According to statistics, by the age of six, approximately 70% of children have dental caries. A large percentage of young children are susceptible to developing so-called bottle caries. What kind of disease is this, why it occurs and whether it can be cured, we will tell you in the article.
In this article
- The mechanism of caries development in children
- What is bottle caries in children?
- How to treat bottle caries?
- How bottle caries is treated using remineralization method
- Treatment of bottle caries using fluoridation
- Treatment of bottle caries using the ICON method
- Is silver plating safe for children?
- Ozone therapy treatment
- What to do if there is a hole in your tooth?
- What should be done to prevent bottle caries?
The mechanism of caries development in children
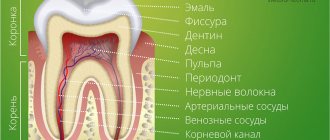
Caries is a slowly occurring pathological process in which the destruction of hard dental tissues occurs. It can affect both baby and permanent teeth and occurs in adults and children of any age.
It is known that caries develops under the influence of several factors - both external and internal. The main cause of carious lesions is the activity of cariogenic bacteria. They coat the teeth with a biofilm we call plaque. Bacteria feed on carbohydrates that enter our body with food. They ferment sugars and convert them into acids, which have a negative effect on superficial and deep dental tissues. If plaque is not removed from the surface of the enamel in time, the acids will destroy its structure and sooner or later penetrate into the dentin - the bone tissue under the enamel. Thus, it is organic acid, a product of bacterial activity, that has a damaging effect on teeth.
There are factors that increase the risk of developing caries. These include:
- a large amount of carbohydrate and sweet foods in the diet;
- multiple snacks, keeping food in the mouth for long periods of time (for example, sucking on lollipops, bottle-feeding babies at night);
- infrequent or improper brushing of teeth, which does not effectively remove plaque;
- a diet lacking healthy foods rich in calcium and fluoride.
Causes of the disease
The main reasons for the development of bottle caries are the same as those characteristic of other types of carious lesions: damage and further destruction of dental tissue under the influence of acids produced by bacteria multiplying in the oral cavity. The food for these bacteria is mainly carbohydrate residues that settle on the teeth after feeding. But the reasons for the presence of such food debris in the mouth and the inability of the body to suppress the activity of bacteria are secondary and have different effects on the risk of developing bottle caries.
<
On a note
As a rule, bottle caries occurs in children with reduced immunity and various concomitant pathologies, but there are frequent cases of its development in healthy children due to the defective tissue structure of the enamel and other factors that cause caries. These include mainly incorrect feeding regimen and lack of proper oral hygiene after it. Remains of food after feeding (especially at night) with weak salivation and (or) insufficient mineral content of saliva allow the microorganisms of plaque that forms on the teeth to quickly lead to tooth destruction.
Most dentists believe that the main reason for the development of bottle caries is night feeding of the child. And it doesn’t matter whether the baby eats from a bottle or suckles - lactose (milk sugar) is found in both formula and breast milk, and it is also an ideal substrate for the development of bacteria.
But this reason in itself does not always lead to the onset of the disease: in many cases, children who are fed at night do not develop caries. And, on the contrary, in some young patients, signs of bottle caries appear even with a clear feeding schedule with the last meal before bed and brushing the teeth after it.
<
Therefore, other reasons also play an important role in the occurrence of bottle caries:
- Weakened immunity and insufficient bactericidal properties of the child’s saliva: in normal cases, the child’s body’s own defenses should be sufficient to suppress the activity of bacteria in the mouth. In children who (or who) do not brush their teeth, eat at night and do not have caries, it is saliva that protects teeth from decay. The opposite statement is also true: if the ability of saliva to resist bacteria is less pronounced, then teeth can be affected even with high-quality oral hygiene. At the same time, other diseases of the body can affect the decrease in the bactericidal qualities of saliva - for example, diabetes, influenza, and intestinal infection. In any case, the child can be weaned from night feedings and teeth can be properly brushed. In such conditions, the development of caries will be significantly slowed down, and attentive parents will always have time to show their child to the dentist when the tooth can still be saved and left unharmed.
