Localization and nature of toothache
It's hard to go wrong with a sore mouth. A person can easily describe where and what hurts. Painful sensations can differ both in intensity (sharp and strong or weak and aching) and frequency (for example, at night - that’s another test). Toothache can affect one tooth or several in a row, on one or both jaws. The pain can radiate to the temple, affecting not only the eye and ear, but also causing migraines. Moreover, the trigger (trigger mechanism) for such sensations is not necessarily hot tea or cold ice cream. Sometimes a person describes their occurrence as “out of the blue.”
Let's try to summarize the types of toothache:
- Aching, sensations are dull and not intense.
- Shooting, sharp, in the form of sharp impulses, causing suffering.
- Sharp, unexpected, independent of the time of day.
- Long-lasting, “background”, tolerable, so the patient puts off seeing a doctor.
Each of the above types of pain indicates a particular pathology. With a timely visit to the dentist, there is every chance of maintaining a beautiful smile and healthy teeth. Otherwise, unpleasant consequences will not keep you waiting.
Sinusitis, maxillary sinus cyst, loss of sense of smell after visiting the dentist
The roots of the teeth of the upper jaw can normally be adjacent to the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses of the nose and even survive in them . Sinusitis, maxillary sinus cyst and loss of smell are possible when infection or filling material penetrates from the teeth into the paranasal sinuses. Unfortunately, this is not uncommon. Moreover, some cases of persistently recurrent sinusitis are associated with infection penetrating from the roots of the teeth . In this case, a possible symptom is a strong unpleasant odor from the nose and mouth.
Odontogenic sinusitis after treatment by a dentist
Odontogenic sinusitis (scheme). Teeth and maxillary sinus. On the left is the norm. On the right – the root of the “seven” (tooth 2_7) is destroyed, inflammation around the destroyed root, pus in the maxillary sinus.
Filling material in the maxillary sinus and sinusitis after filling the “six” canals (tooth 2_6). Pain in the left side of the face after visiting the dentist.
1 – roots of teeth, 2 – normal, air in the right maxillary sinus (front view, the air looks black in the picture), 3 – in the left maxillary sinus there is a fragment of filling material surrounded by an inflammatory shaft. The patient had been mistakenly receiving treatment for trigeminal neuralgia for a long time.
Cysts of the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses in diseases of the roots of the teeth.
1 – roots of the teeth, 2 – cysts of the maxillary sinuses, growing from the roots of the teeth (cysts are round “bubbles”, they look gray in the picture).
How can we help you:
- Let's find the source of pain after dental treatment;
- We will treat inflammatory processes, sinusitis, sinusitis and neurological complications; if necessary, your health will be taken care of jointly by a neurologist and an ENT doctor. Treatment of sinusitis without puncture
Diagnosis of toothache. Features of complications in the absence of treatment
The correct diagnosis can only be established after examining the oral cavity. The dentist must analyze complaints, obtain information about concomitant ailments, previous injuries and find out the nature of the pain. Then prescribe adequate treatment
A visual examination by a doctor may include the following manipulations:
- applying light tapping movements to the tooth to determine the location of the pathology;
- determining the reaction to exposure to heat;
- examination of the condition of the enamel using a special lamp or laser;
- study of the condition of dentures, if any;
- X-ray diagnostics to identify foci of inflammation, root fractures and other hidden problems;
- 3D computed tomogram, which allows you to obtain a three-dimensional model of an organ, view the internal structure of the bones, identifying neoplasms and cysts.
CT scan.
Network of dentists “Smile”, Shchelkovo Whatever the toothache is - severe, low-intensity, nagging, sharp, appeared today or has been lasting for several days - make an appointment with a dentist. Even if the pain has subsided and does not manifest itself at all, you cannot cancel the visit. Some insidious diseases (such as pulpitis) can behave changeably: after a sudden exacerbation, some relief may occur. However, you should not wait for the next attack or hope that the disease has gone away on its own and the pathological process has stopped.
Note! Before visiting the dentist, do not take medications that relieve pain - analgesics (tablets, injections). This will blur the symptoms, and it will be difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis, not to mention the correct treatment regimen, due to the dulling of symptoms by painkillers.
Pain after dental implantation, tooth implant hurts
During dental implantation, the trigeminal nerve and its branches, the alveolar nerve plexus, may be damaged as a result of:
- Screwing the implant into the canal where the trigeminal nerve or its branches lies;
- Inflammation in the implant area (infection and/or implant rejection).
