Principle of operation
Human anatomy in the first stages of its formation forced scientists to ask the question: why does a person need this appendage?
Some believed that it was an underdeveloped second language that we inherited from reptiles. Others, on the contrary, were inclined to think that its presence was useless, and in some cases it even interfered. One way or another, with the evolution of medicine, the importance of this pyriform process has been scientifically proven.
The principle of its operation explains all its importance: when food enters the oral cavity and moves further, a spasm of the throat occurs, during which the mechanism of the hyoid muscle is triggered, closing the trachea from food entering them.
In addition, the tongue also takes part in the reverse process. That is, when the regurgitation process occurs, he completely controls it, not allowing food to rise into the oral cavity.
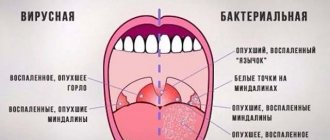
Symptoms of inflammation of the uvula
With uvulitis, the uvula first turns red, then gradually swells and swells.
The disease develops rapidly. In most cases, uvulitis is characterized by a sharp and sudden onset. The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- gagging;
- difficulty swallowing movements;
- pain when swallowing food and saliva;
- difficulty speaking;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- excessive salivation.
Symptoms become more pronounced when a person eats, coughs, or sneezes.
If you experience the symptoms described above, you should immediately go to the doctor. People who have their tonsils removed are most susceptible to uvulitis.
The disease is especially severe in young children. If a child's tongue is swollen, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Functions
The tongue performs such important functions as:
- Separation and redistribution of air and food flow.
- Preventing foreign objects from entering the respiratory tract, causing a spasm of the throat, narrowing its lumen.
- Participates in the formation of the gag reflex and cough.
- It divides the pharynx conditionally into two symmetrical parts; by its presence, one can determine the anatomical state of the tonsils and compare their sizes.
- Actively participates in heating air masses during mouth breathing.
- Helps to give tone to the voice by regulating air flows and their strength.
The many functions of this important organ suggest that it is necessary in the human body.
Causes of enlarged uvula
A healthy tongue is so small that it is not felt at all.
You can see it only by opening your mouth wide in front of the mirror. The Latin name for the small organ is uvula, which is why the disease is called uvulitis.
The enlargement of the palatine process is caused primarily by an inflammatory reaction.
Less commonly, the organ swells due to allergies, trauma, temperature exposure, irritation with chemicals, tumor development and some other negative factors.
Inflammatory pathologies
Not all diseases of the respiratory system are accompanied by an enlargement of the uvula. Typically, the palatine process swells during an intense inflammatory reaction, involving large areas of tissue in the throat and oral cavity.
This pathological phenomenon is observed either with high activity and toxicity of pathogenic microorganisms that provoked the disease, or with a weakened immune system.
Swelling of the uvula is diagnosed in the following inflammatory pathologies:
- acute and chronic tonsillitis;
- rhinitis;
- pharyngitis;
- adenoiditis;
- paratonsillitis;
- retropharyngeal abscess;
- dental infections;
- stomatitis, gingivitis and other inflammatory processes of the oral cavity;
- diphtheria;
- mononucleosis;
- inflammation of the salivary glands;
- tuberculosis, syphilis, immunodeficiency virus and other internal infections.
In what cases does pathology occur?
The tongue, like any other organ, may have pathologies in the process of its formation and functioning. There are several types of the most common pathologies that limit the full functioning of the organ.
Inflammatory process
As a result of microbes, mainly staphylococci and streptococci, getting on the surface of the tonsils, there is a possibility of inflammation on the surface of the uvula. This is mainly observed in advanced stages of the development of the disease, when the inflammatory process takes on an extensive form, penetrating and completely affecting the blood.
A long-term lack of proper treatment leads to the fact that the uvula becomes covered with ulcers and trophic lesions, completely disrupting the blood supply to the organ. In this case, its work is reduced to a minimum, limiting the throat capacity and also causing pain.
Sticking to the tonsils
Situations often occur in which the tongue sticks to the tonsil.
The reason for this may be either an inflammatory process (mainly of a chronic type) or a congenital pathology.
Temporary partial adhesion does not cause much discomfort, limited to the sensation of a lump in the throat and pain when swallowing. In this case, appropriate treatment is prescribed, which includes inhalations, rinsing and irrigation of the mucous membrane.
Adhesion may be temporary but may involve complete fusion of soft tissue. This pathology is quite dangerous, since with a strong cough it can provoke bleeding. The problem can only be solved surgically, so if you discover such a symptom, you should definitely consult a doctor.
No tongue
This diagnosis is congenital and is very rare. It is quite difficult for such people to control the eating process.
Quite often, food particles can enter the nasopharynx, causing significant discomfort. But, there are many ways to eliminate this defect, and get used to living fully in such conditions, following only the doctor’s recommendations regarding the pathology.
Reasons for the tongue sticking to the tonsil
The uvula, like other organs, can malfunction and have pathologies. There are situations when the uvula is stuck to the tonsil. This occurs due to the presence of inflammatory processes or congenital defects in the form of soft tissue fusion.
