| Appointment with a surgeon in Moscow on the same day of treatment | Reception is strictly by appointment, make an appointment by phone: +7 | Prices for services | Reviews about the clinic |
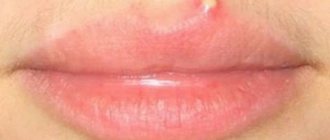
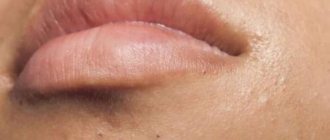
Abscess on the lip
- this is the formation of a purulent process that develops as a result of the penetration of pathogenic pathogens into the tissues of a given area. The starting mechanism for the formation of an abscess is trauma to the mucous membrane of the lips from the oral cavity or damage to the skin on the face. Another reason for the formation of deep abscesses is multiple pustular rashes on the face.
An abscess on the lip is an extremely dangerous condition, since the likelihood of its spreading throughout the cellular spaces is extremely high. Due to the intensive blood supply to the face, the spread of the purulent process to the infraorbital and buccal area occurs extremely quickly.
Make an appointment with a surgeon by phone or by filling out the online form
| Select a clinic | Abdominal ultrasound | Gastroenterologist | Calling a surgeon to your home |
Useful information on the topic:
- Abscess
- Abscess on the stomach
- Abscess of the buttocks
- Opening an abscess
- Abscess treatment
- Causes of abscess
What is an oral abscess?
An oral abscess is an acute inflammatory disease characterized by the formation and accumulation of pus in the tissues of the gums, tongue or cheeks. The abscess is accompanied by local swelling and hardening of soft tissues, severe pain on palpation, fever and general weakness. The disease is diagnosed by a dentist after a visual examination of the tissue, after which immediate surgical intervention is required: opening the abscess, followed by cleaning and taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
Oral abscess is one of the most common complications in the practice of dental surgery. It can be observed in patients of different ages. Untimely treatment can lead to the transition of inflammation to the chronic stage. Against this background, sepsis and phlegmon can develop. That is why, if the slightest symptoms of an abscess occur, you should immediately visit a dentist.
Diagnosis of bartholinitis:
Diagnosing bartholinitis is not particularly difficult. The doctor will be able to make a diagnosis during examination at the first appointment. In the presence of an abscess, swelling and redness of the Bartholin gland is determined; palpation of the formation causes sharp pain. In the chronic form of bartholinitis (in the presence of a Bartholin gland cyst), a tumor-like formation is detected, painless on palpation. In addition to the examination, the following tests must be taken:
- a regular vaginal smear;
- PCR diagnosis of major sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, herpes, human papillomavirus);
- bacteriological culture of vaginal discharge to establish sensitivity to anitibiotics;
- bacteriological examination of pus when an abscess ruptures (or the secretion can be obtained from the excretory duct of the gland by light pressure).
Types of abscess by location
An abscess is classified based on the location of the inflammation. The following types of pathology are distinguished:
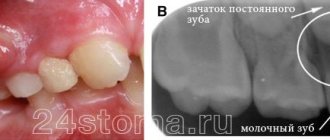
Gum abscess The most common type, inflammation forms near a specific tooth. If left untreated, an abscess can provoke: leakage of pus from the formed fistula, putrid odor from the mouth and intoxication of the body. Abscess of the floor of the mouth Forms under the tongue, which causes severe pain and discomfort during communication or eating. When the abscess spontaneously opens, the infected fluid pours into the oral cavity and can provoke a new outbreak in the pharynx and neck. Abscess of the palate Occurs against the background of uncured or previous periodontitis of the teeth of the upper jaw. In the future, inflammation can spread to the peritonsillar region and other tissues of the palate, leading to osteomyelitis of the palatal plate. Cheek abscess The depth of damage to this area of the mucosa determines the localization of inflammation, which can sit inside the cheek or extend to the outer surface. Such abscesses are extremely dangerous, because the infection can affect nearby facial organs and tissues. Tongue Abscess Obvious signs include a swollen tongue, pain during meals, and difficulty communicating and breathing. This type of abscess, according to doctors, is the most dangerous and requires immediate treatment.
Causes of development of abscess in the oral cavity
An abscess in the oral cavity occurs as a complication of advanced periodontal disease and periodontitis. These diseases are characterized by damage to the teeth and gums with the subsequent formation of pockets in the periodontium. They accumulate pathogenic microorganisms that provoke inflammation. Among other things, an abscess can occur due to infection in a damaged area of soft tissue (trauma, syringe needle, instrument). The cause of the disease is often staphylococcal and streptococcal sore throats, as well as boils on the face.
Inflammation in the oral cavity also appears as a complication after suffering from influenza or ARVI, which weaken the immune system, as a result of which the body is not able to fight infection.
