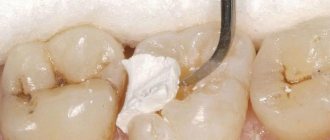
A filling in dentistry is an individually created and installed structure in a patient’s tooth, the purpose of which is to restore the anatomical shape of the tooth and its functional qualities, seal the canals, and also prevent the development of caries or other dental problems.
Fillings are made from filling materials, which are selected by the dentist depending on the disease, structural features of the teeth, the patient’s age and other individual factors. The most common reasons leading to the need for fillings are caries, pulpitis , and tooth trauma.
One of the criteria for choosing a material for making a filling is its purpose. There are temporary fillings that are installed for a short period of time. Their goal is to provide a short-term effect with the help of the components included in the composition. These could be medications, a preparation for depulping, etc. There are no special requirements for such fillings in terms of strength, service life, adhesion (sticking), aesthetics: they will be removed from the cavity for further treatment of the tooth.
The second category of fillings are permanent; they last for several years, becoming practically part of the restored tooth. Materials for them are selected taking into account all criteria, including strength, abrasion resistance, aesthetic properties, and safety for the patient. What types of fillings are there and what influences the choice of material for installing permanent fillings?
Basic requirements for fillings
The purpose of filling is to seal the cavity formed as a result of the pathological process and prevent bacteria from entering the tooth tissue. In order for this problem to be solved without complications, fillings must meet certain criteria [1]:
- safety for the patient - non-toxic, minimal risk of developing an allergic reaction;
- tissue compatibility - for example, amalgam in dental fillings can cause increased sensitivity to food temperature due to irritation of the pulp;
- stability - a high-quality filling does not expand or contract, but fills the cavity evenly and hermetically when working with it;
- strength, ability to withstand loads - when chewing or holding food, the filling should not crumble or crack;
- good adhesion is attachment to the canal walls, adhesion to living tooth tissues;
- aesthetics - even unnoticeable, “distant” fillings should not be noticeable and look contrasting;
- acceptable cost is one of the important criteria for patients, since many, due to the high cost, may refuse treatment for years, worsening the condition of the dental system and health in general.
Rating of filling materials:
| Filling material | Manufacturer | Rated by The Dental Advisor | Year of last assessment |
| Estelite Sigma Quick | Tokuyama Dental (Japan) | 99% | 2021 |
| Herculite Ultra | Kerr (USA) | 98% | 2016 |
| Tetric EvoCeram | Ivoclar Vivadent (Liechtenstein) | 97% | 2017 |
| Harmonize | Kerr (USA) | 96% | 2019 |
| Filtek Supreme Universal Restorative | 3M (USA) | 96% | 2019 |
| Filtek Supreme Plus | 3M (USA) | 96% | 2018 |
| Filtek Supreme Ultra | 3M (USA) | 96% | 2018 |
| Brilliant EverGlow | Coltene (Switzerland) | 96% | 2018 |
| Beautiful II LS | Shofu (Japan) | 96% | 2018 |
| Grandio SO | VOCO (Germany) | 96% | 2012 |
| Gradia | GC (Japan) | 96% | 2007 |
| Omnichroma | Tokuyama Dental (Japan) | 94% | 2020 |
| Beautiful II | Shofu (Japan) | 94% | 2009 |
| Admira Fusion | VOCO (Germany) | 93% | 2019 |
| Venus Pearl | Kulzer (Germany) | 91% | 2021 |
| Premise | Kerr (USA) | 91% | 2005 |
Types of fillings
The variety of fillings in modern dentistry is understandable and justified - it is impossible to create a material that would simultaneously meet all the needs of doctors and their patients: ease of preparation and application; in terms of strength and aesthetics; similarity to “living” tissues and resistance to abrasion. Professional classifications and characteristics of filling materials are extensive and complex, so their review concerns only general aspects.
Amalgams are dental fillings based on compounds of certain metals. Used to restore chewing teeth - molars, premolars.
A material based on mercury with the addition of copper, silver, and tin has been used for a very long time; a large amount of data on its quality and effect on the body has been accumulated. Many dentists refuse to use amalgams in their practice, but fillings made from them, nevertheless, do not lose their relevance. This is due both to the low cost and to the fact that the presence of silver compounds gives a good antimicrobial effect. Another modern option for amalgam-based fillings is copper. They are stronger, more ductile than silver ones, and practically do not change color during use.
Pros: durable, suitable for restoring severely damaged teeth. Inexpensive.