- Mistakes in planning your baby's diet. Sweets, sweet cereals and juices, confectionery and flour products, the remains of which linger on the teeth, most contribute to the reproduction and prosperity of microflora in the mouth. The condition of teeth is also affected by a lack of rough food: carrots, apples, which, when chewed, erase plaque. There may also be a lack of foods high in calcium and phosphorus in the diet - fish, natural dairy products.
- A regional factor may also have an effect: if there is a lack of fluoride in drinking water, tooth enamel is weakened and more quickly damaged by aggressive acids.
<
<
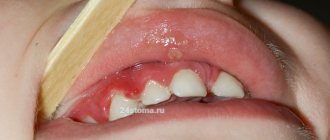
It all starts with ordinary zones of focal demineralization or spots in the cervical area, and then the destruction that has begun can turn into a severe form of cervical caries - circular caries, up to the breaking off of part or the entire tooth crown. At the same time, teeth may not hurt for a long time due to the protective ability of them to form replacement dentin, which saves from accidental opening of the pulp (“nerve”).
If treatment is not started in time, the consequences of bottle caries can be very serious. No one knows exactly on what day the pain from decaying teeth will begin, but it is at the most inopportune moment that the baby will refuse to eat normally and even sleep.
<
Multiple extractions of primary teeth result in malocclusion. Carious infection, inflammation, premature removal of baby teeth - all this directly or indirectly affects the normal development and eruption of permanent teeth. In order to prevent such terrible consequences, it is necessary to promptly treat caries even on baby teeth, without justifying inaction by saying that they will soon fall out.
<
In general, proper oral hygiene is always important - a bottle of milk before bed will be less harmful to the teeth if the child's teeth are brushed after feeding.
Heredity is also considered to be the cause of bottle caries, but in the vast majority of cases, parents use heredity to justify their laziness and reluctance to brush their child’s teeth or teach him to do it himself. Remember: even if you have a genetic predisposition, proper oral hygiene and a healthy diet will significantly reduce the likelihood of developing caries!
<
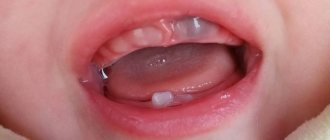
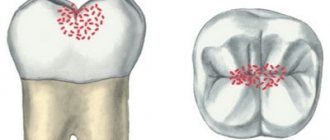
At the earliest stages, bottle caries can appear in the form of light matte spots (the stage of a white or chalky spot), which over time take on the appearance of roughness on the enamel, gradually deepening and darkening.
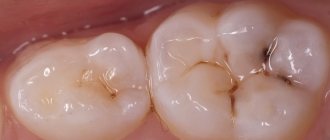
Next in the photo is a medium-sized caries that has affected several teeth at once. Such simultaneous damage is a characteristic diagnostic sign of bottle caries:
<
As a rule, bottle caries first affects the front upper four teeth of a child. The carious process often begins in the gingival zone, quickly covers the perimeter of the entire tooth above the gum and penetrates into the deep layers of enamel. Damage to the gingival zone of the tooth is a characteristic feature of bottle caries.
Generally speaking, deep bottle caries indicates an irresponsible attitude of parents towards the child’s health: it is easy to notice the pathology in the early stages, and only parents who pay attention to the child’s teeth only when he constantly complains can bring a child with teeth half eaten away by caries to the clinic.
<
Important!
Bottle caries can develop not only on several front teeth at once, but also on one single tooth and on molars. Therefore, the child should regularly and carefully examine all of his teeth, not just the front ones.
What is bottle caries in children?
Childhood caries can occur for various reasons. One of the most common forms of the disease does not occur in adults, but is characteristic of young children. This is the so-called baby bottle caries. Another name is circular. What are its features and reasons?
The main cause of bottle caries can be understood from the name - long-term feeding of a child from a baby bottle with a pacifier. The disease is also typical for children who have been breastfed for a long time.
The essence of the problem is as follows. When a baby is given a bottle and breastfeeding before bedtime or nap time, baby's teeth are left with large amounts of sweet carbohydrates, a food source for bacteria. At the same time, at night the amount of saliva in the mouth decreases, which has a bactericidal effect and could at least partially protect the teeth. It turns out that all night or several hours during the day, while the child is sleeping, there are food remains in the oral cavity, which microbes happily convert into acid. At the same time, the enamel of children's teeth is not yet as strong as that of adults. Therefore, caries begins and spreads much faster. In just a few months or even weeks, it can go from early stage staining to deep dentin damage.
