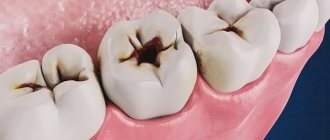
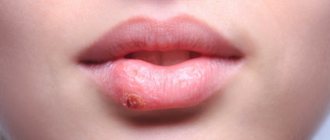
Dental diseases of the teeth are a group of pathologies that affect the enamel, gums, oral cavity, as well as the jaw and chewing muscles. Dentists call them harmless to humans, since the mortality rate is negligible. However, it is these disorders that determine the patient’s overall well-being: they affect self-esteem and an internal sense of comfort.
Experts recommend not to let the situation get worse and to closely monitor the condition of your teeth. Due attention allows you to avoid serious complications, as well as promptly identify defects that need correction.
In this article we examine in detail the most common problems, as well as methods of treating them.
Basic terms in dentistry: names and causes of inflammatory diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
It plays a vital function in the digestion process: it is responsible for grinding food and influencing its subsequent breakdown by enzymes. In addition, there is a huge number of microorganisms that create natural microflora, but are considered opportunistic. This nuance determines the fact that any dental disorders progress extremely quickly.
Among the key factors in the occurrence of dental diseases are:
- poor hygiene;
- mechanical injuries and damage;
- chronic illnesses;
- metabolic disorders and abnormalities;
- the presence of thermal irritants in the body;
- bad environment;
- hereditary predisposition.
The branch of medicine that studies the emergence and development of pathologies is called etiology. It is partially correlated with diagnostic procedures, as it helps in determining pathogenesis.
Classification: types of main dental diseases of the teeth
Conventionally, all violations can be divided into two broad categories - those associated with damage to the enamel, and those caused by processes occurring in periodontal tissues. There is another classification principle - based on “carious” affiliation:
- with existing caries lesions;
- non-carious deviations.
The second option is considered the simplest and most convenient to treat if the problem is detected at an early stage. In addition, it is easier for patients to comply with prescriptions, which simplifies the process of rehabilitation measures.
Note that congenital and hereditary pathologies stand apart. They are formed in the womb and are very difficult to correct.
How does oral hygiene change with age?
Age is not kind to teeth. Just like the musculoskeletal system, teeth and gums wear and change with age. Diseases, one-sided nutrition and medications, unfortunately, leave their mark: they lead to dry mouth and reduce salivation. And the latter is very important due to its antibacterial properties, which inhibit the growth of bacteria that cause caries and periodontal disease. In addition, saliva regulates the acid-base balance in the mouth and helps reduce the effects of acids responsible for disrupting the mineralization of tooth enamel and the occurrence of caries.
Developmental and eruption disorders
What are the different dangerous dental diseases? Perhaps the most serious problems are caused by congenital or hereditary causes. In these cases, the exacerbation does not begin due to pathogenic bacteria, pathogens or other factors. Such pathologies, as a rule, play a symptomatic role. They signal about malfunctions occurring in the body and force you to take immediate action.
Edentia
A pathological process accompanied by the loss of individual units or complete rows. In extremely severe stages, complete tooth loss occurs. The disease begins to develop during intrauterine development. The main factor is poor heredity or serious illnesses suffered by the mother while carrying the fetus. Due to jaw overload, even healthy teeth can become loose.
Superset
A disease in which excess elements appear in the oral cavity, which have an extremely negative effect on the state of the bite, and provokes additional speech and chewing problems. Dentists recommend removing such units, and the sooner the better.
Fusion and Merger
A rather rare deviation, expressed in the connection of tooth buds with dental cement. The main processes unfold during the formation of elements. Only 1% of people are prone to this disease. As a rule, the disease is diagnosed as part of a temporary dentition. In adulthood, pain is approximately 5-6 times less, so patients often do not suspect the presence of a problem until a visit to the dentist.
Spear-shaped teeth
A disease that affects crowns. It is considered infrequent - it occurs in one case in a thousand. It causes both aesthetic, psychological and physiological inconvenience. Usually it is a consequence of chronic injury to the inner surface of the cheeks, lips, and tongue. In some patients it is accompanied by hypoplasia.