We know how to cure ORAL ABSCESS
In the near future, a medical coordinator will contact you and advise you on the conditions and cost of treatment, select a doctor and make an appointment for you.
| Make an appointment | Or call us +375 29 699-03-03 +375 33 319-03-03 |
Causes and methods of treating boils on the labia
A decrease in the protective functions of the skin provokes the occurrence of various diseases. The most common of them is pyoderma. These are purulent-inflammatory skin lesions caused by staphylococci, less commonly - streptococci, and other bacteria. A frequently diagnosed deep staphyloderma is a boil (abscess, abscess, boil).
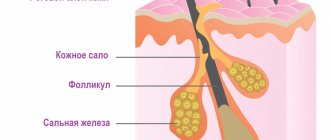
They occur on areas of the skin that have hair, as pathogens penetrate the follicle and infect it. Therefore, a boil is often detected on the labia in women.
A certain number of opportunistic staphylococci always live on the surface of the skin. Most of them are located around the opening of the follicle. They exhibit pathogenic properties only under certain conditions favorable for activation.
Microorganisms penetrate the hair follicle through wounds, cracks, abrasions, and diaper rash. They multiply and cause an inflammatory process with the formation of an infiltrate. Pus appears with dead tissue cells, which fills the follicle. This is the core of the boil.
Inflammation gradually affects adjacent tissues. Its distribution is limited. The infection typically penetrates deep into the skin. After the rod matures, the abscess is opened, the purulent-necrotic contents are released, the inflammation decreases and quickly disappears, and the wound heals. If the development of suppuration is unfavorable, complications may occur.
The degree of exposure to infection depends on the state of the patient’s body’s defenses. The activity of staphylococci is promoted by the influence of internal and external factors.
The internal reasons are as follows:
- primary immunodeficiency (congenital);
- serious illnesses, operations, injuries;
- HIV infection, AIDS;
- oncological diseases;
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands);
- increased amount of male sex hormone (testosterone) in a woman’s body;
- metabolic disorders;
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- decreased immunity from long-term use of certain medications (cytostatics - antitumor drugs, immunosuppressants);
- vitamin deficiency due to unbalanced, poor-quality nutrition.
External etiological factors are:
- violation of the norms and rules of body hygiene, especially the skin and genitals;
- promiscuity;
- prolonged hypothermia or overheating;
- chronic fatigue from physical overload, lack of sleep, lack of rest;
- bad ecology;
- professional activities associated with dust, dirt, lubricating oils, aggressive substances that reduce the protective functions of the skin;
- frequent nervous stress and tension;
- using tight underwear made of synthetic fabrics in which the skin does not breathe;
- poor quality depilation;
- alcoholism, drug addiction, smoking.
Also, a boil on the labia, at the entrance to the vagina, can be a complication of other infectious and inflammatory skin lesions, bartholinitis, sexually transmitted diseases, genital herpes.
Staphylococcal bacteria can enter the hair follicle through the bloodstream from the internal source of infection and cause inflammation. Most often these are diseases of the genital organs, urinary system, and rectum, since they are closely located. But infection is also possible from distant foci.
A boil on the genitals is treated in accordance with the stage of its development:
- inflammatory infiltration;
- formation and maturation of a purulent-necrotic core;
- opening an abscess;
- cleansing and healing of the wound.
Typically, all stages of the disease last 10 - 12 days. With single boils, signs of intoxication rarely appear. There are cases of fever, deterioration of general condition, headache and muscle pain.
The purulent core matures in a few days. Many patients speed up the opening of boils with the help of medications or folk remedies. Some are trying to squeeze him out. Doctors prohibit doing this on your own. Even a mature rod can only be opened correctly by a specialist. Also, boils on the labia minora can easily be confused with pustules of hidradenitis (inflammation of the apocrine glands). A non-professional will not determine the degree of ripening of the boil. It is important to know the rules for performing this medical procedure.
Important! Self-squeezing often leads to the development of furunculosis, phlegmon, abscess, carbuncle, inflammation of blood and lymphatic vessels, and sepsis. Complications of abscesses on the labia minora are especially dangerous.
After studying the anamnesis, the doctor will provide recommendations for eliminating external provoking factors that contribute to the occurrence of boils. He will prescribe proper nutrition, rich in vitamins and microelements. Internal medicine patients are referred for consultation to appropriate specialists.
It is recommended to limit spicy, salty, smoked and pickled foods as much as possible in your diet. It is advisable to avoid fatty, fried foods, processed foods, and canned foods. It is important to significantly reduce the amount of food containing carbohydrates, which stimulate the development and proliferation of staphylococcal infections. At the same time, the content of protein foods, vegetables, fruits, and juices is increased. It is advisable to eat only low-fat varieties of meat and fish. The diet must be balanced, and it is also necessary to follow a routine.