The peculiarity of bottle caries is that most often it affects the front incisors: whitish spots appear on them in the contact areas and near the gums. This is due to the peculiarities of gripping a bottle or the mother's breast when feeding. The circular arrangement of bottle dental caries on the front teeth, in areas of contact with food, gave it the name circular. This type of caries is often diagnosed in a one-year-old child who continues to eat from a bottle, although he can receive complementary foods from a spoon. In addition to babies of the first year of life, children's bottle caries can appear in two- and three-year-olds, who are allowed to eat sweets and drink juices more than three times a day. The mechanism of dental damage is the same as with bottle feeding.
Prevention at home
Preventive measures at home necessarily include:
- Proper oral care for your child.
It must begin from the moment the first tooth erupts. At the initial stages, until the child has his first chewing teeth, cleaning is carried out using gauze wrapped around a finger, a special fingertip with rubber bristles, or special wipes soaked in xylitol. Xylitol reduces the activity of cariogenic infections, and in particular Str. mutans.
- Transfer the child to daytime feeding only.
At night, instead of a bottle of formula, sweet water or juice, give regular or bottled water. It is also important to teach your child to drink from a cup.
- Nutrition correction is being carried out.
With the mandatory inclusion of fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet and a decrease in the proportion of sugar-containing products. Revising the snack menu: give preference to cheese, nuts, and fresh vegetables.
- It is advisable to give your child fermented milk products and yoghurts daily.
This will populate the oral cavity with beneficial microorganisms and reduce the percentage of cariogenic bacteria.
- Preventing the transmission of cariogenic bacteria from caregivers.
To do this, they strictly ensure that adults do not lick the pacifier, do not eat with children's cutlery, or drink from the child's cup. Also an important part of the prevention of caries in a child is the treatment of carious lesions in parents and in particular the mother, as the person most often in contact with the baby. This is explained by the fact that caries pathogens can be transmitted through kissing on the lips.
Toothpaste
Brushing your teeth (after the appearance of the first chewing tooth) should be done with toothpastes twice a day. At the initial stages, toothpaste without fluoride is used, and from the moment the child learns to spit, you can switch to fluoride-containing products. Until the age of 3, it is enough for there to be trace amounts of paste on the brush; later (from 4 years), the amount is increased to the size of a grain of rice, and then to a pea.
For children under 2 years of age, pastes containing 500 ppm of fluoride are recommended. With a high risk of developing caries, as well as for children aged 2-6 years, the concentration of fluoride in toothpaste can be increased to 900-1100 ppm. Children over 6 years old are allowed to use toothpaste with a fluoride content of about 1400-1500 ppm.
Dental foam
Dental foams are intended for remineralization at home. For this purpose, foams are used, which contain organic calcium, fluorine and lactic enzymes. The easiest way to use them is to moisten gauze wrapped around your finger with the composition and wipe your teeth with it up to three times a day. Foams are safe and therefore suitable for very young children.
Tooth gel
An anti-caries gel can be used as a home remedy, which can seal the dentinal tubules, thereby preventing infection from getting deeper into the tooth. The gel is applied to the teeth for 1 minute after basic cleaning of the oral cavity. Then they rinse the spaces between the teeth, after which the gel is washed off. The composition cannot be swallowed, so the gel can be used by children over 3 years of age. After the procedure, it is not recommended to eat for 2-3 hours.
There are also dental gels on sale that contain substances that protect teeth from caries: calcium, fluorine, phosphorus, potassium, silicon. Remineralization occurs due to the transfer of substances from the gel to saliva, and then to dental tissue. Such gels contain from 0.1% to 1.5% fluoride, which allows them to be used for medicinal purposes when caries is detected at the spot stage. They are used once a day, preferably before bed: the gel is rubbed into the teeth with a toothbrush for 1-2 minutes. As a rule, baby gels have a pleasant taste and smell.
Only a pediatric dentist can tell which dental gel is right for a child after examining the mouth and talking with the parents. In this case, the age of the child must be taken into account.
How to treat bottle caries?
Treatment of children with bottle caries is carried out using different methods, depending on the age of the child, the stage of development of the disease, and the technical capabilities of the dental clinic. There are two main approaches to treatment - conservative and surgical. The first involves treatment without preparation, drilling the tooth with a drill, or installing a filling. These are non-invasive and completely painless methods. But, unfortunately, they are effective only in the early stages.