Impacted teeth
An ailment in which the teeth are unable to fully erupt. As medical practice shows, the problem begins to bother people due to the gums being blocked by bone layers. Another reason is premature loss of elements.
Dystopian teeth
A disease in which the incorrect location of units is recorded. The displacement occurs as a result of deviations of the alveolar ridges from the norm. It causes psychological discomfort, disrupts the beauty of a smile, and interferes with the correct functioning of the masticatory muscles.
Macrodentia and microdentia
Congenital hereditary anomalies that determine the specifics of development. Manifested in improper formation and scaling of teeth. They have a negative impact on the bite and the aesthetics of the smile. They are also extremely rare - in every 20 people (in the context of not a single state, but the whole world).
Diseases associated with enamel
What are the possible dental problems due to enamel damage? In the vast majority of cases, they are associated with violations of the structure and integrity of the rows. Usually they are a consequence of internal failures in the body. They are eliminated only at the moment when the factor that provoked their exacerbation disappears.
Fluorosis
A chronic disease that develops during eruption. Accompanied by structural damage, darkening, and loss of dentin. The reason is excess fluoride, which is explained by long-term use of fluoridated water, medications, etc.
Cracks
Deviation, usually localized on the anterior chewing row. It looks like vertically or horizontally located defects of a non-carious nature. Appears due to sudden temperature changes, aggressive chemical exposure, or due to injury.
Turner teeth
An advanced form of local manifestations of hypoplasia. It is fixed long before the first eruptions and has nothing to do with carious lesions. Externally it looks like an enamel layer. Sometimes accompanied by excessive sensitivity.
Hypoplasia
Pathological phenomena of a congenital nature, which is characterized by a complete or partial absence of enamel. If we talk about the external picture, then it is worth noting depigmented or white spots, rather large grooves based on the surface, as well as small depressions. Caused by incorrect structure of hard dental tissues. If left untreated, it is complemented by acute forms of caries.
Wedge-shaped defect
Disadvantages expressed in wedge-shaped cavities in the cervical region of the units. This occurs due to the fact that certain areas of the enamel disappear, resulting in wedge holes. The problem can be registered on any element, but more often on fours and fives.
Types of pathologies
In accordance with the ICD-10 classification for dentistry, treatment of diseases of the oral mucosa is carried out in four categories. There are inflammatory, infectious, viral and fungal diseases. The treatment plan depends both on the severity of negative symptoms and on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, which are manifested, among other things, in the reaction to certain groups of medications.
Infectious viral processes
The form of development is directly related to the source of occurrence - thus, the following varieties are characteristic of pathological cycles provoked by a viral infection:
- Catarrhal is a condition characterized by severe swelling and rashes, on the surface of which a gray coating forms.
- Aphthous - damage to the oral mucosa, associated with the formation of painful blisters, leaving behind areas of erosion.
- Ulcerative – similar in symptoms to the first option, but differs in a more pronounced pain syndrome.
Let's consider the main diseases classified as infectious.
Pharyngitis
An inflammatory process affecting the pharynx area, caused both by the introduction of the pneumococcal virus and by systematic inhalation of smoke, polluted or cold air. It is accompanied by discomfort when swallowing, increased sensitivity and a persistent feeling of tickling, as well as general malaise and fever. Diagnosed by visual examination and by examining a smear sample. In difficult cases, it is treated with antibiotics, but in most situations a therapeutic course, including regular inhalations, rinses and compresses, is sufficient.
Glossitis
A disease of the mucous surface of the tongue, leading to a change in its structure and shade. The likelihood of infection increases with the systematic consumption of hot or alcoholic drinks and spicy food, non-compliance with hygiene standards, as well as burns and mechanical damage to tissues. Primary symptoms are characterized by discomfort and a burning sensation. As the pathology develops, areas of redness form, the intensity of salivation increases, and taste perception worsens.
Prolonged absence of medical intervention leads to extensive swelling, which makes it difficult to perform normal functions, as well as to the formation of growths. The drug course of treatment for glossitis involves a special dietary regimen that excludes solid foods from the diet.