Some pain during the implant healing process is normal. If the pain after dental implantation lasts too long, is very severe, or is accompanied by numbness of the lip or cheek, we can check the condition of the trigeminal nerve using electromyography and a neurological examination based on the characteristic loss of facial sensitivity and the spread of pain along the trigeminal nerve system.
The rejection reaction and inflammatory processes in the implant area are usually clearly visible with CORRECT X-ray examination and computed tomography.
Implants in the lower and upper jaw. Pain after dental implantation
There may be direct pressure from the implant on the nerve or inflammation in the implant area with tissue swelling, edema and subsequent pressure on the nerve.
Reasons why a tooth may hurt
The appearance of toothache often comes as a surprise, because it can occur even if the teeth appear to be completely healthy. In any case, if you feel pain in your teeth, you should immediately visit a dentist.
First, the specialist will find out the cause of the pain (hypersensitivity, caries or something else). There are several types of causes of tooth pain:
- bacterial (gum disease, pulpitis, caries);
- mechanical damage to the enamel;
- general diseases.
Let's look at the most common causes of toothache in more detail:
Caries. Toothache due to enamel destruction
The most common cause of toothache is diseases caused by the proliferation of bacteria that can destroy tooth enamel from the outside and inside.
A lot of people have caries, and not all of them know about it. The disease manifests itself in the form of darkened spots on the surface of the teeth. It is interesting that at first the spots are white and can stand out against the background of the darker surface of healthy enamel - this is the stage when bacteria are still destroying the tooth shell with the products of their vital activity.
As caries progresses, bacteria penetrate deeper into the center of the tooth, the focus of the disease becomes wider and can cover neighboring teeth. By breaking through the mineral layer and reaching the soft dentin, the carious process accelerates.
At the culmination stage of caries, if the disease is not treated properly, bacteria penetrate the pulp, covering the vascular and nervous tissue, as a result of which the tissue becomes inflamed and begins to ache. This is how pulpitis develops. Treatment of this disease consists of cleaning the soft insides of the tooth, disinfecting the tooth cavity and placing a filling, sometimes (in particularly advanced situations) requiring removal of the affected nerve.
Pulpitis. Dental nerve pain
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the neurovascular bundle located in the tooth. The pulp (vessels and nerves of the tooth) swells and affects the walls of the chamber, which causes pressure on the nerve endings. This is where severe pain arises, intensifying every day. A common cause of pulpitis is caries, which progresses too much due to lack of timely treatment. Microbes, toxins and other harmful substances make their way from there to the nerve and interact harmfully with its tissues.
Powerful painkillers will help you quickly get rid of acute pain. But for complete and high-quality treatment, you need to contact qualified specialists. How do dentists deal with infection that affects the nerve of a tooth?
- Anesthesia is used for the affected area;
- The pulp chamber is opened;
- The nerve is removed;
- Clean the canals located at the root;
- The canals are washed and then filled;
- Place a filling on the crown
The pain with pulpitis and with caries is different. With caries, it is not strong, it increases with the consumption of cold and hot drinks and dishes, and inhalation of cold air. The pain associated with pulpitis is acute and unbearable, appears at unexpected moments, for example, in the middle of the night, and can radiate to the temples, cheeks and nose (if a tooth in the upper jaw is affected), ear and neck (if a tooth is affected in the lower jaw). With pulpitis, the pain persists for a long time, without subside or weakening, but with caries it subsides when the irritant disappears (example: sweets fall on a tooth affected by caries - the tooth hurts, remove the sweets - the pain subsides).
Another possible cause of pain is diseases resulting from untreated or neglected caries or pulpitis - cysts, granulomas, periostitis (festering of the gums in addition to symptoms of pulpitis or caries), periodontitis (swelling of the gums, mucous membranes, sometimes parts of the face, often with any absence of pain).
Eruption of wisdom teeth and the appearance of pericoronitis
During the growth of the last tooth in a row, people experience severe pain that affects the cheeks, jaw and even throat. Toothache during tooth growth is aching and pulling, and can be accompanied by pain in the head and neck, as well as pericoronitis - inflammation of the gum tissue caused by a lack of available space on the jaw. A tooth can erupt under the gum hood correctly or incorrectly. In the first case, the gum hood is excised to facilitate its development and save the patient from suffering.