Much more often it is necessary to carry out surgical treatment, in which the tooth is opened and a filling is installed. This is due to the fact that in most cases, bottle caries is diagnosed too late - when the tooth already has cavities and preparation cannot be done without.
Features of treatment in children at different ages
With bottle caries in children, treatment is required in any case - regardless of the degree of damage to the teeth and the age of the little patient. The most effective methods of therapy are Icon enamel infiltration, ozone treatment and classic filling. In addition, silver plating and deep fluoridation are used in pediatric dentistry.
Silvering is an outdated method that consists of alternately treating tooth tissue with special solutions. Covering carious cavities with silver nitrate leads to stopping the pathological process, but only at the initial stages of the disease. In private dental practice, doctors try not to use silver plating, as it causes severe darkening of tooth enamel and deterioration of its strength.
Ozone therapy - treatment of tooth tissue with ozone-containing preparations, such as Prozone, Ozone UM-80, Healzone, helps destroy almost all cariogenic bacteria and stop the worsening of bottle caries in its early stages. When treated with ozone, the child does not experience discomfort or pain; the session lasts up to 10 minutes.
The Icon infiltration method of dental treatment is a modern and effective way to stop bottle caries if it is detected before the formation of a surface defect. The enamel is impregnated with a special preparation, which replenishes the missing microelements of the tissue, and then polymerizes under the light of a lamp. This treatment does not require anesthesia or the use of a drill.
Dental filling is the most common method of therapy, especially in cases where bottle caries in children did not receive treatment at the initial stages of the disease. Pediatric dentists use materials that are safe for children and non-toxic. For deep carious cavities, a calcium-containing medicine is also placed under the filling, which strengthens the natural tissues of the tooth.
Despite the highly aesthetic nature of light-composite restorations, its use in the treatment of temporary teeth is still not recommended due to possible toxic effects. Preference is given to glass ionomer fillings, which, even years after installation, continue to release fluoride into the enamel and dentin, and are also erased simultaneously with children's teeth.
Effective pain relief ensures painless, comfortable treatment and reduces the likelihood of injury. However, multiple cavities with bottle caries are difficult to cure for a small child. In order to safely treat all carious cavities in one visit and the child leaves the clinic with white and beautiful teeth, it is recommended to use anesthesia.
This is also enshrined in law: all serious dental interventions in children under 3 years of age must be carried out under general anesthesia.
How bottle caries is treated using remineralization method
Early bottle caries can often be found on the teeth of children aged 10-20 months. Signs of carious lesions at this stage are white spots on the enamel and in the area of contact of the dental crown with the gum and adjacent jaw. A small child does not show any signs of anxiety, because teeth with early caries do not hurt or cause discomfort. To notice the lesion, parents should regularly examine the baby’s mouth and, if they detect changes in the enamel, immediately contact the dentist.
For early caries in children, treatment will consist of strengthening the enamel, restoring its mineral composition and stopping further pathological process.
There are different options for treating caries without a drill. One of the methods is remineralization therapy. The mineral composition of tooth enamel consists of 57% calcium and phosphorus. When these substances are not enough, gradual destruction of the enamel structure occurs. Retherapy is carried out to restore its normal mineral composition and strength. For the purpose of remineralization, the surface of the teeth is covered with gels, pastes and other preparations with calcium and phosphorus. To consolidate the result, the dentist may prescribe additional fluoride-containing medications. They reduce the solubility of tooth enamel, prevent the leaching of calcium, and increase its resistance to acid.
In order for retherapy to give the expected result, a number of conditions must be met. Firstly, remineralizing compounds are applied only to teeth that have been cleaned of plaque, because they must come into contact with the enamel. Secondly, the contact must be long-lasting. Thirdly, minerals must be present in them in the form of phosphorus and calcium ions.
Correct retherapy, which will give the best results in the treatment and prevention of bottle caries, can be carried out by a qualified dentist.
Treatment of caries of primary teeth –
Treatment of caries in children under 3 years of age differs from treatment in older children. The choice of technique will primarily depend on 1) the age of the child and his behavior in the doctor’s chair, 2) the depth of the carious lesion, 3) as well as the behavior of the child’s parents. Typical inadequate demands of parents are “not to paint your teeth black”, “not to give an anesthetic injection”, “not to drill your teeth”, etc. All this makes it difficult to choose the optimal treatment method for a particular child.
