for correcting malocclusion with Invisalign aligners, sign up for a consultation now!