Incorrect eruption of wisdom teeth is caused by a lack of space in this area of the gum. Its further growth will be accompanied by severe pain, inflammation, complications and may even lead to death. To avoid this, doctors advise immediately removing the harmful tooth and not allowing it to develop further.
In this case, you must immediately contact a surgeon. Self-treatment will not bring results, but will only hasten the development of sepsis, phlegmon, and in the worst case, death.
Gingivitis. Gum inflammation
The gums can be affected by diseases such as periodontal disease or periodontitis. With such inflammation, bleeding and pain in the gums are observed, and chewing food becomes especially painful. Most patients perceive these sensations as toothache. Such diseases can lead to exposure of tooth roots, which explains increased sensitivity. If the infection passes quickly or is not noticed in time, then pathogenic bacteria can penetrate even into the pulp, which can lead to the loss of a tooth, or even several.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is characterized by inflammation of the tissues around the tooth root. The dead pulp remains inside the canal and its purulent contents flow to the gum. This provokes severe acute pain that prevents you from even touching the tooth. The patient has difficulty chewing food and drinking too cold/hot drinks.
Periodontitis is an exacerbation of gingivitis, periodontitis, and pulpitis. Another cause of the disease can be poor oral hygiene, bad habits, and careless surgical procedures.
It is impossible to get rid of pain during periodontitis on your own; urgent and mandatory medical intervention is needed. Doctors will open the canal for a certain amount of time to allow the pus to drain out. Thanks to soda/soy rinses, microbes will begin to die, and therefore inflammation will stop.
ARVI, sinusitis, sinusitis
Bacterial and viral diseases such as sinusitis or sinusitis affect the mucous membranes of the sinuses, which is dangerous for the teeth due to their close proximity to the jaw.
Such inflammation can lead to pain in the upper row of teeth. A similar situation can happen to the lower jaw if a person has a sore throat or pharyngitis, for example, since with such inflammation the lymph nodes suffer.
Injuries, tooth root fracture, cracks and chips
Chips of fillings, injuries to the tooth roots and cracks in the enamel can be the consequences of mechanical damage caused by bruises or chewing too hard food. In this case, the patient may experience pain not only from the injury, but also due to inflammation, which appears as a result of infection entering the pulp through cracks. The pain in this case can be sharp, dull, strong or weak, so an x-ray or orthopantomogram (OPTG) is necessary to identify the exact cause of the disease.
Whitening procedures and pastes with abrasive particles
Teeth whitening can lead to increased sensitivity (hyperesthesia). This happens during the procedure because the removal of the bacterial layer is followed by a violation of the mineral composition of the enamel. If this happens, then usually all teeth suffer, but the front teeth receive the greatest damage, since they are in the visible zone, and they are whitened especially carefully.
A hard toothbrush and strong pressure while brushing
Everyone knows that brushing your teeth should be done twice a day for 2 minutes , but few people know that it is also important to choose a toothbrush with the right level of hardness and not put too much pressure on your teeth during procedures. Fulfilling these conditions is very important for maintaining healthy teeth and oral cavity. If you ignore these factors, you can easily damage the enamel, which will result in aching pain in your teeth or increased sensitivity to high and low temperatures.
Hypothermia and inflammation of the facial nerves
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is a well-known and unpleasant ailment. Undoubtedly, spending time outside is very beneficial for the health and immunity of people of all ages. But long walks when the temperature on the thermometer has exceeded -20 and the absence of a hat in windy weather can lead to such a painful and aching pathology as inflammation of the dental nerves.
General diseases of the body
In the fast pace of modern life, not every person can remain completely healthy. A large information load leads to chronic fatigue, stress and neurological disorders. The listed ailments affect the functioning of the brain: it begins to transmit distorted nerve signals that can reach the teeth and cause aching pain. In this case, you should first go not to the dentist, but to a psychotherapist or neurologist.
Pain in the lower jaw or lower molars may be due to cervical chondrosis. This pathology appears in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, mainly at the computer. The head remains in one position for a long time, which causes the spine to bend and lead to compression of blood vessels/nerves, and all this has an extremely negative effect on the sensations in the teeth.
Stomach pathologies have a negative impact on the condition of teeth. For example, with heartburn, stomach acid enters the oral cavity and destroys the enamel. Because of this, dentin is exposed, which leads to increased sensitivity of the tooth.
