The reason for the appearance of plaque on the tongue
A large amount of plaque on the tongue, a change in its color, as well as the appearance of such unpleasant symptoms as bad breath, unpleasant taste and dry mouth become causes for concern.
Why does plaque form on the tongue in children?
Most often, parents notice a coating on the child’s tongue in the morning - immediately after sleep. At night, the child's body produces a limited amount of saliva, the cheeks and tongue are not cleaned, and bacteria multiply rapidly in humid conditions. With the partial destruction of leukocytes, which appear to suppress bacteria, the tongue becomes covered with a whitish film.
Plaque on the tongue of an infant or a child 1.5 years old and older should not cause concern if:
- lies in a thin layer;
- does not lead to a change in the overall color of the tongue;
- can be easily cleaned with a brush without leaving any scarlet spots underneath;
- not accompanied by alarming symptoms (high fever, nausea, vomiting, etc.)
In infants, plaque forms in response to regurgitation or consumption of dairy products. If the baby has no signs of inflammation in the mouth, this condition is considered normal.
However, plaque on the tongue in children of different ages often forms as a result of the development or after suffering from certain diseases. Most often the cause is a common cold. Children with rhinitis or adenoiditis have impaired nasal passage; they try to breathe through their mouth. The mucous membrane dries out and plaque forms on it.
Causes of plaque on the tongue in adults
If we are talking about plaque, as a result of the vital activity of microorganisms that make up the natural microflora of the oral cavity, an adult observes the following signs:
- the layers have a white-pink tint;
- plaque is visualized in the morning, mainly at the back wall of the receptor organ (at the base, root of the tongue);
- the film is easily removed and does not form again.
Most often, the cause of the appearance of deposits is the banal consumption of coloring foods (coffee, tea, chocolate, carrots, beets, etc.). The second most common cause of the phenomenon is smoking. Often this symptom accompanies certain therapeutic courses, for example, taking antibiotics.
A change in the color of plaque, its active formation, which is accompanied by other unpleasant signs, indicate the pathological nature of the phenomenon. More often, the cause is gastrointestinal pathologies, for example, gastritis, which occurs against the background of stomach pain and heartburn.
Let's talk in more detail about what diseases can provoke excessive plaque formation on the tongue in adults and children.
Healthy tongue color
A healthy tongue is distinguished by a delicate pink color, and taste buds are evenly distributed over its entire area. The middle fold has clearly defined edges.
Due to the intake of certain foods, drugs and medicines, and all kinds of drinks, the color of the tongue can change. Some give such a reaction due to the specific substances contained in the composition, others simply contain a lot of coloring pigments, which color the tongue and the coating on it in the corresponding color.
There is also a slight dependence of the color of the tongue on the time of year. For example, in summer the tongue becomes redder, and in autumn and winter it becomes slightly yellow.
What diseases can plaque indicate?
Among the pathologies that provoke the formation of whitish deposits on the tongue: infections, gastrointestinal diseases, immune pathologies and others. Below are the most likely ones:
- colds, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, flu, sore throat. The formation of plaque on the tongue indicates an uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms;
- glossitis or “geographic tongue”. Inflammation of the tongue caused by injury and of an infectious nature. Red spots form on the tongue, which often go away on their own.
- gastritis, gastric ulcer, enterocolitis. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa, in which a grayish-white coating appears on the tongue;
- candidiasis or thrush. The plaque caused by a fungal infection is localized under the tongue, it is uneven and appears in spots;
- chlamydia. Failure of the immune system, which leads to the formation of a thick sticky coating not only on the tongue, but also on the palate;
- bronchitis and pneumonia. Diseases of the upper respiratory tract stimulate the formation of a whitish film along the edges of the receptor organ;
- first stages of cancer. Whitish lesions lack clear boundaries. They are formed in all forms of cancer;
- lichen planus. Small grayish-white nodules appear in the patient’s mouth, which form a layer similar to lace;
- jaundice and liver disease. The color of the plaque is predominantly yellow; when bile stagnates, it acquires a greenish tint;
- diabetes. The film appears in response to a deficiency of saliva in the mouth, the disease is accompanied by the development of candidiasis in the oral cavity;
- chronic constipation. The film is thick, dense, with a repulsive odor;
- acute and chronic radiation sickness. The tongue swells, becomes covered with a thick film, cracks, hemorrhage and necrosis appear in the root area of the organ.
As you can see, plaque on the tongue can be a symptom of both minor health problems and serious pathologies that require an immediate comprehensive approach.
Principles of diagnosis by language
Determining diseases by the condition of the tongue is an undervalued technique in European diagnostics, but is widely used in Asian countries, especially in traditional Chinese medicine. According to clinical observations, there is a close connection between damage to internal organs and different parts of the mucous membrane.
When carrying out diagnostics, the color, density and smell of plaque are taken into account.
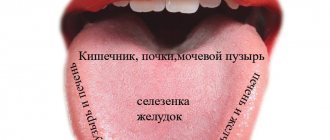
To accurately determine the affected organs, it is necessary to understand which parts of the mucous membrane react to which organs. In accordance with the classic map of interconnected departments, the following matches are distinguished:
- the tip and anterior edge of the tongue react to changes in the functioning of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- a longitudinal groove indicates problems in the gastrointestinal tract;
- the lateral surfaces are connected with the organs of the hepatobiliary and urinary systems;
- the basal transverse line coincides with the spine and other parts of the musculoskeletal system.