1) Treatment of caries in children under 3 years of age –
In children of this age (depending on the depth of the carious process, as well as on behavior in the dentist’s chair), the following treatment methods can be used:
- remineralizing therapy,
- silvering (Fig. 11),
- deep fluoridation (Fig. 12),
- gentle filling of teeth (Fig. 13).
The method of tooth remineralization - remineralization of tooth enamel (saturation of it with calcium and phosphates) is carried out for the initial and superficial forms of caries of primary teeth. The course ranges from 5 to 10 procedures. As therapeutic agents, drugs such as, for example, calcium phosphate gel “GC Tooth Mousse” containing the complex “CPP-ACP” (casein-phospho-peptide-amorphous calcium phosphate) are used. An example of another product is “ROCS-mineral” based on calcium glycerophosphate and xylitol.
All these products can be used not only in the dentist’s office, but also at home. The main requirements are regular oral hygiene and a complete absence of plaque (plus the exclusion of the consumption of easily digestible carbohydrates, including sugary drinks). Treatment will not be effective if these requirements are not met. The drug “GC Tooth Mousse” will be more effective; it is easy to buy online and easy to use at home.
Deep fluoridation method (Fig. 12) - this method is also carried out in the presence of initial caries in the white spot stage, as well as in superficial caries. It is best to apply it in the second stage, i.e. immediately after the remineralization course. In total, a fluoridation course consists of 3-5 procedures, which consist of applying preparations based on sodium fluoride, tin fluoride, amino fluoride (optimally in the form of a varnish, which after application hardens on the enamel surface) to the surface of the tooth enamel.
The effectiveness of the fluoridation process greatly depends on the composition of the product used. It is important to choose an effective and at the same time safe concentration of fluoride for the child. You can read more about optimal medications at the link above. In addition, there is the drug “Enamel-sealing liquid Tiefenfluorid” (Germany), which is two-component and allows you to combine both remineralization and fluoridation at once.
Teeth silvering method (Fig. 11) - this method is used to treat initial caries in the white spot stage, superficial and medium caries. The silvering method is used only for the treatment of baby teeth, because... it causes areas of the tooth affected by caries to turn black. It is usually indicated in children no older than 3 years, because After 3-3.5 years of age, in most cases it is already possible to agree with the child on the traditional option of dental treatment (here, everything basically depends on the ability and desire of the dentist to find an approach to the child).
Of course, it is not entirely optimal to use it for the treatment of foci of demineralization in the form of white spots, as well as superficial caries, because Ideally, in these cases, it is advisable to conduct courses of remineralization and fluoridation. But with average caries (circular and planar forms), this method is not so bad, because In some children, it may be the only opportunity to survive until the physiological change of teeth, i.e. will allow you to do without their premature removal.
The optimal drug is Saforide (based on 38% silver diaminofluoride). According to the recommendations of the Russian Dental Association, silvering of teeth should be carried out not just once, but from 3 to 5 times. Only in this case is it possible to achieve stabilization of the process, but further maintenance repeated courses will be necessary, the period between which can be 1-3-6 months. The duration between repeated courses will depend on a number of factors, for example, the level of oral hygiene, the rate of caries progression, etc.
Gentle filling of teeth in children under 3 years of age - this method is carried out for superficial and medium caries. Don’t worry, filling teeth in children of this age is quite possible, and many dentists treat even 1.5-year-old children in this way. The most important thing here is the approach, and that the child is not scared from the very beginning. For example, it is very important not to cause any unpleasant sensations to the child during 1 visit, and therefore the child first only has his teeth brushed with polishing brushes and a tasty paste, and enamel strengthening agents are also applied to the teeth.
On the second visit, you can begin gentle filling. First, it is necessary to remove the sharp edges of the enamel and softened dentin. This can be done not only with a drill, but also with the help of scraping with hand tools specially designed for this. This is possible because the enamel and dentin in children of this age are much softer than in adults. It is also very important that in young children pain sensitivity in the teeth is reduced, and usually everything is painless.