Lack or improper intake of vitamins, dietary disorders
It is known that acids can cause hyperesthesia, accompanied by pain in the teeth. For children, the elderly and people with sensitive enamel, it is best to avoid foods with vinegar and citric acid. You should take vitamin C only when necessary and with non-acidic foods (for example, rosehip decoction). By the way, rose hip decoction contains more vitamin C than lemon.
Berries, fruits, vegetables, herbs, cottage cheese, eggs and nuts are essential components of a healthy person’s diet. Due to their absence, the mineralization of the enamel worsens, which means the oral mucosa suffers. Without beneficial and useful substances in the body, the enamel is destroyed: it becomes thin, susceptible to cold and hot, and reacts sharply to solid foods.
Imaginary acute toothache really exists! Many believed that it was a fantasy of overly emotional and impressionable people. However, there is a scientific explanation for this. After a tooth is removed, the nerve endings of the gums in its place begin to actively recover, which leads to phantom sensations. This condition can last for several weeks and goes away on its own.
Prevention of dental diseases
Proper prevention of dental diseases should be carried out from an early age. This will help avoid many problems that lead to constant pain, acute and chronic diseases, as well as tooth loss. Doctors recommend the following methods of prevention:
- daily oral hygiene using toothpaste and rinses;
- removing plaque in the dental office when it appears;
- timely correction of bite and incorrect position of teeth;
- regular dental check-ups.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can undergo a comprehensive diagnosis of headaches, as well as receive recommendations for their treatment. Our center has modern equipment that allows you to quickly make an accurate diagnosis and establish the cause of pain. It is important to follow doctors’ instructions and go through all stages of treatment - this will help get rid of dental problems, correct bite and other congenital or acquired pathologies, and also prevent their further development.
Why does a tooth ache under a filling?
The filling, placed several years ago (6-7), could be pressed through and deteriorate under the influence of external factors. The tooth will hurt if the pulp is alive and the position of the filling is disturbed. Pain also occurs in the following cases:
- Pain after a short period of time after seeing a doctor is most likely a medical error, for example, the canal was not cleaned well enough, there is still an infection inside, an instrument broke during the procedure;
- Pain after a long time after seeing a doctor is a violation of the seal of the old filling.
In any case, you cannot get rid of such an illness on your own. Contact your dentist in a timely manner so as not to start an inflammatory pathological process.
How is trigeminal nerve inflammation diagnosed?
If you only feel aching pain in your teeth, then first you need to make an appointment at a dental clinic. Only a competent dentist can determine the nature of the pain, its cause and the exact source. Typically, an examination of the oral cavity is performed, followed by palpation and tapping of painful areas. To accurately verify the neuralgic nature of the disease, you will need to undergo a CT scan of the teeth (this will show the presence of inflammatory processes in the teeth and gums, and will also allow you to detect abscesses and other pathologies). You may need to consult an ENT specialist, since problems with the maxillary sinuses may also cause pain. Well, if you experience characteristic shooting pains, you should immediately contact a neurologist.
Once the presence of tertiary nerve inflammation is confirmed, the doctor decides how to treat the patient. You should not hope that the pain will go away on its own. These cases are extremely rare; moreover, it is important to determine the true cause of the discomfort and exclude other more dangerous and serious pathologies.
Why does a dead tooth hurt suddenly?
Many people believe that a dead tooth cannot hurt? But what does the expression “dead tooth” mean? This is a tooth with dead or removed pulp. Yes, due to periodontitis, the nerve dies, but remains inside the pulp, which is why it begins to decompose over time. From there, the pus goes to the root, causing the surrounding tissue to become inflamed. This is how acute pain occurs.
There are several reasons why a dead tooth becomes especially sensitive (due to complications) before and after treatment:
- Low-quality treatment and cleaning of dental canals;
- Medical violations when placing a filling: the edges of the filling extend too far beyond the root;
- Not all tooth canals have been cleaned, some of them are missed or not completed;
- Allergy to the material from which the filling is made
It is important to understand that tooth disease after treatment is a normal and natural process. It is called post-filling syndrome, which lasts for several weeks (1-2). If it really is him, then the pain will weaken every day. However, if the pain does not disappear and even increases daily, then this is a significant reason to repeat the appointment with the doctor.