- the location of the projections of the internal organs on the tongue coincides with the schematic placement of the internal organs.
Do not forget that the appearance of plaque and ulceration of the mucous membrane in any part of the tongue indicates the presence of pathological processes in interconnected organs.
Plaque and dental problems
The topic of plaque and dental problems deserves special attention. Any dental disease occurs against the background of active activity of pathogenic microorganisms. Obviously, this factor contributes to the formation of pathological plaque in the mouth.
Plaque on the tongue, cheeks and palate can appear as a result of a banal failure to comply with the rules of oral hygiene, or the picture can be much more serious. In particular, such a dangerous disease as Vincent's stomatitis manifests itself by the formation of a whitish film.
The conclusion is obvious: if the amount of plaque increases or its structure changes, you must immediately contact your dentist to undergo a detailed diagnosis and, by starting timely treatment, prevent undesirable consequences.
Correct tongue position - why is it important?
For the correct formation of a bite and coherent speech, the correct functioning of all elements of the dental system is important.
The position of the tongue also plays an important role. Under normal conditions, the tongue should exert slight pressure on the upper row of teeth, which contributes to the formation of a correct bite in childhood. The physiological position of the tongue has the following positive effects:
- The development of the upper jaw is stimulated, both in length and width.
- Blood microcirculation in the nasopharynx area improves. This helps strengthen local immunity, which is important, in particular, for protection against respiratory infections.
- Balance improves, which is a prerequisite for the formation of correct posture.
- The normal tone of the facial muscles is maintained in a calm state.
Types of plaque
When assessing the nature of the phenomenon, it is worth taking into account not only the amount of deposits, but also their color and structure. Below we will tell you what the color of the plaque says:
- white. A thin white mucous coating after night is not a deviation. An increase in the density of the membrane indicates chronic constipation. A cheesy light coating is a symptom of Candida infection.
- red. Indicates the development of an infection, such as a sore throat. A dark red tint will indicate problems with the kidneys; the plaque acquires this color when the body is poisoned by various poisons;
- yellow. A bright color indicates the development of hepatitis A. If there are problems with the gallbladder, in addition to the yellow film, cracks appear on the tongue;
- green. Visualized during inflammation of the organ - glossitis. Most often, the provoking factor is a fungal infection (yeast glossitis);
- brown. This purulent tint is associated with liver intoxication (alcohol addiction). However, coffee, tea, and chocolate can also give brown color to deposits;
- grey. A characteristic symptom of pathologies of the stomach and duodenum, and also appears when the immune system is damaged. The same diseases also affect tooth enamel (it also takes on a dark shade);
- bluish. This is a symptom of an experienced smoker. The root of the tongue becomes blue and becomes slightly thicker;
- orange. A rare phenomenon that indicates the release of acid from the stomach into the oral cavity. However, this condition should not be confused with staining the surface of the organ with food coloring;
- black. A dangerous sign indicating a strong sludge in the body or a specific disease, for example, Crohn's disease. Black spots on the tongue are visualized due to metal intoxication.
A spotted coating on the tongue (when the surface of the organ is covered with uneven spots) appears in people of different age categories. Most often, this condition does not pose any danger and goes away on its own. Today, the reason for this phenomenon has not been fully identified. Each clinical case is individual - the cause of the spots can be either candidal stomatitis and allergies, or the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Types of tongue malposition
There are 7 options for tongue position. The first one is correct, and all the others are variants of the incorrect location of the organ. Let's take a closer look at them.
Option 1 – physiologically correct tongue position
The palatal position of the tongue is considered correct1. The tongue at rest is pressed against the palate and is located behind the upper incisors. With this arrangement of the organ, a physiologically correct bite is initially formed (unless, of course, there are other reasons and factors for the development of pathological occlusion). In this case, for the formation of a correct bite, the general muscle tone of the face, the work of the temporomandibular joint and other elements of the dental system are also important.
Option 2 – loose fit to the palate
In this case, the tongue rests approximately 0.5 cm above the lingual tubercles. Also, the tongue may drop down by about 0.5-0.8 cm. Under such circumstances, the organ is not pressed tightly against the palate.
When swallowing in this case, the tongue will rest against the upper or lower incisors. This leads to tension in the muscles of the lower lip, which in turn tilts and crowds the lower teeth.
Option 3 - the tongue passes between the molars
With this arrangement, the tongue covers the lingual cusps. The tone of the lower lip is impaired, which leads to the formation of a deep bite. In this case, the lower teeth often crowd together due to lack of space.
It is noteworthy that over time, the severity of a deep bite may increase, and the lower jaw may shift to a posterior position. In this case, the person complains of limited mobility of the lower jaw (in particular, when opening the mouth).