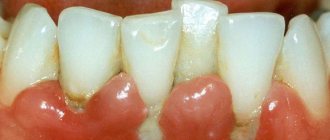
Gingivitis
An inflammatory disease of the gum mucosa, most often diagnosed in adolescence, as well as in pregnant patients. Various forms of manifestation determine the presence of an additional classification:
- Ulcerative-necrotic - affects the tissues of the oral cavity, provokes enlargement of the lymph nodes and is characterized by severe pain.
- Catarrhal and atrophic - cause swelling, itching, bleeding, an acute reaction to temperature changes, as well as weakening of the structure.
- Hypertrophic – manifested by a noticeable increase in the size of the gingival papillae, accompanied by bleeding and pain.
The timing of treatment for gingivitis depends on the stage at which the pathology is detected. The dentist’s priority task is to remove plaque and relieve inflammatory processes.
Stomatitis
Infection is introduced in different ways, most often as a result of mechanical damage to tissue. As it develops, characteristic round ulcers are formed, localized on the inside of the lips and cheeks, as well as in the area of the root of the tongue.
When diagnosing, it is recommended to treat the oral mucosa, having previously excluded products containing sodium lauryl sulfate from everyday use, since the active component provokes additional irritation. Anesthetics help relieve pain, and antiseptic and anti-inflammatory compounds are used to remove the film.
Other dental diseases: list of dental diseases with photos
Next, we propose to analyze ailments that may appear as a result of teething or age-related changes.
Grinding
A pathology in which there is a rapid decrease in hard tissue. Provokes thinning of enamel and damage to dentin. It can affect both individual units and full-fledged rows.
Erosion
A process in which a violation of enamel integrity is recorded. Some areas are damaged symmetrically. Main signs: changes in pigment, various cosmetic defects, painful reaction to cold or spicy food.
Pathological resorption
Loss of root tissue caused by chronic diseases, advanced periodontal disease or progressive pulp disease. It can be one-sided or combined. In the absence of rehabilitation and therapeutic therapy, tooth loss occurs.
Deposits and build-ups
They are mineralized residues that form above or below the gums. The main material for formation is food particles, the results of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, as well as components of saliva. They trigger processes that provoke periodontitis.
List of neurotic dental diseases
Stressful periods have a particularly detrimental effect on the state of the body. In addition, as practice shows, the quality of oral hygiene deteriorates sharply. A person simply forgets about cleaning or does not do it thoroughly enough, which increases the risk of developing caries. The parallel use of sedative medications disrupts the production of saliva and causes a feeling of dryness.
Gradually, all this is reflected in psychosomatics - muscle spasms and pain are detected. The most common occurrence is excessive clenching of the jaw.
Bruxism
A disorder characterized by uncontrollable grinding of teeth caused by emotional stress. As a rule, it makes itself felt during sleep. The causes of its appearance include stress, prolonged depression, and malfunctions of the masticatory apparatus.
Grinding
This is not so much a full-fledged disorder as a symptom. Occurs when muscle spasms occur when the patient clenches his jaw tightly. In the vast majority of cases, the person does not even know there is a problem. It is detected during routine dental examinations.
How to brush your teeth
Good hygiene is of great importance for older people. Retirees who have good oral care experience fewer dental problems. If necessary, teach your elderly relative how to care for their teeth and select suitable hygiene products for them.
Brushing your teeth should be done in the morning and evening. Cleansing lasts at least 3 minutes. It is better to choose a fluoride toothpaste: it restores the balance of minerals in teeth and reduces the risk of developing caries.
It is necessary to follow the correct technique for brushing teeth - from the gums to the cutting edges, to clean both the outer and inner surfaces. Hard-to-reach places and the space between teeth should be thoroughly cleaned.
It is important to take into account age-related characteristics: the gums shift, the necks of the teeth become exposed, and the distance between the teeth increases. For these reasons, teeth must be brushed carefully to avoid damage.