There is another way to facilitate the removal of enamel and dentin affected by caries. This method involves first applying a special gel (for example, Carisolv, Switzerland), which softens tissues affected by caries and does not affect healthy enamel and dentin. After this, all that remains is to carry out very light scraping with hand tools. Nevertheless, it must be recognized that in some cases, high-quality filling can be carried out only after preparing the carious cavity with a drill, and in this case, only small carious cavities can be cured without anesthesia.
Important points that parents need to know before getting a filling -
- It is very important that the dentist has a “caries marker” drug, which helps the dentist determine whether he has completely removed the dentin affected by caries. In children of this age, this can be very difficult to determine. If the dentist leaves even a little bit of carious dentin, caries will occur under the filling, which will very quickly turn into pulpitis and acute pain. Those. If the doctor doesn’t have such a drug initially, I wouldn’t even sign up for treatment if I were you.
- Selection of material for filling - after removing all tissues affected by caries and appropriate antiseptic treatment, the actual filling begins. The second important point is the choice of filling material. Children of this age can and should have their teeth filled only with “glass ionomer cements” (GIC), for example, “Ketak-molar”, “Ionofil”, “Fuji IX”, “Cemion”, etc. In addition, even with average caries in children, a therapeutic pad made of calcium-containing material is always placed under such a filling.
2) Treatment of caries in children from 3 to 6 years old –
If your child has an initial form of caries (in the form of white chalky spots), then the treatment will be the same as for children under 3 years of age - remineralizing therapy, deep fluoridation, and in the worst case - silvering. We provided a link to these methods just above. For superficial, medium and deep caries in children of this age, it is optimal to use the technique of filling teeth with glass ionomer cements (GIC).
Before filling, carious tissues should preferably be drilled out with a drill, and only as a last resort can scraping of carious tissues with curettage spoons or smoothers be used. Under the glass ionomer filling (if the caries is medium or deep), a spacer made of calcium-containing material must also be placed.
Only if the child is emotionally unbalanced, is very afraid of the sound of the drill, in children who do not allow anesthesia or have a contraindication for it, in children with diseases of the central nervous system, it is preferable to use not a drill, but alternative methods of removing tissue affected by caries. It is also worth considering that if we are talking about a child’s very first visit to the dentist, then no invasive procedures should be performed during this visit (you should limit yourself to only polishing the teeth and applying fluoride varnish). This will allow the child to have a more positive attitude towards the dentist in the future.
Treatment of bottle caries using fluoridation
A disease such as bottle caries can be cured at an early stage using simple or deep fluoridation.
The essence of fluoridation is that tooth enamel is saturated with fluoride - a substance that reduces tooth sensitivity, strengthens the enamel, and makes it less susceptible to negative external influences.
With simple fluoridation, a fluoride-containing composition is applied to the teeth, which forms a thin protective film. With deep fluoridation, in addition to fluorine, the preparations include calcium and other compounds. Their complex action promotes the penetration of beneficial substances into the enamel structure and strengthens it from the inside.
After fluoridation, teeth become less sensitive, the surface of the tooth enamel becomes smoother, less plaque accumulates on the teeth, and light and dark spots disappear.
Why bottle caries develops: etiology of the disease
Despite the name, bottle caries affects not only artificial babies, but also breastfed babies (BF). A valuable criterion is the duration of feeding from a bottle or breast in general: if the period is less than a year, only 6% of babies develop caries; up to one and a half years - already every fourth child has affected teeth; up to two years - up to 40% of the child population suffer from this disease.
Bottle caries and its other varieties arise due to focal demineralization of the enamel under the influence of acids produced by cariogenic bacteria. First, a microbial plaque is formed on the surface of the teeth - a shell consisting of microorganisms and food debris. Microflora really “loves” quickly broken down carbohydrates, and actively grows in the presence of foods rich in glucose, fructose, sucrose, lactose, and starch.
During their life, microbes release substances that corrode the enamel, causing the once smooth surface to become porous and permeable. Through these micropores, during the development of caries, the tooth becomes infected. Pathogenic bacteria enter the tissue through the enlarged dentinal tubules, where they multiply and continue to secrete acids. If hygiene is not maintained satisfactorily, plaque covers the teeth, which only helps caries develop faster. In a confined space, the pH becomes maximally acidic.