Option 4 – the tongue covers the buccal and lingual cusps
If the tongue covers the buccal and lingual cusps of the lower molars and/or premolars, then in childhood this leads to problems with teething. The tongue puts pressure on the buds of baby teeth, preventing the latter from erupting. In the future, this may lead to disruption of the formation of the roots of permanent teeth. There is even a risk of tooth root resorption, which leads to adentia (tooth loss).
With the 4th variant of the tongue position, the muscle tone of the lips decreases. In such a situation, an inadequate load is placed on the temporomandibular joint, which leads to disruption of its function.
Option 5 – low tongue position
When the tongue is low, it becomes stiff. Often the tip and middle part of the tongue have increased tone. For this reason, such a language visually appears to be overly large. However, it is not. The tongue is of normal size, but the volumetric effect creates tone.
The low position of the tongue has a significant impact on the dental system, in particular the lower jaw. For this reason, excessive development of the lower jaw (macrognathia) with the formation of a mesial bite is possible. There is also a danger of underdevelopment of the upper jaw, which also forms a mesial bite.
When the jaw moves forward, the functioning of the jaw joints is also disrupted. This leads to characteristic clicking and pain when trying to open the mouth.
Option 6 – tongue between the upper and lower incisors
Often, with this position of the tongue, the orbital muscles of the mouth are weakened and the masticatory tone of the muscles is reduced. This is another option for the “low” location of the organ. Most often, in the 6th position, the tongue is not active enough, which leads to the development of speech defects. The distortion of whistling sounds is especially noticeable.
If with this arrangement the tone of the masticatory muscles is also disturbed, then lengthening of the face is possible, as well as discomfort and pain in the jaw joints. This is due to a violation of the distribution of loads on the facial muscles.
Option 7 – lateral position
Most often, the reason for this position of the tongue is bad habits (thumb sucking, biting nails, pens, etc.). Impaired innervation is another reason for lateral displacement of the tongue.
When the tongue is in a lateral position, swallowing is impaired. The tongue will put pressure on the side of the dental system where it deviates. This leads to uneven development of the jaws.
How to get rid of plaque and prevent it? TOP methods
Before you start getting rid of plaque, you should determine the exact cause of the phenomenon. White-yellow plaque can be eliminated using regular hygiene procedures:
- proper brushing of teeth and tongue. After brushing the surface of the teeth, you should make several longitudinal movements from the base of the tongue to the end to clean the receptor organ from the plaque that has formed. This should be done not only in the morning, but also in the evening to eliminate food residues;
- use of antibacterial rinses and sprays. It is worth using the mentioned products between meals: they allow you not only to freshen your breath, but also to eliminate some of the bacteria. Such rinses and sprays are especially relevant when it is not possible to perform full oral hygiene;
- use of an irrigator. The device allows you to maintain healthy microflora in the mouth due to its ability to remove food debris and deposits in hard-to-reach places, including periodontal pockets. An indispensable device when wearing braces, as well as for patients with crowns and implants;
- professional cleaning by specialists. Regular hygiene and prevention in the dental clinic will avoid the development of oral diseases and prevent unwanted accumulation of microorganisms in the oral cavity. Hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity in the dentist’s office will not only help get rid of plaque on the tongue, but will also save you from dental plaque, whitening your smile by 1-2 shades.
A separate group of methods for getting rid of whitish plaque includes traditional medicine. Among the most effective of them:
- rinsing with infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants. Herbs such as mint, sage, chamomile, and eucalyptus have performed well in this matter. These plants can be bought at the pharmacy (in dry form). Rinsing with herbal decoctions will get rid of the film and prevent gum disease;
- rinsing with vegetable oil. You should prepare 1-2 tbsp. l. vegetable oil and rinse your mouth with it for several minutes. The effect will be similar to the action of an absorbent, which absorbs all harmful components. After rinsing, the mouth should be rinsed with running water;
- resorption and chewing of propolis pieces. This natural disinfectant will reduce the number of bacteria in your mouth;
- rinsing with a weak solution of salt and soda. Such compositions help cleanse the oral cavity of food debris after eating. Rinsing takes 2-3 minutes.
If there is a suspicion that pathology is the cause of plaque formation, it is necessary to begin comprehensive treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating the provoking factor. The above methods of dealing with an unpleasant phenomenon are used as supportive ones.
How to maintain tongue hygiene?
Just like your teeth, you need to take care of your tongue. It is enough to carry out procedures at the beginning and end of the day. A toothbrush is brushed along the tongue from root to tip. In this process, the main thing is not to overdo it.
There are several tools available for cleaning your tongue:
- Double-sided toothbrush with textured tongue coating.
- Spoon-shaped tongue cleaner. Alternatively, a simple teaspoon.
- Tongue scraper in the form of a plastic spatula.
Brushing your teeth without brushing your tongue leaves a large number of bacteria in your mouth for the development of pathological diseases.
Proper cleaning of the tongue
Previously, silver spoons with three slits in the form of three months and a special edge, taking into account all the anatomical features of the tongue, were very popular in Russia. Nowadays, plastic products are popular and need to be updated no less often than toothbrushes.
From the following articles you will learn about diagnostics:
- Trichomoniasis in women
- Pathologies of the placenta during pregnancy
- Morris syndrome
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Gilbert's syndrome