Starting from the first stage of boil development, drug treatment is used:
- The affected surface is disinfected with antiseptics to prevent the spread of infection. This can be 3% hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine, Fukortsin. This is done with hands thoroughly washed with soap and treated with alcohol using a sterile swab or napkin.
- The doctor may prescribe penicillin, tetracycline or macrolide antibiotics (Azithromycin, Erythromycin) for oral administration.
- They accelerate the maturation and separation of the purulent core with pulling ointments with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects - Sintomycin, Ichthyol.
- After opening the abscess on the labia majora and rejecting the rod, the wound is carefully treated with hydrogen peroxide and a sterile cloth soaked in saline is applied to clean it.
- Healing ointments (Zinc, Vishnevsky) and antibacterial with anti-inflammatory properties (Levomekol, Bepanten, Tetracycline) are used. They are applied with clean hands onto a sterile napkin and applied to the treated surface. A clean wound becomes overgrown with granulation tissue and scars.
- Complexes containing vitamins, microelements and minerals that strengthen the immune system are also prescribed.
The doctor makes the decision to open a boil on the genitals surgically in case of severe or complicated development of the disease. It is performed in a medical facility. Antibiotics are prescribed: Levofloxacin, Avelox, Vancomycin and others.
At the first stage of development of the abscess and at the healing stage, physiotherapy (electrophoresis, UHF, irradiation with infrared rays, Darsonval treatment) is effective. It helps cope with inflammation and speed up healing.
Symptoms
The abscess is characterized by rapid development. At first, the patient may be bothered only by minor attacks of pain, similar to the sensations that arise during caries or periodontitis. Subsequently, the pain is localized in one place and gradually increases. In a specific place there is swelling, sometimes a new formation on the gum, sometimes reaching the size of a walnut. If the inflammation is localized closer to the outer surface, then swelling and redness can be observed with the naked eye. If you notice the first symptoms, we recommend that you consult a dentist.
An abscess of the tongue is characterized by an increase in the organ's volume, difficulty swallowing, chewing, and even suffocation. Any abscess is accompanied by fever, deterioration and general weakness, insomnia, and loss of appetite. The progression of the disease leads to a breakthrough of the abscess, which is manifested in a decrease in temperature, a decrease in swelling and an improvement in overall well-being. However, there is no reason to stop treatment, since inflammation can continue and develop into a chronic form. This can lead to tooth loss, sepsis and phlegmon.
Symptoms
There are several different types of lip inflammation, each of which has individual signs and symptoms. If we take the general picture of cheilitis, the symptoms characteristic of all types are as follows:
- Most often, patients complain of dryness, burning and flaking of the skin of the lips;
- with some types of cheilitis, small painful blisters, ulcers and cracks may appear;
- the standard location of inflammation is limited to the mucous membrane and red border of the lips, but in some cases it can spread to surrounding tissues;
- with systemic diseases, painful plaques and purulent discharge may appear on the lips.
In the case of allergic reactions, the inflammatory process can last for several months in a row, however, if the inflammation does not go away for more than six months, there is a reason to get tested and look for the cause of cheilitis in other diseases. The risk of the inflammatory process transforming into a malignant tumor cannot be excluded.
Treatment of oral abscess
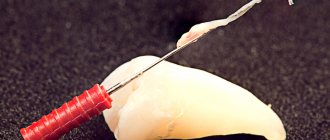
Treatment of an abscess requires surgery. In order to eliminate the source of infection and stop the spread of inflammation, the dental surgeon step by step:
- opens an abscess;
- drains the cavity;
- cleans the pocket;
- Rarely applies stitches if the size of the incision is large.
After removal of the pus, the patient’s well-being improves, and facial geometry is restored. Taking antibiotics, antihistamines, immunostimulants and a vitamin complex significantly speeds up the healing process. Sometimes the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures (UHF therapy and fluctuarization).
For some time, the patient needs to exclude solid foods from the diet and adhere to healthy eating rules.
Prognosis and prevention of oral abscess
The success of treating oral abscesses depends on at what stage of the disease the patient seeks help and how strong the body’s defense mechanism is. With timely treatment, the prognosis for eliminating inflammation is quite favorable. In the absence of complications, strong immunity and a high-quality opening of the lesion, an oral abscess can be cured in a couple of weeks.
Prevention of the disease consists of following the following recommendations:
- regular teeth cleaning and professional oral hygiene at least once every six months;
- minimizing the risk of injury to the mucous membrane;
- timely treatment of caries and periodontal diseases;
- visiting a dentist for a preventive examination once every 6 months.