Thus, with constant “feeding” of bacteria and irregular removal of plaque, the risk of bottle caries is extremely high. Both the contents of the baby’s diet and the timing of meals are important. When feeding on demand, the teeth remain in contact with fast carbohydrates often and for a long time (2-3 hours are enough to activate the microflora and start fermentation processes in the oral cavity).
In addition to sugars and poor hygiene, other factors predisposing to the development of bottle caries should be taken into account:
- The weakening of general immunity leads to deterioration of local immunity, so resistance to dental diseases becomes insufficient.
- The presence of chronic diseases, especially those accompanied by reflux (belching), metabolic changes, infections
- The properties and composition of saliva do not correspond to the norm - viscous saliva with a low pH level, low content of bactericidal enzymes, and immunoglobulins does not do a good job of protecting a child from caries.
- Antibiotic therapy, stress, and poor nutrition of a pregnant woman cause defective formation of teeth and their tissues in the unborn baby.
- Heredity - if close relatives of a young patient also suffered from early tooth decay in childhood, a genetic anomaly in the formation of enamel and dentin is possible. But if you take preventive measures seriously and follow a diet, even against the backdrop of a disappointing family history, there is a chance to preserve temporary teeth until the moment of physiological change.
Treatment of bottle caries using the ICON method
Children over three years old with early stages of caries can be treated with a minimally invasive infiltration method. It is absolutely safe, but requires sitting still for about 20 minutes, so is not suitable for younger children.
The essence of the ICON method is that after preliminary preparation, damaged tooth enamel is coated with a sealant gel. It penetrates the pores of the enamel, seals them and prevents bacteria and acid from penetrating deep into the tooth.
Symptoms of the disease
Clinical manifestations are directly dependent on the neglect of the pathological process. At first, the upper incisors and canines suffer, since they are actively involved in sucking the breast or bottle and come into contact with milk.
The disease begins with damage to the area where the coronal part adjoins the gums, which are least protected from negative effects. Then the entire crown is damaged.
At the very beginning, barely noticeable whitish spots appear on the teeth. Then they darken, and the baby experiences discomfort when eating. In the later stages of development of the pathology, the teeth are destroyed to the ground, and acute pain is noted.
Is silver plating safe for children?
The superficial form of bottle caries most often occurs in children between 16 and 24 months. At this stage of the lesion, dentin is exposed - the hard tissue of the tooth located under the enamel, the enamel becomes more sensitive. Gradually, carious spots change shade: instead of light, they become dark. Caries at this stage is also treated with remineralizing therapy, fluoridation, and infiltration. In some cases, it is advisable to carry out silvering.
Although this method is considered outdated and has a negative impact on the aesthetics of teeth (they darken), silver plating is still used in pediatric dentistry.
The essence of the method is that the surface of the teeth is coated with silver nitrate. It forms a film on the teeth that has an antimicrobial effect. Silvering does not cure bottle caries, but it can stop its development for a certain period of time.
Bottle caries: how it begins - symptoms of the stages of pathology development
Bottle caries of primary teeth is accompanied by the appearance of multiple lesions. In children, the first signs are noted immediately on a group of teeth - most often these are the upper milk incisors, which come into more contact with food when feeding the child, so plaque accumulates in this area more quickly.
The neck of the baby tooth undergoes demineralization first, since this zone is the least mineralized at the time of eruption. Gradually, bottle caries in children covers the cervical area of the tooth in a circular manner, and spreads along the enamel and onto the dentin.
The stages of caries quickly replace each other in children due to the fact that the formation of enamel during the eruption of a baby tooth is not yet complete. The tissues are loose, soft, and cannot resist the effects of acids.
Food remains, combined with poor hygiene, contribute to the dense coating of temporary teeth with bacterial plaque, under which the action of acids destroys enamel and dentin at an increasing rate. Already by school, children with untreated bottle caries lose their front primary teeth.
Stages of dental caries
- Initial (stain stage) - the baby tooth does not yet have visible damage; a whitish or yellowish spot with a matte sheen appears. At this stage of bottle caries, children have no complaints; some sensitivity to cold and sweet things is possible.
- Superficial stage of caries - a defect appears on the tooth within the thickness of the enamel. Complaints of pain caused by contact of teeth with cooled or hot, sour, sweet foods, frosty air.