SIGN UP ONLINE
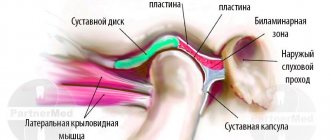
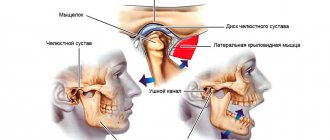
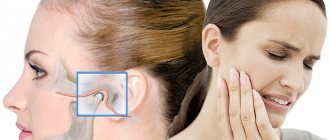
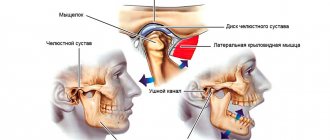
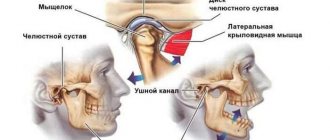
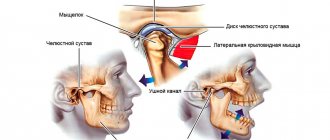
The jaw hurts and clicks after prosthetics or dental treatment
Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. The lower jaw is connected to the skull by two temporomandibular joints. Impairment of the function of these joints is possible after the installation of a denture, crown, bridge, any treatment or tooth extraction if this leads to malocclusion and/or damage to the temporomandibular joint. This is a typical complication after dental prosthetics. Read more about treating TMJ dysfunction here
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
The green arrow indicates a healthy joint. The red arrow points to the joint that remains in the “open” position when the mouth is closed. This leads to wear and tear of the articular cartilage, pain and clicking when opening and closing the mouth. One of the reasons is the incorrect position of the upper right “eight” (tooth 1_8 lies horizontally).
How can we help you:
- Anti-inflammatory treatment will help relieve pain. If necessary, we inject anti-inflammatory medication directly into the lower jaw joint . This brings relief within a few minutes .
- Injection of botulinum toxin preparations (for example, Botox or Dysport) into spasmodic muscles. This is relevant in the case of an excessive increase in the tone of the masticatory muscles, if it is the muscles that are the “culprit” of dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint.
- Treatment by an osteopath. An osteopath works with the joints and muscles of the jaw using gentle manual techniques. This way you can solve a lot of problems that cannot be solved in classical dentistry. More about osteopathy
- Introduction of chondroprotectors (medicines for nutrition and restoration of cartilage) into the temporomandibular joint. Read more about cartilage restoration
When to see a doctor
Wound healing after removal of the figure eight is always a painful process, but sometimes it is accompanied by complications. To avoid causing a serious deterioration in your health, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms appear:
- the pain intensifies every day, analgesics help little;
- the pain does not go away a week after tooth extraction;
- the pain is not aching, but pulsating, it radiates to the neck, eye, temple, and interferes with sleep. Such sensations are a sign of an inflammatory process; you should consult a doctor immediately;
- swelling does not disappear completely on the 2nd–3rd day after surgery, but, on the contrary, increases;
- temperature rises above 37.5 °C;
- the temperature does not drop to normal on the 2nd–3rd day after surgery;
- an allergic reaction to a hemostatic sponge or analgesics occurs;
- alveolitis (inflammatory disease) occurs in the socket. This happens if a part of the root remains in the hole, a blood clot did not form or was washed out during hygiene procedures, the patient violated the rules of oral care, which is why an infection got into the wound;
- your health worsens on the 2nd–3rd day after the procedure.
Causes of pain
As a rule, before installing a crown, the tooth is depulped - that is, the neurovascular bundle in the root and coronal part is removed, after which the canals are filled. Pain may be caused by some features of these manipulations:
- incomplete filling of the canals - as a result of the formation of voids in the root canals, an infectious process may begin to develop; Pus accumulates at the root tip, which causes pain. This is a common complication of endodontic treatment, especially in cases where the canals are too narrow or curved;
- subsidence of filling materials over time - even if the root canals are completely filled, changes in the physical properties of the materials can also lead to the appearance of voids - infection develops in them, inflammation spreads to the tissues near the apex of the tooth root;
- removal of the filling material beyond the root apex - “excess” material in the periodontal tissues can provoke irritation and inflammation.
Pulpitis. Inflammation of the pulp can occur in cases where a decision was made to preserve it - tooth processing can lead to a burn, the infectious process may already begin in the pulp and be asymptomatic, which becomes the cause of inflammation. Preserving living pulp before installing a crown on a tooth is a rare occurrence; as a rule, the “nerve” must be removed.