Disadvantages: rather “rigid”, not plastic, especially with a small volume of the cavity to be filled. They require certain skills from the doctor and are not suitable for patients with metal allergies [2].
Cement fillings. Made from dental cement, these types of dental fillings are considered classics in dentistry, especially for children. Dental cement is a mixture based on metal oxides (zinc, silicon, magnesium, aluminum). This is a popular, long-used filling material.
Modern cement mixtures are divided into glass ionomer, made on the basis of silicon quartz, and phosphate (zinc-phosphate), in which the main component is zinc oxide. Depending on the additives and combination of components, cement fillings can be used in pediatric dentistry , in adults - for closing carious cavities, for fixing bridges and crowns.
An important property of cement fillings is the release of fluoride ion, that is, they have a preventive anti-caries effect, which is used in the treatment of baby teeth. The advantages include the low cost of fillings, their density, ability to fill tooth cavities well, and sufficient resistance to abrasion. Cement fillings with silicon ions are characterized by good transparency, stability, durability, and adhesion.
The disadvantages include slightly reduced adhesion, a tendency to crumble and fall out under chewing loads. Due to the presence of metal oxides, allergic reactions may develop. Phosphate fillings are not suitable for teeth in the smile area [3].
Composite materials. Modern types of composite fillings are a mixture of polymers, fibers, and fluid filler. They require curing using light, a chemical reagent, or a combination of both.
Composite materials differ in many parameters and, accordingly, in properties: strength, abrasion, transparency, aesthetics, adhesion, polishability. Depending on them, the doctor selects the necessary material.
There is an opinion among patients that composite fillings are used exclusively for filling teeth in the smile area. However, this is not true: there are composites that change color over time, and there are those that initially differ in appearance from tooth tissue. However, they may have properties that are excellent for teeth with high work loads. The doctor, knowing what types of dental fillings there are and how they behave after installation, makes the optimal choice of the type of material suitable for a specific clinical case.
Pros: Most composite fillings have high strength, good adhesion and cavity filling properties. Separately, it is worth noting the ability of composites to behave like a “native” tooth, that is, to wear away simultaneously with the natural crown, and not to affect the condition of the antagonist tooth (on the opposite jaw).
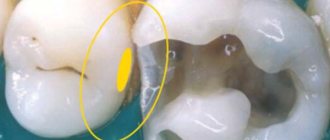
secondary caries often develops on an already cured tooth. There may be some surface roughness, which requires polishing by the doctor and the patient getting used to the new sensations.
Glass ionomer materials and their variants (hybrids): polymer glass ionomers - curing resins are added; compomers - with the addition of methacrylates; ceramic metals - with the addition of glass ceramics; metal-modified glass ionomer materials with the addition of metal powders.
Depending on the additives, such fillings harden either under the influence of light (light curing) or through the action of a self-curing resin. Individual glass ionomers harden with the help of both light and a chemical. They are physically similar to tooth tissues; they can be matched exactly to the natural color and shade of the enamel. In operation, they are fluid, completely cover cavities, and have good adhesion. They have anti-caries activity due to the release of fluoride .
Of the minuses: they do not always provide the required strength and ductility; they can change properties over time. Not all types of filling with glass ionomers can be used to restore a tooth with significant destruction [4].
The summary table [1] presents the approximate ratio of the main indicators of different types of fillings.
Even after a quick acquaintance with what dental fillings are and their types, it becomes clear that the choice of a suitable design is determined by many factors, including the individual characteristics of the patient’s dentition and the physicochemical properties of filling materials.
List of sources
- Ibragimov T. I., Dobrovolsky P. V., Markin V. A., Vikulin A. V. // Materials used to restore the tooth stump during subsequent prosthetics with fixed orthopedic structures. // State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Moscow State Medical and Dental University. Department of Orthopedic Dentistry FPDO. URL: https://www.e-stomatology.ru/stomadent/dentacor/art_1.htm (date of access: 07/19/2020).
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of dental caries. Updated August 2, 2022. URL: https://www.e-stomatology.ru/director/protokols/protokols_30-09-2014/4_karies_8aug2018.doc (access date: 07.19.2020).
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of complete absence of teeth (complete secondary adentia, loss of teeth due to an accident, extraction or localized periodontitis). Approved by Resolution No. 15 of the Council of the Association of Public Associations “Dental Association of Russia” dated September 30, 2014. URL: https://www.e-stomatology.ru/director/protokols/protokols_30-09-2014/2_full_absent.doc (access date: 07.19.2020).