- Middle stage - the carious process deepens to the dentin-enamel border, affecting the outer layer of dentin of the teeth. Children have the same complaints.
- Deep - significant destruction of the tissues of baby teeth, right down to the pulp chamber.
Attention: any form of bottle caries in a child requires treatment - both when the process is just beginning, and when it seems that there is no point in therapy.
Bottle caries can be acute or chronic. In acute caries, the pathology develops quickly, but the teeth do not have time to darken. The chronic course is accompanied by the slow spread of caries; defects on the teeth become pigmented - they become gray and black.
What to do if there is a hole in your tooth?
The above methods will help cure caries in the initial stage, when there is no cavity in the tooth. As soon as a hole has formed in the dentin, this means that caries has entered the medium or deep stage. In this case, treatment is carried out surgically.
The affected teeth are prepared, cleaned, dried, the cavity is prepared for the installation of a filling, and then filled with modern composite materials.
Children of any age do not like to visit dentists; some of them are difficult to even sit in a dental chair, let alone carry out treatment with a drill. This is why early diagnosis is so important, which is only possible with regular visits to the dentist.
What should be done to prevent bottle caries?
The development of bottle caries can be avoided if you monitor children’s teeth from early childhood and take comprehensive preventive measures:
- Teeth brushing begins immediately with the eruption of the first tooth. In the first year, you should use a soft brush without toothpaste or with a small amount of children's toothpaste. After a year, teeth are brushed with toothpaste; dentists also recommend using dental floss.
- In order to prevent tooth decay, you should not bottle feed your baby for a long time. When introducing complementary foods, it is advisable to immediately teach the baby to eat with a spoon from a plate. A similar recommendation applies to those children who are bottle-fed.
- Do not feed children before bed or during the day, and do not leave bottles in the crib for the baby to suck on throughout the night.
- Instead of sweet drinks, introduce your child to clean water and unsweetened tea.
- To avoid the transfer of cariogenic bacteria from an adult to a child, you should not share a spoon with children or give a child a pacifier from your mouth.
- In order to promptly notice pathological changes in the structure of the enamel and the condition of children's teeth, visit the dentist at least once every six months, even if it seems that the child has no signs of caries.
- Dental caries in children develops rapidly, and it is better for the dentist to once again confirm the healthy state of the oral cavity than to immediately detect pulpitis.
These simple recommendations will protect children's teeth from bottle caries and help maintain a beautiful smile.
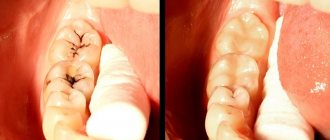
Silvering of teeth.
PHOTO: Silvering of baby teeth in children. The teeth turned black, but caries did not stop its development. Teeth after repeated silvering. The teeth turned black, but the carious process did not stop, since bacterial plaque continues to accumulate in the carious cavities.
One of the oldest methods of prevention and treatment of the initial stage of caries (in the stain stage) is silvering of teeth. Yes Yes. It consists of sealing, or more precisely, infiltrating, porous enamel with silver salts. The silver nitrate included in the solution, settling on the surface of the enamel, firmly seals the porous areas of the enamel, impregnating them deeply, preventing further penetration of new bacteria and their metabolic products into the enamel. Bacteria located in the pores die, since silver nitrate has a bactericidal effect. Over time, the silver nitrate film requires renewal, so this procedure must be repeated at least every month. Otherwise, the carious process will begin to progress under the silver. A significant disadvantage of silvering is the need to constantly repeat the procedure. After silvering, teeth become black, which makes it impossible to timely diagnose the progression of caries. At the BabySmile Clinic, we abandoned teeth silvering due to the low effectiveness of this technique.
EVEN IF THE SILVER PLATING METHOD IS CORRECTLY PERFORMED AND ALL THE DOCTOR'S RECOMMENDATIONS ARE FOLLOWED, THERE IS NO CHANCE THAT CARIES WILL NOT CONTINUE TO PROGRESS UNDER THE SILVER FILM! SINCE TEETH BLACKEN AFTER SILVERING, THE DEVELOPMENT OF CARIES MAY REMAIN UNNOTEED FOR A LONG TIME.
The advantage of the method is its extreme simplicity, allowing it to be carried out even by the smallest children! The technique of silvering teeth is obsolete, due to the impossibility of guaranteeing any result.