Perforation of the walls of the root canal. Perforation is the creation of a hole in the root canal, a phenomenon that occurs for several reasons:
- perforation may be a consequence of mechanical processing of the canal with a thin instrument - it must enter the canal along its entire length. If the canal is curved, then even a slight pressure can cause the instrument to pass through the tooth tissue;
- installation of a pin can lead to perforation - it is installed in the root canal, which, given the appropriate anatomical features of the structure of the root system, can also lead to the formation of a hole.
The hole is a “gateway” for infection—the tissue becomes inflamed some time after the pin is installed or endodontic treatment is performed, which causes pain.
Why does the tooth under the crown hurt?
The reason for this may be the presence of a foreign body in the canal. During endodontic treatment, the tip of the instrument may break off; subsequent filling of the canal with a foreign body leads to pain. There can be several reasons for breakage - the most common of them is the curvature of the canals. If they are difficult to pass, the tool may break due to the high load.
As a rule, in this case, the patient feels pain when exposed to temperatures, and the tooth under the crown also hurts when pressed. Pulsation may appear during exertion or chewing on the side with the crown installed. Tapping on a tooth also causes discomfort.
In order to avoid such a complication, the dentist must perform an x-ray diagnosis before installing a crown or any other dental prosthesis.
If the technology for processing and preparing the tooth for prosthetics is followed, installing a crown can also cause pain - if the design is too high for the bite, the patient feels discomfort when closing the jaws. This is why the stage of “trying on” the crown before its final installation is important - a good orthopedic dentist will first assess the degree of comfort for the patient.
How to prevent pain?
Prevention of toothache under a crown includes following your doctor’s recommendations: crowns should be brushed just like your own teeth - at least 2 times a day. It is worth paying special attention to cleaning the spaces between the teeth and around the gums - this is where the largest amount of food debris and plaque accumulates. It is recommended to use not only a toothbrush and toothpaste, but also dental floss and, if possible, an irrigator.
You will have to refrain from eating solid foods - seeds, nuts, in order to avoid damage to the crown.
Visit your dentist at least once a year to monitor the quality of your dentures.
How is inflammation of the trigeminal nerve treated?
Correct treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can only be prescribed by a neurologist. Depending on the complexity of inflammation, the following agents are included in therapy:
- Drugs to combat symptoms (pain);
- Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants of central action;
- Alcohol blockades (for severe inflammation);
- Metabolic drugs;
- Anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, finlepsin);
- B vitamins;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
The measures are aimed at relieving inflammation and completely eliminating pain symptoms. Properly prescribed treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can not only restore excellent health, but also prevent relapses.
This information is for informational purposes only. Only a professional specialist can prescribe treatment after examination and diagnosis.
When is pain normal?
Even a perfectly installed crown can provoke painful sensations immediately after prosthetics - as the local anesthesia wears off. The pain may be constant or occur with pressure. How to distinguish these sensations from those caused by pathology?
Firstly, pain normally lasts no more than 1-3 days - this is due to the adaptation of tissues to the new structure in the oral cavity.
Secondly, the pain tends to subside. Increasing sensations indicate a pathological process.
Rules for oral care after wisdom tooth removal
In order for healing to proceed normally, without any additional problems, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- remove the tampon 20 minutes after surgery;
- for 3 hours after removing the figure eight, do not eat or drink;
- Do not rinse your mouth on the day of surgery;
- In the first few days after surgery, avoid hard foods and eat warm, soft foods. Chew food on the other side of the jaw, protecting the wound from foreign particles getting into it. Do not drink anything hot;
- in the first 7–10 days, avoid alcohol (it slows down healing and cannot be combined with analgesics);
- in the first week, do not visit training rooms and swimming pools, do not work in the garden, do not do cleaning, avoid physical activity, especially those associated with bending;
- in the first week do not visit baths, saunas, solariums, or sunbathe in the open air;
- do not heat the socket area (do not use warming compresses), do not use a UHF device;
- Do not brush your teeth for the first 24 hours after surgery, then for 10 days when brushing your teeth, try not to catch the socket with the brush;
- on the 2-3rd day after the operation, make passive baths with chlorhexidine or another antiseptic (spiking the solution into your mouth and tilting your head towards the hole, just hold for a while, then spit), starting from the 4th day - use chamomile or sage decoctions ;
- take only those analgesics prescribed by the doctor, apply cold compresses.
If the pain intensifies or other alarming symptoms appear, you should never touch the socket with your fingers to check its condition. You need to see a doctor: if there really is a problem, he can prescribe an x-ray, and then select a treatment regimen.