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocols) for the diagnosis of dental pulp disease. Approved by Resolution No. 15 of the Council of the Association of Public Associations “Dental Association of Russia” dated September 30, 2014. Updated August 2, 2018. URL: https://www.e-stomatology.ru/director/protokols/protokols_30-09-2014/1_pulpa_8aug2018.doc (access date: 07.19.2020)
The best filling materials (as of 2022)
In the dental world, the greatest authority in the assessment of restorative materials currently belongs to the American publication The Dental Advisor. For the last 12 years (from 2010 to 2022), the highest award in the “universal composites” category has been awarded to the Japanese filling material Estelite Sigma Quick. Selection criteria: percentage of inorganic filler, amount of shrinkage, correspondence of shades to the natural color of the tooth, ease of use, radiopacity, polishability. A survey of dentists showed that they switch to Estelite more often than to other filling materials. Clinical success of Estelite is 99%.2
Among aesthetic composites in 2015, 2016, 2022, according to the same publication, the filling material from Germany, Venus Pearl, took the highest position. Its clinical effectiveness is 91%.3 In 2021, it received the title of “preferred product”. It can also be used for chewing teeth.
In 2022 and 2022, first place in the category of aesthetic composites was taken by the Harmonize material of the American manufacturer Kerr Restorative.4
Other good quality filling materials should also be mentioned. These include those who received awards in 2016-2019: Omnichroma, Brilliant EverGlow, Admira Fusion, Filtek Supreme Plus and Filtek Supreme Ultra.
How much does the procedure cost?
The exact cost of dental filling is usually announced by the doctor at the initial consultation. The price will depend on the filling material used and the amount of work. Filling canals will cost more than simply installing a filling.
| Type of filling | Price |
| Cement filling | From 900 rubles |
| Glass ionomer filling | From 1,500 rubles |
| Filling made from a light-curing composite of the latest generation | From 3,500 rubles |
| Filling made from a chemocurable composite of the latest generation | From 2,500 rubles |
What to consider when choosing medicinal pads for dentistry
High-quality cushioning materials must meet the following requirements:
- performing insulating functions;
- no effect on the properties of composite or acrylic restoration materials;
- acceleration of natural tissue regeneration;
- ensuring rapid formation of secondary dentin;
- protection of the pulp from negative external influences, the ability to maintain its viability;
- preventing the entry of various microorganisms into the pulp.
also offers a large selection of dental restoration products. In the corresponding section of the catalog you can order splinting tape, articulation spray, saliva ejectors, gum compresses, carpule needles, bib napkins for patients, hemostatic fluid and other products.
Where to go
You can make an appointment with a dentist in Ivanteevka at our Sanident clinic. We provide all types of dental care to patients from Shchelkovo and the urban district of Ivanteevka.
In case of significant damage in the oral cavity, our specialists:
- install pins of various types;
- restore the angle of the tooth;
- carry out complete anatomical restoration of the coronal part and other types of work.
High-quality filling and anesthetic materials are used for treatment.
A consultation with a dentist at the Sanident clinic is your first step to a healthy smile!
Filling of anterior teeth
In the case of front teeth, the aesthetic aspect comes to the fore, so the filling material must have the appropriate properties. Although the front teeth receive better hygiene due to their accessibility, they are also susceptible to caries. Installing a filling on the front teeth is considered a more complex procedure: it is necessary not only to give the filling the desired shape, but also to choose the right color. In most cases, filling of anterior teeth is carried out using compomers, as well as light composite fillings, which harden under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Be that as it may, in case of serious damage, it is impossible to achieve good aesthetics with the help of filling, so you often have to turn to orthopedic solutions.
Teeth filling process
- Initial consultation, taking x-rays.
- Coordination of treatment methods and selection of the type of fillings to be installed.
- Anesthesia before therapeutic intervention (local anesthesia, sedation, in rare cases - general anesthesia).
- Preparation of damaged or caries-affected tooth tissues.
- Grinding and processing the surface of the filling for proper closure.
Filling temporary teeth (baby teeth) follows the same plan, however, in pediatric dentistry, more compatible and safe materials are used.
Why do you need dental filling?
The first experiments with the installation of fillings were carried out before our era. Holes in the teeth were filled with resin and various mixtures. However, the archaic technique of filling teeth brought almost no positive results. Fortunately, today everything has changed dramatically. Modern fillings are successfully used to perform a variety of tasks, in particular for:
- functional filling
- aesthetic dental filling
- filling root canals
- temporary sealing of a damaged tooth