Inflammation
The penetration of the virus into the blood causes an inflammatory process in the tonsils. If timely, comprehensive treatment is not carried out, then the possibility of infection entering the uvula cannot be ruled out. Trophic lesions and ulcers appear on its surface. This leads to a complete disruption of the blood supply to the organ and the cessation of its proper functioning. Severe pain occurs in the throat, swallowing becomes difficult. The tonsils become loose and more mucus is produced. This causes the uvula to stick to the tonsil. After recovery, this disorder returns to normal on its own.
We also recommend reading Loose tonsils: description of pathology, causes, symptoms
Increasing the size of the tongue
Sometimes the uvula is elongated. Because of this, he constantly touches his tonsils. During coughing and sneezing, free vibrations of the tongue occur. At the same time, he touches the tonsils, tongue and reaches the larynx. This pathology causes a lot of inconvenience and is removed surgically.
Fusion of soft tissues
The most difficult and dangerous situation is when the uvula completely adheres to the tonsil. As a result, soft tissues connect, grow together and form a single organ. New capillaries and vessels appear in it. In this state of affairs, there is a danger of bleeding, which can cause severe coughing. The problem can only be solved surgically, which also presents difficulties in dividing the resulting circulatory system. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, and partial removal of the tonsils is performed.
This pathology occurs more often in people with diseases of the endocrine system, who experience frequent inflammations in the pharynx, and who have tumors on the tonsils.
The situation when the tongue is stuck to the tonsil in a child should definitely worry parents. During the growth and formation of a child's body, disruptions are possible that can cause fusion in the soft tissues. It is necessary to carry out preventive examinations of the child’s oral cavity, to observe the slightest changes in the size of the uvula and tonsils. If adhesion or increase in size is detected, you should consult an otolaryngologist.
Why can the tongue stick to the tonsil?
In fact, there can be a lot of reasons for this process: from anatomy to complex inflammatory processes. So, let's consider each of them, as well as the opportunity to avoid negative consequences.
Inflammation
The inflammatory process that occurs naturally on the tonsils, as a result of the virus entering the blood, makes the tonsils loose.
The amount of mucus produced increases several times. As a result of this, there is a possibility of the tongue sticking to the tonsil, which is eliminated on its own once the person has fully recovered.
Increased tongue size
There are cases when the tongue has an elongated shape, which makes it possible for it to constantly hit the tonsils in any order. When coughing or sharp sneezing, the tongue is able to independently change its location, relying not only on the outer walls of the tonsils, but also “falling” into the larynx.
This pathology causes a lot of discomfort, which can only be removed by surgery.
The uvula interferes
People who are bothered by the uvula may experience snoring, a feeling of a lump in the throat, a feeling of discomfort, difficulty breathing, especially at night, and sometimes nausea due to pressure on the root of the tongue.
The appearance of this symptom is most often associated with either an anatomically low location of the soft palate or an enlargement of the uvula. A number of factors can lead to its occurrence. When snoring, the beating of the tongue against the walls of the pharynx causes mechanical damage, when smoking, tar has a negative chemical effect on its mucous membrane, and infections of the tonsils or allergic reactions lead to severe swelling. All these processes lead to chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane, and against this background, the muscles of the uvula are replaced by connective tissue and lose their tone. As a result, the uvula can no longer be pulled up and hangs down, sometimes even touching the root of the tongue.
Is the uvula getting in the way? Contact our Center and we will help you effectively! Sign up by phone.
Fortunately, the uvula has minimal impact on the lumen of the pharynx and does not make a significant contribution to the occurrence of sleep apnea. At the same time, its changes cause snoring, because the uvula is the most mobile part of the pharynx, which vibrates when air passes and produces a characteristic sound.
Patients with this problem are often recommended surgical treatment, for example, partial or complete removal of the tongue using the radio wave method. As a result, the vibration of the palate decreases and snoring disappears. This is possible if the uvula was the only cause of snoring, but we must remember that one person may have several factors that cause an unpleasant sound during sleep. This may be weight gain, a deviated nasal septum, polyps, adenoids and other changes in the walls and lumen of the pharynx. With this “set” there are often pauses in breathing during sleep - obstructive apnea syndrome.
In this case, soft palate surgery may not be the right choice. This is due to scarring of the walls of the pharynx and narrowing of the airway, which is unacceptable during apnea. It is much more effective to eliminate snoring in combination with apnea CPAP therapy, which prevents vibration and collapse of the pharyngeal walls, protecting your sleep and health at night.
Therefore, before removing the interfering tongue, you should consult a somnologist. If sleep apnea is present, the doctor will diagnose it, determine the severity of the disease, determine the causes and risk factors and, based on all this, recommend the optimal treatment regimen.
Assess yourself for signs of illness. These are shortness of breath at night, cough, sweating during sleep, severe daytime sleepiness, frequent urination, high blood pressure, decreased potency, and heartburn. You can also take an OSA test.
Patients with sleep apnea should begin treatment as quickly as possible. The disease is dangerous, it several times increases the risk of heart attack and stroke, accelerates the development of cardiovascular and other diseases, contributes to the appearance of endocrine disorders, and daytime sleepiness with OSA greatly increases the likelihood of injury or getting into an accident.
Is the uvula getting in the way? Contact our Center and we will help you effectively! Sign up by phone.