After cleaning, it is useful to use a rinse aid. Rinsing will prevent the development of caries and other dental problems, and eliminate bad breath. The mouthwash should be pleasant and not too spicy. You can choose the right one at a pharmacy or store (“Forest Balsam” and others).
In addition to brushing your teeth twice a day, it is recommended to use dental floss or a special brush at least once a day. These products will help you get rid of pieces of food between your teeth. Rinsing is also recommended after each meal.
Even if a person has no teeth, he needs to wash his mouth regularly to prevent dental problems. If you don’t have a rinse aid, you can use regular warm water with a small amount of salt dissolved in it. It is important to rinse your mouth thoroughly. The procedure can be performed before bed after brushing your teeth.
The main dental diseases in humans: what they are and how to treat them
Modern medical practice, implemented in the Dentika dental clinic, actively uses innovative methods of diagnosis and treatment. Almost any disease can be eliminated provided that you seek help in a timely manner, as well as follow all doctor’s prescriptions and prescriptions. Among the measures used by dentists are:
- filling;
- surgical intervention;
- prosthetics;
- implantation;
- aesthetic correction.
In addition, professional hygiene methods are used: bleaching, restoration, etc.
Prevention
Above, we examined in detail what dental diseases are called and what are the main reasons for their occurrence. Now let's talk about preventive measures to avoid serious problems and pathologies.
If you experience any strange sensations in your mouth, it is recommended that you make an appointment with your dentist immediately. He will conduct an initial examination and draw up an individual treatment program. However, in some cases it is possible not to resort to aggressive measures of influence and limit oneself to supportive manipulations.
So, what needs to be done to prevent the development of diseases?
- Do not ignore the symptoms that appear - go to the doctor immediately.
- Do not let the disease worsen, follow all dental recommendations and prescriptions.
- Get professional examinations every six months.
- Maintain hygiene at home, use only high-quality products.
- Don’t forget about professional hygiene - ultrasonic cleaning should be done once every six months to a year.
In addition, it is important to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition and give up bad habits.
How to care for dentures
Dentures require regular careful care. Elderly people are advised to remove dentures after eating, clean off food debris and plaque with a toothbrush, then rinse thoroughly with water.
Cleaning tablets and denture powders can be used once a week. They are good at removing stains that regular toothpaste cannot deal with, and also disinfect dentures. You can use a special antiseptic, which must be dissolved in water for use. You can purchase a ready-made solution.
For additional care, you can use antibacterial tablets that will fight bacteria and get rid of bad breath. Such tablets are dissolved in a glass of water (one at a time) and the prosthesis is immersed in the solution for 15 minutes.
At night, dentures are stored in a suitable container with cold water.
If removable dentures move when chewing food, they need to be fixed with special glue. If possible, dentures should be removed for a short time to give the gums a rest, but no more than a day.
Dentures should be protected from shock and heat. Damage to them can injure the gums and mucous membranes.
If salivation increases while wearing dentures, you can cope with this by sucking on sugar-free lollipops or drinking water.
Dentures need to be replaced every five years.
Let's sum it up
Dentistry studies the etiology, symptoms, and treatment features of the most common dental diseases. There are a huge number of reasons that provoke oral problems. Some of them are easily eliminated, others are subject to only partial correction. However, for both cases the rule is true: the sooner you start working on dental treatment, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome. That is why it is important not to let things take their course and undergo regular medical examinations.
How to restore lost teeth
The loss of one tooth in old age provokes the loss of the rest. After the loss of one tooth, the dentition closes and shifts, the teeth and bite become crooked, and this gradually leads to the loss of the remaining teeth. Lack of teeth affects the appearance, health of the entire oral cavity, food intake, and psychological comfort of a person. This problem needs to be solved - the sooner the better. If teeth have been extracted or fallen out, their deficiency can be filled with dentures or implants.
Let's look at their types:
• Removable denture. Replaces missing teeth, imitating real ones. It can be complete (used when there is a complete absence of teeth on one or both jaws) or partial (used when several teeth are missing). • Prosthesis on implants. Dental implants are inserted into the jawbone to provide greater stability. • A permanent restoration implant solves the problem by using individual crowns or bridges that support natural teeth.